14.1 动物 -- -- 先进
章节大纲
-
What do all animals have in common?
::所有的动物有什么共同点?The ability to smile? No. But they are all eukaryotic, heterotrophic, and multicellular.
::微笑的能力?All organisms on earth are divided up, or classified, into six primary groups called kingdoms. The six kingdoms of organisms are:
::地球上的所有生物都分为六大类,称为王国,或分类为六大类。- .
-
Eubacteria.
::欧巴塞亚 -
Protista
.
::普罗蒂斯塔。 - .
-
Plantae.
::普兰泰 -
Animalia.
::动物。
In these concepts we will examine the animal . Members of the animal kingdom have a number of characteristics that distinguish them from organisms within other kingdoms, such as the internal organization of their and how they obtain nutrients . The animal kingdom is subdivided into a number of different groups called phyla. In the three Animals concepts, we will explore the characteristics of animals, the of animals into different phyla, and the major trends that can be seen in the evolution of animals.
::在这些概念中,我们将研究动物。动物王国的成员有若干特点,它们与其他王国内的生物有区别,例如它们的内部组织及其如何获得营养。动物王国被细分为若干不同的群体,称为“植物”。在三种动物概念中,我们将探讨动物的特性,动物的特性,动物的特性,以及从动物的进化中可以看到的主要趋势。Characteristics of Animals
::动物的特征There is enormous variation among the different that make up the of the animal kingdom, as shown in Figure . Despite this variation, there are a number of basic characteristics that are shared by all animals. In this section, we will first consider how it is that such a diverse group of organisms are evolutionarily related to each other, and then we will examine the common traits that exist among all animals.
::如图所示,动物王国的不同构成差异很大。尽管存在这种差异,但所有动物都具有一些共同的基本特征。在本节中,我们将首先考虑这样一个不同的生物组是如何演变成相互联系的,然后我们将研究所有动物的共性。Examples of some of the many diverse species that make up the animal kingdom. (A) Sponge, (B) Flatworm, (C) Flying Insect, (D) Frog, (E) Tiger, (F) Gorilla. How are All Animals Related to Each Other?
::所有动物如何彼此相亲相爱?All organisms on earth descend from a single common ancestor . This ancestor is thought to have originated approximately 3.5 to 4 billion years ago. Over long periods of time, the process of evolution and led to a divergence of the descendants of this ancestor. Divergence is the evolutionary process by which some individuals within a species develop traits - due to random - that make them different from other members of the species. Divergent evolution results in the formation of a new species when these differences become so large that the different individuals can no longer interbreed with the original members of the species. This process is called . Over time, divergence and speciation ultimately result in the diversity of species that we see on earth today (see the Concept Evolution (Advanced) chapter).
::地球上的所有生物都来自同一个共同祖先。 这个祖先被认为大约35至40亿年前就起源于这个物种。 很长一段时间以来, 进化过程和导致这个祖先后代的分裂。 差异是一个物种中的某些个体由于随机而发展特征的进化过程,使得它们与物种的其他成员不同。 当这些差异变得如此巨大,以至于不同的个体无法再与物种的原始成员发生接触时, 差异演变导致新物种的形成。 这个过程被称为 。 随着时间的推移, 差异和物种的分化最终导致我们今天在地球上看到的物种的多样性(见概念进化(高级)一章)。All members of the animal kingdom are more closely related to each other than to organisms in any other kingdom because they diverged more recently from each other than they did from members of other kingdoms. This can be compared to the difference between siblings and cousins. You are related to your cousins, but you have to go back to two generations, to your grandparents, to find an ancestor that you all share. You are more closely related to your siblings because you only have to go back one generation to find a common ancestor: your parents. Of course, all animals have to go back an enormous number of generations to reach their shared common ancestor, but not as far back as an animal and a plant would have to go to find a common ancestor.
