11.16 前体感染 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
Shouldn't tuberculosis be controlled?
::不应该控制肺结核吗?Yes it should. Tuberculosis is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease was at a low for a long time but is now a problem again, because of multiple-drug-resistant strains that have evolved due to the overuse of antibiotics . These bacteria live in the lungs and destroy lung tissue .
::当然应该如此。肺结核是由Mycobiterium结核病引起的。这一疾病长期处于低位,但现在又是一个问题,因为抗药性抗药性多种菌株由于过度使用抗生素而演变。这些细菌生活在肺部,并摧毁肺组织。Modes of Infection
::感染模式Bacteria can cause disease in two ways: by physically growing and invading tissues and or by releasing toxins into the body.
::细菌可通过以下两种方式造成疾病:身体生长和侵入组织,或将毒素释放到身体中。Endotoxins are usually structural components of the bacterial cell wall which are released mainly when bacteria are lysed. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are endotoxic molecules that are found in the outer membranes of various Gram-negative bacteria . There are, however, endotoxins other than LPS. Endotoxins are, in large part, responsible for the symptoms of infections by pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria, such as Neisseria meningitidis, the that causes meningitis .
::内分泌毒素通常是细菌溶液时释放出来的细菌细胞墙的结构成分,而内分泌毒素主要是在各种克格朗阴性细菌的外膜中发现的内分毒分子,但内分泌毒素除外,内分泌毒素是导致脑膜炎的脑膜炎等致病性克-阴性细菌感染症状的主要原因。Exotoxins are excreted by many microorganism, including bacteria, , , and . An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting cellular metabolism . Both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria produce exotoxins. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, similar to endotoxins, may be released during cell lysis. Most exotoxins can be destroyed by heating. They may exert their effect locally or produce systemic effects.
::排毒因被许多微生物(包括细菌、细菌、和.)排毒因破坏细胞或破坏细胞代谢而可能对宿主造成损害。克格朗阴性细菌和克格伦阳性细菌都会产生排毒因,它们非常有效,可能对宿主造成重大损害。异氧因可能被秘密化,或类似于内分泌毒素,在细胞透析过程中释放。大多数异氧因可以通过取暖来销毁。它们可能在当地产生效果或产生系统效果。Well known exotoxins include the botulinum toxin produced by Clostridium botulinum. Botulinum toxin, which causes botulism, blocks nerve function, leading to paralysis of the respiratory and death. Exotoxins can be blocked by antibodies produced by the immune system , but many exotoxins are so toxic that they may be fatal to the host before the immune system has a chance to mount defenses against them. In these cases, it may be necessary to provide antibodies raised in other hosts to fight the toxins and provide immediate protection.
::众所周知的外毒包括由肉毒杆菌生产的肉毒毒素。 肉毒杆菌毒素导致肉毒杆菌、神经功能阻塞、呼吸系统瘫痪和死亡。 免疫系统生产的抗体可以阻塞外毒毒素,但许多外毒毒素毒性过大,在免疫系统有机会对宿主进行防疫之前,可能会对宿主致命。 在这种情况下,也许有必要提供其他宿主培养的抗体来对抗毒素并立即提供保护。Food-Borne Illness and Bacteria
::食 食 病 病 病 病 病 和 细菌Pathogenic bacteria can cause diseases by contaminating food . A foodborne illness is any illness that results from eating or drinking food that is contaminated with a chemical or biological toxin or a pathogen. Most cases of foodborne illness are caused by a variety of foodborne pathogenic bacteria and .
::由食物传染的疾病是指因食用或饮用食物而受化学或生物毒素或病原体污染的任何疾病,大多数由食物传染的疾病是由食物传染的病原体和各种病原体引起的。Foodborne illness is often called food poisoning, even though the physical effects of foodborne illness are not always caused by a toxin. True food poisoning occurs when a person eats food contaminated with a toxin. Botulism is a food intoxication. Bacteria can also cause illness by growing inside the host’s body after the bacteria have been swallowed in food. The bacteria may invade the cells lining the intestines or may produce a toxin inside the body.
::食物传播的疾病通常被称为食物中毒,尽管食物传播的疾病对身体的影响并不总是由毒素引起的。 真正的食物中毒发生在一个人食用被毒素污染的食物时。 肉毒杆菌是一种食物中毒。 细菌也可以在细菌被食物吞噬后在宿主体内生长,从而引起疾病。 细菌可能会侵入肠内细胞,也可能在体内产生毒素。The most common bacterial foodborne infections are caused by the bacteria Campylobacter, Salmonella, and E. coli O157:H7. All can be transmitted by the fecal-oral route. The bacteria are excreted in feces and may be transmitted through fecally contaminated , food, or by person to person contact.
::最常见的细菌食物传染感染是由Campylobacter、Salmonella和E.coli O157:H7.细菌引起的,所有细菌都可以通过粪便途径传播,细菌在粪便中排出,可以通过胎儿污染、食物或人与人接触的方式传播。Campylobacter
::装甲突击车Campylobacter is a bacterial pathogen that causes fever, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps within two to five days after exposure to the organism . The diarrhea may be bloody, and both nausea and vomiting may occur as well. The illness usually lasts one week. Some people who are infected with Campylobacter don't have any symptoms at all. It is the most commonly identified bacterial cause of diarrheal illness in the world. Campylobacter live in the intestines of healthy , cattle, pigs, cats, and dogs. The bacteria are spread throughout the environment by their hosts’ feces. As a result, Campylobacter are commonly found in soil . Most raw poultry meat has Campylobacter on it. Eating undercooked chicken or food that has been contaminated by raw chicken meat are the most frequent causes of this infection.
::Campylobacter是一种细菌病原体,在接触该有机体后二至五天内引起发烧、腹泻和腹部抽搐。腹泻可能是血腥的,也可能发生恶心和呕吐。 疾病通常持续一周。 一些感染Campylobacter的人没有任何症状。 这是世界上最常见的腹泻病的细菌原因。 Campylobacter生活在健康的肠子、牛、猪、猫和狗的肠子里。细菌通过宿主的粪便散布在环境中。结果,Campylobacter经常在土壤中发现。大多数生禽肉都有Campylobacter。食用未经煮熟的鸡肉或被生鸡肉污染的食物是这种感染的最常见原因。Salmonella
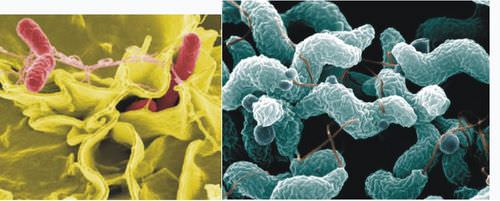
::鲑鱼Salmonella is also a bacterium that is commonly found in the intestines of birds, , and mammals . It can be spread to humans in many different foods of origin that have been contaminated by feces. Salmonellosis usually includes fever, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps within 12 to 72 hours after infection. The symptoms are a result of the bacteria invading the cells of the intestines, as shown in Figure . The illness usually lasts four to seven days, and most people recover without treatment. However, in some people diarrhea may be so severe that the patient needs to be hospitalized. In people with poor health or weakened immune systems, the bacteria can invade the bloodstream and cause life-threatening infections.
::沙门氏菌也是一种细菌,常见于鸟类和哺乳动物的肠胃中。它可以传播到人类中许多不同来源的食物中,这些食物受到粪便的污染。沙门氏菌通常包括感染后12至72小时内的发烧、腹泻和腹部抽筋。这些症状是细菌侵入肠细胞的结果,如图所示。这种疾病通常持续四至七天,大多数人不接受治疗就康复。然而,在一些人中,腹泻可能非常严重,病人需要住院治疗。在健康不良或免疫系统衰弱的人中,细菌可以侵入血液,造成危及生命的感染。Color-enhanced scanning electron micrographs of Salmonella typhimurium (red cells on the left) invading cultured human cells. S. typhimurium can lead to a form of human gastroenteritis sometimes called salmonellosis. The characteristic spiral, or corkscrew, shape of C. jejuni cells can be seen in the micrograph on the right. C. jejuni are the most common cause of bacterial food-related illness in the United States. E. coli O157:H7
::E. 科里O157:H7E. coli O157:H7 is one of hundreds of strains of the bacterium Escherichia coli. Although most strains are harmless, this strain produces a powerful toxin that can cause severe illness. E. coli O157:H7 has been found in the intestines of healthy cattle, deer, goats, and sheep. Human illness usually follows consumption of food or water that has been contaminated with very small amounts of cow feces. Drinking unpasteurized milk, swimming in or drinking fecally contaminated water, and eating contaminated vegetables have also been linked to infection by E. coli O157:H7. The symptoms of this infection are often severe and bloody diarrhea and painful abdominal cramps, usually without fever. In about five percent of cases, a severe complication causes intestinal bleeding, anemia, kidney failure , and possibly death.
::E. E. Coli O157:H7是数百种细菌Esherichia coli菌株之一。尽管大多数菌株都是无害的,但这种菌株会产生一种可导致严重疾病的强力毒素。E. coli O157:H7在健康的牛、鹿、羊和羊的肠道中发现。人类疾病通常发生在食用食物或水时,这种食物或水被极少量的牛粪污染之后。饮用未经洗涤的牛奶、在水中游泳或饮用胎儿污染的饮水,以及食用受污染的蔬菜也与E. Coli O157:H7的感染有关。这种感染的症状往往是严重和血腥的腹泻以及痛苦的腹部抽搐,通常没有发烧。在大约5%的病例中,严重的并发症导致肠出血、贫血、肾衰竭以及可能死亡。Contamination of Food
::食品污染Bacterial contamination of food usually arises from improper handling, improper preparation, or improper food storage. Good hygiene practices before, during, and after food preparation can reduce the chances of getting an illness. Many foodborne illnesses can be avoided by selecting, cooking, storing, and handling food correctly:
::细菌对食物的污染通常是由于处理不当、准备不当或食物储存不当造成的。 食品准备之前、期间和之后良好的卫生习惯可以减少生病的可能性。 许多食物传播的疾病可以通过选择、烹饪、储存和正确处理食物来避免:-
Check that the food you are about to buy is not damaged, bruised, or spoiled.
::请检查您即将购买的食物是否损坏、淤青或损坏。 -
Wash your hands often with warm water and soap.
::经常用热水和肥皂洗手。 -
Wash your knives, utensils, and the surfaces on which you prepare food with hot, soapy water.
::洗洗你的刀子,用具, 和表面 你准备食物的表面 用热,肥皂水。 -
Wash
fruits
and vegetables before you eat them.
::在你吃之前,先洗水果和蔬菜。 -
Store raw and cooked food separately.
::将生菜和熟食分开储存。 -
Cook foods to the proper recommended temperatures.
::烹饪食物达到适当的建议温度。 -
Store leftovers promptly in a refrigerator set at 4
o
C (40
o
F).
::在4oC(40oF)的冰箱中迅速储存剩菜。
Thorough cooking of foods and use of hot water kill most of the disease-causing bacteria that can be found in foods. Ingestion of contaminated food and water remains a leading cause of illness and death in the developing world, particularly for children.
::食用食物和热水的烹饪和热水的彻底烹饪使食品中大部分致病细菌死亡,食用受污染的食物和水仍然是发展中世界,尤其是儿童疾病和死亡的主要原因。Summary
::摘要-
Better food safety, improved hygiene practices, and water treatment have reduced the threat of some pathogens. Though many medical advances have been made to safeguard against infection by pathogens through the use of vaccination and antibiotics, pathogens continue to threaten human life. Personal behaviors also have an influence on a person’s chances of catching an infectious disease.
::更好的食品安全、更好的卫生习惯和水处理减少了某些病原体的威胁。 尽管通过使用疫苗和抗生素防止病原体感染病原体已经取得了许多医学进步,但病原体继续威胁着人的生命。 个人行为也会影响个人感染传染病的机会。
Review
::回顾-
How has the overuse of antibiotics affected the ability to fight bacterial infections?
::抗生素的过度使用对防治细菌感染的能力产生了何种影响?
-
Check that the food you are about to buy is not damaged, bruised, or spoiled.