7.5 儿科功能的频率和时期
章节大纲
-
Introduction
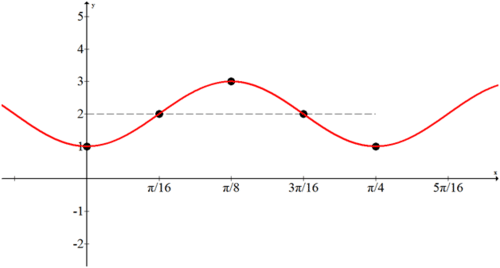
::导言In Chicago there is a public sculpture called Cloud Gate that looks like a giant bean. This sculpture can be modeled by a sinusoidal function as you walk around it. Similarly, the temperature standing next to it can be modeled with a sinusoidal function.
::在芝加哥,有一个叫云门的公共雕塑,看起来像一个巨型豆子。这个雕塑可以在你绕着它走动时用一个正弦函数模拟。同样,旁边的温度也可以用正弦函数模拟。
A mathematical model that fits this data is
As covered in another section, it is clear that the of the sine function is 28, and the vertical shift is up 56 units, which is the average of the maximum and minimum temperatures. From the second form of the function, the horizontal or phase shift is 3.77. How does the coefficient of affect the graph?
::符合此数据的数学模型是y=28sin(0.48x-1.81)+56=28sin(0.48(x-3.77)+56.A 如另一部分所述,正弦函数明显为28,垂直变化为56个单位,即最高和最低温度的平均值。从该函数的第二种形式来看,水平或阶段变化为3.77。(x-3.77)的系数如何影响图形?Sinusoidal Functions
::科性函数A sinusoid is the graph of the sine function. The general equation for the sine function provides the necessary information to graph the function: . The sign on controls the reflection across the -axis, and the value of controls the amplitude. The constant controls the vertical shift and the horizontal or phase shift. The coefficient controls the horizontal stretch .
::正弦函数的图示为正弦值。正弦函数的一般方程提供必要的信息来显示函数 : f(x)=asin(b(x-h))+k。控制 x 轴反射的符号以及控制振幅的值。恒定 k 控制垂直移动和 h 水平或相向移动。系数b 控制水平拉伸。General Form of S inusoidal Function:
::Sinusoidal 函数的一般形式 :
:xx) = asin (b(x-h)+k,
where is the amplitude, is the period, is the horizontal or phase shift, and is the vertical shift.
::在“aa”是振幅,“2b”是周期,“h”是水平或阶段转换,“k”是垂直转换。Horizontal stretch for sinusoidal functions is connected to the function's p eriod. Since t his is the basis for the periodic function family, the period is a critical characteristic. The period of a sine graph is the length of a complete cycle. For basic functions, the period is . This length can be measured in multiple ways. In applications , it may be most useful to measure from peak to peak.
::等离子函数的水平拉伸与函数的时段相关。 由于这是周期函数族的基础, 此时段是一个关键特征。 正弦图的时段是整个周期的长度。 对于基本函数, 此时段为 2++。 此时段可以用多种方式测量。 在应用中, 测量从峰值到峰值可能最为有用 。
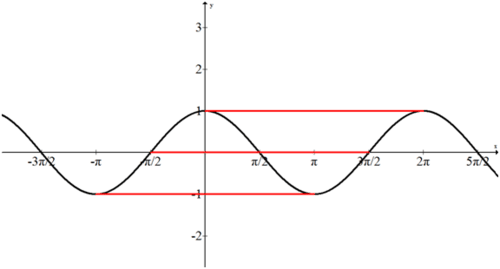
The ability to measure the period of a function in multiple ways allows multiple equations to model the same graph. In the image above, the top red line would represent a regular cosine wave. The center red line would represent a regular sine wave with a horizontal shift. The bottom red line would represent a reflected cosine wave with a horizontal shift. Any cosine function can be written as a sine function, since This flexibility in perspective means that graphs have multiple solutions. Unless you are directed otherwise, choose the function that has a period starting at or the closest option.
