4.3 流行病
章节大纲
-
Feel the Burn
::感受烧灼The person in this photo is no doubt feeling the burn — sunburn , that is. Sunburn occurs when the outer layer of the skin is damaged by UV light from the sun or tanning lamps. Some people deliberately allow UV light to burn their skin, because after the redness subsides, they are left with a tan. A tan may look healthy, but it is actually a sign of skin damage. People who experience one or more serious sunburns are significantly more likely to develop skin cancer . Natural pigment molecules in the skin help protect it from UV light damage. These pigment molecules are found in the layer of the skin called the epidermis.
::照片中的人无疑感觉到烧伤——晒伤,也就是说。当皮肤外层受到太阳或晒黑灯光的紫外线的破坏时,就会发生太阳灼伤。有些人故意允许紫外线烧伤他们的皮肤,因为在红度下沉后,他们留下的是晒黑。晒黑可能看起来健康,但实际上是皮肤损伤的征兆。经历一次或一次以上严重太阳灼伤的人更可能患上皮肤癌。皮肤中的天然色素分子有助于保护皮肤免受紫外线损害。这些色素分子在皮肤层中被发现,叫做皮皮皮皮。What is the Epidermis?
::什么是神仙号?The epidermis is the outer of the two main layers of the skin. The inner layer is the dermis . It averages about 0.10 mm thick, and is much thinner than the dermis. The epidermis is thinnest on the eyelids (0.05 mm) and thickest on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet (1.50 mm). The epidermis covers almost the entire body surface. It is continuous with — but structurally distinct from — the mucous membranes that line the mouth, anus, urethra , and vagina .
::皮层是皮肤两大层的外皮,内层是皮层,平均厚约0.10毫米,比皮层薄得多;皮层在眼皮上薄(0.05毫米),在手掌和脚底掌上厚(1.50毫米),皮层几乎覆盖整个身体表面,与嘴部、肛门、尿道和阴道的粘膜保持连续,但结构上不同于。Structure of the Epidermis
::流行病结构结构There are no and very few nerve in the epidermis. Without to bring epidermal cells oxygen and nutrients , the cells must absorb oxygen directly from the air and obtain nutrients via of fluids from the dermis below. However, as thin as it is, the epidermis still has a complex structure. It has a variety of cell types and multiple layers.
::皮层中没有神经,神经也很少。 如果不带来上皮细胞氧气和营养,细胞必须直接吸收空气中的氧气,通过下面皮层中的液体获得营养。然而,皮层虽然薄,但仍然有一个复杂的结构。它有各种各样的细胞类型和多层。Cells of the Epidermis
::流行病细胞There are several different types of cells in the epidermis. All of the cells are necessary for the important functions of the epidermis.
::后皮细胞有几种不同类型的细胞,所有细胞对于后皮的重要功能都是必要的。-
The epidermis consists mainly of stacks of keratin-producing epithelial cells called
keratinocytes
. These cells make up at least 90 percent of the epidermis. Near the top of the epidermis, these cells are also called squamous cells.
::上皮细胞主要由堆堆堆的氯丁二烯生成的上皮细胞组成,叫做牛皮细胞。这些细胞至少占上皮细胞的90%。在上皮细胞的顶部,这些细胞也被称为肮脏的细胞。 -
Another eight percent of epidermal cells are
melanocytes
. These cells produce the pigment
melanin
that protects the dermis from UV light.
::另外8%的上皮细胞是甲状腺素。这些细胞产生色素梅兰素,可以保护皮肤免受紫外线光的影响。 -
About one percent of epidermal cells are
Langerhans cells
. These are
immune system
cells that detect and fight
entering the skin.
::大约1%的上皮细胞是Langerhans细胞。这些是免疫系统细胞,用来检测和抗争进入皮肤的细胞。 -
Less than one percent of epidermal cells are
Merkel cells
, which respond to light touch and connect to nerve endings in the dermis.
