12.4 极地和笛卡尔转变
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言In 1959, geographer Richard J. Chorley drew the conclusion that the shape of a drumlin (which is an elliptical, streamlined hill made of till found under glacial ice) could be modeled by .
::1959年,地理学家Richard J. Chorley得出结论说,鼓形(由冰冰下发现的石料制成的精细石浆山)可由r=Lcosk制成。Coordinate points can be converted from rectangular form to polar form with a little algebra and some trigonometry.
::坐标点可以从长方形转换为极形,使用略微代数和一些三角测量法。Can the equation of a shape also be converted? How about a circle, for instance?
::形状的方程式能否也转换为正方形? 例如圆形如何 ?Polar Form to Rectangular Form
::极表到矩形表Sometimes you'll be given a problem with coordinates in polar form, but you need rectangular form.
::有时你会遇到极形坐标的问题 但你需要长方形坐标To transform the polar point into rectangular coordinates, first identify . In this point, and .
::将极点(4,34)转换成矩形坐标,首先标明(r,_)。在此点,r=4和34。Second, draw a vertical line from the point to the polar axis (the horizontal axis). The distance from the pole to where the line you just drew intersects the polar axis is the -value, and the length of the line segment from the point to the polar axis is the -value.
::其次,从点到极轴(水平轴)绘制一条垂直线。从极线到您刚才所画的线交叉的极轴的距离是X值,从点到极轴的线段长度是y值。These distances can be calculated using trigonometry:
::这些距离可以用三角测量法计算:
::x=cosy=sin
::x=4cos34andy=4sin34 x22andy=22In , is equivalent to in rectangular coordinates.
::在矩形坐标(4,34)中,等于(-22,22)的矩形坐标。The following video provides several examples of how to convert polar equations to rectangular equations:
::以下视频举例说明如何将极方程式转换成矩形方程式:Rectangular Form to Polar Form
::矩形窗体到极形的矩形窗体Going from rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates is also possible, but the process takes a bit more work. Suppose we want to find the polar coordinates of the rectangular point (2, 2). To begin doing this operation, we have to determine the distance that the point (2, 2) is from the origin (the radius ). The radius can be found by:
::从矩形坐标到极地坐标也是可能的,但这一过程需要多做一点工作。 假如我们想找到矩形点的极坐标(2, 2) 。 要开始此操作, 我们必须确定点(2, 2) 与原点(半径 r) 之间的距离。 半径可以通过以下方式找到 :
::r= rx2+y2
::r=22+22
::r=8=22The angle that is created by the line segment between the point and the origin can be found by the following procedure:
::点与源之间的线段所创造的角可通过下列程序找到:
::tanyx
::丹 丹 22
::晒黑 #% 1
::~ 坦 - 11 ~ 坦 - 塔 - 11 ~ 坦 - 塔 - 11 ~ 塔 - 塔 - 11 ~ 塔 - 塔 - 11 ~ 塔 - 塔 - 11 ~ 塔 - 塔 - 11 ~ 塔 - 塔 - 塔 - 11 ~ 塔 - 塔 - 塔 - 塔 - 11 ~ 塔 - 塔 - 塔 - 塔 - 塔 - 塔 - 11Since this point is in the 1st quadrant (both the - and -coordinates are positive), the angle must be 45° or radians. It is also possible that when the angle can be in the 3rd quadrant, or radians. But this angle will not satisfy the conditions of the problem, since a 3rd- quadrant angle must have both and negative.
::由于此点位于第1象限( x 和 y 坐标均为正) , 角度必须是 45 ° 或 + 4 弧度 。 当 tan 1 时, 角度可以是 第 3 象限, 或 5 4 弧度 。 但这个角度无法满足问题的条件, 因为 第 3 象限 角度必须同时有 x 和 y 负 。Note: When using to find the measure of you should first consider the quotient and find the 1st-quadrant angle that satisfies this condition. This angle will be called the reference angle , denoted . Find the actual angle by analyzing which quadrant the angle must be in, given the signs of and .
::注意 : 当使用 tan yx 来找到 的度量时, 您应该首先考虑 tan , 并找到符合此条件的 1- quamont 角 。 这个角度将被称为 参考角度 , 表示 ref 。 如果 x 和 y 的 符号 , 则通过分析 角度的 Q 值, 找到实际角度 。Play, Learn, and Explore Polar Coordinates:
::播放、学习和探索极地坐标 :Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Transform the polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates.
::将极坐标(2,116)转换为矩形坐标。Solution:
::解决方案 :
::r=2 和116Using the trigonometric conversion equations:
::使用三角转换方程式:
::x=rcosandy=rsinx=2cos116andy=2sin116x=3andy1Therefore, is equivalent to .
