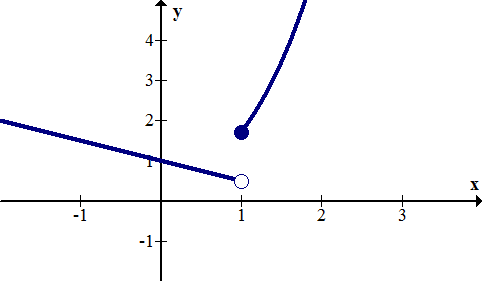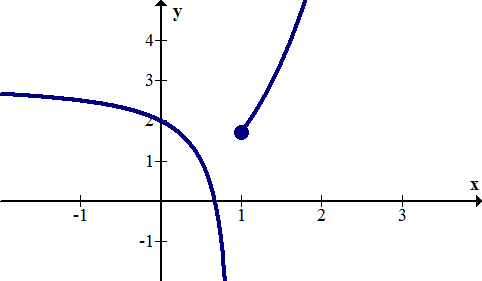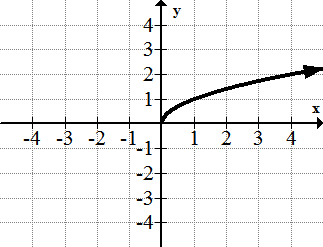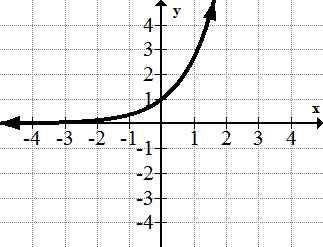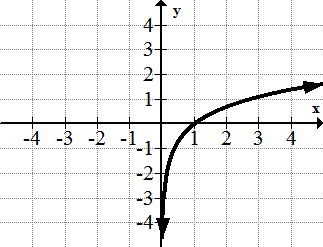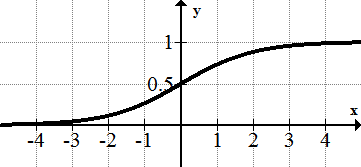2.11 连续性和中断性
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言An important part of mathematical analysis is to uncover surprises. Mathematical functions with predictable behavior reflect unsurprising situations. Consider the following function, which describes a text-messaging pricing plan. The cost is based on the number of texts, , and changes based on the domain. This style of function definition is called piecewise .
::数学分析的一个重要部分是发现意外。 具有可预测行为的数学函数反映了不奇怪的情况。 考虑以下函数, 描述文本信息定价计划。 P(x) 成本基于文本数、 x 和基于域的变化。 此函数定义的样式被称为“ 拼图 ” 。
::P(x) @% 25if 0 <x<2000.4xx 200__x < 50050+12xxx_500
This function certainly has some unexpected changes in pricing. These breaks in the graph are called discontinuities . The function is discontinuous at and at . A function without discontinuities is called c ontinuous . Informally, a function is continuous if its graph can be drawn without lifting the pencil. Functions that cannot be drawn without lifting the pencil are discontinuous.
::此函数在定价方面肯定有一些意外的变化。 图形中的这些断裂被称为不连续。 该函数在 x=200 和 x=500 时不连续。 一个不连续的函数被称为连续的。 非正式地说, 一个函数是连续的, 如果可以绘制其图形而不用举铅笔。 不举铅笔就无法绘制的函数是不连续的。Types of Discontinuities
::中断类型As seen in the video, there are two types of discontinuities: r emovable and non-removable discontinuities. And there are two types of non-removable discontinuities: jump and infinite discontinuities.
::从视频中可以看出,不连续有两种类型:可移动和不可移动的不连续。有两种不可移动的不连续:跳跃和无限不连续。A removable discontinuity occurs when the graph of a function has a hole.
::当函数的图形有一个洞时,会出现可移动的不连续状态。For example, consider the following function:
::例如,考虑以下功能:
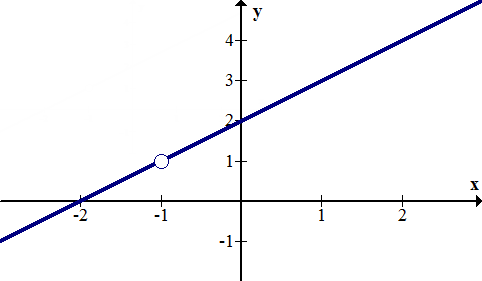
::f(x) = (x+2)(x+1) x+1Notice that the set of factors can be removed or canceled to get the function . The graph will then resemble , except there will be a hole at to account for the removed factor . The reason for the hole is that a lthough the original function c an be simplified, -1 must be excluded from the domain of the function. Thus, graph the line as usual, but remove the point at :
::请注意, x+1 的因子集可以被删除或取消以获取函数 f( x) =x+2 。 图形将随后类似 y=x+2, 除非 x\\\ 1 上有一个洞来计算删除的因子 x+1 。 原因是虽然原始函数可以简化, 但是 - 1 必须从函数的域中排除。 因此, 请按常态绘制 y=x+2 的行图, 但删除 x\ 1: 的点 :Removable discontinuities can be “filled in” if you make the function a piecewise function and define a part of the function at the point where the hole is. In the example above, to make continuous, you could redefine it as:
::可移动的不连续性可以“填充 ” , 如果您将函数变成一个片段函数, 并在洞所在点定义函数的一部分。 在以上示例中, 要让 f( x) 连续, 您可以将其重新定义为 :
::f( x) ( x+2)( x+1x+1, x%11, x%1)A jump discontinuity occurs when a function has two ends that don’t meet, even if the hole is filled in at one of the ends. In order to satisfy the vertical line test and make sure the graph is truly that of a function, only one of the end points may be filled. Below is an example of a function with a jump discontinuity:
::当函数有两端无法满足时,即发生跳跃不连续的情况,即使洞洞被填满在其中一个端。为了满足垂直线测试,确保图形是函数的垂直线测试,只有一个端点可以填满。下面是跳跃不连续函数的例子:An infinite discontinuity occurs when a function has a vertical asymptote on one or both sides. This is shown in the graph of the function below at :
::当函数在一面或两边有一个垂直同质点时,就会出现无限不连续的情况。这在以下 x=1 的函数图中显示。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Identify the discontinuity of the function algebraically and then graph the function:
::识别函数代数的不连续性,然后绘制函数图示:
:xx) = (x-2) (x+2) (x-1) (x-1)
Solution:
::解决方案 :The factor can be removed or canceled in both the numerator and the denominator to result in . Because was canceled, there is a removable discontinuity or hole at .
::分子和分母中的乘数 x-1 可以删除或取消, 从而导致 f( x) = (x-2)(x+2) 。 由于 x-1 被取消, x= 1 时存在可移动的不连续或空洞 。The graph will resemble with a hole at , so graph as usual and then insert a hole in the appropriate spot at the end:
::图形将类似 y= (x-2)(x+2) , 在 x=1 处有一个洞, 所以像往常一样, 图形y= (x-2)(x+2) , 然后在结尾处的适当位置插入一个洞 :Example 2
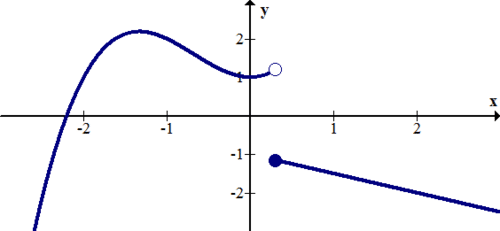
::例2Identify the discontinuity of the piecewise function graphically:
::图形化识别片段函数的不连续性 :
::f( x) x2 - 4x < 1 - 1x=1 - 12x+1x > 1Solution:
::解决方案 :There is a jump discontinuity at . The piecewise function describes a function in three parts; a portion of a parabola on the left, a single point in the middle, and a portion of a line on the right.
::x=1 时有跳跃不连续性。 字形函数描述三个部分的函数; 左边的抛物线的一部分, 中间的一个点, 右边的一条线的一部分 。Example 3
::例3Identify the discontinuity of the function below:
::确定以下函数的不连续性:Solution:
::解决方案 :Since there is a vertical asymptote at , this is an infinite discontinuity.
::由于 x=1 时有垂直空点, 这是无限的不连续性 。Example 4
::例4Describe the continuity or discontinuity of the function .
::描述函数 f( x) =sin( 1x) 的连续性或不连续性 。Solution:
::解决方案 :The function seems to oscillate infinitely as approaches 0. One thing that the graph fails to show is that 0 is clearly not in the domain. The graph does not shoot to infinity, nor does it have a simple hole or jump discontinuity. However, it is not continuous at .
::当 x 接近 0 时,该函数似乎无穷无尽地显示。 图表未能显示的一件事是, 0 显然不在域内。 该图形不会射向无限, 也没有简单的洞或跳跃不连续。 但是, 在 x=0 时, 它不是连续的 。Example 5
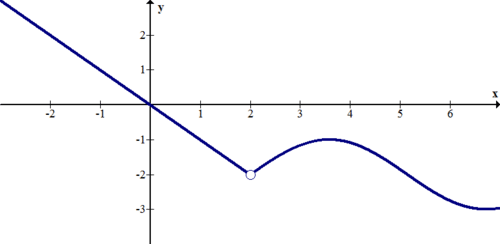
::例5Describe the discontinuities of the function below:
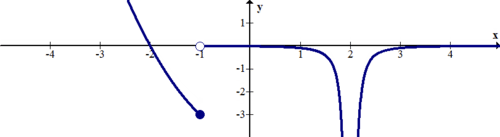
::以下描述该函数的不连续性:Solution:
::解决方案 :There is a jump discontinuity at and an infinite discontinuity at .
