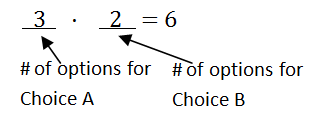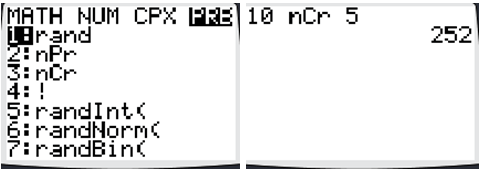14.2 以变异和组合计数
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics that focuses on the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Combinatorics has applications in optimization, computer science, and statistical physics. There are times that it makes sense to count the number of ways an event could occur by looking at each possible outcome . However, when a large number of outcomes exists, this method becomes inefficient. If someone asked you how many possible regular license plates there are for the state of Oregon , it would not be feasible to count each and every one.
::混合体是数学的一个分支,侧重于研究有限或可计数的离散结构。组合体在优化、计算机科学和统计物理学方面有各种应用。有时,通过观察每一种可能的结果来计算一个事件可能发生的方式的数量是有道理的。然而,当有大量结果存在时,这种方法就变得效率低下。如果有人问你俄勒冈州有多少可能的普通牌照,那么计算每一个结果是不可行的。
Instead, you could use the fact that on the typical Oregon license plate, there are 4 numbers and 3 letters. Using this information, about how many license plates could there be?
::相反,你可以使用以下事实:在典型的俄勒冈州牌照牌照上,有4个号码和3个字母。使用这个信息,可以找到多少个牌照?The Counting Principle
::计算原则Consider choice A with 3 options ( A 1 , A 2 , A 3 ) , and choice B with 2 options ( B 1 , B 2 ) . If you had to choose an option from A and then an option from B , the overall total number of options would be 3 ⋅ 2 = 6 . The options are A 1 B 1 , A 1 B 2 , A 2 B 1 , A 2 B 2 , A 3 B 1 , A 3 B 2 .
::考虑选择A,3个选项(A1,A2,A3),选择B,2个选项(B1,B2),如果从A中选择一个选项,然后从B中选择一个选项,选项总数将为32=6。 这些选项是A1B1,A1B2,A2B1,A2B2,A3B1,A3B2。You can see where the 6 comes from by making a decision tree and using the . A decision tree is a graph that models the options possible at each stage of an experiment . To make a decision tree, you 1st need to determine how many decisions you are making. Here, there are only two decisions to make: 1) choose an option from A , and 2) choose an option from B , so you will have two "slots" in your decision tree. Next, think about how many possibilities there are for the 1st choice (in this case there are 3), and how many possibilities there are for the 2nd choice (in this case there are 2). The Fundamental Counting Principle says that you can multiply those numbers together to get the total number of outcomes.
::您可以通过决策树和使用 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 您可以从 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 从 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .The following video explains how to find the number of ways an event can occur:
::以下影片解释如何寻找事件发生方式的多寡:Combinations and Permutations
::组合和变式Another type of counting question is when you have a given number of objects, you want to choose some (or all) of them, and you want to know how many ways there are to do this. For example, a teacher with a class of 30 students wants 5 of them to do a presentation, and she wants to know how many ways this could happen. These types of questions have to do with combinations and permutations. The difference between combinations and permutations is whether or not the order you are choosing the objects matters.
::计算问题的另一类型是当您有指定数量的对象时, 您想要选择其中的一部分( 或全部) , 您想要知道有多少方法可以这样做。 例如, 一个有30名学生的教师想要其中5人做演示, 她想要知道这可以发生的方式。 这些类型的问题与组合和变异有关。 组合和变异之间的区别在于您是否选择对象事项的顺序 。-
A teacher choosing a group to make a presentation is a
problem, because
order does not matter.
::选择一组教师进行演示是一个问题,因为秩序无关紧要。 -
A teacher choosing 1st-, 2nd-, and 3rd-place winners in a science fair is a
problem, because the
order does matter.
(1st place and 2nd place are different outcomes.)
::在科学博览会上选择第一、第二和第三位优胜者的教师是一个问题,因为顺序很重要。 (第一和第二位结果不同。 )
T he symbol, !, means to multiply every natural number up to and including that whole number together. For example, 5 ! = 5 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1 . The factorial symbol is used in the formulas for permutations and combinations.
::符号“ ! ” 是指将每个自然数字乘以, 直至并包含整个数字。 例如 5! = 5= 54321 。 该系数符号用于变换和组合的公式中 。Combination Formula
::组合公式The number of ways to choose k objects from a group of n objects where order does not matter is
::从一组 n 对象中选择 k 对象的方法数,如果顺序无关紧要n C k = ( n k ) = n ! k ! ( n − k ) ! .