::因此,(2,116)相当于(3,1/1)。Example 2
::例2Find the polar coordinate for the rectangular coordinate .
::查找矩形坐标(3,-33)的极地坐标。Solution:
::解决方案 :To calculate , draw a right triangle and calculate the distance the point is from the origin.
::要计算 r, 请绘制一个右三角形, 并计算点从源点的距离 。 x=3andy\\\\ 33
::r=32+(-33)2=9+27=36=6The angle created by the line segment between the point and the positive -axis is:
::点与正 X 轴之间的线段所创建的角是 :
::tanref=3ref=tan -13ref3in the 1st quadrant. Now determine the corresponding 4th-quadrant angle. is a 4th-quadrant angle.
::=====================================================================================================================================================;Therefore, the rectangular coordinate is equivalent to the polar coordinate .
::因此,矩形坐标(3,-33)相当于极地坐标(6,53)。Example 3
::例3Convert the rectangular coordinates below to polar coordinates.
::将下面的矩形坐标转换为极坐标。1)
Solution:
::解决方案 :
:6,60)或(6,%3)
2)
Solution:
::解决方案 :
:22,135)或(22,34)。
Example 4
::例4Convert the polar coordinates below to rectangular coordinates.
::将下面的极坐标转换为矩形坐标。1)
Solution:
::解决方案 :2)
Solution:
::解决方案 :Example 5
::例5Recall the question from the Introduction: Can the equation of a shape also be converted? How about a circle, for instance?
::回顾导言中的问题:形状的方程式能否也转换?例如圆形如何?Solution:
::解决方案 :is the equation of a circle with a radius of in rectangular coordinates.
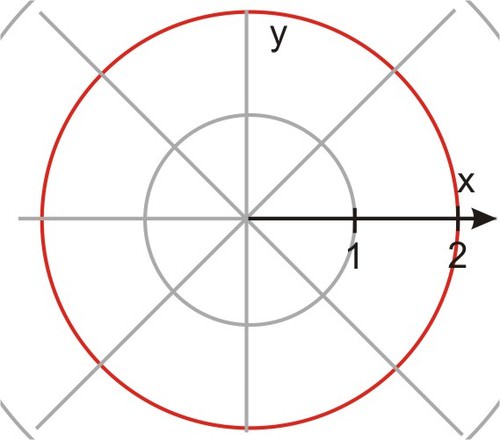
::x2+y2=k2 是一个圆的方程,方形坐标为 k 半径。The equation of a circle is extremely simple in polar form. In fact, a circle on a polar graph is analogous to a horizontal line on a rectangular graph.
::圆形的方程式以极的形式非常简单。事实上,极图上的圆形类似于矩形图上的水平线。You can transform this equation to polar form by substituting the polar values for . Recall a nd .
::您可以用 X, y. recall x=rcos 和 y=rsin 来替换极值, 以此将这个方程式转换为极形 。
:rcos)2+(rsin)2=k2r2cos2r2sin2k2
Factor the common factor on the left side of the equation:
::公式左侧共同系数 r2 的乘数 :
::r2 (cos2) sin2 ) =k2Recall the trigonometric identity
::回顾三角特征2=sin2=1=1
::r2=k2Therefore, is an equation for a circle in polar. When r is equal to a constant, the polar graph is a circle.
::因此, rk 是极中圆形的方程式。 当 r 等于常数时, 极图是一个圆形 。Example 6
::例61) Convert to rectangular coordinates.
::1) 转换(3,-45)为矩形坐标。Solution:
::解决方案 :Using the trigonometric conversion equations:
::使用三角转换方程式:Therefore, in rectangular is equivalent to in polar.
::因此,矩形中的(2.121,-2.21)在极地中相当于(3,-45)。2) Convert to rectangular coordinates.
::2) 转换(-3,4)为矩形坐标。Solution:
::解决方案 :Using the trigonometric conversion equations:
::使用三角转换方程式:
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}不... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}不... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}不...Therefore, in rectangular is equivalent to in polar .
::因此,(-2.21,-2.21)矩形中的矩形等于(-3,4)极地中的(-3,4)Example 7
::例71) Express the polar equation in rectangular form: .
:1) 以矩形形式表达极方程式:r=6cos。
Solution:
::解决方案 :Multiply both sides of the equation by .
::用 r. r2= 6rcos 乘以方程式的两边Substitute and .
Therefore, is the equivalent rectangular equation to the polar equation .
