3.8 理性函数
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言Students at a college are currently required to demonstrate their understanding of their classwork at a level of 75% or higher to move on to more advanced material.

::目前,学院的学生必须表明他们对其班级工作的理解程度达到或超过75%,才能继续学习更先进的教材。Suppose a study of the link between grade and study time suggests that t he amount of homework time T in hours required for each student based on an understanding level of p % is given by T ( p ) = ( 18 p ) ( 100 − p ) .
::假设对年级与学习时间之间的联系进行研究后发现,T(p)=(18p)=(100)-p给出了每名学生根据理解水平(p%)所需的按小时计算的功课时间T。The domain of T ( x ) is [ 0 , 100 ) . If the college administration decides to raise the minimum level of understanding to 82%, how will this affect the students' homework time?
::T(x)领域是[0,100]。如果大学行政部门决定将最低理解水平提高到82%,这将如何影响学生的功课时间?This mathematical model is an example of a rational function . These functions have characteristics that are very different from those of polynomial functions, but like that class of functions, specific techniques can be established for analysis.
::这个数学模型是理性函数的一个例子。 这些函数的特性与多元函数的特性大不相同, 但和这一类函数一样, 可以建立用于分析的具体技术。Standard Form of Rational Functions
::理性函数标准格式A function can be written in the form
::函数可以在窗体中写入f ( x ) = P ( x ) Q ( x ) ,
:fx)=P(x)Q(x),
where P ( x ) and Q ( x ) are , and Q ( x ) ≠ 0 is called a rational function. The domain of a rational function includes all real numbers x so that the denominator is not zero.
::P(x) 和 Q(x) 是, Q(x) 和 Q(x) 是 , 和 Q(x) = 0 被称为 理性函数。 理性函数的域包括所有真实数字 x , 这样分母就不会为零 。An example of a rational function is f ( x ) = 1 x .
::合理函数的示例是 f( x) = 1x 。Asymptotes
::单生数An asymptote is a line or curve to which a function's graph approaches continuously but does not reach (with certain exceptions) . There are three types of asymptotes: vertical , horizontal, and oblique (also known as slant). F unctions cannot intersect a vertical asymptote . The horizontal asymptote denotes the end behavior of the function as x → ± ∞ . There are certain instances in which the graph of a function intersects the horizontal asymptote.
::线状图是一个线条或曲线,函数的图形持续接近,但没有达到该线或曲线,但该线或曲线没有达到(除某些例外情况外)。有三种线状图类型:垂直、水平和斜体(也称为斜体)。函数不能交叉垂直的线状图。水平的线状图表示函数的末端行为为 x。在有些情况下,函数的图形交叉水平的线条。Vertical Asymptotes
::垂直单位数Find by setting the denominator to zero and then solving for x . For
::通过将分母设置为零,然后为 x 解析,查找 x。forr ( x ) = P ( x ) Q ( x ) ,
::r(x) = P(x) Q(x),the solution to Q ( x ) = 0 will give the vertical asymptote(s).
::Q(x)=0 的解决方案将给出垂直静态。So if
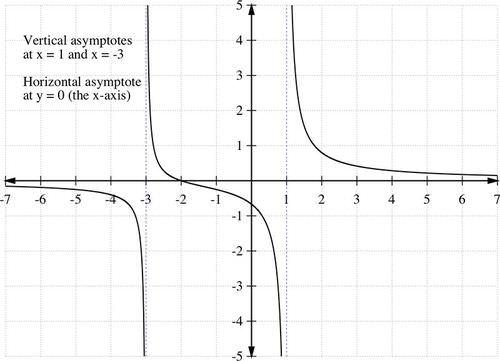
::如果f ( x ) = x + 2 ( x − 1 ) ( x + 3 ) ,
::f(x) =x+2(x-1)(x+3) =x+2(x-1)(x+3) =x+2(x-1)(x+3)setting
::设置设置设置设置设置设置设置设置设置( x − 1 ) ( x + 3 ) = 0
:x-1)(x+3)=0
will give the vertical asymptotes at x = 1 and x = − 3 .
::将给予 x=1 和 x3 的垂直小数 。Horizontal Asymptote
::水平渐移The horizontal asymptote is a line parallel to the x − axis, which the function approaches but does not intersect as x → ∞ and x → − ∞ . (Note that a rational function can cross a horizontal asymptote at other places on the graph.) To find the horizontal asymptote, follow the procedure below:
::水平静态是与 x- 轴平行的一条线, 函数会接近 x- 轴, 但不会与 x- 轴相交 。 (注意, 理性函数可以在图中其他位置跨过水平静态 。 ) 要找到水平静态, 请遵循以下程序 :How to Find the Horizontal Asymptote
::如何查找水平单点-
Expand the numerator and denominator if they are written in a
factored form
.
