12.7 复杂数字极表
Section outline
-
Introduction
::导言can be graphed on a polar graph in a few different ways. This section discusses how to write a complex number in standard form, polar form , and trigonometric form . Then, based on these forms, it covers how to graph a complex number on the rectangular and polar coordinate systems.
::可以用几种不同的方式在极图中绘制图表。 本节讨论如何以标准形式、极形式和三角形式写出一个复数。 然后, 以这些形式为基础, 它涵盖了如何用矩形和极坐标系统绘制一个复数。Polar Form of Complex Numbers
::复数极表There are three common forms of complex numbers you will see when graphing:
::有三种常见的复杂数字形式, 图形化时您可以看到 :1) The standard form of a complex number, , can be graphed using rectangular coordinates where represents the -coordinate and represents the -coordinate.
::1) 复数标准格式z=a+bi,可以用矩形坐标(a,b)绘制图表,其中表示x坐标,b表示Y坐标。2) The polar form, , can also be used to graph a complex number. Recall that you can convert between rectangular and polar forms with
andUnfortunately, there is a problem with using a conversion from rectangular form to polar form:orNotice that we no longer see the in this form.
3) The trigonometric form, which is often abbreviated as , comes from the substitutions and . Suppose . Note that in polar form, this complex number is .
The complex number can be written as a rectangular point , a polar point , or in trigonometric form or .
::2)极形,(r, ) 也可以用来绘制一个复杂的数字。 提醒注意, 您可以用 r=x2+y2 和 tan ärefyx 来转换矩形和极形, r=x2+y2 和 tan ärefyx 。 不幸地, 使用从矩形转换成极形有问题: a+bi(r, }) 或-1- i3-i3-i3 (cos443+is%43) 。 3 注意, 复数 z1-3i 可以写成矩形点(-1-3), 极点(2, 43) 和 y rsin 。 假设z1-i3 。 注意, 在极形中, z=2,43 + sin3 =2( 43) 或三角形 (43) 。Conversion
::改划To convert from r ectangular to polar form, the distance that the point (2, 2) is from the origin can be found by
::要从矩形向极形转换成极形,点(2,2)与源的距离可以由下列方式找到:or
::r= rx2+y2或r=22+22=8=22。The reference angle (i.e. the corresponding angle in the 1st quadrant) that the line segment between the point and the origin can be found by using
::参考角(即第1象方图中相应的角),即点与源之间的线段通过使用
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}我... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}我... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}我... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}我...For
::z=2+2i, tanref=22=1。Since this point is in the 1st quadrant (both the x- and y- coordinates are positive), the angle must be 45° or radians.
::由于此点位于第1象限( X 和 Y 坐标均为正),角必须是 45 ° 或 4 弧度。It is also possible that when the angle can be in the 3rd quadrant or radians. However, this angle will not satisfy the conditions of the problem, since a 3rd-quadrant angle must have both and as negatives.
::当 tan1 1 时, 角也有可能在 3 象限或 5 4 弧度中。 但是, 这个角无法满足问题的条件, 因为 3 象限角度必须同时有 x 和 y 的负值 。Note: When using , you should consider the quotient and find the 1st-quadrant angle that satisfies this condition. This angle will be called the reference angle, denoted . Find the actual angle by analyzing which quadrant the angle must be in, given the signs of x and y .
::注意: 使用 tan yx 时, 您应该考虑 yx 的商数, 并找到符合此条件的 1- quamont 角度。 这个角度将被称为参考角度 , 表示 ref 。 如果 x 和 y 的标记, 则通过分析角必须进入的方位数来查找实际角度 。The complex number or (2, 2) in rectangular form has .