::NCK=(nk)=n.k! (n-k)! (n-k)!The following video introduces combinations and explains how to evaluate combinations and solve counting problems using combinations:
::以下视频介绍组合,并解释如何评估组合,并用组合解决计算问题:Play, Learn, and Explore with Combinations:
::与组合一起玩、学习和探索:Permutation Formula
::变换公式The number of ways to choose and arrange k objects from a group of n objects is
::从一组 n 对象中选择和排列 k 对象的方法数是n P k = k ! ( n k ) = k ! ⋅ n ! k ! ( n − k ) ! = n ! ( n − k ) ! .
::NPKK! (nKK) ! (nK) ! (nK) ! (nK) ! (nK) ! (nK) ! (nK) !The following video explains how to evaluate factorials, use permutations to solve problems, and determine the number of permutations with indistinguishable items :
::以下影片解释如何评估保理因素, 使用变相来解决问题, 以及确定与不可区分物品的变异次数:Play, Learn, and Explore with Permutations:
::玩耍、学习和探索与变异:Notice that in both combination and permutation problems, you are not allowed to repeat your choices. Any time you are allowed to repeat and order does not matter, you can use the Fundamental Counting Principle. (Problems with repetition where order does not matter are more complex and not discussed in this section. )
::请注意,在组合和混合问题中,不允许重复选择。允许重复和顺序的任何时间都无关紧要,您可以使用基本计算原则。 (如果顺序无关紧要的重复问题更为复杂,本节不讨论。 )Whenever you do a counting problem, the 1st thing you should decide is whether the problem is a Fundamental Counting Principle problem , a permutation problem, or a combination problem. You'll find that can also be solved with the Fundamental Counting Principle, but the opposite is not true. There are many Fundamental Counting Principle problems (ones where you are allowed to repeat choices) that cannot be solved with the permutation formula.
::当你做一个计数问题时,你首先应该决定的问题是基本计数原则问题、变异问题还是组合问题。你会发现,这也可以用基本计数原则解决,但事实并非如此。有许多基本计数原则问题(允许重复选择的问题)不能用调整公式解决。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1You are going on a road trip with 4 friends in a car that fits 5 people. How many different ways can everyone sit if you have to drive the whole way?
::你和4个朋友在一辆适合5人的汽车里旅行。
Solution:
::解决方案 :The Fundamental Counting Principle is a great way of thinking about this problem. You have to sit in the driver's seat. There are 4 options for the 1st passenger seat. Once that person is seated, there are 3 options for the next passenger seat. This goes on until there is one person left with 1 seat.
::基本计票原则是思考这一问题的好方法。 您必须坐在驾驶员座位上。 第一位乘客座位有四个选项。 一旦该乘客座位就座, 下一个乘客座位有三个选项。 直到有一个人剩下一个座位为止 。1 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1 = 24
Example 2
::例2How many different ways can the gold, silver, and bronze medals be awarded in an Olympic event with 12 athletes competing?
::在有12名运动员参加比赛的奥林匹克活动中,金、银和铜奖章可以授予多少种不同的方式?
Solution:
::解决方案 :Since the order does matter with the 3 medals, this is a permutation problem. You will start with 12 athletes and then choose and arrange 3 different winners.
::由于顺序与3个奖牌有关系,所以这是一个变换问题。你将从12名运动员开始,然后选择和安排3名不同的获奖者。12 P 3 = 12 ! ( 12 − 3 ) ! = 12 ! 9 ! = 12 ⋅ 11 ⋅ 10 ⋅ 9 ⋅ … 9 ⋅ … = 12 ⋅ 11 ⋅ 10 = 1 , 320
::12P3=12!(12- 3)!=12!9!=1211_ 11_ 10_ 9. 9...=1211_ 10=1,320Note that you can also use the Fundamental Counting Principle to decide how many possibilities are there for gold (12), how many possibilities are there for silver (11, since one already has gold), and how many possibilities are there for bronze (10). You can use the Fundamental Counting Principle for any permutation problem.
::请注意,您也可以使用基本计数原则来决定金(12)有多少可能性,银(11)有多少可能性,因为已有金(11)有多少可能性,青铜(10)有多少可能性。您可以使用基本计数原则来解决任何变换问题。12 ⋅ 11 ⋅ 10 = 1 , 320
Example 3
::例3You are deciding which awards you are going to display in your room. You have 8 awards, but you only have room to display 4 awards. Right now you are not worrying about how to arrange the awards, so the order does not matter. How many way s could you choose the 4 awards to display?
