15.39 昆虫生殖和发展 -- -- 高级
Section outline
-
Where do butterflies come from?
::蝴蝶从哪里来?Most everyone knows they are not born as butterflies but as caterpillars. After mating , the black swallowtail butterfly lays small, yellow eggs . The caterpillars grow to about two inches and are green and black banded with yellow spots around every second black band. They have short, black spikes around some of the black bands, although these disappear as the larva nears pupation and undergoes a complete metamorphosis .
::大部分人知道它们不是作为蝴蝶出生的,而是作为毛虫出生的。交配后,黑燕尾蝴蝶产下小黄蛋。毛尾虫长到两英寸左右,每第二个黑带周围就有绿色和黑色的斑点。它们围绕一些黑带有短的黑尖,尽管它们随着幼虫接近幼崽而消失,并经历了彻底的变形。Reproduction and Development in Insects
::昆虫的繁殖和发展Nearly all reproduce by . This involves the formation and fusion of gametes : from the testes and eggs from the ovaries . There are some of insects that can also reproduce asexually. They do this by a process called parthenogenesis . During parthenogenesis, a female’s egg can produce a new organism without being fertilized by sperm. This usually requires that the females can produce eggs that have two copies of each (diploid) instead of the one copy that an egg normally contains (haploid). Parthenogenesis generates an exact clone of the female. There are several other forms of parthenogenesis found in some insect species. One of them is extremely interesting because it allows the female to choose whether she will produce male or female offspring. In these species, including some ants, bees, and wasps, females are diploid and are the result of sexual reproduction (fusion of egg and sperm), whereas males are haploid and are the result of parthenogenesis. The female produces haploid eggs, and she can choose whether or not to fertilize them with sperm obtained from a male and stored in her body. If she fertilizes the eggs by allowing them to fuse with sperm, they will become diploid and produce female progeny. If she chooses not to fertilize the eggs, they will still develop, but they will produce haploid male progeny.
::几乎全部由精子繁殖。 这涉及到调子的形成和融合: 来自卵巢的睾丸和卵子。 有一些昆虫也可以以性方式繁殖。 它们中有一些昆虫也可以以性的方式繁殖。 它们中有一个过程叫作异性起源。 在发酵过程中, 雌蛋可以产生一个新的有机体, 而不用精子来施肥。 这通常要求雌卵可以生产出两个副本的蛋( 卵子) , 而不是一个蛋通常含有的( 黄瓜) 。 帕赫诺的产卵可以产生一个精确的雌性克隆。 在一些昆虫物种中, 也发现了几种其他的异性繁殖形式。 其中一种非常有趣, 因为它允许雌虫选择自己是否会生产男性和女性后代。 在这些物种中, 包括一些蚂蚁、 蜂群和黄瓜, 雌卵可以产生两本( 蛋和精子的繁殖) , 而雄卵子仍然有机, 它们是雌卵子的产卵子。 她可以选择用预产的精精, 但是她可以将精精精制成精精精, 。 如果让雌蛋产产, 产, 她可以生产精精精精精精制成精制成卵, , , 将精制成精制成精制成精制成精制成精, , 将精制成精制成精制成精制成精制成精, , , , 将精制成精制成精制成精制成精制成精制成精制成精制成精制成精制成卵, 。Unlike that can release their sperm into the open ocean where they will swim to the eggs in the female’s body, most insects have to either deliver sperm directly or indirectly into the female’s body for internal fertilization . There are some species that package their sperm into sealed pouches that they leave on the ground for females to find. The females then use the packaged sperm to fertilize their eggs. This is less efficient than directly delivering sperm into the female’s body by copulation, and it runs the risk of the pouch not being found.
::与那些可以将精子释放到露天海洋,让她们游到雌性体内的卵蛋中去的昆虫不同,大部分昆虫必须直接或间接地将精子送到雌性体内进行体内授精。 有一些物种将精子包装在密封的袋子中,让雌性在地上找到。 雌性然后用包装的精子给卵子施肥。 这比直接通过交接将精子送入雌性体内要效率低,而且有可能找不到。Insect Life Cycle. This diagram represents the life cycle of a mosquito. Most insects have a similar life cycle. Metamorphosis
::变形Many of the invertebrates that we have examined so far go through one or more larval stages during their from an embryo to an adult. These larval stages are often very different in form from the adult . This is called indirect development, and it differs from direct development in which the young organisms hatch resembling smaller versions of the adult. The process of developing from a larva to the recognizable adult form is called metamorphosis. Most insects go through some form of metamorphosis. In some insect species, the transition to involves relatively minor changes, but, in the majority of species, it is a drastic and profound transformation.