::2+2i或(2,2)的矩形复合体有(22,%4)。The following video demonstrates how to write complex numbers in trigonometric form:
::以下视频展示如何以三角形式写出复杂的数字:
Examples
::实例Example 1
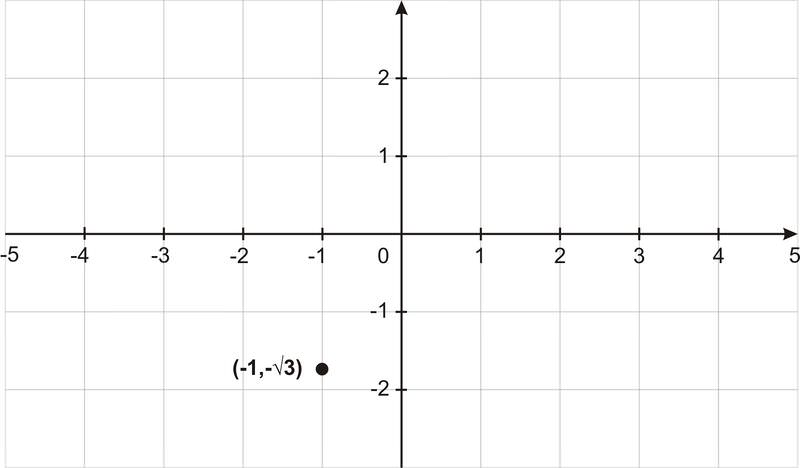
::例1Convert into polar form: .
::转换成极形: z1- i3。Here is what it looks like in the rectangular coordinate system:
::以下是矩形坐标系统中它的样子:Solution:
::解决方案 :To convert to polar , first determine and .
::将z1-i3转换为极地,首先确定 R和 。
::r=a2+b2=(-1)2+(-3)2=1+3=3=4=2
::3133333333413333Since this angle is in the 3rd quadrant, .
::由于这个角度位于第3象限, 43。Example 2
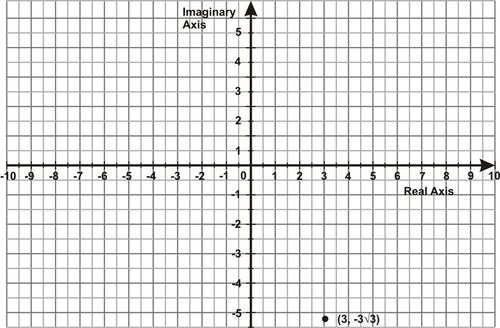
::例2Find the polar coordinates that represent the complex number .
::查找代表复数z=3-333i的极坐标。Solution:
::解决方案 :a = 3 and b = , so the rectangular coordinates of the point are .
::a = 3和b =-33,因此点的矩形坐标为(3,-33)。Now, draw a right triangle in standard form. Find the distance the point is from the origin, and the angle the line segment that represents this distance makes with the +x axis:
::现在, 以标准格式绘制一个右三角形。 查找点与源的距离, 以及代表此距离的线段与 +x 轴的角 :We know a = 3, .
::我们知道a=3,b33.r=32+(-33)2=9+27=36=6
::$$333$3$3$3$3$3$3$3$3$3$3$3$3$3$3$Since it is a 4th-quadrant angle, .
::因为它是第四赤道角 53The rectangular point is equivalent to the polar point .
::矩形点(3,-33i)相当于极点(6,53)。In trigonometric form, is .