::上皮细胞中只有不到1%是默克尔细胞,这些细胞对光触和皮肤神经末端有反应。
Layers of the Epidermis
::宇宙的层层The epidermis in most parts of the body consists of four distinct layers. A fifth layer occurs in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, where the epidermis is thicker than in the rest of the body. The layers of the epidermis are shown in the figure , and described in the following text.
::身体大部分部位的皮层由4个不同的层组成,第5层出现在手掌和脚底的掌上,皮层厚于身体其他部位。皮层在图中显示,下图中则说明。The epidermis has multiple layers, and structures (such as hairs from the dermis below it) pass through them. This diagram illustrates the five layers that exist on the palms and soles of the feet.
::上皮层有多个层,结构(如下皮层的毛发)经过它们。本图说明了掌上和脚底的五层。Stratum Basale
::巴萨勒平原The stratum basale is the innermost (or deepest) layer of the epidermis. It is separated from the dermis by a membrane called the basement membrane . The stratum basale contains cells — called basal cells — which divide to form all the keratinocytes of the epidermis. When keratinocytes first form, they are cube-shaped and contain almost no keratin . As more keratinocytes are produced, previously formed cells are pushed up through the stratum basale. Melanocytes and Merkel cells are also found in the stratum basale. The Merkel cells are especially numerous in touch-sensitive areas, such as the fingertips and lips.
::底栖细胞是上皮层的最深层(或最深层)层,与底栖细胞分离,由叫做地下室膜的薄膜分离,底栖生物含有细胞——称为巴萨细胞——它们分裂成上皮层的所有乳腺细胞,头形的乳腺细胞是立方体形,几乎没有氯丁二烯。随着更多的乳腺细胞的产生,以前形成的细胞会通过底栖生物圈推高。在底栖生物圈中也发现了梅拉诺细胞和默克尔细胞。默克尔细胞在接触敏感的地区特别多,如指尖和嘴部。Stratum Spinosum
::Staltum 脊柱石Just above the stratum basale is the stratum spinosum . This is the thickest of the four epidermal layers. The keratinocytes in this layer have begun to accumulate keratin, and they have become tougher and flatter. Spiny cellular projections form between the keratinocytes and hold them together. In addition to keratinocytes, the stratum spinosum contains the immunologically active Langerhans cells.
::顶部的脊椎结核是脊椎结核。 这是四个上皮层中最厚的。 这个层的脊髓细胞开始积累氯丁酸, 并且变得更加坚硬和受宠若惊。 脊髓细胞在脊髓细胞之间形成脊椎细胞预测, 并把它们绑在一起。 除了脊髓细胞外, 脊髓脊髓结核还含有免疫活跃的兰汉细胞 。Stratum Granulosum
::普拉努苏姆The next layer above the stratum spinosum is the stratum granulosum . In this layer, keratinocytes have become nearly filled with keratin, giving their cytoplasm a granular appearance. are released by keratinocytes in this layer to form a lipid barrier in the epidermis. Cells in this layer have also started to die, because they are becoming too far removed from blood vessels in the dermis to receive nutrients. Each dying cell digests its own and , leaving behind only a tough, keratin-filled shell.
::底脊髓脊髓的下一层是地壳颗粒体。 在这个层中, 乳腺细胞已经几乎填满了氯酸盐, 给细胞以颗粒的外观。 乳腺细胞在这个层中释放出来, 在皮层中形成脂肪屏障。 这个层中的细胞也开始死亡, 因为它们离皮肤里的血管太远, 无法接收营养物质。 每个垂死的细胞都消化了自己的体外, 留下的只是一块坚硬的、 填满氯酸盐的外壳。Stratum Lucidum
::斯特拉图姆·卢西杜姆Only on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, the next layer above the stratum granulosum is the stratum lucidum . This is a layer consisting of stacks of translucent, dead keratinocytes that provide extra protection to the underlying layers.
