7.5 单元格周期 - 高级
Section outline
-
What is a cell's life like?
::细胞的生活是怎样的?The eukaryotic cell spends most of its "life" in interphase of the cell cycle, which can be subdivided into the three phases, G1, S and G2. During interphase, the does what it is supposed to do. Though cells have many common functions, such as DNA replication , they also have certain specific functions. That is, during the life of a heart cell, the cell would obviously perform certain different activities than a cell or a liver cell. The remainder of the cell cycle is devoted to : dividing the and cytoplasm . During interphase, the is unwound as chromatin , so that it can be exposed to the cellular machinery.
::eukaryatic 单元格的大部分“寿命”都花在细胞循环的中间阶段,可以细分为三个阶段,即G1、S和G2。在中间阶段,它应该做什么。虽然细胞有许多共同功能,例如DNA复制,但是它们也有某些特定的功能。也就是说,在心脏细胞的寿命期间,细胞显然会进行与细胞或肝细胞不同的活动。细胞循环的其余部分用于:分解细胞和细胞托盘。在中间阶段,细胞作为染色素是不健康的,因此可以接触细胞机器。The Cell Cycle
::细胞周期Cell division in eukaryotic cells is much more complex than in prokaryotic cells because of the many within the nucleus. Both the cytoplasm and the genetic material must be divided, ensuring that each resulting daughter cell receives 46 separate chromosomes (in human cell). To ensure this, in addition to the cell performing its necessary functions, the DNA must be copied, as must many , prior to cell division.
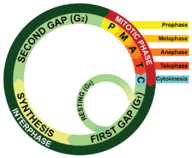
::eukaryatic 细胞的细胞分解比 prokary 细胞的分解复杂得多,因为细胞核中的细胞多。 细胞托盘和遗传物质必须分开,确保每个产卵细胞得到46种不同的染色体(在人体细胞中 ) 。 为了保证这一点,除了细胞发挥必要功能之外,DNA必须在细胞分解之前复制,许多DNA也必须复制。The life of a eukaryotic cell is a cycle, known as the cell cycle ( Figure ). The cell cycle is a repeating series of cellular growth and division. The cell cycle has four phases: the first growth (G 1 ) phase, the synthesis (S) phase, the second growth (G 2 ) phase, and the mitotic ( ) phase, which ends with cytokinesis . The cell spends the majority of the cycle in the first three phases of the cycle, collectively known as interphase . After cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are formed. Progression of the cycle into each phase is dependent on the completion of the previous phase. Cells that have temporarily or reversibly stopped dividing are said to have entered the resting phase or the G 0 phase, a indefinite phase of quiescence. The cell cycle is a vital process by which a zygote develops into a mature organism , as well as the process by which hair, skin, cells, and some internal organs consistently regenerated. After cytokinesis, each resulting daughter cell is in G 1 of the next cell cycle.
::单体细胞的生命周期是一个循环,称为细胞循环(图)。细胞循环是细胞生长和分裂的重复系列。细胞循环有四个阶段:第一个生长阶段(G1),合成阶段(S),第二个生长阶段(G2),以及以细胞细胞结束的线性()阶段。细胞在循环的前三个阶段(统称为间歇阶段)度过周期的大部分。在细胞循环之后,形成两个基因相同的女细胞。进入每个阶段的周期的进展取决于前一个阶段的完成情况。暂时或可逆停止分裂的细胞据说已经进入休息阶段或G0阶段,一个不确定的松散阶段。细胞循环是一个关键过程,一个zygote发展成成熟的有机体,以及一个毛发、皮肤、细胞和一些内部器官的不断再生过程。在细胞生长后,每个导致细胞分裂的细胞都进入下一个细胞周期的G1。This diagram represents the cell cycle in eukaryotes. The cell cycle depicts the life of an eukaryotic cell. The cell cycle has four phases: the first growth or gap (G 1 ) phase, the synthesis (S) phase, the second growth or gap (G 2 ) phase and the mitotic (M) phase. The M phase includes mitosis and cytokinesis. The cell spends the majority of the cycle in the first three phases (G 1 , S, G 2 ) of the cycle, collectively known as interphase. After cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are formed.
::此图代表了 eukaryotes 中的细胞循环。 细胞循环描述了 eukaryotes 中的细胞生命周期。 细胞循环有四个阶段: 第一个增长或差距( G1) 阶段、 合成( S) 阶段、 第二个增长或差距( G2 ) 阶段和 动物( M) 阶段。 M 阶段包括 mitodis 和 cytokinesis 。 细胞在循环的前三个阶段( G1, S, G2) 度过周期的大部分, 共称为 间段 。 在细胞生长或差距( G1) 阶段之后, 形成两个基因相同的女儿细胞 。The Phases
::阶段-
The cell spends most of its life in the first gap (sometimes referred to as growth) phase, G
1
. During this phase, a cell undergoes rapid growth and the cell performs its routine functions. During this phase the biosynthetic and metabolic activities of the cell occur at a high rate. The synthesis of
amino acids
and hundreds of thousands or millions of
that are required by the cell occurs during this phase. Proteins produced include those needed for DNA replication. If a cell is not dividing, the cell enters the G
0
phase from this phase.