::到目前为止,我们所检查的许多无脊椎动物在胚胎到成年期间经历了一个或一个以上的幼年阶段。这些幼年阶段的形式往往与成年人大不相同。这被称为间接发育,与幼小的成年生物体形成类似体的直接发育不同。从幼虫到可识别成人形态的发育过程被称为变形。大多数昆虫都经历了某种形式的变形。在一些昆虫物种中,向相对小的变化过渡,但在大多数物种中,它是一个剧烈和深刻的转变。Insects that do not undergo a metamorphic change during their development are called ametabolous insects. These include members of the Apterygota subclass and Paleoptera infraclass. The only change that these species undergo is an increase in size and the maturing of sexual organs . Among insects that experience metamorphosis, there are two types:
::在发育过程中没有发生变形变化的昆虫被称为代谢性昆虫,其中包括Apterygota亚类和Paleoptera次类成员。这些物种唯一的变化是性器官的大小和成熟。在经历变形的昆虫中,有两种类型:-
Hemimetaboly (superorder Exopterygota).
::Hemimetaboly(超导体外心电图) -
Holometaboly (superorder Endoterygota).
::Holometabol(超级指令Enterygota) 。
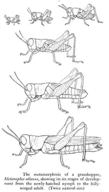
Hemimetabolous insects, such as cockroaches, grasshoppers, and dragonflies, go through gradual changes as they slowly develop from juvenile forms, called nymphs, to the adult form. These changes often include the budding and growth of their wings . The overall forms of the nymphs and the adults are not drastically different from each other, and most of the body parts are the same between the two. The stages of development of a hemimetabolous insect, the grasshopper, are shown in Figure .
::昆虫,如蟑螂、和等,随着幼虫的发育,即所谓的昆虫,逐渐演变成成人,这些变化往往包括翅膀的发育和生长。鼻虫和成人的总体形式并不大不相同,大部分身体部位在两者之间是相同的。青蛙是幼虫,其发育阶段如图所示。A grasshopper undergoing hemimetabolous development. Notice that the overall features do not drastically change during the grasshopper’s development from a nymph to an adult, but wings begin to emerge and develop during this process, and the grasshopper increases in size. Holometabolous insects are another story altogether. Think of the difference between a maggot and a fly. The larval stages are distinctly different from the adult stage. Insect larvae are focused on two main activities: eating and growing. At the end of the larval stage, they still do not have any obvious adult features. They then enter a transition stage called a pupa (plural pupae ). Pupae are immobile, and sometimes they are encased in a cocoon made of silk or a hard shell. During the pupal stage, the tissues and appendages of the larval stage are broken down and reorganized into new adult tissues, organs, and limbs. Figure shows an insect at various times during the pupal stage. The mature adults emerge from the pupal stage able to move and reproduce, looking nothing like the preceding larval stage. As with molting , this process is controlled by that trigger the drastic internal changes needed to undergo metamorphosis.
::和苍蝇之间的差别。 幼虫的幼虫主要集中于两种活动: 食用和生长。 在幼虫阶段的末端, 它们仍然没有明显的成年特征。 然后它们进入一个过渡阶段, 叫做幼虫( 花生虫 ) 。 Pupae 是不流动的, 有时它们被困在由丝状或硬壳组成的圆锥体中。 在幼虫阶段, 幼虫阶段的组织与附附体被打破, 并重组为新的成年组织、 器官和肢体。 图显示幼虫在幼年阶段的不同时期的昆虫。 成年成人从幼年阶段开始能够移动和繁殖, 看上去不像前幼虫阶段那样。 与摩托一样, 这一过程受到触发进化所需的急剧内部变化的控制。A honeybee shown in different phases of the pupal stage. Notice the progressive formation of the adult limbs and body regions as the pupa develops. How is this complex process of metamorphosis advantageous to the animals? One advantage is that it allows them to divide certain functions between different stages of the . In some species, the extensive feeding and energy storage of the larval stage is adequate to last the lifetime of the insect. The main benefit of this process is that these stages in the life cycle can adapt independently of each other. Evolutionary changes can occur that modify the larval stage, to improve feeding and nutrient uptake, for example, without affecting the adult stage and vice versa. Not all aspects of the organism’s form and function are affected by changes that are compartmentalized in this way. Let’s take a specific example. The mouthparts of a larva can be modified to adapt to a different type of food source that has become more available. This change will not affect the mouthparts or head appendages of the adult form, allowing them to adapt independently for other functions such as sensory perception.