::只有在手掌和脚底的掌上方,层粒子上方的下一层是直流清晰度。这是一个层,由多层的半透明、死心肌细胞组成,为底层提供了额外的保护。Stratum Corneum
::直角角角The uppermost layer of the epidermis everywhere on the body is the stratum corneum . This layer is made of flat, hard, tightly packed dead keratinocytes that form a waterproof keratin barrier to protect the underlying layers of the epidermis. Dead cells from this layer are constantly shed from the surface of the body. The shed cells are continually replaced by cells moving up from lower layers of the epidermis. It takes a period of about 48 days for newly formed keratinocytes in the stratum basale to make their way to the top of the stratum corneum to replace shed cells.
::身体上最上层的皮层是角膜。 这个层由平坦的、硬的、紧紧包装的无脊椎细胞组成,形成防水的克朗屏障,以保护皮层的底部。 这个层的死细胞不断从身体表面脱落。 从皮层下层向上移动的细胞不断取代棚室的细胞。 在河口的河口,新形成的脊椎细胞需要大约48天的时间才能到达顶部,以取代棚房的细胞。Functions of the Epidermis
::流行病的功能The epidermis has several crucial functions in the body. These functions include protection, retention, and vitamin D synthesis.
::外皮在身体上有若干关键功能,包括保护、保留和维生素D合成。Protective Functions
::保护功能The epidermis provides protection to underlying tissues from physical damage, pathogens, and UV light.
::皮层保护底部组织免受身体损伤、病原体和紫外线光的影响。Protection from Physical Damage
::保护免受身体伤害Most of the physical protection of the epidermis is provided by its tough outer layer, the stratum corneum. Because of this layer, minor scrapes and scratches generally do not cause significant damage to the skin or underlying tissues. Sharp objects and rough surfaces have difficulty penetrating or removing the tough, dead, keratin-filled cells of the stratum corneum. If cells in this layer are pierced or scraped off, they are quickly replaced by new cells moving up to the surface from lower skin layers.
::皮层大部分的实物保护由硬外层、直角角提供。由于这一层,细刮和刮痕一般不会对皮肤或底部组织造成重大损害。尖锐的物体和粗糙表面难以穿透或去除直角的硬性、死性、氯酸盐填充的细胞。如果这一层的细胞被穿透或刮掉,它们很快被从下层向表层移动到表层的新细胞所取代。Protection from Pathogens
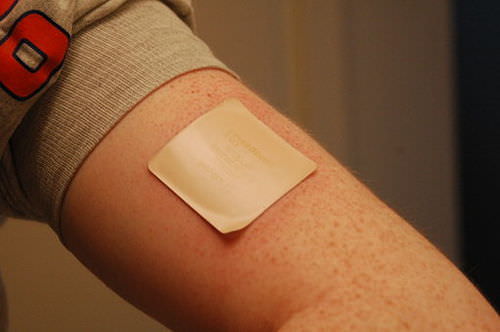
::保护免受病原体影响When pathogens such as and try to enter the body, it is virtually impossible for them to enter through intact epidermal layers. Generally, pathogens can enter the skin only if the epidermis has been breached, for example by a cut, puncture, or scrape (like the one pictured ). That’s why it is important to clean and cover even a minor wound in the epidermis. This helps ensure that pathogens do not use the wound to enter the body. Protection from pathogens is also provided by conditions at or near the skin surface. These include relatively high acidity (pH of about 5.0), low amounts of water, the presence of antimicrobial substances produced by epidermal cells, and with non-pathogenic microorganisms that normally live on the epidermis.
::当病原体像病原体那样试图进入身体时,病原体几乎不可能通过完整的上皮层进入皮肤。 一般来说,病原体只有在皮皮被切割、刺穿或刮伤(如照片所描述的 ) 等破坏的情况下才能进入皮肤。 这就是为什么在皮皮细胞中清洁甚至覆盖小伤口的重要性。 这有助于确保病原体不使用伤口进入身体。 皮肤表面或附近的条件也提供了抗病原的保护,其中包括相对较高的酸度(pH值约为5.0 ) , 低量的水、上皮细胞产生的抗微生物物质的存在,以及通常在皮皮皮细胞上生活的非病原微生物。This scrape on the arm provides an opportunity for bacteria to enter the body through the broken skin.
::手臂上的这种刮痕为细菌通过破损的皮肤进入身体提供了机会。Protection from UV Light
::防紫外光防护UV light that penetrates the epidermis can damage epidermal cells. In particular, it can cause in that lead to the of skin cancer, in which epidermal cells grow out of control. UV light can also destroy vitamin B9 (in forms such as folate or folic acid), which is needed for good health and successful . In a person with light skin, just an hour of exposure to intense sunlight can reduce the body’s vitamin B9 level by 50 percent.
::穿透上皮细胞的紫外线光可能会损害上皮细胞。 特别是,它可能导致皮肤癌,导致上皮细胞失控。 紫外线光也能摧毁维他命B9(如叶酸或叶酸 ) , 这是健康、成功所需的。 在有浅皮的人身上,只有一小时的强光照射就可以将身体维他命B9水平降低50%。Melanocytes in the stratum basale of the epidermis contain small organelles called melanosomes , which produce, store, and transport the dark brown pigment melanin. As melanosomes become full of melanin, they move into thin extensions of the melanocytes. From there, the melanosomes are transferred to keratinocytes in the epidermis, where they absorb UV light that strikes the skin. This prevents the light from penetrating deeper into the skin, where it can cause damage. The more melanin there is in the skin, the more UV light can be absorbed.
::皮皮底膜底部的梅拉诺细胞含有小有机物,叫做美兰素,它生产、储存和运输黑棕色色色素。随着黑棕色色色素成形,它们会移入梅兰尼素的稀薄延伸。从那里,黑兰素被移到皮皮层的红皮细胞中,它们吸收了撞击皮肤的紫外线光。这防止了光深入皮肤,从而造成伤害。皮肤中黑兰素越多,紫外线的光就会被吸收得越多。Water Retention
::储水量Skin's ability to hold water and not lose it to the surrounding environment is due mainly to the stratum corneum. Lipids arranged in an organized way among the cells of the stratum corneum form a barrier to water loss from the epidermis. This is critical for maintaining healthy skin and preserving proper water balance in the body.
::皮肤保持水的能力,而不是将水丢弃给周围环境,这主要归因于脊椎角膜。 在脊椎角膜的细胞之间有组织地安排的嘴唇构成了对上皮水流失的障碍。 这对保持健康皮肤和保持身体适当的水平衡至关重要。Although the skin is impermeable to water, it is not impermeable to all substances. Instead, the skin is selectively permeable, allowing certain fat-soluble substances to pass through the epidermis. The selective permeability of the epidermis is both a benefit and a risk.
::尽管皮肤对水是不可渗透的,但并非对所有物质都是不可渗透的。 相反,皮肤是选择性渗透的,允许某些脂肪溶解的物质通过皮层。 皮层的选择性渗透既是一种好处,也是一种风险。-
Selective permeability allows certain medications to enter the blood stream through the capillaries in the dermis. This is the basis of medications that are delivered using topical ointments, or patches (see photo
) that are applied to the skin. These include
steroid hormones
, such as
estrogen
(for
replacement therapy), scopolamine (for motion sickness), nitroglycerin (for heart problems), and nicotine (for people trying to quit smoking).
::选择性的渗透性使某些药物能够通过皮肤的刺膜进入血液流,这是使用局部药膏或对皮肤施用补丁(见照片)的药物的基础,其中包括类固醇激素,如雌激素(替代疗法)、胺(运动疾病)、硝化甘油(心脏病)和尼古丁(试图戒烟的人)。 -
Selective permeability of the epidermis also allows certain harmful substances to enter the body through the skin. Examples include the heavy metal lead, as well as many pesticides.
::外皮的选择性渗透性还允许某些有害物质通过皮肤进入身体,例如重金属铅和许多杀虫剂。
This skin patch delivers small amounts of nicotine through the skin of a person in a smoking cessation program.