::x1 有跳跃不连续, x=2 有无限不连续。Example 6
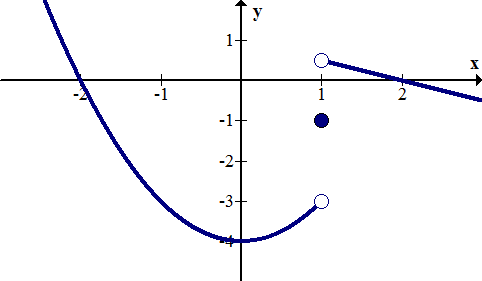
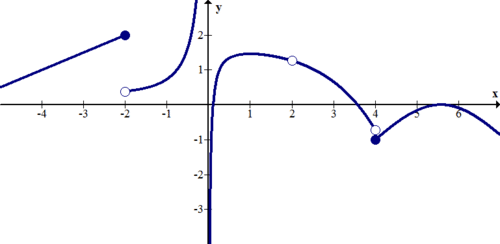
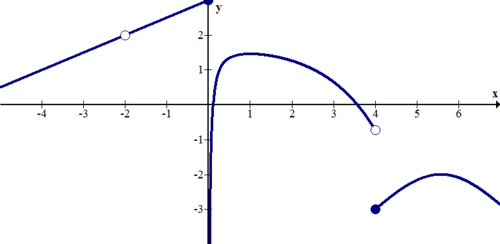
::例6Describe the discontinuities of the function below:
::以下描述该函数的不连续性:Solution:
::解决方案 :There are jump discontinuities at and . There is a removable discontinuity at . There is an infinite discontinuity at .
::x2 和 x=4 有跳跃不连续的情况。 x=2 有可移动不连续的情况。 x=2 有无限不连续的情况。 x=0 有无限不连续的情况。Summary
::摘要-
There are two
types of
discontinuities
:
removable and non-removable. Then there are two types of non-removable discontinuities: jump or
infinite
discontinuities.
::有两种不连续:可移动和不可移动。然后有两种不可移动的不连续:跳跃或无限不连续。 -
Removable discontinuities
are also known as holes. They occur when factors can be algebraically removed or canceled from rational functions.
::可移动的不连续性也被称为孔。 当因素可以代数删除或取消理性功能时, 就会出现孔。 -
Jump discontinuities
occur
when a function has two ends that don’t meet, even if the hole is filled in at one of the ends.
::当函数有两端无法满足时,即使洞洞被填满在其中一个端,也会出现不连续的情况。 -
Infinite discontinuities
occur when a function has a vertical asymptote on one or both sides.
::当函数的一方或双方垂直无序时,就会出现无限的不连续性。
Review
::回顾Describe any discontinuities in the functions below:
::描述下列职能中的任何不连续性:1.
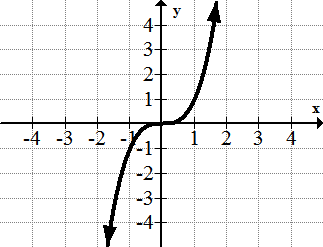
::1.y=x2.
::2. y=x23.
::3. y=x34.
::4.y=x5.
::5. y=1x6.
::6. y=ex7.
::7.y=ln(x)8.
::8. y=11+e-x9.
10.
11.
12. has a jump discontinuity at , a removable discontinuity at , and another jump discontinuity at . Draw a picture of a graph that could be .
::12.f(x) 在 x=3 时有跳跃不连续性,在 x=5 时有可移动不连续性,在 x=6 时有另一个跳跃不连续性。13. has a jump discontinuity at , an infinite discontinuity at , and another jump discontinuity at . Draw a picture of a graph that could be .
::13. g(x) 在 x2 上具有跳跃不连续性,在 x=1 上具有无限不连续性,在 x=3 上则具有另一个跳跃不连续性。14. has a removable discontinuity at , a jump discontinuity at , and another jump discontinuity at . Draw a picture of a graph that could be .
::14. h(x) 在 x4 上具有可移动的不连续性,在 x=1 上具有跳跃不连续性,在 x=7 上具有另一个跳跃不连续性。15. has an infinite discontinuity at , a removable discontinuity at , and a jump discontinuity at . Draw a picture of a graph that could be .
::15. j(x) 在 x=0 时具有无限不连续性,在 x=1 时具有可移动不连续性,在 x=4 时具有跳跃不连续性。绘制一张可能是 j(x) 的图形。Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
There are two
types of
discontinuities
:
removable and non-removable. Then there are two types of non-removable discontinuities: jump or
infinite
discontinuities.