8.14 变异 - 高级
Section outline
-
What causes albinism?
::白化病的原因是什么?This rare albino alligator must have the specific "instructions," or , to have this quality. Albinism is inherited in a recessive fashion. The cause of albinism is a mutation in a gene for melanin , a found in skin and . Such a mutation may result in no melanin production at all or a significant decline in the amount of melanin.
::这个稀有的白化病患者必须拥有特定的“实验 ” , 或, 才能具有这种质量。 白化病患者以休眠的方式继承。 白化病的起因是梅拉宁基因的突变,皮肤上的突变和皮肤上的突变。 这种突变可能完全没有梅拉宁生产,或梅拉宁数量显著下降。Mutations
::变异You have learned that an is an alternative form of a gene. Most, if not all genes have alternative forms causing the resulting protein to function slightly differently. But are there alleles that cause proteins to function dramatically differently or not function at all? A mutation is a change in the DNA or sequence, and many mutations result in new alleles. Some mutations have no effect on the protein, whereas others are either beneficial or harmful. In fact, evolution could not take place without the that results from beneficial mutations . In humans, harmful mutations can result in genetic diseases. There are also chromosomal mutations, large changes with dramatic effects.
::您已经学会了一种基因的替代形式。 大多数,如果不是所有基因都有其他形式,导致由此产生的蛋白质的功能略有不同。 但是,有没有所有基因都导致蛋白质的功能完全不同或完全不起作用?突变是DNA或序列的变化,许多突变导致新的异变。有些突变对蛋白没有影响,而另一些则有利或有害。事实上,进化不可能没有有利的突变的结果发生。在人类中,有害的突变可能导致基因疾病。还有染色体突变,还有巨大的变化和剧烈的影响。New Genes
::新建基因It is believed that large mutations form new genes. Mutations that duplicate large sections of DNA are a major source of genetic material for new genes. It is thought that tens to hundreds of genes are duplicated in genomes every million years. Most genes belong to larger families of genes of shared ancestry. These gene families have within the protein with a particular and independent function. These domains have corresponding conserved regions within their genes. It is through duplication mutations that such gene families formed. Genetic recombination after duplication of different domains forms new combinations of domains with new functions. For example, the human eye uses four genes to make structures that sense light: three for color and one for night vision; all four arose from a single ancestral gene.
::据认为,大型突变形成新的基因。重复大量DNA的突变是新基因的主要遗传材料来源。据认为,每百万年有几十至数百个基因在基因组中复制。大多数基因属于共同祖先基因的较大家族。这些基因家庭在蛋白质中具有特定和独立的功能。这些基因家庭在基因中具有相应的受保护区域。正是通过重复突变,这些基因家庭才形成这样的基因家庭。在不同领域重复之后的基因重组形成了具有新功能的基因领域的新组合。例如,人类眼睛使用四种基因来形成感知光的结构:三种是颜色的,一种是夜视的;所有四个基因都来自单一的祖传基因。Alu Sequences
::Alu 序列DNA sequences that can translocate around the genome comprise a significant fraction of the genetic material of plants and animals. There may be some evolutionary significance to these movable elements . One example is the Alu sequence or Alu element. More than a million copies of the Alu sequence are present in the , making this transposon equivalent to just under 11% of the human genome.
::可以在基因组周围转移的DNA序列占植物和动物基因材料的相当一部分。 这些可移动元素可能具有某种进化意义。 一个例子是Alu序列或Alu元素。 超过100万份的Alu序列存在于基因组中, 这使得这种转基因相当于人类基因组的11%。Alu insertions are sometimes disruptive and can result in inherited disorders. The insertion or deletion of Alu sequences are associated with some specific effects in humans, including breast , familial hypercholesterolemia, hemophilia and neurofibromatosis.
::在乳房、家庭高胆固醇症、血友病和神经纤维化病等人体中,插入或删除Alu序列与某些特定影响有关。Alu elements are about 300 base pairs long and are classified as short interspersed elements (SINEs) among the class of repetitive DNA elements. It is believed modern Alu elements evolved from a head to tail fusion of two distinct antique RNA monomers over 100 million years ago. The monomers are opposing but complementary RNA fragments joined by an A-rich linker. Alu elements are derived from the signal recognition particle RNA. This RNA is the RNA component of the signal recognition particle (SRP) ribonucleoprotein complex. This complex is a universally conserved ribonucleoprotein that directs the traffic of proteins within the and allows them to be secreted. The Alu element probably originated from a 7SL RNA gene after deletion of a central sequence.
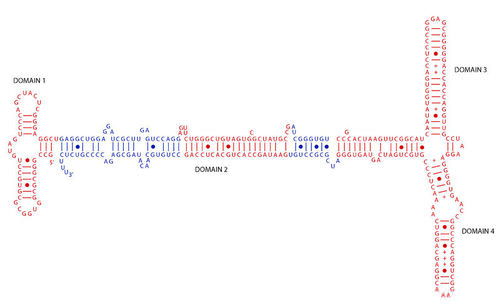
::Alu元素长约300个基对,被归类为重复性DNA元素类中的短跨元素(SINEs),据信现代Alu元素在1亿多年前从头部演变为尾部融合了两种不同的RNA单质古董单质体。单质元素对RNA的碎片形成对立,但互补的RNA碎片与富含A的链接连接在一起。Alu元素来自信号识别粒子RNA。这一RNA元素是信号识别粒子(SRP)肋骨核蛋白质复合体的RNA元素。这一复合体是一个普遍保存的肋骨蛋白素化合物,引导蛋白质在其中的流通,并允许将其秘密化。Alu元素在删除核心序列后可能源于7SLRNA基因。Human SRP RNA. Alu elements were derived from a similar sequence. Notice all the hairpin loops of repeating complementary sequences. New Chromosomes
::新染色体How do new form? Is it possible for two chromosomes to fuse? In short, yes it is. In the hominids that arose after the split from the orangutans, two chromosomes fused to produce what is chromosome 2 in humans. This fusion did not occur in the lineage of the other apes, and they retain these separate chromosomes. This may have occurred to keep two from interbreeding, as they would be genetically incompatible, accelerating the divergence of the populations.
::新的形式是怎样的? 两种染色体能否结合起来? 简言之,是的。 在从猩猩分裂后产生的小猩猩中,有两种染色体被结合,产生人体中的染色体2。这种结合没有发生在其他猿系中,它们保留了这些不同的染色体。这可能是为了防止两种染色体相互交织,因为它们在基因上互不相容,从而加速了人口的分裂。Summary
::摘要-
A mutation is a change in a DNA or RNA sequence.
::突变是DNA或RNA序列的改变 -
Mutations may have no effect, they may be beneficial or harmful.
::变异可能没有效果,也可能有利或有害。 -
Alu sequences are repetitive elements that form a significant part of the human genome.
::Alu序列是构成人类基因组重要部分的重复性元素。
Review
::回顾-
Define mutation.
::定义突变。 -
Discuss mutations and gene formation.
::讨论突变和基因形成 -
What are Alu elements? Why are they significant?
::什么是阿卢元素?为什么它们重要?
-
A mutation is a change in a DNA or RNA sequence.