::这种皮肤补丁通过戒烟方案的人的皮肤提供少量尼古丁。Vitamin D Synthesis
::维生素D合成Vitamin D is a nutrient that is needed in the for the absorption of calcium from food . Molecules of a lipid compound named 7-dehydrocholesterol are precursors of vitamin D. These molecules are present in the stratum basale and stratum spinosum layers of the epidermis. When UV light strikes the molecules, it changes them to vitamin D3. In the , the vitamin D3 is converted to calcitriol, which is the form of vitamin D that is active in the body.
::维生素D是从食物中吸收钙所需的一种营养素。一种称为7-de氢胆固醇的脂质化合物的分子是维生素D的前体。这些分子存在于皮皮层的骨浆和脊髓脊髓层中。当紫外线光击中分子时,它们会变成维生素D3。 在(......)中,维生素D3被转化成碳酸盐,这是体内活跃的维生素D形式。What Gives Skin Its Color?
::是什么给皮肤颜色的?Melanin in the epidermis is the main substance that determines the color of human skin. It explains most of the variation in skin color in people around the world. T wo other substances also contribute to skin color, however, especially in light-skinned people: carotene and hemoglobin .
::皮下皮革中的梅兰宁是决定人类皮肤颜色的主要物质,它解释了世界各地人肤色的多数差异,但另外两种物质也助长了肤色,特别是皮肤浅的人:甲状腺素和血红素。-
The pigment
carotene
is present in the epidermis and gives skin a yellowish tint, especially in skin with low levels of melanin.
::皮皮薄膜中含有颜料的胡萝卜,皮肤有黄色色的色素,特别是低米氏素的皮质。 -
Hemoglobin
is a red pigment found in
red blood cells
. It is visible through skin as a pinkish tint, mainly in skin with low levels of melanin. The pink color is most visible when capillaries in the underlying dermis dilate, allowing greater blood flow near the surface.
::血红蛋白是一种红色色素,存在于红血细胞中,通过皮肤作为粉色色色素可见,主要是在皮质低的梅兰宁皮肤中。 红色色在底部皮层膨胀的刺青中最明显,允许更多血流接近表面。
Bacteria on Skin
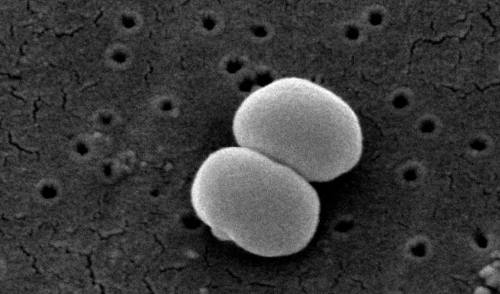
::皮肤上的细菌The surface of the human skin normally provides a home to countless numbers of bacteria. Just one square inch of skin normally has an average of about 50 million bacteria. These generally harmless bacteria represent roughly one thousand bacterial (including the one pictured ) from 19 different bacterial phyla. Typical variations in the moistness and oiliness of the skin produce a variety of rich and diverse habitats for these microorganisms. For example, the skin in the armpits is warm and moist and often hairy, whereas the skin on the forearms is smooth and dry. These two areas of the human body are as diverse to microorganisms as rainforests and deserts are to larger organisms . The density of bacterial on the skin depends largely on the region of the skin and its ecological characteristics. For example, oily surfaces, such as the face, may contain over 500 million bacteria per square inch. Despite the huge number of individual microorganisms living on the skin, their total volume is only about the size of a pea.
::人类皮肤表面通常为无数细菌提供了栖息地。只有一平方英寸的皮肤通常平均有大约5 000万细菌。这些一般无害的细菌代表19种不同的细菌的大约一千种细菌(包括一幅图象)。皮肤湿润和油润的典型变化为这些微生物创造了丰富多样的栖息地。例如,毛皮上的皮肤是温暖的、湿润的,而且往往毛细的,而前臂上的皮肤是光滑的和干燥的。人类身体的这两个区域与微生物一样多种多样,如同雨林和沙漠是更大的生物。皮肤上的细菌密度主要取决于皮肤的面积及其生态特征。例如表面等油质表面可能含有5亿多种细菌/平方英寸。尽管生活在皮肤上的个别微生物数量巨大,但其总量仅相当于一个豆的大小。The bacterium Staphylococcus epidermidis is a common microorganism living on healthy human skin.
::脑膜球菌菌是一种普通微生物,靠健康的人体皮肤生存。In general, the normal microorganisms living on the skin keep one another in check, and thereby play an important role in keeping the skin healthy. I f the balance of microorganisms is disturbed, however, there may be an overgrowth of certain species, and this may result in an infection. For example, when a patient is prescribed antibiotics , it may kill off normal bacteria and allow an overgrowth of single-celled yeast. Even if skin is disinfected, no amount of cleaning can remove all of the microorganisms it contains. Disinfected areas are also quickly recolonized by bacteria residing in deeper areas (such as hair follicles) and in adjacent areas of the skin.
::一般说来,皮肤上的正常微生物相互保持检查,从而在保持皮肤健康方面起着重要作用;但如果微生物的平衡受到干扰,则某些物种可能会过度生长,这可能导致感染;例如,当病人被处方抗生素时,它可能会杀死正常细菌,并允许单细胞酵母的过度生长;即使皮肤经过消毒,任何清洁都无法消除其中的所有微生物;如果微生物的平衡受到干扰,则某些物种可能会过度生长,这可能导致感染;例如,当病人被处方抗生素时,它可能会杀死正常细菌,并允许单细胞酵母的过度生长;即使皮肤被消毒,任何清洁措施都无法消除其中的所有微生物;如果感染,则在较深的地区(如毛囊)和皮肤邻近地区的细菌也迅速重新移植。Feature: Myth vs. Reality
::特征:神话对现实Because of the negative health effects of excessive UV light exposure, it is important to know the facts about protecting the skin from UV light.
::由于过度的紫外线光照射对健康造成负面影响,必须了解保护皮肤免受紫外线照射的事实。Myth: Sunblock and sunscreen are just different names for the same type of product. They both work the same way and are equally effective.
::传说:防晒霜和防晒霜只是同一种产品的不同名称。 它们的工作方式相同,同样有效。Reality: Sunscreens and sunblocks are different types of products that protect the skin from UV light in different ways. They are not equally effective. Sunblocks are opaque, so they do not let light pass through. They prevent most of the rays of UV light from penetrating to the skin surface. Sunblocks are generally stronger and more effective than sunscreens. Sunblocks also do not need to be reapplied as often as sunscreens. Sunscreens, in contrast, are transparent once they are applied the skin. Although they can prevent most UV light from penetrating the skin when first applied, the active ingredients in sunscreens tend to break down when exposed to UV light. Sunscreens, therefore, must be reapplied often to remain effective.
::真实性:日光屏和遮光板是不同种类的产品,以不同的方式保护皮肤不受紫外光的照射。 它们的效果不尽相同。 太阳屏和遮光板是不透明的, 它们不会让光线穿透。 它们防止大部分紫外光线穿透到皮肤表面。 太阳屏和遮光板通常比太阳屏更强大、更有效。 太阳屏和遮光板也不必像太阳遮光板那样频繁重现。 相比之下, 太阳屏在皮肤上施用时是透明的。 尽管它们可以防止大多数紫外光在第一次施用时穿透皮肤, 但太阳屏中的活性成分在暴露于紫外光时往往会断裂。 因此,太阳屏必须经常重新恢复,才能继续有效。Myth: The skin needs to be protected from UV light only on sunny days. When the sky is cloudy, UV light cannot penetrate to the ground and harm the skin.
::传说:只有在阳光明媚的日子,皮肤才需要保护,免受紫外线照射。 当天空多云时,紫外线无法穿透地面,伤害皮肤。Reality: Even on cloudy days, a significant amount of UV radiation penetrates the atmosphere to strike Earth’s surface. Therefore, using sunscreens or sunblocks to protect exposed skin is important even when there are clouds in the sky.