::替代 x2+y2=r2 和 x= rcos. x2+y2= 6xEstherforee, x2+y2= 6x是极方 r= 6cos 等量的矩形方程。2) Express the polar equation in rectangular form: .
:2) 以矩形形式表达极方程式:r=6。
Solution:
::解决方案 :Square both sides of the equation.
::方程式两侧的正方形 .r2=36Substitute
::替代 x2+y2=r2。Therefore, is the equivalent rectangular equation to the polar equation .
::x2+y2=36 因此, x2+y2=36 是极方公式r=6的等量矩形方程。Summary
::摘要Relationships between polar and rectangular coordinates where are being converted to rectangular .
::P=(r,)正被转换成矩形(x,y)的极地和矩形坐标之间的关系。
::x=rcosy=rsinx2+y2=r2tanyxReview
::回顾-
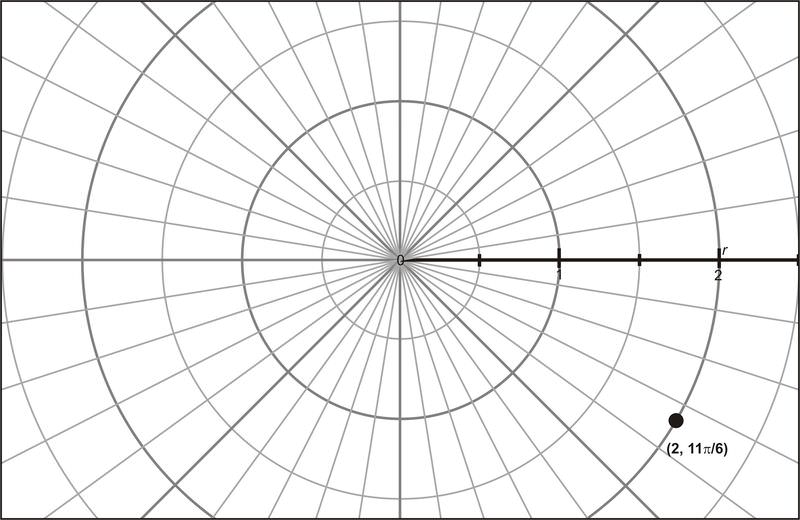
How is the point with polar coordinates
represented in rectangular coordinates?
::矩形坐标中以极坐标(5 )表示的点值(5 )如何?
Plot each point below in polar coordinates . Then write the rectangular coordinates for the point.
::在极坐标(r, ) 中绘制下方的每个点。 然后写出点的矩形坐标( x, y) 。Below, the rectangular coordinates are given. For each question: a) Find two pairs of polar coordinates , one with and the other with r < 0 . b) Express in radians, and round to the nearest hundredth.
::下面给出矩形坐标(x,y)。每个问题a) 查找两对极坐标(r, ),一对极坐标(r, ),一对极坐标(r) r>0,另一对角坐标(r < 0r>0.b) 弧度为 < 0r>.b) Express ,圆到最近的一百度。
Transform each polar equation to an equation using rectangular coordinates. Identify the graph, and give a rough sketch or description of the sketch.
::使用矩形坐标将每个极方程转换为方程。 标明图形, 并给出粗略的草图或草图描述 。-
::r=8 -
::罗辛7 -
::rcos 3
Transform each rectangular equation to an equation using polar coordinates. Identify the graph, and give a rough sketch or description of the sketch.
::使用极坐标将每个矩形方程式转换为方程式。 标明图形, 并给出粗略的草图或草图描述 。-
::x2+y2 - 2x=0 -
::y=3x y=3x -
::y 5 -
::xy= 15 -
The area of a drumlin at Glacier National Park
in Montana
is 4,380 square yards. If its length is 132 yards, find its polar equation.
::蒙大拿州格拉西耶国家公园的圆球场面积为4,380平方码,如果长度为132码,请找到极方程。 -
If a drumlin is modeled by the equation
and its area is 7,542 square meters, find its length.
::如果鼓林的模型是方程式r=lcos5,其面积为7,542平方米,请找到其长度。 -
The sonar screen of a submarine is a polar system. On the screen, the submarine is the origin of the graph. If the path of the ship in the polar system can be represented by find the linear equation of the movement of the ship.
::潜艇的声纳屏幕是极地系统。 在屏幕上, 海底是图的起源。 如果极地系统中的船舶路径可以由 6 = 17 rcos( 25 ) 来代表, 找到船只移动的线性方程 。
::潜艇的声纳屏幕是极地系统。 在屏幕上, 海底是图的起源。 如果极地系统中的船舶路径可以由 6 = 17 rcos( 25 ) 来代表, 找到船只移动的线性方程 。
Review ( Answers )
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -