12.28 菌菌生态 -- -- 高级
Section outline
-
Do all feed only on dead organisms ?
::所有的食物都只吃死生物吗?Not all. This fungus is a lichen and it provides nutrients for the tree. In return, the lichen gets sugars from the tree. Both benefit from this relationship.
::不是全部,这些真菌是一块地衣,它为树提供养分。作为回报,地衣从树上得到糖。两者都从这种关系中受益。Ecology of Fungi
::蘑菇的生态学Fungi as Decomposers
::Fingi 作为解析器Although decomposers , such as fungi, are generally located at the bottom of , food webs , and energy pyramids, decomposers in the are vital for the health of the environment. By breaking down dead material, they provide the nutrients that other organisms need to survive. As decomposers feed on dead organisms, they release nutrients into the soil .
::尽管真菌等分解器通常位于食物网和能源金字塔的底部,但环境健康则至关重要。 通过分解死亡物质,它们提供了其他生物需要生存的养分。 作为分解器食用死亡生物,它们向土壤中释放养分。Because they do not photosynthesize, fungi rely on organic sources of energy; they are heterotrophic. They are the primary decomposers (or saprotrophs ) in many . Most saprotrophic fungi grow as a branching network of hyphae . While can grow and feed only on the exposed surfaces of organic matter, fungi can use their hyphae to penetrate larger pieces of organic matter. Additionally, only fungi have evolved the necessary to break down plant like lignin and cellulose . Lignin is the tough complex carbohydrate found in wood, and cellulose is the complex carbohydrate found in plant cell walls . These two factors make fungi the primary decomposers in forests, where dead matter has high concentrations of lignin and is often in large pieces.
::因为他们不光合体,真菌依赖有机能源;它们是异氧营养学。它们是许多植物中主要的分解器(或盐分化器 ) 。 大部分盐分菌都是作为合金的分支网络而生长的。 虽然它们只能在有机物的露天表面生长和饲料,但真菌可以使用它们的合金穿透更大的有机物。 此外,只有真菌才演变出拆解木质和纤维素等植物所必需的真菌。 利尼因是木质中发现的硬性复合碳水化合物,而纤维素是植物细胞壁中发现的复杂的碳水化合物。 这两个因素使真菌成为森林中的主要分解器,在森林中,死亡物质具有高浓度的丁和大块。Decomposers eventually convert all organic matter into carbon dioxide and nutrients. This releases raw nutrients (such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and magnesium) in a form usable to plants and . This process resupplies nutrients to the ecosystem, which allows for greater primary production. Fungi also use the nutrients for their own growth and repair.
::分解器最终将所有有机物转化为二氧化碳和养分,释放出原生养分(如氮、磷和镁),其形式可用于植物和植物。这一过程为生态系统提供养分,从而可以增加初级生产。真菌还利用养分进行自己的生长和修理。Symbiotic Relationships of Fungi
::蘑菇的共生关系Another major ecological role of fungi is in the mutualistic relationship they have with plants. A mycorrhiza (Greek for fungus ) is a symbiotic (or occasionally weakly pathogenic) association between a fungus and the roots of a plant. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus may colonize the roots of a host plant either intracellularly or extracellularly. It is estimated that about 95% of plant families live in with mycorrhizal fungi. Figure shows the fruiting bodies of the bicolored deceiver mushroom that is often associated with tree roots.
::菌类的另一个主要生态作用是它们与植物的相互关系。 菌类的另一种主要生态作用是它们与植物的相互关系。 菌类和植物根部之间的共生关系( 偶尔是弱病原体) 是菌类和植物根部之间的共生关系。 在菌类协会中,菌类可能在细胞内或细胞外的宿主植物根部殖民化。 据估计,95%的植物家庭与菌类真菌一起生活。 图中显示了通常与树根相关的双色蘑菇的果实。The bicolored deceiver mushroom, Laccaria bicolor, is a mychorrhizal Basidiomycete that usually forms the symbiotic relationship with woody plants, such as trees. It is sometimes used in agriculture and horticulture to improve plant growth. Many fungi grow in symbiosis with certain plants, which is one way to identify the fungus. This mutualistic relationship provides the fungus with easy access to carbohydrates, such as glucose , which are made by the plant during . The carbohydrates are translocated from the site of photosynthesis to the root tissues and then to the fungal partners. In return, the plant gains the use of the mycelium's very large surface area to absorb and mineral nutrients from the soil, thus improving the absorption capabilities of the plant roots.
::这种相互关系为真菌提供了易于获取的碳水化合物,如葡萄糖,这是植物在......期间制造的。碳水化合物从光合作用地点移到根组织,然后转到真菌伙伴。反过来,植物利用的面积很大,从土壤中吸收和矿物质养分,从而提高植物根的吸收能力。Studies have shown that plants grown in sterile soils and growth media often grow poorly without the addition of fungal spores or hyphae of mycorrhizal fungi to the soil. The mycorrhizal fungi colonize the plant roots and aid in the uptake of soil mineral nutrients. The absence of mycorrhizal fungi can also slow in early or on disturbed soil. Phosphate is one of the mineral nutrients made available to the plant through this association. Plant roots alone may not be able to take up phosphate ions in alkaline soils. The mycelia of the mycorrhizal fungus can access the phosphate ions and make them available to the plants they colonize. Mycorrhizal mycelia are much smaller in diameter than the smallest plant roots and can explore a greater volume of soil, providing a larger surface area for absorption. Mycorrhizae are especially beneficial for its plant partner in nutrient-poor soils.
::研究显示,在无菌土壤和生长介质中生长的植物往往生长不良,而没有在土壤中添加真菌的真菌或新菌的脊椎菌菌,植物生长的植物往往不会生长不良。 菌菌菌真菌将植物根植于植物,帮助吸收土壤的矿质养分。 早期或受扰动的土壤中,没有菌菌菌真菌也会减慢。 磷酸盐是植物通过这一联系获得的矿质养分之一。 植物根可能无法单独吸收碱性土壤中的磷酸盐离子。 菌菌菌的神话可以接触磷酸离子,并提供给它们殖民的植物。 菌菌菌微菌微菌的直径比最小的植物根小得多,可以探索更大的土壤,为吸收提供更大的地表面积。 菌素贫瘠土壤中的植物伙伴尤其受益。Mycorrhizal plants are often more resistant to diseases, such as those caused by microbial soil-borne , and are also more resistant to the effects of drought. These effects are perhaps due to the improved water and mineral uptake in mycorrhizal plants.
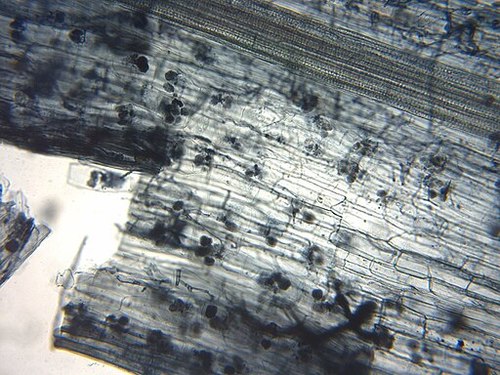
::出血杆菌植物往往更耐抗疾病,如微生物土壤传播引起的疾病,也更耐抗干旱影响,这些影响或许是由于在出血杆菌植物中水和矿物吸收的改善。Root tissue of a flax plant with a mycorrhizal fungus inside some of the root cells. Flax plants depend on their micorrhizal partners to help them absorb phosphorus from the soil. Lichens
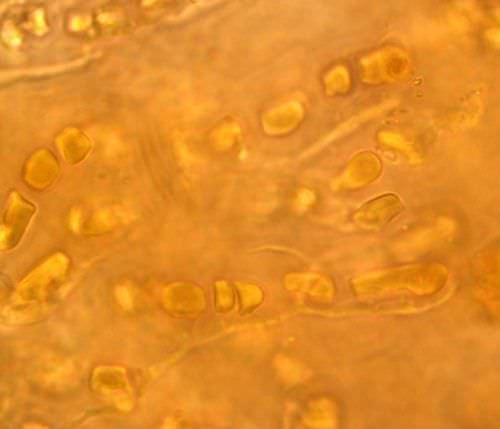
::厕所Lichens are not single organisms, they are symbiotic associations of a fungus (the mycobiont ) with a photosynthetic partner (the photobiont ), as shown in Figure . Lichens are referred to as "composite organisms." The photobiont is usually either a green alga or a cyanobacterium that produces food from sunlight. A few lichens are known to contain yellow-green algae or, in one case, a brown alga. The fungus surrounds the algal or bacterial , often enclosing them within special fungal tissues that are unique to lichen symbioses.