::如果分子和分母以乘数形式写成,则展开该分子和分母。 -
There are three possibilities:
-
If the
degree
of the numerator is smaller than the degree of the denominator, then the horizontal asymptote
equals
y
=
0
, the
x
−
axis itself.
::如果分子的大小小于分母的分母的分量,则水平的单数等于y=0,即 x - 轴本身。 -
If the degree of the denominator and the numerator are the same, then the horizontal asymptote equals the ratio of the leading coefficients.
::如果分母和分子的大小相同,则水平零点等于主要系数的比率。 -
If the degree of the numerator is larger than the degree of the denominator, then there is no horizontal asymptote.
::如果分子的大小大于分母的分母的大小,则没有水平的零星。
::有三种可能性:如果分子的分量小于分母的分量,那么水平的同量数等于y=0,那么水平的同量数等于y=0, x - 轴本身。如果分量和分子的分量相同,那么水平的同量数等于主要系数的比率。如果分子的分量大于分母的分量,那么就没有水平的同量数。 -
If the
degree
of the numerator is smaller than the degree of the denominator, then the horizontal asymptote
equals
y
=
0
, the
x
−
axis itself.
Oblique Asymptotes
::简缩缩缩缩W hen the degree of the numerator is 1 greater than the degree of the denominator, there is no horizontal asymptote. However, there is another type of asymptote , the oblique or slant asymptote . Note that there is no linear if the degree of the numerator is 2 or more greater than the degree of the denominator.
::当分子的度比分母的度高1时,就不会有水平的零星。 但是, 还有另一种类型的单体, 斜体或斜体的零星。 请注意, 如果分子的度比分母的度高2 或2 以上, 就不会有线性 。To determine the oblique asymptote, divide the polynomial in the numerator by the polynomial in the denominator. The resulting quotient polynomial is the oblique asymptote.
::要确定单向无位数, 将分子中的多位数除以分母中的多位数。 由此得出的商数多位数是斜向无位数 。Graphing Rational Functions Using Transformation
::使用变换来图形化理性函数Just like polynomials, rational functions can be graphed using transformations . S ome transformations change the asymptotes while others do not.
::和多面性一样, 理性函数可以用变换来图形化。 有些变换会改变无符号, 而另一些变换则不会。-
r
(
x
)
+
c
is a vertical
shift
that moves each horizontal asymptote up
c
units (or down if
c
<
0
).
::r( x) +c 是一个垂直移动, 将每个水平的单点向上移动 c 单位( 如果 c< 0 ) , 或向下移动 。 -
r
(
x
−
c
)
is a
horizontal shift
that moves each vertical asymptote right
c
units (or left if
c
<
0
).
::r( x- c) 是一个水平移动, 移动每个垂直的向中点( 或如果 c< 0 ) , 则向左移动 。 -
a
⋅
r
(
x
)
is a vertical
stretch
that moves
by a multiple of
a
(so this moves the horizontal asymptote closer to the
x
−
axis if
a
<
1
).
::ar(x) 是一个垂直伸展, 以一个形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形色色( 因此, 如果 a< 1 ) , 则会移动水平等同线向接近 x- 轴形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形色色色的线形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形形色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色色 -
r
(
a
⋅
x
)
is a horizontal
compression
that moves the vertical asymptotes closer to
y
−
axis by a
factor
of
1
a
.
::r(ax) 是一个水平压缩, 将垂直微粒移到y- 轴上, 移动系数为 1a 。 -
r
(
−
x
)
is a
reflection
about the
y
−
axis. All vertical asymptotes are also reflected.
:- x) 是 Y - 轴的反射。 所有垂直的微粒也均被反射 。
-
−
r
(
x
)
is a reflection about the
x
−
axis. All horizontal asymptotes are also reflected.
::~r(x) 是 X - 轴的反射。 所有水平的单位数也都被反射 。
Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1What is the domain of f ( x ) = 1 x ?
::f( x) = 1x 的域是什么 ?Solution:
::解决方案 :Determine any values that would make the denominator zero. In this case, when x = 0 , the function is undefined .
::确定使分母为零的任何值。在此情况下,当 x=0 时,函数未定义。Therefore , the domain of this function is all real numbers except x = 0 . In set notation , the domain is { x | x ≠ 0 } .
::因此,除 x=0 外,此函数的域都是真实数字。在设置符号时,此域是 {x\\\\\\\\\\\\\\0}。Example 2
::例2What is the domain of f ( x ) = x + 2 ( x − 1 ) ( x + 3 ) ?