::这种复杂的变形过程对动物有利吗?一个好处是,它允许动物在不同阶段之间分配某些功能。在有些物种中,幼虫阶段的广泛喂养和能量储存足以维持昆虫的寿命。这个过程的主要好处是生命周期的这些阶段可以相互独立地适应。进化变化可能发生,改变幼虫阶段,改善喂养和营养摄入,例如,不影响成年阶段,反之亦然。生物形态和功能的方方面面并非都受到以这种方式分割的改变的影响。让我们举个例子。幼虫的口部可以被修改,以适应已经越来越容易得到的不同种类的食物来源。这一变化不会影响成人形态的口部或头部,使其能够独立地适应感官感知等其他功能。Despite the type (or absence) of metamorphosis during development, all insects periodically shed their exoskeleton through the process of molting that you learned about in previous lessons of this chapter. Molting is a type of behavior that is carried out by insects. This might be considered a fairly simple behavior, particularly if you compare it to building a pyramid or competing in a chess tournament. However, even insects are capable of some fairly complex behaviors or interactions with their environments. These will be the topics of the next concept.
::尽管在开发过程中存在变形类型(或不存在),但所有昆虫都定期通过您在本章先前的教训中所学到的磨擦过程而脱去它们的外骨骼。 熔化是昆虫的一种行为。 这可能是一种相当简单的行为, 特别是如果你把它比作金字塔或者在国际象棋比赛中竞争的话。 但是, 即使是昆虫, 也会有一些相当复杂的行为或者与其环境的相互作用。 这将是下一个概念的主题 。Summary
::摘要-
Nearly all insects reproduce by sexual reproduction.
::几乎所有昆虫都通过性繁殖繁殖繁殖。 -
In some insect species, the female can choose to produce male or female offspring.
::在一些昆虫物种中,雌性可以选择生出雄性或雌性后代。 -
Insects that do not undergo a metamorphic change during their development are called ametabolous insects.
::在发育过程中没有发生变形变化的昆虫被称为代谢昆虫。 -
Among insects that experience metamorphosis, there are two types: hemimetaboly and holometaboly.
::在经历变形的昆虫中,有两种类型:雌雄激素和雌雄激素。 -
Insect larvae are focused on two main activities: eating and growing.
::昆虫幼虫集中于两个主要活动:饮食和生长。 -
During the pupal stage the tissues and appendages of the larval stage are broken down and reorganized into new adult tissues, organs, and limbs.
::在幼年阶段,幼年阶段的组织和附属物被分解并重组为新的成人组织、器官和肢体。
Review
::回顾-
What does parthenogenesis allow insects to do?
::昆虫的发病让昆虫做什么? -
One type of parthenogenesis found in insects involves the female choosing the gender of their offspring. What kind of mechanism does the female use to control the gender of her offspring?
::在昆虫体内发现的一种同源产生方式是女性选择其后代的性别。 女性使用哪种机制来控制其后代的性别? -
Some insects simply deposit pouches of sperm for females to find. Why is this form of fertilization less efficient?
::某些昆虫仅仅存着精子袋供雌性寻找。 为什么这种施肥方式效率不高? -
Which insects undergo metamorphosis? Which do not?
::哪些昆虫会变形? -
Describe the differences between hemimetabolous insects and holometabolous insects.
::描述六氯代谢性昆虫和全息性昆虫之间的区别。
-
Hemimetaboly (superorder Exopterygota).