::动物王国的所有成员比其他任何王国的生物都更紧密地联系在一起, 因为他们最近与其它王国的成员不同。 这可以比作兄弟姐妹和堂兄弟的区别。 你与你的堂兄弟有关系, 但你必须回到两代人, 祖父母, 找到你们都共有的祖先。 你与兄弟姐妹的关系更密切, 因为你只需要回到一代人, 才能找到一个共同的祖先: 你的父母。 当然,所有动物都必须回到一代人, 才能回到他们共同的祖先, 但是不能追溯到动物和植物, 才能找到一个共同的祖先。As a result of this comparatively close relationship, members of the animal kingdom share a number of basic traits. They are all defined as multicellular organisms that must obtain organic nutrients by consuming other organisms and whose cells do not have cell walls . In the next three subsections, we will examine this description in more detail, and we will consider a number of other characteristics that distinguish animals from organisms within the other five kingdoms. These characteristics are roughly divided into three categories: structure, function, and reproductive .
::由于这种相对密切的关系,动物王国的成员具有一些基本特征,它们都被定义为多细胞生物,它们必须通过食用其他生物获得有机养分,而细胞没有细胞壁。在接下来的三个小节中,我们将更详细地研究这一描述,我们将考虑将动物与其他五个王国内的生物区别开来的若干其他特征。这些特征大致分为三类:结构、功能和生殖。Animal Structure
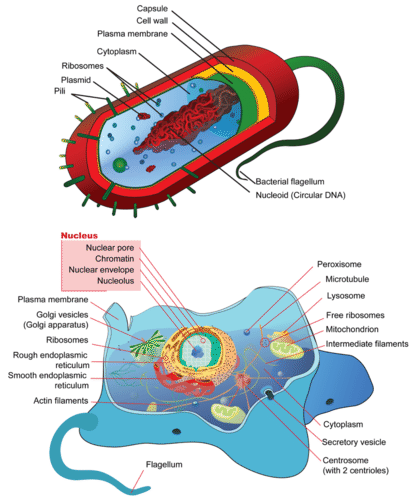
::动物结构Animal cells are eukaryotic. This trait is shared with organisms of three other kingdoms: plants, fungi, and . Cells of the bacterial kingdoms are prokaryotic. The major difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell is the presence of a . The nucleus is a membrane-bound within the cell that contains genetic information in the form of composed of . In prokaryotic cells the chromosomes are not enclosed by a membrane compartment. There are generally other membrane-bound organelles within a eukaryotic cell that are specialized for specific cellular functions. An example of a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell are shown in Figure . These cell types are extensively discussed in the Concept Cell Biology (Advanced) chapter.
::动物细胞是乳腺细胞。 这种特性与另外三个王国的生物共有:植物、真菌和.细菌王国的细胞是蛋白质的。 prokary细胞和eukary细胞之间的主要区别是存在。 核是细胞内含有以基因信息的形式构成的膜。 在 prokary细胞中, 染色体没有被膜隔膜包着。 通常, 在精液细胞内, 还有其他受膜约束的有机器官, 专门用于特定的细胞功能。 图中展示了 prokary细胞和eukary细胞的例子。 这些细胞类型在概念细胞生物学( 防腐化) 一章中广泛讨论。A prokaryotic bacterial cell (top) and a eukaryotic animal cell are shown (bottom) for comparison. Various internal structures are labeled. Note the many organelles within the eukaryotic cell that are not present in the prokaryotic cell. The most prominent of these organelles is the cell nucleus, which contains the genetic material. The cells of plants, fungi, some protists, and some have a cell wall. A cell wall is a rigid layer that surrounds the and is usually composed primarily of molecules. The cell wall functions to provide structural support and protection to the cell. Animal cells do not have a cell wall. This allows them to have more flexibility and to adopt different shapes. Some animal cells, such as the shown in Figure , have an extremely elongated shape that is essential to their function. In the case of neurons, an extended cell shape is necessary for transmitting nerve signals over long distances. This shape would not be feasible if the cell were surrounded by a rigid wall. Neurons are discussed in the The concepts under Anatomy and Physiology .
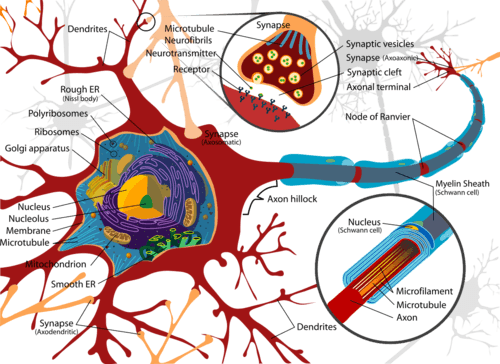
::植物细胞、真菌细胞、一些原生细胞细胞和一些人有细胞墙。 细胞墙是一个硬层, 环绕着细胞, 通常主要由分子组成。 细胞墙功能为细胞提供结构支持和保护。 动物细胞没有细胞墙。 这允许它们有更大的灵活性并采用不同的形状。 一些动物细胞, 如图所示, 其形状非常长, 对其功能至关重要。 对于神经细胞来说, 长的细胞形状是长距离传送神经信号所必须的。 如果细胞被硬墙包围, 这个形状是行不通的。 “ 解剖学和生理学” 的概念中讨论了神经元。A diagram of a neuron, illustrating the extended shape and specialized cell regions such as the dendrites (that receive information) and the axon (that transmits information to the next cell). Most animals have specialized tissues and organs that carry out specific functions within the animal, such as the nervous system and the muscular system . These are discussed in the next section.
::大多数动物有专门的组织和器官,在动物体内发挥特定功能,如神经系统和肌肉系统,下一节将讨论这些问题。Animal Function
::动物功能In addition to the absence of a cell wall, animals differ from plants in another important way. Plants are capable of using the energy from the sun to generate their own organic nutrients from inorganic molecules by . An organism that can synthesize its own nutrients is called an autotroph . In contrast, animals are heterotrophs . Heterotrophs obtain organic nutrients by consuming either autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
::除了没有细胞墙之外,动物在另一个重要方面与植物不同,植物能够利用太阳的能量从无机分子中产生自己的有机养分。可以合成自己养分的有机体称为自发养分。相反,动物是血化动物。通过食用自发或其他血化物质获得有机养分。At some stage in their life cycle, all animals are capable of movement . For most animals, it is the adult stage that is motile. This is mediated by the muscular system. The muscular system allows animals to actively seek food resources as well as mating partners for . It also allows them to escape from predators . Movement would not be possible, however, without a nervous system. Nearly all animals have some type of nervous system. It consists of a network of tissue that enables animals to sense what is going on in their environment and to respond to these events. Animals detect stimuli from their environment using sensory organs. This information is transmitted between cells of the nervous system through both electrical impulses and biochemical molecules released by the cells. As the information is transmitted and processed, the nervous system mediates behavioral responses, such as movement. The organization of the nervous system ranges from a very simple net of nerve cells (jellyfish, for example) to a highly complex network with a centralized brain , such as that of vertebrates .
::在生命周期的某个阶段,所有动物都能够运动。对于大多数动物来说,这是成人阶段,是运动阶段。这是由肌肉系统调节的。肌肉系统允许动物积极寻求食物资源以及交配伴侣。它也允许动物逃离掠食动物。但是,没有神经系统,运动是不可能的。几乎所有动物都有某种神经系统。它由组织网络组成,使动物能够感知到环境中正在发生的事情并对这些事情作出反应。动物通过感官器官从环境中检测刺激。这种信息通过电动和细胞释放的生化分子在神经系统的细胞之间传播。随着信息的传输和处理,神经系统介质反应,例如运动。神经系统的组织从非常简单的神经细胞网(例如,大象大象)到一个高度复杂的网络,有中央大脑,例如脊椎动物的网络。Another feature unique to animals is internal digestion . While many other organisms absorb nutrients directly from their environments, most animals eat other organisms. They must first digest their food and then absorb the nutrients derived from the digestion process. This requires an internal made up of a digestive cavity. Similar to the variety in the nervous system, digestive systems can also range from very simple systems to highly complex systems. These will be discussed in The Digestive System concepts.
