13.57 植物激素 - 高级
Section outline
-
Plant Hormones
::植物激素For the decade leading up to 1971, the United States Government used a set of chemicals named Rainbow Herbicides to conduct chemical warfare. The purpose of this military operation was to defoliate Vietnamese rainforests in order to deprive the opposition of food and cover. The infamous Agent Orange, named for the orange-striped barrels in which it was shipped, was the primary “weapon”, with some 12 million gallons used ( Figure ).
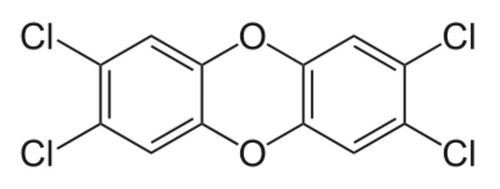
::在1971年以前的十年里,美国政府使用一套名为彩虹除草剂的化学剂进行化学战,这次军事行动的目的是为了除掉越南雨林,以剥夺反对派的食物和遮掩,以装货的橘色桶命名的臭名昭著的橙色剂是主要“武器”,使用了约1 200万加仑(图)。Chemical warfare during the Vietnam War sprayed Rainbow Herbicides including Agent Orange to destroy food and cover for the enemy. The herbicides killed plants by mimicking natural plant hormones. Unfortunately, in addition to destroying vegetation and , Agent Orange was contaminated with TCDD, the most toxic chemical in a group of compounds known as dioxins ( Figure ). TCDD is a by-product of the production of one of the herbicides. We know that the dioxin TCDD is teratogenic, mutagenic, carcinogenic, immunotoxic, and hepatotoxic, causing birth defects, , and , and poisoning immune systems and livers. Like DDT and methyl mercury, this chemical bioaccumulates ; it builds up in fatty tissue .
::不幸的是,除破坏植被和植物外,橙剂还被三丁二烯污染,三丁二烯是二恶英(图示)一类化合物中毒性最大的化学品。三丁二烯是生产一种除草剂的副产品。 我们知道二恶英三丁二烯是致畸、诱变、致癌、免疫毒性和肝中毒,造成先天缺陷,并毒害免疫系统和肝脏。与滴滴涕和甲基汞一样,这种化学生物累积,在脂肪组织中积聚。One of the herbicides in Agent Orange contains TCDD (above) as a by-product. TCDD is the most toxic of a group of chemicals known as dioxins, named for the two oxygen atoms that connect two benzene rings. Because TCDD causes birth defects, mutations and cancer, the EPA has banned the use of the herbicide containing it. Why discuss chemical warfare as an introduction to a lesson on plant ?
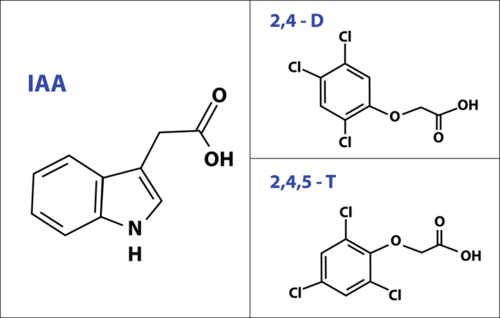
::为何讨论化学战,An herbicide , by definition, kills plants. Agent Orange contained 2 kinds of herbicides, known as 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T. You may have seen the effects of at least one of these chemicals if your family or neighbors try to control dandelions, because 2,4-D is the most widely used herbicide in the world. The dandelions begin to grow rapidly and quickly develop long, curled and leaves – and then they die. However, the grass appears unaffected; 2,4-D is especially popular because it kills dicots, but not . Farmers can use it on corn and wheat to kill weeds without affecting the crop itself.
::一种除草剂,顾名思义,会杀死植物。 橙剂含有2种除草剂,称为2,4-D和2,4,5-T。 如果你的家人或邻居试图控制dandelion,你可能已经看到过至少一种这些化学剂的影响,因为2,4-D是全世界使用最广泛的除草剂。 花草开始迅速生长并迅速生长,长长的、卷发的和叶子 — — 然后它们就死了。 然而,草不受影响;2,4-D特别流行,因为它杀死dicots,但不会。 农民可以在玉米和小麦上使用它来杀死杂草,而不会影响作物本身。The uncontrolled growth that occurs before death suggests the link to this lesson on hormones. These chemicals kill because they imitate a natural plant hormone known as indoleacetic acid (IAA) ( Figure ), which controls growth. Like all hormones, IAA has powerful effects on plant at very low concentrations. Spraying large doses of a chemical that behaves like this hormone causes unsustainable growth – and death. The message is that hormones are powerful molecules. In this lesson, you will explore the basics of what is currently known of plant hormones.