::f( x) =x+2( x-1)( x+3) 的域是什么 ?Solution:
::解决方案 :The domain is all real numbers except those that cause the denominator to become zero: x = 1 and at x = − 3 .
::域名是所有实际数字,但导致分母为零的数字除外: x=1 和 x3 。Example 3
::例3Find the vertical and horizontal asymptotes of
::查找垂直和水平的f ( x ) = 2 x 3 − 2 x 2 + 5 3 x 3 − 81 .
:x)=2x3-2x2+53x3-81。
Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: To find the vertical asymptote(s), set the denominator to zero and then solve for x :
::步骤 1: 要找到垂直静态, 将分母设为零, 然后解决 x:3 x 3 − 81 = 0 3 x 3 = 81 x 3 = 27 x = 3 √ 27 x = 3.
::3x3-81=03x3=81x3=27x=327x=3。Thus, the graph has a vertical asymptote at x = 3 .
::因此,该图在 x=3 时有一个垂直空位。Step 2: To find the horizontal asymptote, consider the leading terms :
::第2步:为找到横向零点,考虑以下主要术语:2 x 3 3 x 3 .
::2x33x3 。Notice that the degree of the numerator and the denominator are the same and therefore the horizontal asymptote is the ratio of the coefficients,
::注意分子和分母的程度相同,因此水平零点为系数之比,2 x 3 3 x 3 = 2 3 .
::2x33x3=23。So the horizontal asymptote is at y = 2 3 .
::所以水平的静态是 y=23 。Example 4
::例4Find the asymptotes of
::查找f ( x ) = 3 x − 2 4 x 4 − 9 .
:x)=3x-24x4-9.
Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: To find the vertical asymptote(s), set the denominator equal to 0 and solve for x :
::步骤 1: 要找到垂直的单点, 将分母设为 0, 并解决 x :4 x 4 − 9 = 0 x 4 = 9 4 x = 4 √ 9 4 x = ( ( 9 4 ) 1 2 ) 1 2 x = ± √ 3 √ 2 x = ± √ 6 2 .
::4x4-9=0x4=94x=494x=((94)12)12x=32x*62。Thus, the graph has a vertical asymptote at x = √ 6 2 and x = − √ 6 2 .
::因此,该图在 x62 和 x62 上有一个垂直空位。Step 2: To find the horizontal asymptote, consider the leading terms :
::第2步:为找到横向零点,考虑以下主要术语:3 x 4 x 4 .
::3x4x4,3x4x4, 3x4x4, 3x4x4, 3x4x4, 3x4x4, 3x4x4, 3x4x4, 3x4x4, 3x4, 3x4x4, 3x4, 3x4x4, 3x4, 3x4, 3x4x4, 3x4, 3x4x4, 3x4, 3x4x4, 3x4x4, 3x4, 3x4x4.Notice that the degree of the numerator is less than the degree of the denominator. Therefore, the horizontal asymptote is at y = 0 , so the x − axis plays the role of the horizontal asymptote.
::注意分子的程度小于分母的程度。 因此, 水平静态为y=0, 所以 x - 轴发挥水平静态的作用 。Example 5
::例5Find the of the rational function:
::查找理性函数 :g ( x ) = 2 x 4 − 9 3 x − 2 .
::g(x)=2x4-93x-2。Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: To find the vertical asymptote(s), set the denominator equal to zero and solve for x :
::步骤 1: 要找到垂直静态, 将分母设为零, 并解决 x :3 x − 2 = 0.
::3x-2=0。Thus, the graph has a vertical asymptote at x = 2 3 .
::因此,该图在 x=23 时有一个垂直空位。Step 2: To find the horizontal asymptote, consider the leading terms :
::第2步:为找到横向零点,考虑以下主要术语:2 x 4 3 x .
::2x43x. 20x43x. 20x43x.Here, the degree of the numerator is larger than the degree of the denominator. Thus, there is no horizontal asymptote.
::在此, 分子的度大于分母的度。 因此, 没有水平的零点 。Example 6
::例6Graph
::图图图图图图图T ( x ) = 2 x + 1 x − 1 .
::T(x) = 2x+1x- 1。Solution:
::解决方案 :To graph T , there are four important items you need to find: the y − intercept , the x − intercept, the vertical asymptote, and the horizontal asymptote.
::图T需要找到四个重要项目:y - 截取、 x - 截取、 垂直断线和水平断线。The y − intercept can be found by finding y = T ( 0 ) :
::y- interview 可以通过找到 y=T( 0) 来找到 y- interview :y = T ( 0 ) = 2 ( 0 ) + 1 0 − 1 = − 1.
::y=T(0)=2(0)+10-1=1.Thus the y − intercept is at point (0, -1).
::因此,y- 界面在点( 0, - 1) 。The x − intercept can be found by setting y = T ( x ) = 0 :
::x- interview 可以通过设置 y= T( x)= 0 来找到 :2 x + 1 x − 1 = 0.
::2x+1x-1=0。Note that a reduced fraction a b = 0 if and only if a = 0 . Solve
::请注意,如果且仅在a=0的情况下,减少的分数 ab=0。2 x + 1 = 0 x = − 1 2 .
::2+1=0x12。In general, for a rational function, P ( x ) Q ( x ) , set P ( x ) = 0 to find the x − intercept for any rational function. Make sure the x − value is in the domain of the function. Note that if both P ( x ) = 0 and Q ( x ) = 0 for the same value of x , then the graph has a hole in it instead of a vertical asymptote at that value, if the multiplicity of that factor is the same in the numerator and denominator.
::一般而言,对于理性函数,P(x)Q(x),设置 P(x)=0 以查找任何理性函数的 x- intercut 。确保 x- value 位于函数的域内。请注意,如果 P(x)=0 和 Q(x)=0 的值与 x 的值相同,那么,如果分子和分母中该系数的多重性相同,则图形在其中有一个洞,而不是该数值的垂直等同点,如果该系数的多重性相同。Next, the vertical asymptote: set Q ( x ) = 0 :
::下一步, 垂直的静态: 设定 Q( x)=0 :x − 1 = 0 x = 1.
::x-1=0x=1。And the horizontal asymptote:
::和水平的单点数 :2 x + 1 x − 1 → 2 x x = 2.
::2x+1x-1xx-2xx=2。Therefore, the vertical asymptote is at x = 1 , and the horizontal asymptote is at y = 2 . From this information, and calculating the value of a few other points if needed, sketch the graph:
::因此,垂直的单点为 x=1, 水平的单点为y=2, 根据此信息, 如果需要, 计算其他几个点的值, 绘制图表 :Example 7
::例7Graph
::图图图图图图图g ( x ) = 2 x 2 + 1 2 x 2 − 3 x .
::g(x)=2x2+12x2-3x。Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: T he y − intercept is
::第1步:Y - 界面是y = g ( 0 ) = 1 0 = undefined ,
::y=g( 0)=10=未定义,so there is no y − intercept.
::所以没有y - interview。Step 2: The x − intercept can be found by setting the numerator to zero:
::第2步:通过将分子设置为零,可以找到 x - 界面 :2 x 2 + 1 = 0 2 x 2 = − 1 x 2 = − 1 2 x = √ − 1 2 .
::2x2+1=02x2=1x2=1x2=1x2=12x*12=12Notice this equation has no real solution. Therefore, there is no x − intercept.
::注意这个方程式没有真正的解决方案。 因此, 没有 X- intermission 。Step 3: The vertical asymptote can be found by setting the denominator to zero:
::第3步:通过将分母设为零,可以找到垂直零位数:2 x 2 − 3 x = 0 x ( 2 x − 3 ) = 0.
::2x2-3x=0x(2x-3)=0。The two solutions are x = 0 and x = 3 2 , and these are the vertical asymptotes.
::两个溶液是 x=0 和 x=32, 这些是垂直的静态。Step 4: Finally, the horizontal asymptote is found by analyzing the leading terms:
::步骤4:最后,通过分析主要术语,发现横向零点:2 x 2 + 1 2 x 2 − 3 x → 2 x 2 2 x 2 = 1.
::2x2+12x2 -3x%2x22x2=1That is, y = 1 is a horizontal asymptote. After finding a few points on the graph, the sketch of the graph of g ( x ) is created:
::也就是说, y=1 是一个水平的零点。 在找到图形上的几个点后, g( x) 图形的草图会被创建 :Example 8
::例8Recall the problem from the Introduction. The study time function was T ( p ) = 18 p 100 − p . How does the administration's change from 75% to 82% mastery affect student study time?
::回顾导言中的问题。学习时间函数是 T(p)=18p100-p。政府从75%到82%的掌握率如何影响学生的学习时间?Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Calculate by evaluating at the given values:
::第1步:以给定值进行估测计算:
::T(75)=18(75)100-75=54T(82)=18(82)100-82=82。
::第2步:当行政部门将费率从75%提高到82%时,学习时间从54小时增加到82小时。Example 9
::例9Graph
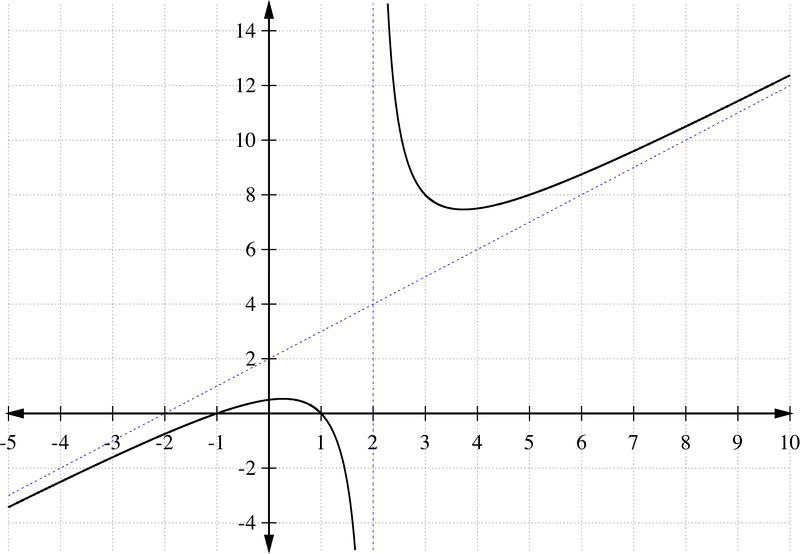
::图图图图图图图g ( x ) = x 2 − 1 x − 2 .
::g(x) =x2 - 1x-2。Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Find your y -intercept.
::第1步: 找到你的Y接口。g ( 0 ) = ( 0 ) 2 − 1 0 − 2 = 1 2
Step 2: Find y our x -intercept, which occurs when y is zero, so the numerator is zero.
::g( 0) =( 0) 2- 10- 2= 12 标准 2: 查找您在 y 零 时出现的 X 界面, 所以分子为 0 。0 = x 2 − 1 0 = ( x − 1 ) ( x + 1 ) x = ± 1
Since neither of the above cause the denominator to be zero, both are valid intercepts .
::0=x2- 10=(x-1)(x+1)x=1x=1Since上述两种情况均未导致分母为零,两者均为有效拦截。Step 3: O bserve that the vertical asymptote is at x = 2 . Notice the degree of the numerator is greater than the degree of the denominator. This function has an oblique asymptote. To identify it, change the form of the rational expression using long division . Any rational functions can be written as
::第3步 : 3 : 注意垂直单点为 x=2 。 注意 分子的程度大于分母的程度。 此函数有一个斜线的单点。 要识别它, 使用长分隔法更改合理表达式的形式。 任何合理函数都可以写成为f ( x ) D ( x ) = Q ( x ) + R ( x ) D ( x ) ,
:fx)D(x)(x)+R(x)D(x),
where f ( x ) is the original numerator, D ( x ) is the divisor, Q ( x ) is the quotient, and R ( x ) is the remainder.
::此处 f( x) 是原分子, D( x) 是 divisor, Q( x) 是 商数, R( x) 是 剩余 。Step 4: The long division:
::步骤4:长期划分:x + 2 x − 2 ) ¯ x 2 + 0 x − 1 − ( x 2 − 2 x ) ↓ _ 2 x − 1 − ( 2 x − 4 ) _ 3
::x2x - 2) x2+0x - 1 -(x2 - 2x) *2x - 1 - (2x - 4) _ 3allows the function g ( x ) to be rewritten as
::允许将函数 g( x) 重写为g ( x ) = x 2 − 1 x − 2 = x + 2 + 3 x − 2 .
::g(x) =x2- 1x-2=x+2+3x-2。Step 5: As x → ∞ or x → − ∞ , the graph of g ( x ) = x + 2 + 3 x − 2 gets closer and closer to the line y = x + 2 . To see this, let x = 1 , 000 , 000 . Then the remainder of this rational function becomes 3 999 , 998 ≈ 0 , and g ( x ) is nearly the same as x + 2 . This behavior is denoted with a dotted line, an oblique asymptote .
::第5步:as x 或 x, g(x) =x+2+3x-2 的图形越来越接近于 y=x+2 的直线, 可以看到, let x= 1000,000。 然后, 此理性函数的剩余部分变成 3999, 998, 0, g(x) 几乎与 x+2 相同 。 此行为用虚线表示, 斜线是单线 。Example 10
::例10Graph
::图图图图图图图f ( x ) = x 2 − x − 2 x − 1 .
:xx) =x2 -x-2x-1。
Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Factor the numerator :
::第1步:将分子数乘以:f ( x ) = x 2 − x − 2 x − 1 = ( x − 2 ) ( x + 1 ) x − 1 .
:x) =x2-x-2x-1=(x-2)(x+1)x-1;
The vertical asymptote is x = 1 since it would make the denominator zero and its factor doesn't cancel out with any factors in the numerator .
::垂直静态为 x=1, 因为它会使分母为零, 其因子不会与分子中的任何因素取消 。Step 2: Since the degree of the polynomial in the numerator is larger than the degree of the polynomial in the denominator, there is no horizontal asymptote. Instead, divide x 2 − x − 2 by x − 1 to yield:
::第2步:由于分子中的多数值度大于分母中的多数值度,因此没有水平的单数度。相反,除以 x2 - x-2 乘以 x- 1 以产生 :f ( x ) = x − 2 x − 1 ,
:xx) =x-2x-1,
which indicates an oblique asymptote at y = x .
::表示 Y=x 上的斜线渐移。Step 3: Notice that the x − intercepts are at x = 2 and x = − 1 .
::第3步:注意X=2和x=1的截取值。Step 4: Find the y -intercept.
::步骤4:找到Y的接口。f ( 0 ) = 0 2 − 0 − 2 0 − 1 = 2
Step 5: Draw the asymptote lines, plot the intercepts , and sketch the graph of the rational function:
::f( 0) = 02- 0-20- 1= 2Step 5 : 绘制无线线, 绘制拦截图, 绘制合理函数图示 :Example 11
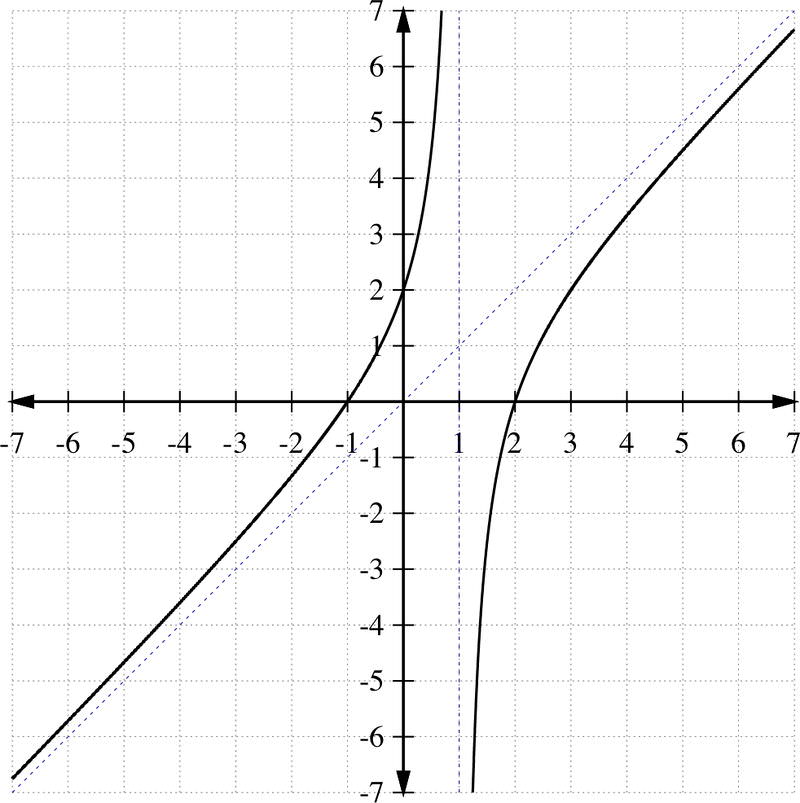
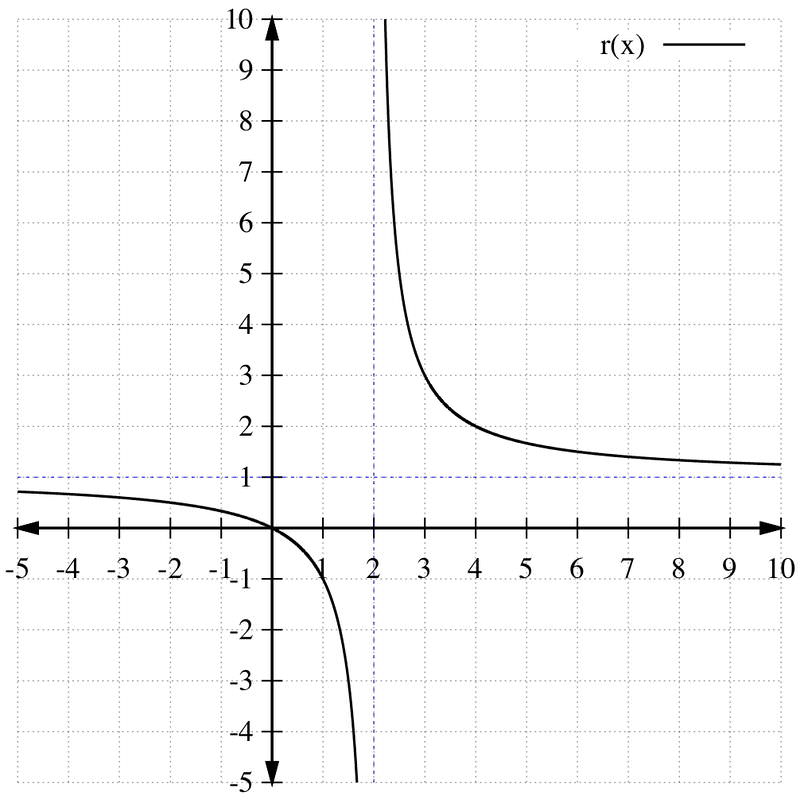
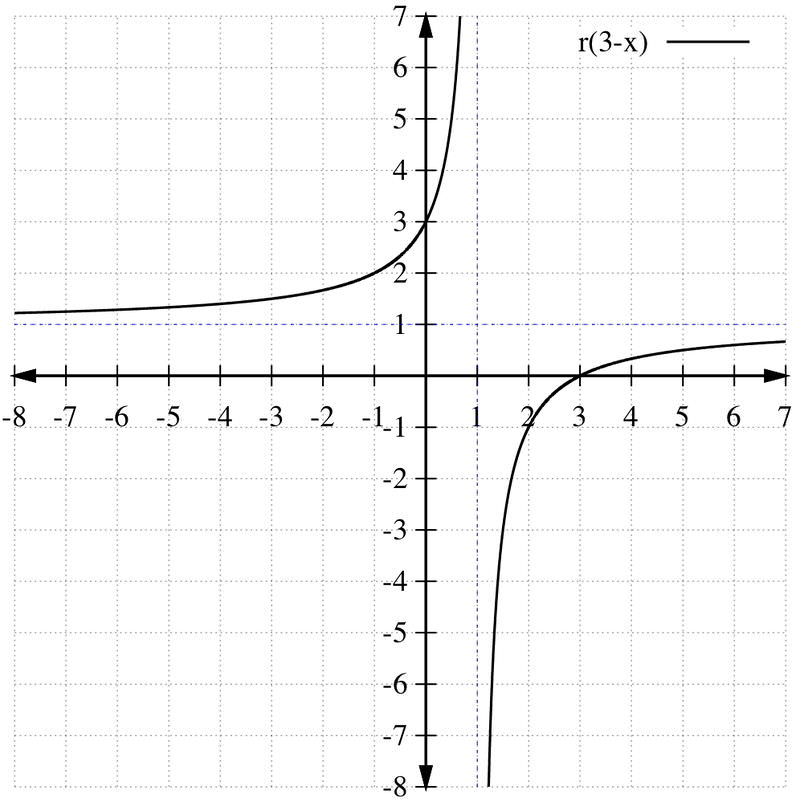
::例例11A rational function r ( x ) is shown in the figure below. Use the graph of r ( x ) to sketch a graph of: a) r ( x ) − 3 ,
::合理函数 r(x) 显示在下图中。 使用 r( x) 图形绘制 r( x)- 3 的图形 。b) r ( − x ) ,