::不是单一生物体,而是如图所示的,菌类与光合作伙伴(光生生物)的共生联系。 菌类被称为“复合有机体”。光生生物通常不是绿色藻类,就是从阳光中产生食物的氰化物。已知有几片类含有黄绿色藻类,或者,在一种情况下,含有棕藻。菌类环绕藻类或细菌,通常将它们包含在特殊真菌组织中,而这些真菌组织对藻类和细菌而言是独特的。The cyanobacterium, Hyella caespitosa, as observed within the lichen, Pyrenocollema halodytes. Notice the thread-like fungal hyphae (long and thread-like) around the bacteria. The bacterial cells are surrounded by a special fungal tissue, but the bacterial cells are not inside the fungal cells themselves. The fungus usually makes up the majority of the body mass of the lichen. Lichens take the shape of the fungal partner, so they are named after the fungus. The fungus in a lichen is usually an Ascomycete but can also, more rarely, be a Basidiomycete. A lichen is either called an ascolichen or a basidiolichen. The photobiont provides sugars and other carbohydrates, while the fungus provides minerals and water. The functions of both symbiotic organisms are so closely intertwined that they function almost as a single organism.
::菌类通常占地衣质量的多数。 菌类以真菌伙伴的形状组成, 以真菌为代号。 菌类中的菌类通常是Ascomycete, 但更罕见的是, 也可以是Basidiomycete 。 菌类称为 ascolichen 或 basidiolichen 。 光生生物提供糖和其他碳水化合物, 而真菌则提供矿物质和水。 两种共生生物的功能相互密切交织, 几乎可以作为单一有机体运作 。Lichens do not have roots and do not need to have access to water, like most higher plants do. They can therefore grow in locations impossible for most plants, such as bare rock, sterile soil, sand, and various artificial structures, such as walls, roofs, and monuments. Lichens can survive very harsh conditions and live in the , the Antarctic, deserts, and mountaintops. They can withstand extreme temperatures. Many lichens grow as ( epi - on the surface, phyte - plant) on other plants, particularly on the trunks and branches of trees. When growing on other plants, lichens are not parasites ; they neither consume any part of the plant nor kill it.
::柳木没有根,不需要水,像大多数高原植物一样,他们不需要水。因此,他们可以在大部分植物无法种植的地方生长,例如裸露的岩石、无菌的土壤、沙子和各种人工结构,例如墙壁、屋顶和纪念碑。 柳木可以生存得非常艰苦,住在南极洲、沙漠和山顶。他们可以承受极端的温度。许多像(地表、植物)一样生长在其他植物上,特别是在树干和树枝上。在其他植物生长时,衣具不是寄生虫,它们既不消耗植物的任何部分,也不杀死植物的任何部分。Lichens are sensitive to environmental pollutants and have been used as indicator organisms in studies on environmental pollution. They are also important pioneer species ; they are usually one of the first eukaryotic organisms to colonize disturbed ecosystems in the process of succession. To read more about pioneer species and ecological succession , see the Community: Succession (Advanced) concept.
::食堂对环境污染物很敏感,在环境污染研究中被用作指标性生物体,也是重要的先驱物种;它们通常是在继承过程中殖民受破坏生态系统的第一批食堂生物之一,关于先驱物种和生态继承的更多信息,见共同体:继承(先进)概念。-
Edit here for caption
::编辑此标题 -
Edit here for caption
::编辑此标题
Tough organisms. (left-right) A Map lichen (Rhizocarpon geographicum) and a wall lichen (Xanthoria parietina Messinglav) growing on rocks. Lichens of these species were exposed to the harsh environment of space for 15 days and survived unharmed. The European Space Agency has discovered that lichens can survive unprotected in space. In an , two of lichen – Rhizocarpon geographicum and Xanthoria elegans, shown in Figure – were sealed in a capsule and launched on a Russian Soyuz rocket on May 31, 2005. Once in orbit the capsules were opened and the lichens were exposed directly to the vacuum of space as well as to the large temperature changes and cosmic radiation of open space. After 15 days the lichens were brought back to Earth and were found to be alive. They did not have any observable damage.