::现实:即使在多云的日子里,大量紫外线辐射也会渗透到大气中以撞击地球表面。 因此,使用防晒霜或防晒罩来保护暴露的皮肤即使天空有云也是很重要的。Myth: People who have dark skin, such as African Americans, do not need to worry about skin damage from UV light.
::例如非裔美国人等有皮肤皮肤的人不需要担心紫外线光线的皮肤损伤。Reality: No matter what color skin you have, your skin can be damaged by too much exposure to UV light. Therefore, even dark-skinned people should use sunscreens or sunblocks to protect exposed skin from UV light.
::真实性:无论皮肤有何种颜色,你的皮肤都可能因为接触紫外光过多而受损。 因此,即使皮肤黑的人也应该使用防晒霜或防晒霜来保护暴露的皮肤免受紫外光的影响。Myth: Sunscreens with an SPF (sun protection factor) of 15 are adequate to fully protect the skin from UV light.
::传说:有15个SPF(日光保护系数)的日光屏足以充分保护皮肤免受紫外线光照射。Reality: Most dermatologists recommend using sunscreens with an SPF of at least 35 for adequate protection from UV light. They also recommend applying sunscreens at least 20 minutes before sun exposure and reapplying sunscreens often, especially if you are sweating or spending time in the water.
::现实:大多数皮肤科医生建议使用至少35个防紫外光防晒霜的防晒霜和防紫外光防晒霜。他们还建议在太阳照射前至少20分钟使用防晒霜,并经常重新使用防晒霜,特别是当你在水中出汗或花时间时。Myth: Using tanning beds is safer than tanning outside in natural sunlight.
::使用日光浴床比在自然阳光下晒太阳更安全。Reality: The light in tanning beds is UV light, and it can do the same damage to the skin as the natural UV light in sunlight. This is evidenced by the fact that people who regularly use tanning beds have significantly higher rates of skin cancer than people who do not. It is also the reason that the use of tanning beds is prohibited in many places in people who are under the age of 18, just as youth are prohibited from using harmful substances, such as tobacco and alcohol.
::现实:日光是紫外线光,对皮肤的损害可以与阳光下天然紫外线一样,这表现在经常使用日光线的人患皮肤癌的比率大大高于不使用日光线的人,这也是为什么在18岁以下的人中许多地方禁止使用日光线床的原因,正如青年被禁止使用烟草和酒精等有害物质一样。Summary
::摘要-
The epidermis is the outer of the two main layers of the skin. It is very thin, but has a complex structure.
::皮层是皮肤两大层的外层,非常薄,但结构复杂。 -
Cell types in the epidermis include keratinocytes that produce keratin and make up 90 percent of epidermal cells, melanocytes that produce melanin, Langerhans cells that fight pathogens in the skin, and Merkel cells that respond to light touch.
::上皮细胞类型包括:产氯丁二烯(Keratin)并占90%的上皮细胞的乳腺细胞、产美兰宁(Melanalanin)的甲状腺细胞、与皮肤病原体抗争的Langerhans细胞和与轻触反应的默克尔细胞。 -
The epidermis in most parts of the body consists of four distinct layers. A fifth layer occurs only in the epidermis of the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
::身体大部分部位的皮层由四层不同的层组成,第五层只在手掌和脚底掌的皮层上出现。 -
The innermost layer of the epidermis is the stratum basale, which contains stem cells that divide to form new keratinocytes. The next layer is the stratum spinosum, which is the
thickes
t layer and contains Langerhans cells and spiny keratinocytes. This is followed by the stratum granulosum, in which keratinocytes are filling with keratin and starting to die. The stratum lucidum is next, but only on the palms and soles. It consists of translucent dead keratinocytes. The outermost layer is the stratum corneum, which consists of flat, dead, tightly packed keratinocytes that form a tough, waterproof barrier for the rest of the epidermis.
::上皮细胞最深层的一层是直肠直肠,其中含有分解形成新乳腺细胞的干细胞。下一层是直肠脊髓柱,这是最厚的层,含有兰汉细胞和脊椎脊髓细胞。接下来是直肠颗粒,其中脊髓细胞填满了氯拉丁,并开始死亡。直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠直肠。它由半转性死脊椎细胞组成。最外层是直肠角,由扁、死、紧紧凑的脊髓细胞组成,形成一个坚硬的、防水的外皮细胞屏障。 -
Functions of the epidermis include protecting underlying tissues from physical damage and pathogens. Melanin in the epidermis absorbs and protects underlying tissues from UV light. The epidermis also prevents loss of water from the body and synthesizes vitamin D.
::皮皮的功能包括保护底部组织免受物理损害和病原体的伤害。皮皮皮的梅兰宁吸收并保护底部组织免受紫外线光的影响。皮皮皮还防止身体水的流失,合成维生素D。 -
Melanin is the main pigment that determines the color of human skin.
T
he pigments carotene and hemoglobin, however, also contribute to skin color, especially in skin with low levels of melanin.
::Melanin是决定人类皮肤颜色的主要色素。 但是,色素胡萝卜和血红蛋白也助长了肤色,特别是在梅兰宁含量低的皮肤中。 -
The surface of healthy skin normally is covered by vast numbers of bacteria representing about one thousand species from 19 phyla. Different areas of the body provide diverse habitats for skin microorganisms. Usually, microorganisms on the skin keep each other in check unless their balance is disturbed.
::健康的皮肤表面通常包含大量细菌,代表19个植物群的大约1 000种物种,身体的不同区域为皮肤微生物提供了不同的栖息地,通常皮肤上的微生物相互调节,除非它们的平衡受到干扰。
Review
::回顾1. What is the epidermis?
::1. 后遗症是什么?2. Identify the types of cells in the epidermis.
::2. 确定上皮细胞的种类。3. Describe the layers of the epidermis.
::3. 描述下皮层。4. State one function of each of the four epidermal layers found all over the body.
::4. 说明全身四层上皮层各有一功能。5. Explain three ways the epidermis protects the body.
::5. 解释皮皮人保护身体的三种方式。6. What makes the skin waterproof?
::6. 是什么使皮肤防水?7. Why is the selective permeability of the epidermis both a benefit and a risk?
::7. 为什么有选择地渗透后遗症既是一种好处,也是一种风险?8. How is vitamin D synthesized in the epidermis?
::8. 维生素D如何在皮层中合成?9. Identify three pigments that impart color to skin.
::9. 识别给皮肤染色的三色色素。10. Describe bacteria that normally reside on the skin, and explain why they do not usually cause infections.
::10. 描述通常居住在皮肤上的细菌,并解释为什么它们通常不造成感染。11. Explain why the keratinocytes at the surface of the epidermis are dead, while keratinocytes located deeper in the epidermis are still alive.
::11. 解释为什么在皮层表面的乳腺细胞死亡,而在皮层深处的乳腺细胞仍然活着。12. Which layer of the epidermis contains keratinocytes that have begun to die?
::12. 上皮细胞的哪一层含有开始死亡的麦地诺细胞?13. True or False: The extra layer of epidermis found on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is located on the very outer surface of the skin.
::13. 真实或假:在手掌和脚底掌上发现的额外皮层位于皮肤外表。14. True or False: Melanin can be found in keratinocytes.
::14. 真实的或假的:米拉宁可以在麦拉蒂诺细胞中找到。15. Explain why our skin is not permanently damaged if we rub off some of the surface layer by using a rough washcloth.
::15. 解释为什么如果我们使用粗糙的毛巾擦掉表层,我们的皮肤就不会永久受损。Explore More
::探索更多You can learn more about the sea of microbes that live in and on the human body by watching this TED talk.
::通过观看本次TED演讲,你可以更多地了解生活在人体内和人体上的微生物的海洋。Many people blush when they are embarrassed, but why? Learn more here:
::许多人在尴尬时脸红,但为什么? -
The epidermis consists mainly of stacks of keratin-producing epithelial cells called
keratinocytes
. These cells make up at least 90 percent of the epidermis. Near the top of the epidermis, these cells are also called squamous cells.