::在三角形式中,(3,-33i)为6(5°3+i sin 53)。Example 3
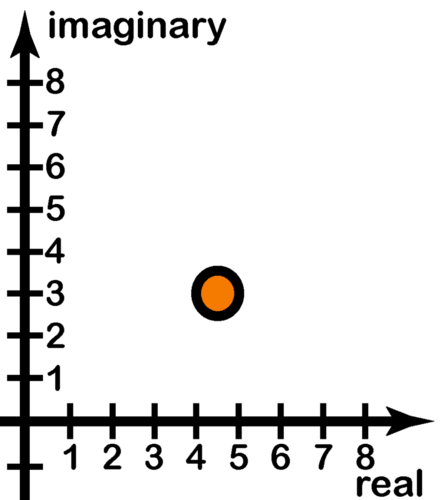
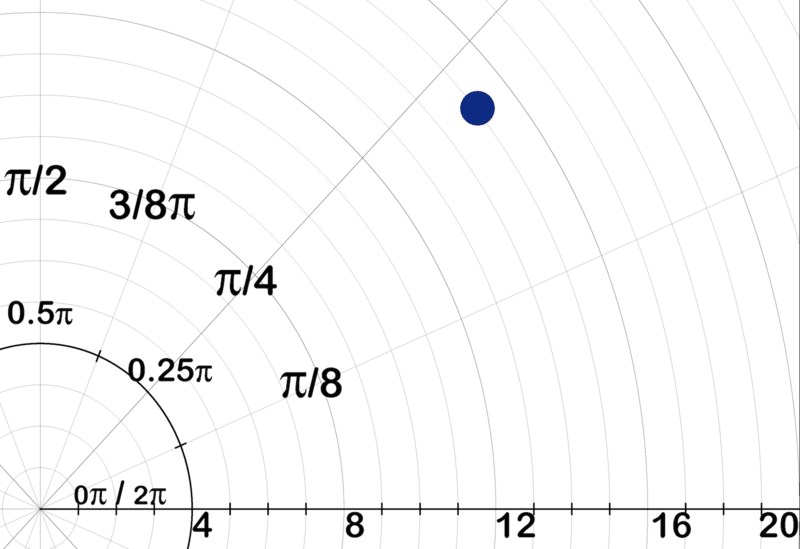
::例3Plot the complex number .
::绘制复合号z=12+9i。Solution:
::解决方案 :To plot on a polar graph, first determine and .
::要在极图上绘制 z=12+9i,首先确定 r 和 。
::r=122+92=144+81=225=15
::912 -1 912 36.9°looks like the image below when plotted on a polar plane.
::z=12+9i 绘制在极平面上时看起来像下面的图像 。Example 4
::例4In what quadrant does occur when graphed?
::当图表显示时, z3+2i 在什么象限中发生 ?Solution:
::解决方案 :The point occurs 3 units to the left and 2 units up, placing it in quadrant 2.
::点 z3+2i 向左3个单位,向上2个单位,放在象限2中。Example 5
::例5What are the coordinates of in polar form and trigonometric form?
::z3+2i 以极形和三角形表示的坐标是多少?Solution:
::解决方案 :To convert , first determine and .
::要转换 z3+2i,首先确定 R和 。
::r=(-3)2+22=13
::2323771237Therefore, is the coordinate in polar form, and is the coordinate in trigonometric form.
::因此,(13,33.7)是极形的坐标,13cis(33.7)是三角形的坐标。Example 6
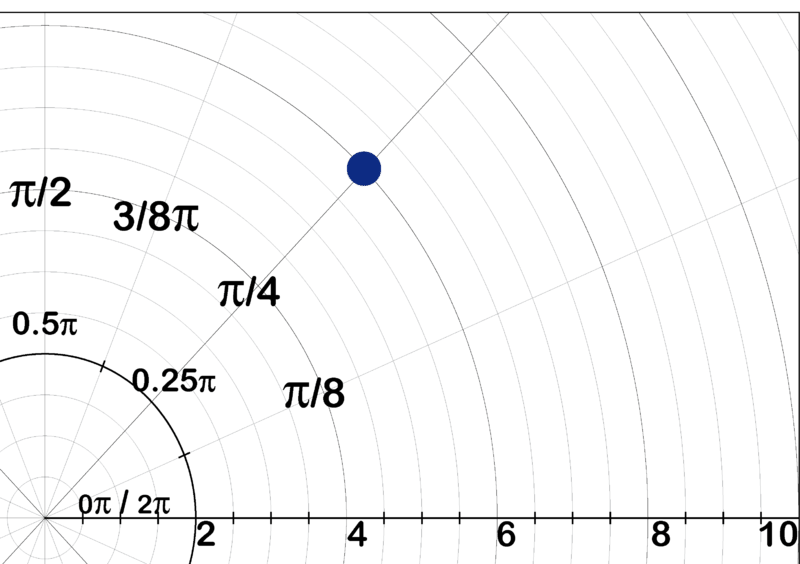
::例6What would be the polar coordinates of the point graphed below?