::动物独有的另一个特点是内消化。虽然许多其他生物直接从环境吸收养分,但大多数动物食用其他生物。它们必须首先消化食物,然后吸收消化过程产生的养分。这需要由消化洞组成的内部。与神经系统的多样性相似,消化系统也可以从非常简单的系统到高度复杂的系统。这些将在“消化系统”概念中讨论。Animal Reproduction and Life Cycle
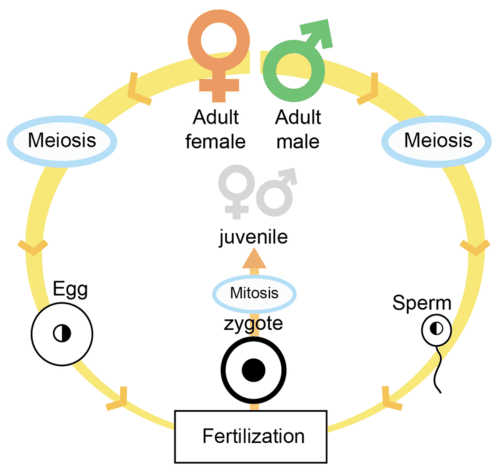
::动物生殖和生命周期Throughout most of its life cycle, an animal is generally diploid . Diploid refers to having two copies of the genetic material , or chromosomes, one copy from the female parent and one copy from the male parent. Most animals reproduce by . This involves the formation of two types of gametes : eggs and . Each gamete is formed from specialized reproductive organs in the animal, through a process called . Gametes contain half of the genetic information within the parental cells and are therefore haploid . Haploid means having only one copy of each chromosome. Sexual reproduction occurs when a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell to generate a diploid cell. This process is called . A fertilized egg, called a zygote , then undergoes a number of cleavage events to form a mass of cells known as an embryo . The embryo goes on to develop into a new individual. This cycle is shown in Figure . For more information on meiosis, see the Meiosis concepts.
::在动物的整个生命周期中,动物一般都是低血球。 Diploid是指有两份遗传物质或染色体,一份来自母母体,一份来自母体,一份来自母体,一份来自母体。大多数动物繁殖。这涉及形成两种类型的调子:蛋和。每个调子都是由动物的专门生殖器官通过一个叫做“胚胎”的过程形成。网叶含有父母细胞遗传信息的一半,因此是杂交的。Haploid意味着每个染色体只有一份。当精子细胞与卵细胞发生结合以产生低血球细胞时,性繁殖就会发生。这个过程被称为:一个发酵的蛋,称为zygote,然后进行一系列分离事件,形成一个被称为胚胎的细胞群。胚胎继续发展成一个新的个体。图中显示了这一循环。关于肾病的更多信息,请参见Meisic概念。Animal Life Cycle. An animal life cycle that includes only sexual reproduction is shown here. Some animals also reproduce asexually. How does the animal life cycle compare with the life cycle of a plant? Animals generally develop through several different embryonic stages. These stages include the formation of a blastula and gastrulation. A blastula is a hollow sphere of cells. Gastrulation is the process by which one region of the ball retracts, or invaginates, into the hollow space. You can imagine this looking similar to pushing your finger into a partially deflated balloon. The resulting embryo is shaped like a sac encircled by two cell layers. Further and cell differentiation result in a fully developed organism. In the Animals: Evolution (Advanced) concept we will consider how these embryonic stages reflect the steps that occurred during the evolution of the earliest animals.
::动物一般会通过几个不同的胚胎阶段发育。 这些阶段包括形成一个爆炸性球和星座。 爆炸性球是细胞的空空球。 放大是球的一个区域向空洞空间移动或渗入的过程。 您可以想象这与将手指推入一个部分减缩的气球相似。 由此形成的胚胎的形状像一个由两个细胞层环绕的sac。 进一步的和细胞分化导致一个完全发达的有机体。 在动物: 进化( 高级) 概念中, 我们将考虑这些胚胎阶段如何反映早期动物进化过程中的步骤 。Summary
::摘要-
All organisms on earth descend from a single common ancestor, but animals are more related to each other than to bacteria, fungi, protists, or plants.
::地球上的所有生物都来自一个共同的祖先, 但动物比细菌、真菌、原生生物或植物更相关。 -
Animals are multicellular organisms that are made up of eukaryotic cells without cell walls.
::动物是多细胞生物,由无细胞壁的乳房细胞组成。 -
Animals are heterotrophs and usually reproduce through sexual reproduction.
::动物是血化动物,通常通过性繁殖繁殖繁殖。
Review
::回顾-
Which four kingdoms contain organisms with eukaryotic cells?
::哪个四个王国 含有含有含尿道细胞的生物? -
What characteristic of animal cells makes it possible for nerve cells to have their elongated shape?
::动物细胞的什么特征使得神经细胞能够长长的形状? -
Why are animals capable of movement, at least in some stage of their life cycle? What system common to all animals makes movement possible?
::为什么动物能够移动,至少在其生命周期的某个阶段如此?什么是所有动物都可以移动的常见系统? -
How do most animals reproduce?
::大多数动物是如何繁殖的?