::细胞在第一个缺口(有时称为生长)阶段,G1。在这一阶段,细胞迅速生长,细胞发挥例行功能。在这一阶段,细胞的生物合成和代谢活动发生率很高。在这一阶段,合成氨基酸和细胞所需要的数以亿计或数以百万计。生产的蛋白质包括DNA复制所需的蛋白质。如果细胞不分离,细胞从这一阶段进入G0阶段。
-
The G
0
phase is a resting phase where the cell has left the cycle and has stopped dividing. Non-dividing cells in multicellular eukaryotic organisms enter G
0
from G
1
. These cells may remain in G
0
for long periods of time, even indefinitely, such as with
. Cells that are completely differentiated may also enter G
0
. Some cells stop dividing when issues of sustainability or viability of their daughter cells arise, such as with DNA damage or degradation, a process called
cellular senescence
. Cellular senescence occurs when normal
diploid
cells lose the ability to divide, normally after about 50 cell divisions.
::G0 阶段是一个休眠阶段,细胞已经离开循环周期,停止了分裂。多细胞雌激素生物中的非分裂细胞从G1进入G0。这些细胞可能长期留在G0,甚至无限期地留在G0,例如:完全有区别的细胞也可以进入G0。有些细胞在出现其子细胞的可持续性或生存能力问题时停止分裂,比如DNA损害或降解,一个叫作细胞观察的过程。正常的浸泡细胞失去分裂能力,通常在大约50个细胞分裂之后,细胞就会出现细胞分裂。
-
Dividing cells enter the Synthesis (S) phase from G
1
. For two genetically identical daughter cells to be formed, the cell's DNA must be copied through DNA replication. When the DNA is replicated, both strands of the
double helix
are used as templates to produce two new complementary strands. These new strands then
hydrogen bond
to the
template
strands and two double helices form. During this phase, the amount of DNA in the cell has effectively doubled, though the cell remains in a diploid state.
::分裂细胞从 G1 进入合成( S) 阶段。 要形成两个基因相同的女细胞, 必须通过DNA复制复制细胞的DNA。 当复制DNA时, 两条双螺旋的两条线被用作模板, 以产生两个新的互补线。 这些新线将氢连接到模板条和两条双螺旋体。 在这一阶段, 细胞中的DNA数量实际上翻了一番, 尽管细胞仍然处于低位状态 。
-
The second gap (growth) (G
2
) phase is a shortened growth period in which many organelles are reproduced or manufactured. Parts necessary for mitosis and cell division are made during G
2
, including
microtubules
used in the mitotic
spindle
.
::第二个差距(增长)(G2)阶段是一个较短的生长期,许多器官被复制或制造,脑硬化和细胞分裂所需的部件是在G2期间制造的,包括用于甲状腺脊椎的微囊。
-
Mitosis is the phase of nuclear division, in which one nucleus divides and becomes two nuclei. Mitosis itself is a multi-phase process and will be the focus of the
Cell Cycle: Mitosis (Advanced)
concept. Immediately following mitosis is cytokinesis, in which the cytoplasm divides in half, producing two daughter cells, each containing a complete set of genetic material.
::分裂症是核分裂的阶段,其中一个核分裂,变成两个核核,它本身是一个多阶段过程,并且将成为细胞循环的焦点:细胞分裂(高级)概念。在细胞分裂症发生后立即是细胞分裂症,细胞结层分裂为二分之一,产生两个子细胞,每个细胞都含有一整套遗传材料。
Cell Cycle Summary
::细胞周期摘要Cell Cycle Summary State Name Abbreviation Description Quiescent Senescent Resting phase G 0 A resting phase where the cell has left the cycle and has stopped dividing. Interphase 1 st growth phase
::第一增长阶段Synthesis phase
::综合阶段2 nd growth phase
::第二增长阶段G 1
::G1 1 G1S
::S S 级G 2
::G2 日内瓦2Cells increase in size in G 1 . Cells perform their normal activities.
::G1. 细胞体积增加的G1细胞进行正常活动。DNA replication occurs during this phase.
::在这一阶段进行DNA复制。The cell will continue to grow and many organelles will divide during their phase.
::细胞将继续生长,许多器官在其阶段将分裂。Cell division Mitosis M Cell growth stops at this stage. Mitosis divides the nucleus into two nuclei, followed by cytokinesis which divides the cytoplasm. Two genetically identical daughter cells result. Summary
::摘要-
The cell cycle is a repeating series of events, characterizing the life of a eukaryotic cell.
::细胞循环是一系列的重复事件, 以表单细胞的寿命为特征 。 -
The cell cycle has four phases: the first growth phase, the synthesis phase, the second growth phase and the mitotic phase.
::细胞循环分为四个阶段:第一增长阶段、合成阶段、第二增长阶段和排他阶段。 -
The DNA is replicated during the S phase of the cell cycle, providing the genetic material for two identical cells.
::DNA在细胞循环的S阶段复制,为两个相同的细胞提供遗传材料。 -
The cycle ends with cytokinesis, in which two genetically identical cells result.
::循环以细胞基质结束,其中产生两个基因相同的细胞。
Review
::回顾-
Define and describe the cell cycle.
::界定和描述细胞循环。 -
What is interphase?
::什么是中继器? -
Summarize each phase of the cell cycle.
::概述细胞循环的每个阶段。 -
What is cellular senescence?
::什么是细胞戒律? -
When do normal cells usually lose their ability to divide?
::正常细胞通常何时会失去分化能力?
-
The cell spends most of its life in the first gap (sometimes referred to as growth) phase, G
1
. During this phase, a cell undergoes rapid growth and the cell performs its routine functions. During this phase the biosynthetic and metabolic activities of the cell occur at a high rate. The synthesis of
amino acids
and hundreds of thousands or millions of
that are required by the cell occurs during this phase. Proteins produced include those needed for DNA replication. If a cell is not dividing, the cell enters the G
0
phase from this phase.