::您正在决定您将在您的房间里显示哪些奖项。 您有8个奖项, 但您只有4个奖项。 现在您并不担心如何安排奖项, 因此命令并不重要 。 您可以选择多少方法来显示4个奖项 ?
Solution:
::解决方案 :Since order does not matter, this is a combination problem. You start with 8 awards and then choose 4.
::由于顺序无关紧要, 这是一个组合问题。 您先从 8 个奖项开始, 然后选择 4 个奖项 。8 C 4 = ( 8 4 ) = 8 ! 4 ! ( 8 − 4 ) ! = 8 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 6 ⋅ 5 4 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1 = 7 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 5 = 70
::8C4=(84)=8!4!(8- 4)!8C4=8C4=8. 4!(8- 4)!8C4=8C4=8C4=8. 4!(8- 4)!8C4=8C4=8C4=8. 4!Note that if you try to use the Fundamental Counting Principle with this question, you will need to do an extra step of reasoning. There are 8 options you could choose 1st, then 7 left, then 6, and lastly 5.
::请注意, 如果您试图使用基本计数原则来解决这个问题, 您需要做额外的推理步骤 。 您可以选择 8 个选项 。 您可以选择 1, 7 个选项 左, 6 个选项 , 最后 5 个选项 。8 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 6 ⋅ 5 = 1 , 680
This number is so big because it takes order into account, which you don't care about. It is the same result you would get if you used the permutation formula instead of the combination formula. To get the right answer, you need to divide this number by the number of ways 4 objects can be arranged, which is 4 ! = 24 . This has to do with the connection between the combination formula and the permutation formula.
::此数字如此大, 因为它会考虑到顺序, 你并不关心。 如果使用变异公式而不是组合公式, 也会得到同样的结果 。 要获得正确的答案, 您需要将这个数字除以 4 对象可以排列的方式数, 也就是 4! = 24 。 这与组合公式和变异公式之间的联系有关 。Example 4
::例4Recall the problem from the Introduction: How many Oregon license plates could be created with 3 letters and 4 numbers?
::回顾导言中的问题:用3个字母和4个号码可以创建多少俄勒冈州牌照?Solution:
::解决方案 :A license plate that has 3 letters and 4 numbers can be represented by the Fundamental Counting Principle with 7 spaces. You can use the Fundamental Counting Principle because order definitely does matter with license plates. The 1st spot is a number, the next three spots are letters, and the last three spots are numbers. Note that when choosing a license plate, repetition is allowed.
::有3个字母和4个号码的牌照可以由基本计数原则代表,有7个空格。您可以使用基本计数原则,因为命令与牌照确实有关系。第一个空位是数字,接下来三个空位是字母,最后三个空位是数字。请注意,在选择牌照时,允许重复。10 ⋅ 26 ⋅ 26 ⋅ 26 ⋅ 10 ⋅ 10 ⋅ 10 = 26 3 ⋅ 10 4 = 175 , 760 , 000
This number is only approximate because, in reality, certain letter and number combinations are not allowed, some license plates have extra symbols, and some commercial and government license plates have more numbers, fewer letters, or blank spaces.
::这个数字只是近似数字,因为在现实中,某些字母和数字组合是不允许的,有些牌照有额外的符号,有些商业和政府牌照有较多的编号、较少的字母或空白。Example 5
::例5There are 20 hockey players on a pro NHL team, 2 of whom are goalies. How many sets of 5 skaters and 1 goalie can be on the ice at the same time?
::有20个曲棍球运动员在亲NHL队,其中2个是守门员。 有多少5个滑雪运动员和1个守门员可以同时在冰上?Solution:
::解决方案 :The question asks for how many on the ice, implying that order does not matter. This is combination problem with 2 combinations. You need to choose 1 goalie out of a possible of 2, and choose 5 skaters out of a possible 18.
::问题在于冰上有多少人, 这意味着顺序无关紧要。 这是两个组合的结合问题。 您需要从可能的两个组合中选择一个守门员, 并选择可能18个组合中的5个滑冰员 。( 2 1 ) ( 18 5 ) = 2 ⋅ 18 ! 5 ! ⋅ 13 ! = 17 , 136
Example 6
::例6How many different ways could you score a 70% on a 10-question test, where each question is weighted equally and is either right or wrong?
::在10个问题测试中,你能用多少种不同的方法 获得70%的分数? 每一个问题都同等加权, 不管是对的还是错的?Solution:
::解决方案 :The order of the questions you got right does not matter, so this is a combination problem.
