15.5确定相对年龄
Section outline
-
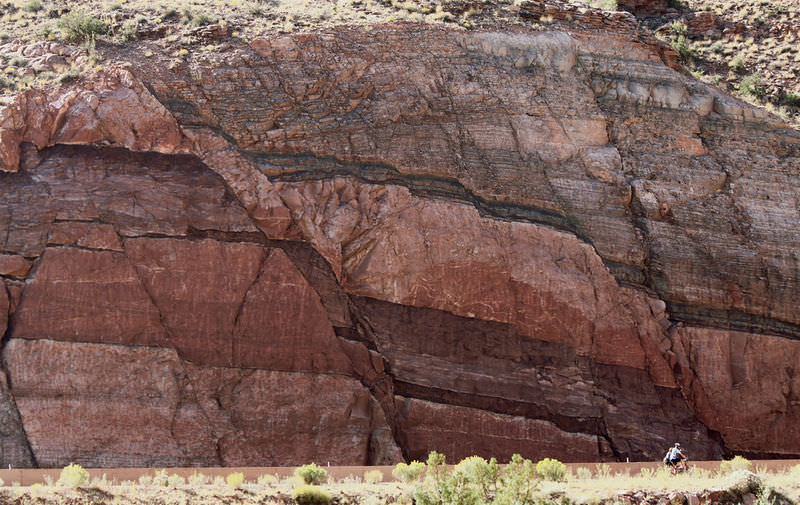
What are the relative ages of these rocks?
::这些岩石的相对年龄是多少?This photo shows layers and a fault—the is the large diagonal crack running through this rock. These features can tell us several things about relative age . Unless the rock was turned over somehow, we can assume that the layers on top are younger than the layers on the bottom. Since the fault separates the layers, we can tell that the fault occurred after all the layers were deposited .
::这张照片显示了层层和一个错误——这是穿过这块岩石的巨大的对角裂缝。这些特征可以告诉我们关于相对年龄的几件事。除非岩石被以某种方式翻转,否则我们可以假设顶部的层比底部的层小。由于断层分开了层,我们可以判断出所有层沉积后发生了断层。Determining the Relative Ages of Rocks
::确定岩石的相对年龄Steno’s laws are essential for determining the relative ages of rocks and rock layers. Remember that in relative dating, scientists do not determine the exact age of a fossil or rock. They look at a sequence of rocks to try to decipher when an event occurred relative to the other events represented in that sequence. The relative age of a rock, then, is its age in comparison with other rocks. (1) Do you know which rock is older and which is younger? (2) Do you know how old the rock's layers are in years? For relative ages, you know #1 but not #2.
::Steno的法律对于确定岩石和岩石层的相对年龄至关重要。 记住, 在相对的约会中, 科学家并不确定一个化石或岩石的确切年龄。 他们看一系列岩石, 试图破解一个事件的发生与该序列中代表的其他事件相对。 那么, 岩石的相对年龄是它与其他岩石相比的年代 。 (1) 你知道哪个岩石更老,哪个更小吗? (2) 你知道这些岩石层在几年中有多老吗? 对于相对年龄来说, 你知道1号, 但不知道2号。In some cases, it is very tricky to determine the sequence of events that leads to a certain formation. In the picture below, can you figure out what happened in what order ( Figure )? Write it down and then check the following paragraphs.
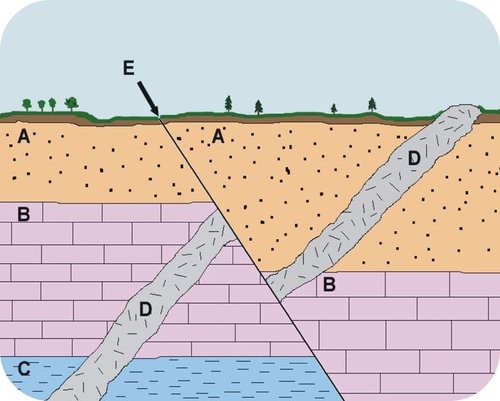
::在某些情况下,很难确定导致形成某种构造的事件的顺序。 在下面的图中,您能否找出按什么顺序(图)发生的事情? 写下来,然后检查下面的段落。A geologic cross section: Sedimentary rocks (A-C), igneous intrusion (D), fault (E). The principle of cross-cutting relationships states that a fault or intrusion is younger than the rocks that it cuts through. The fault cuts through all three sedimentary rock layers (A, B, and C) and also the intrusion (D). So the fault must be the youngest feature. The intrusion (D) cuts through the three sedimentary rock layers, so it must be younger than those layers. By the law of superposition , C is the oldest sedimentary rock, B is younger and A is still younger.
::交叉关系原则指出,过错或入侵比它穿过的岩石要小。断层横跨所有三个沉积岩层(A、B和C)以及入侵(D)。因此,断层必须是最小的特征。侵入三个沉积岩层(D)必须小于这些层。根据叠加法则,C是最古老的沉积岩,B更年轻,A更年轻。The full sequence of events is:
::事件的全部顺序是:- Layer C formed.
::C层形成
- Layer B formed.
::B层形成
- Layer A formed.
::A层形成。
- After layers A-B-C were present, intrusion D cut across all three.
::在A-B-C层存在之后 侵入D层横跨所有三层
- Fault E formed, shifting rocks A through C and intrusion D.
::形成断层, 移动岩石A通过C 和入侵D。
- Weathering and erosion created a layer of soil on top of layer A.
::天气和侵蚀在A层上层形成一层土壤。
Summary
::摘要- The oldest rock units lie beneath the younger ones.
::最古老的岩石单位位于较年轻的岩石单位之下。
- By the principle of cross-cutting relationships (and common sense), we know that something must exist before something else can cut across it.
::根据交叉关系(和常识)原则,我们知道,在有其他东西能够跨越这种关系之前,必须存在某种东西。
- The history of a section of rocks can be deciphered using the principles outlined in this concept.
::利用这一概念概述的原则,可以破译一部分岩石的历史。
Review
::回顾- What is relative age? How does it differ from absolute age?
::相对年龄是多少?它与绝对年龄有何不同?
- Why do the principles of relative dating not indicate the absolute age of a rock unit?
::为什么相对约会原则没有表明岩石单位的绝对年龄?
- Can you think of a way a rock unit with an older fossil could be above a rock until with a younger fossil? Describe the scenario.
::你能想到一个有古老化石的岩石单位 在岩石之上,直到有更年轻的化石吗?描述一下情况。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。- Look at that geologic cross section. Do you think it's possible to determine the geological processes that led to the creation of those rocks in those locations in those orders?
::你是否认为可以确定地质过程 导致这些岩石在这些地点的形成?
- How long a period of Earth history is represented by that diagram?
::该图代表了地球历史的多长时间?
- What is an unconformity? What causes it?
::什么是不符合同?是什么原因?
- What was the first thing that happened to create the first rock layer?
::创造第一个岩层的第一件事是什么?
- What forces and processes create the mountains and valleys seen in the region?
::是什么力量和进程创造了该区域所看到的山区和山谷?
- When lava erupts, does it create a layer similar to a sedimentary rock?
::当熔岩喷发时,它会产生类似于沉积岩层的层吗?
- Layer C formed.