::死亡前的无控制增长与荷尔蒙的这一教训有关。这些化学物质之所以死亡,是因为它们模仿一种天然植物激素,即控制生长的植物激素(IAA)(Figure ) 。 和所有荷尔蒙一样,国际宇航科学院对低浓度的植物有着强大的影响。 大量喷洒类似荷尔蒙的化学物质造成了不可持续的增长 — — 和死亡。 信息是荷尔蒙是强大的分子。 在这个教训中,你会探索目前已知的植物激素的基本原理。The herbicides in Agent Orange, 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T, kill plants by mimicking a natural plant growth hormone, Indoleacetic Acid (IAA). Hormones are active at extremely low concentrations, so the large quantities of mimics used in herbicides quickly overwhelm plants with uncontrolled and unsustainable growth. Production of 2,4,5-T contaminates the herbicide with a highly toxic dioxin, TCDD, so its use today is limited. However, 2,4-D is the most widely used herbicide worldwide today. Overview of Plant Hormones
::植物激素概览The hormones which help to integrate and regulate your body are produced in glands and carried by your bloodstream (or sometimes tissue fluids) to distant “target cells”, where they alter metabolism . Your pancreas , for example, secretes the hormone insulin into your bloodstream; when insulin reaches liver (among others), the molecule “docks” with a receptor protein and opens channels for the uptake of glucose . Although plants lack both glands and bloodstream, they, too, produce molecules that regulate growth and development.
::有助于整合和调节你身体的荷尔蒙是用腺生成的,由你的血液(有时是组织液)携带到遥远的“目标细胞 ” , 从而改变新陈代谢。 比如,你的胰腺将荷尔蒙胰岛素分泌到你的血液中;当胰岛素到达肝脏(以及其他的 ) , 含有受体蛋白的分子“docks ” , 并打开吸收葡萄糖的渠道。 尽管植物缺乏腺和血液,但它们也会产生调节生长和发育的分子。The word hormone comes from a Greek word meaning “that which sets in motion”. Both animal and plant hormones fit this definition. Plants bring about change in an organism by:
::荷尔蒙一词来自希腊一个词,意思是“动动的”。 动物和植物荷尔蒙都符合这个定义。-
altering the expression of
genes
(turning them “on” or “off”)
::改变基因的表达方式(改变基因“开”或“关闭”) -
modifying
of
::修改修改 -
changing
::变动 -
transforming cell growth
::变换细胞增长
Plant hormones are relatively small molecules, and compared to animal hormones, there are relatively few of them. Plants produce hormones locally, in tissues much less clearly defined than animal glands. Plant hormones may act locally, too – sometimes within the cell that produces them. Although plants lack cardiovascular systems, they have at least four ways of moving hormones through tissues. Two types of can move hormones from one part of the plant to another: sieve tubes move sugars from leaves to and flowers , and xylem moves from roots to leaves. Certain hormones may move together with the sugars or water. Cytoplasmic streaming moves substances within cells, and carries ions and molecules between cells. Despite these less glamorous attributes, plant hormones are powerful and essential regulators of and development. They govern leaf, stem, and seed growth, time of flowering, fruit development and ripening, aging of leaves and fruits, lifespan, and even death.
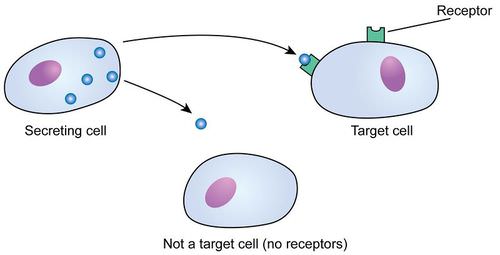
::植物荷尔蒙是相对较小的分子,与动物荷尔蒙相比,植物荷尔蒙相对较少。植物在本地生产激素,在组织上比动物腺更不明确。植物荷尔蒙也可以在当地 — — 有时在生产这些激素的细胞内 — — 发挥作用。 虽然植物缺乏心血管系统,但至少有四种方法可以将激素通过组织移动。 两种类型可以将荷尔蒙从植物的一个部分转移到另一个部分:筛选管将糖从叶子移到花叶和花卉之间,而氧化液则从根部移到叶子之间。 某些荷尔蒙可能与糖或水一起流动。 细胞内潮流物质在细胞内流动,在细胞间携带离子和分子。 尽管这些不那么光亮的特性,植物荷尔蒙是调节和发展的强大和必不可少的调节器。 它们管理叶、干和种子生长、开花的时间、水果开发和成熟的时间、叶和水果的老化、叶和水果的老化、寿命甚至死亡。Plants do resemble animals in that not all cells respond to hormones. In animals, target cells respond to hormones because they have specific receptors in the or . In plants, receptors are probably often involved, but cell response may depend more on timing. At certain points during their growth cycles, plant cells become sensitive to the presence of hormones; before or after that time, they respond little or not at all. Of course, this difference in sensitivity could easily be the difference in presence of receptor proteins ( Figure ).