::下图显示的点的极地坐标是多少?Solution:
::解决方案 :The rectangular coordinates are (4.5, 3), so the complex number is .
::矩形坐标是(4.5, 3), 所以复数是z=4.5+3i. r=4.52+325. 4。
::34.555477Therefore, is the coordinate in polar form, and is the coordinate in trigonometric form.
::因此,(54.33.7)是极形的坐标,5.4cis(33.7)是三角形的坐标。Summary
::摘要-
In the standard form of
a complex number
z
can be graphed using rectangular coordinates
, where
represents the
-coordinate, while
represents the
-coordinate.
::在z=a+bi的标准格式中,可使用矩形坐标(a,b)绘制复数z的图表,其中代表 x 坐标,而b 代表 Y 坐标。 -
Use
x
and
y
to convert between rectangular and polar forms with
and
.
::使用 x 和 y 在 r= x2+y2 和 tan refyx 之间转换矩形和极形。
Review
::回顾Plot each complex number below in the complex plane. Convert its polar form where is in degrees.
::在复杂的平面下绘制每个复数。 转换它的极形( r, ) , 其中 ° 以度表示 。-
::1个+一 -
:1+一)i
-
:-2)(3)(一)
-
::1个+一 -
::1-一 -
:1+一)(1)-(一)
-
::1+i3 1+i3 -
::3- i 3- i -
:1+i3)(3-i)
-
What are the rectangular coordinates for the point graphed below?
::下图点的矩形坐标是多少?
C onvert to rectangular form:
::转换为矩形形式 :-
::15(cos120o+isin120o) -
::12(cos%3+isin%3) 3 -
For the complex number in standard form
find: a) polar form, and b) trigonometric form. (Hint: Recall that
and
)
::对于标准表x+iy的复数,请找到:a)极形,和b)三角形。 (提示:提醒注意 x=rcos- 和 y=rsin- 。 ) -
Find the zeros of
Graph them on the complex plane.
::查找 f( x) =x2-4x+8. 的零 。 在复合平面上绘制图。
Convert to trigonometric form:
::转换为三角形 :-
::1+i6 1+i6 -
::32+12i10 -
::- 3-2i -
::23-2i 23-2ii
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。Resource: Graphing Calculator Instructions
::资源: 图形计算器指令Convert the following complex numbers into polar form, us ing technology:
- a)
- b)
::使用技术将下列复杂数字转换成极形a) 3-i(b) 93+9i
Solution
::解决方案On the TI-84, go to [ANGLE] (or [2nd] function) [APPS] . Scroll down to 5 or "R-Pr(" and press [Enter] . Next, enter the rectangular coordinates and close the parentheses. Press [Enter]; the "r" value appears. Scroll down to 6R-Pθ, and the polar angle appears in decimal radian form.
::在 TI-84 上, 转到 [ANGLE] (或 [第 2 函数) [APPS] 。 向下滚动到 5 或“ R- Pr () ” , 按 [Enter] 。 下一步, 输入矩形坐标并关闭括号 。 按 [Enter] ; 显示“ r” 值。 向下滚动到 6R- P , 极角以小数弧形显示 。Note: Also under the [ANGLE] menu, commands 7 and 8 allow transformation from polar form to rectangular form.
::注:在[ANGLE]菜单下,指令7和8允许从极形转换成矩形。 -
In the standard form of
a complex number
z
can be graphed using rectangular coordinates
, where
represents the
-coordinate, while
represents the
-coordinate.