::b) r(-x),c) r ( 3 − x ) .
::c) r(3-x)。Solutions:
::解决办法:a) r ( x ) − 3
The horizontal asymptote moves down by 3 units:
:a) r(x)-3 水平静态向下移动3个单位:
b) f ( − x )
The function is reflected about the y -axis so the vertical asymptote is also reflected:
:b) f(-x) 函数在 Y 轴上反映,因此垂直的静态也反映如下:
c) r ( 3 − x ) = r ( − ( x − 3 ) )
First graph r ( − x ) , and then shift that graph 3 units to the right to get r ( − ( x − 3 ) ) . The new vertical asymptote is x = 1 .
::c) r(3-x)=r(-(x-3)) 第一个图形 r(-) , 然后将图3 单位移到右侧以获得 r(-(x- 3) 。新的垂直静态为 x=1 。Summary
::摘要-
Asymptotes are critical to analyze rational functions.
::对分析理性功能而言,小症状至关重要。 -
The vertical asymptote is found by setting the denominator of the function equal to zero if the rational function is in reduced form (all common factors have been cancelled). Then solve for
x
.
::如果理性函数的缩放形式(所有常见因素都被取消),则通过设定函数分母为零,以查找垂直静态。然后为 x 解析 。 -
The horizontal asymptote is found by creating a fraction with the dominant terms of the numerator and denominator, and comparing the degrees. There are three possibilities:
-
If the degree of the numerator is smaller than the degree of the denominator, then the horizontal asymptote
equals
y
=
0
, the
x
−
axis itself.