::植物的确与动物相似,因为并不是所有的细胞都对荷尔蒙作出反应。在动物中,目标细胞对荷尔蒙作出反应,因为它们有特定的受体。在植物中,受体可能经常参与,但细胞的反应可能更多取决于时间。在生长周期的某些时间点,植物细胞对荷尔蒙的存在变得敏感;在这种时间之前或之后,它们的反应很少或根本没有。当然,在感应上的这种差异很容易是存在受体蛋白的差别(图示 ) 。Most hormones affect target cells which have very specific protein receptors. Often, these receptors are on the cell surface, as illustrated above. Some receptors are located inside the nucleus, allowing direct effects on gene expression and transcription. Plants can regulate hormone levels in several ways:
::植物可以通过几种方式调节荷尔蒙水平:-
controlling levels of precursor molecules necessary for hormone synthesis
::荷尔蒙合成所需的前体分子控制水平 -
storing excess hormone within cells
::在细胞内储存过量激素 -
moving hormones from one part of the plant to another
::将激素从工厂的一个部分转移到另一个部分 -
inactivating existing molecules by binding them to
,
amino acids
, or peptides
::将现有分子与氨基酸或铅化物结合,从而使其失去活化作用 -
chemically breaking down hormones
::化学分化激素
In both plants and animals, hormones are effective at extremely low concentrations, making their study a challenge for scientists. In both plants and animals, hormones interact, sometimes working together (as synergists) and sometimes opposing one another (antagonists). In plants, often the ratio or proportions of two hormones determine the effect. In other words, the effect of the hormone depends upon the hormone's concentration and interactions with other hormones. Using chemical structure and biological effects, botanists have grouped plant hormones into five basic classes, which are discussed in the next sections of this lesson.
::在植物和动物中,荷尔蒙在极低浓度下有效,使他们的研究成为科学家的挑战。在植物和动物中,荷尔蒙相互作用,有时(作为协同者)一起工作,有时(作为协作者)相互对立。在植物中,两种荷尔蒙的比例或比例往往决定着效果。换句话说,荷尔蒙的效果取决于荷尔蒙的浓度和与其他荷尔蒙的相互作用。使用化学结构和生物影响,植物学家将植物荷尔蒙分为五类基本类别,本课下一节将讨论这些问题。Summary
::摘要-
Some Herbicides mimic hormones that kill plants by causing uncontrolled, unsustainable growth.
::有些除草剂模仿荷尔蒙,导致无节制、不可持续的增长,导致植物死亡。 -
Hormones are effective at extremely low concentrations.
::荷尔蒙在极低浓度条件下有效。 -
Effect of a particular hormone is concentration dependent; hormones may have different effects at different concentrations.
::某一荷尔蒙的影响取决于浓度;荷尔蒙在不同浓度情况下可能具有不同影响。 -
Like animal hormones, plant hormones affect target cells via receptor proteins.
::像动物荷尔蒙一样,植物荷尔蒙通过受体蛋白影响目标细胞。 -
Plant hormones differ from animal hormones because plants lack both glands and cardiovascular systems.
::植物荷尔蒙不同于动物荷尔蒙,因为植物缺乏腺和心血管系统。 -
Plant hormones bring about change by altering gene expression, transcription, cell division, and growth.
::植物荷尔蒙通过改变基因表达、转录、细胞分裂和生长带来变化。 -
Plant hormones control growth, flowering, fruiting, aging, and even death.
::植物荷尔蒙控制生长、开花、结果、衰老甚至死亡。 -
Plants regulate levels of hormones by altering precursors, transport, inactivation, breakdown, or storage.
::植物通过改变前体、运输、停止活动、分解或储存来调节激素水平。
Review
::回顾-
What is a herbicide?
::什么是除草剂? -
How do plants bring about change in an organism?
::植物如何改变有机体? -
Give five examples of how plants regulate hormone levels.
::举五个例子说明植物如何调节激素水平。
-
altering the expression of
genes
(turning them “on” or “off”)