::欧洲航天局发现地衣可以在空间中不受保护地生存。 在图所示的两座地衣 — — Rhizocarpon地理系和Xanthoria Elgans — — 中,2005年5月31日被密封在一个胶囊中,用俄罗斯联盟火箭发射。 一旦在轨道上打开了这些胶囊,地衣就直接暴露在空间真空以及大温度变化和开放空间宇宙辐射之下。 在15天后,地衣被带回地球并被发现还活着。 它们并没有受到任何可见的损害。Fungi as a Food Source
::作为食物来源的真菌The fruiting bodies of fungi provide food for a wide variety of , from , slugs, and snails to rodents and larger mammals , such as deer and wild boars. Humans have collected and grown mushrooms for food for many thousands of years. However, many fungi have developed defense mechanisms that involve the production of toxins to discourage animals from eating them.
::生真菌的果实为各种各样的动物提供食物,从鼻涕虫和蜗牛到老鼠和更大的哺乳动物,如鹿和野猪。 人类收集并种植蘑菇以作为食物已经数千年了。 然而,许多真菌已经发展了防御机制,包括生产毒素来阻止动物食用这些毒素。Fungi and Insects
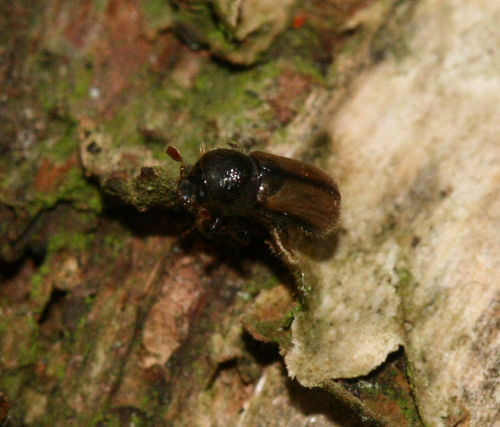
::菌类和昆虫Many insects also have mutualistic relationships with fungi. Several groups of ants, such as Leafcutter ants, grow Basidiomycete fungi as their primary food source. Ambrosia beetles, shown in Figure , cultivate various species of fungi in the bark of trees that they infest. A close association has evolved between ambrosia beetles and ambrosia fungi. Both the beetle and the fungus are completely dependent on each other in multiple stages of life. The beetles depend on the fungi for their successful colonization of a tree, and the fungi depend on the beetles for transport to their food source, the tree. Termites on the African savannah are also known to cultivate certain Ascomycetes in “fungal gardens.”
::许多昆虫也与真菌有相互性的关系。一些蚂蚁群,如Leafcutter 蚂蚁,种植Basidiomycete真菌作为它们的主要食物来源。Ambrosia Beetles,如图所示,在它们所侵袭的树皮中培育各种真菌品种。Ambrosia Beetles和Ambrosia真菌之间有着密切的联系。甲虫和真菌在生命的多个阶段都完全依赖彼此。甲虫依靠真菌成功地将一棵树殖民化,而真菌依靠甲虫将真菌运到其食物来源,即树。非洲热带草原上的白蚁也在“风林园”中培育某些阿斯奎切特人。Ambrosia beetles are common in tropical and subtropical areas worldwide. They cultivate fungal gardens in a unique display of symbiosis. Summary
::摘要-
Although decomposers, such as fungi, are generally located at the bottom of food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids, decomposers in the biosphere are vital for the health of the environment.
::虽然真菌等分解者通常位于食物链、食物网和能源金字塔的底层,但生物圈中的分解者对环境健康至关重要。 -
Fungi form a variety of symbiotic relationships with other organisms, including plants, animals, protists, and even bacteria.
::菌菌与其他生物形成多种共生关系,包括植物、动物、原生生物,甚至细菌。 -
The fruiting bodies of the fungi provide food for a very wide range of animals, from insects, slugs, and snails to rodents and larger mammals, such as deer, wild boars, and humans.
::真菌的果实为种类繁多的动物提供食物,从昆虫、鼻涕虫和蜗牛到鼠类动物和更大的哺乳动物,如鹿、野猪和人类。
Review
::回顾-
What are two main roles of fungi in the environment?
::真菌在环境中的两个主要作用是什么? -
Relate the terms saprotroph and heterotroph to fungi.
::将后退和后退的术语 与真菌相对应 -
Outline the symbiotic relationship that exists within a lichen.
::概括地衣内存在的共生关系 -
Give two examples of foods that are made with the help of fungi.
::举两个用真菌做食物的例子。 -
What is likely to happen if the mychorrhizae in a forest were to suddenly die off?
::如果森林里的短喉会突然消亡 会发生什么情况呢?
-