::如果分子的大小小于分母的分母的分量,则水平的单数等于y=0,即 x - 轴本身。 -
If the degree of the denominator and the numerator are the same, then the horizontal asymptote equals the ratio of the leading coefficients.
::如果分母和分子的大小相同,则水平零点等于主要系数的比率。 -
If the degree of the numerator is larger than the degree of the denominator, then there is no horizontal asymptote.
::如果分子的大小大于分母的分母的大小,则没有水平的零星。
::以分子和分母的主要条件生成一个分数, 并比较度, 从而发现水平的微量。 有三种可能性: 如果分子的量小于分母的程度, 那么水平的量小于 y=0, 则水平的量小于 y=0, x - 轴本身。 如果分母和分子的量大相同, 那么水平的量小于主要系数的比重。 如果分子的量大于分母的程度, 那么没有水平的量小于 分母的程度 。 -
If the degree of the numerator is smaller than the degree of the denominator, then the horizontal asymptote
equals
y
=
0
, the
x
−
axis itself.
-
If the degree of the numerator is 1 greater than the degree of the denominator, rewrite the function by using long division to reveal the oblique (slant) asymptote.
::如果分子的程度比分母的程度高1,则通过使用长的分隔线来显示倾斜(倾斜)断面,重写函数。
Review
::回顾Find all asymptotes of the following functions:
::查找以下函数的所有 asymptotems :-
y
=
x
−
2
x
2
+
6
x
+
8
::y=x- 2x2+6x+8 -
y
=
x
2
−
4
x
+
5
::y=x2 - 4x+5 y=x2 - 4x+5 -
y
=
x
2
x
−
3
::y=x2x- 3 y=x2x- 3 -
Find the
x
-intercepts of the function in number 2.
::在 2 中查找函数的 x 界面 。 -
Find the
x
-intercepts of the function in number 3.
::在编号3中查找函数的 x interviews。
Graph the following functions. Find any intercepts and asymptotes.
::图形显示以下函数。查找任何拦截和微粒。-
y
=
x
+
1
x
2
−
x
−
12
::y=x+1x2-x- 12 y=x+1x2-x- 12 -
f
(
x
)
=
x
2
+
3
x
−
10
x
−
3
:xx) =x2+3x-10x-3
-
y
=
−
8
x
3
−
8
x
2
+
2
x
+
8
x
+
2
::y8x3 - 8x2+2x+8x+2 -
g
(
x
)
=
2
x
2
−
2
3
x
+
5
::g(x) = 2x2 - 23x+5 -
y
=
−
2
x
3
+
2
x
2
+
5
x
+
2
(
x
−
2
)
(
x
+
7
)
::y2x3+2x2+5x+2(x-2)(x+7) -
f
(
x
)
=
x
2
+
x
−
30
2
x
3
−
5
x
2
−
4
x
+
3
:x) =x2+x- 302x3- 5x2-4x+3
-
y
=
7
x
3
+
2
x
2
−
7
x
−
3
x
3
::y= 7x3+2x2- 7x- 3x3 y= 7x3+2x2- 7x- 3x3 -
f
(
x
)
=
2
x
+
5
x
2
+
5
x
−
6
:x)=2x+5x2+5x-6
-
g
(
x
)
=
−
x
2
+
3
x
+
4
2
x
−
6
::g(x) x2+3x+42x-6 -
Determine the slant asymptote of
y
=
3
x
2
−
x
−
10
3
x
+
5
. Now, graph this function. Is there really a slant asymptote? Can you explain your results?
::确定 y= 3x2- x- 103x+5 的倾斜渐移。 现在, 请绘制此函数 。 真的存在倾斜渐移吗 ? 您能否解释您的结果 ? -
In physics, Boyle's Law states that the product of the pressure
P
of a gas and the volume
V
of the container is always a constant. That is,
P
V
=
constant
.
Suppose the constant is equal to 4000 P a ⋅ m 3 (Pascal cubic meters). So P = 4000 V ,where the pressure is measured in Pascals and the volume is in meters cubed . Sketch the graph of the equation for V > 0 .
::Boyle的《物理学法》规定,气体的压力P和容器的体积五始终是恒定的。即PV=contant。假设常数等于4,000帕米(Pascal 立方米)。因此,P=4,000瓦,压力以帕斯卡尔测量,体积以米计。绘制V>0的方程图。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see Appendix.
::请见附录。 -
Expand the numerator and denominator if they are written in a
factored form
.