::以多种方式测量函数周期的能力允许多个方程式来模拟同一图形。 在以上图像中, 上方的红线将代表一个正正弦波。 中方的红线将代表一个正正弦波, 水平变化。 下方的红线将代表一个反射的正弦波, 水平变化。 任何余弦函数都可以写成一个正弦函数, 因为 COs( x) =sin( x) = \\ (x\\\\\ 2) 。 视野中的这种灵活性意味着图形有多个解决方案。 除非您另有指示, 否则, 请选择从 x=0 或最接近的选项开始一个时期的函数 。Frequency is a different way of measuring horizontal stretch. With sinusoidal functions, frequency is the number of cycles that occur in . A shorter period means more cycles can fit in , thus requiring a higher frequency. Period and frequency are inversely related by the equation:
::频率是测量水平伸展的另一种不同方式。 使用正弦函数, 频率是 2 中的周期数。 较短的周期意味着更多的周期可以适应 2 , 从而需要更高的频率。 使用等式, 周期和频率是反向关联的 :Period
::期间The equation of a standard sine function is . In this case, , the frequency, is equal to 1, which means 1 cycle is completed in .
::标准正弦函数的方程式是 f(x)=sinx。 在这种情况下, b, 频率等于 1, 这意味着 1 周期在 2 中完成 。A fractional frequency will increase the length of the period. Note that if you have a function where , the period will be since
::分数频率会延长周期的长度。请注意,如果您在 b=12 的位置有一个函数,则该周期将为 4。
::p=2b=212=4。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Rank the waves from the shortest to the longest period.
::从最短到最长的波浪顺序。
Solution:
::解决方案 :The red wave has the shortest period.
::红波时间最短The green and black waves have equal periods. The difference between these two graphs is in their amplitude.
::绿色和黑色的海浪有相同的时间段。这两个图表的差别在于它们的振幅。The blue wave has the longest period.
::蓝色波浪的周期最长。Example 2
::例2Identify the amplitude, vertical shift, period, and frequency of the function below. Then graph the function:
::标明以下函数的振幅、 垂直移动、 周期和频率。 然后绘制函数图 : f( x) = 2sin( x3)+1 。Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Identify the key information from the general equation: .
::第1步:从一般方程中确定关键信息:A=2,b=13,k=1。Step 2: Calculate the period: Since , then the period is .
::第2步:计算周期:自b=13起,期间为6。Step 3: Since the period is , the graph can be divided into f our parts so that the five guiding points (four sections and the 1st point on the y-axis) of the sine graph can be plotted with the amplitude.
::第3步:由于这一时期是6__年,因此该图可以分为四个部分,以便用振幅绘制正弦图的五个指导点(四个部分和Y轴的第1点)。Identify key points: (0,1) is the first point and ( , 1) is the last point to plot of our five. The midpoint of the points will be found at ( , 1). The midpoint between the 1st and 3rd points will be the maximum, found at ( , 3). The midpoint between the 3rd and last points will be found at ( , -1).
::确定关键点 : (0, 1) 是第一个点, (6, 1) 是五个点的最后一个点 。 点的中点将在 3 和 1 中点 。 第 1 点与 第 3 点之间的中点将是 最大点 , 最高点为 (3 12, 3 ) 。 第 3 点与 最后点之间的中点将在 9 12, - 1 中点 。Step 4: Graph the five key points and sketch the curve:
::第4步:绘制五个关键点图,绘制曲线图:
Example 3
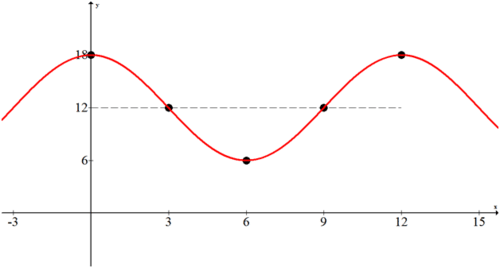
::例3A measuring stick on a dock measures high tide to be 18 feet and low tide to be 6 feet. It takes about 6 hours for the tide to switch between low and high tides. Determine a graphical and algebraic model for the tides, knowing that at there is a high tide.
::码头上的测量杆测量高潮为 18 英尺,低潮为 6 英尺。 低潮需要大约 6 小时才能在低潮和高潮之间转换。 确定潮的图形和代数模型, 知道在 t= 0 时有高潮。 NAME OF TRANSLATORS NAME OF TRANSLATORSSolution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: From the given information, the points below can be found. Notice how the sinusoidal axis can be assumed to be the average of the high and low tides.
::第1步:从给定的信息中,可以找到以下各点。请注意正弦轴如何被假定为高潮和低潮的平均值。Time (hours) Water level (feet) 0 18 6 6 12 18 Step 2: By plotting those points and filling in the sinusoidal axis, we can observe a cosine graph.
::步骤2:通过绘制这些点和填充正弦轴,我们可以观察一个余弦图。
Step 3: The amplitude is 6, so . There is no vertical reflection.
::第3步:振幅是6,所以A=6,没有垂直反射。Step 4: Since the period is 12, is found:
::第4步:由于报告期为12,b 如下:
::12=2bb6Step 5: The vertical shift is 12, so .
::第5步:垂直转变是12,所以k=12。Step 6: Enter the gathered information into the general equation:
::步骤6:将收集的信息输入总方程:
::f(x) = 6cos(x6x)+12。Example 4
::例4Return to the Introduction problem: How does the coefficient 0.48 on affect the graph of ?
::回到引入问题:0.48(x-3.77)上系数0.48(x-3.77)如何影响y=28sin(0.48(x-3.77)+56的图形?Solution:
::解决方案 :The period of the graph is
which is the length of time for the graph to make one full cycle and return to the starting temperature.
::图形的周期为 =20.48\\\\\\13.1, 即图形整个循环和返回到起始温度的时间长度 。Example 5
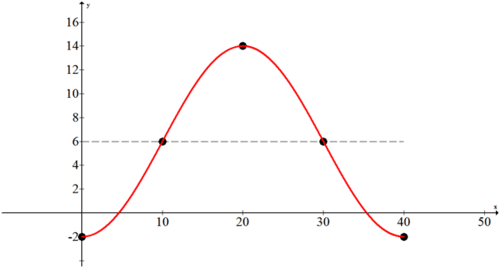
::例5A fish is caught in a water wheel by the side of a river. Initially, the fish is at the bottom of the water wheel, which is 2 feet below the surface of the water. Twenty seconds later the fish is 14 feet in the air at the top of the water wheel. Model the fish’s height with a graph and an equation.
::鱼在河边的水轮中捕获。 最初,鱼在水轮底部,水轮下方2英尺。 20秒后,鱼在水轮顶部的空气中为14英尺。 用图表和方程式来模拟鱼的高度。Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Use logic to identify five key points. Use those key points to come up with a sketch.
::第一步 : 使用逻辑来识别五个关键点。 使用这些关键点来绘制草图 。Time (seconds) Fish height (feet) 0 -2 20 14 40 -2 6 Step 2: Use the sketch to identify information for the equation.
::第2步:利用草图确定方程式的信息。Step 3: Identify the amplitude. The amplitude is 8, so .
::第3步:确定振幅。振幅是8,所以A=8。Step 4: Identify the function. The function looks like a reflected cosine graph, adding a negative to our final equation.
::第4步 : 识别函数。 函数看起来像一个反正余弦图, 给我们的最终方程式添加负值 。Step 5: The vertical shift is .
::第5步:垂直转换为k=6。Step 6: The period is 40.
::第6步:期间为40年。
::40=2bb20Step 7: Insert the gathered information into the general equation:
::步骤7:在一般等式中插入所收集的信息:
::f(x)_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Labeling on the graph can be helpful to identifying the graph . On both the - and -axes, only the most important intervals are labeled. This keeps the sketch accurate, evenly spaced, and easy to read.
::在图形上贴标签可有助于识别图形。在 X 轴和 y 轴上,只有最重要的间隔标记。这样可以保持草图的准确性、均匀的空格和易读。Example 6
::例6Graph the following function: .
::如下的函数图解 : g( x) ( 8x) +2 。Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Identify the amplitude. The amplitude is 1.
::第1步:标明振幅。振幅为 1 。Step 2: The shape is a negative cosine.
::步骤2:形状为负余弦。Step 3: Identify the vertical shift. The vertical shift is up 2.
::步骤3:确定垂直转变。垂直转变是向上移动2。Step 4: Calculate the period. The period is .
::第4步:计算周期。 周期为 284 。Step 5: Identify five key points and graph:
::第5步:确定五个关键点和图表:Example 7
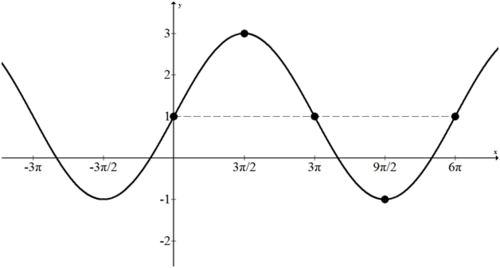
::例7Given the following graph, identify the and create an algebraic model:
::根据下图,确定并创建代数模型:Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Identify the amplitude. The amplitude is 3.
::第1步:确定振幅。振幅为3。Step 2: Identify the function. The shape is a reflected cosine graph.
::第2步 : 识别函数。 形状是一个反射的余弦图 。Step 3: Calculate the period: The period is which implies that since:
::第3步:计算期间:期间为512/2,这意味着b=45,因为:Step 4: Identify the vertical shift. The vertical shift is 1.
::52=25222b=45b=45。第4步:确定垂直变化。垂直变化为 1。Step 5: Insert the gathered information into the general equation:
::第5步:在一般等式中插入所收集的信息:.
::f(x)3cos(45x)+1..Summary
::摘要-
Sinusoidal functions have the form
::Sinusoidal 函数具有 f(x) =asin {(b(x-c)+d) 的表单 f(x) = asin} (b(x-c)+d 。 -
The sine graph has an amplitude
,
period
, frequency
,
phase shift
, and vertical shift
.
::正弦图有一个振幅 a, 周期 2b, 频率 b2, 阶段转换 h 和垂直移动 k 。
Review
::回顾Find the frequency and period of each function below.
::查找以下每个函数的频率和时间段。1.
::1. f(x) =sin(4x)+12.
::2. g(x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\3.
::3. h(x) =cos( 12x+4)+24.
::4. k(x) @ @ @%2sin @( 34x)+15.
::5. j(x)=4cos(3x+6)-1Graph each of the following functions:
::绘制下列函数的每个函数图 :6.
::6. f(x) = 3sin( 2x)+17.
::7. g(x)=2.5cos(xx)-48.
::8. h(x) sin(4x+8)- 39.
::9. k( x) = 12cos @ ( 2x+6)10.
::10. j(x)_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Create an algebraic model for each of the following graphs:
::为下列每个图表创建代数模型:
11.12.
13.
14. At time 0 it is high tide, and the water at a certain location is 10 feet high. At low tide 6 hours later, the water is 2 feet high. Given that tides can be modeled by sinusoidal functions, find a graph that models this scenario.
::14. 那时是高潮,某个地方的水位是10英尺高,6小时后是低潮,水位是2英尺高,鉴于潮位可以用正弦形功能模拟,请用图表来模拟这一情景。15. Find the equation that models the scenario in the previous problem.
::15. 找出在前一个问题中模拟设想情景的方程式。Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
Sinusoidal functions have the form