::你问对了问题的顺序无关紧要 所以这是一个合并问题( 10 7 ) = 10 ! 7 ! 3 ! = 120
Example 7
::例7How many different 4-digit ATM passwords are there? Assume you can repeat digits.
::有多少不同的 4 位数 ATM 密码? 假设您可以重复数字 。Solution:
::解决方案 :Order does matter. There are 10 digits, and repetition is allowed. You can use the Fundamental Counting Principle for each of the 4 options.
::顺序很重要。 有 10 位数字, 允许重复。 您可以对 4 个选项中的每个选项使用基本计数原则 。10 ⋅ 10 ⋅ 10 ⋅ 10 = 10 , 000
Summary
::摘要-
The
Fundamental Counting Principle
states that if one event has
m
possible outcomes and a 2nd event has
n
possible outcomes, then there are
m
⋅
n
total possible outcomes for the two events together.
::基本计数原则指出,如果一项活动可能取得结果,而第2项活动可能取得结果,那么,这两项活动可能取得的总结果是总共可能取得的结果。 -
A
combination
is the number of ways of choosing
k
objects from a total of
n
objects (order does not matter).
n
C
k
=
(
n
k
)
=
n
!
k
!
(
n
−
k
)
!
::一个组合是从总计 n 对象中选择 k 对象的方法数( 顺序无关紧要) 。 nCk=( nk)=n! k! (n- k) ! -
A
permutation
is the number of ways of choosing and arranging
k
objects from a total of
n
objects (order does matter).
n
P
k
=
k
!
(
n
k
)
=
k
!
⋅
n
!
k
!
(
n
−
k
)
!
=
n
!
(
n
−
k
)
!
::变式是指从总计 n 对象中选择和排列 k 对象的方法数( 顺序很重要 ) 。 nPk=k! (nk)=k! k! k!!
!
!
!
!
!
Review
::回顾Simplify each of the following expressions so that they do not have a factorial symbol:
::简化下列表达式,使其没有系数符号:1. 7 ! 3 !
2. 110 ! 105 ! 5 !
3. 52 ! 49 !
4. In how many ways can you choose 3 objects from a set of 9 objects?
::4. 从一组9个对象中选择3个对象的方式有多少?5. In how many ways can you choose and arrange 4 objects from a set of 15 objects?
::5. 从一组15个天体中选择和安排4个天体的方式有多少?First state whether each problem is a permutation/decision tree problem or a combination problem. Then solve.
::首先说明每个问题是变形/决定树问题还是合并问题。然后解决。6. Suppose you need to choose a new combination for your combination lock. You have to choose 3 numbers, each different and between 0 and 40. How many permutations are there?
::6. 假设您需要为您的组合锁选择一个新的组合组合。 您必须选择三个数字, 每个数字不同, 介于0到40之间, 有多少变异?7. You just won a contest where you can choose 2 friends to go with you to a concert. You have 5 friends who are available and want to go. In how many ways can you choose the friends?
::7. 你刚刚赢得了一场比赛,在那里你可选择两个朋友与你一起参加音乐会,有五个朋友可以参加并愿意参加音乐会,可以选择多少朋友?8. You want to construct a 3-digit number from the digits 4, 6, 8, 9. How many possible numbers are there?
::8. 你想用4、6、8、9等数字 构建一个3位数的数字吗? 有多少位数?9. There are 12 workshops at a conference, and Sam has to choose 3 to attend. In how many ways can he choose the 3 to attend?
::9. 会议有12个讲习班,Sam必须选择3个参加,他可以选择多少方式选择3个参加?10. A contest has 9 girls and 5 boys as finalists. In how many ways can 1st-, 2nd-, and 3rd-place winners be chosen?
::10. 比赛有9名女孩和5名男孩作为决赛选手,以多少方式选出第一、第二和第三位获胜者?11. For the special at a restaurant, you can choose 3 different items from the 10-item menu. How many different combinations of meals could you get?
::11. 对于餐厅的特餐,您可以从10项菜单中选择3个不同的项目,可以提供多少份不同的餐食组合?12. You visit 12 colleges and want to apply to 4 of them. In how many ways could you choose the 4 to apply to?
::12. 你访问了12所大学,希望申请其中4所。你能够以多少方式选择4所大学申请?13. For the 12 colleges you visited, you want to rank your top 5. In how many ways could you rank your top 5?
::13. 在你访问的12所学院中,你想排在前5级,以多少种方式排在前5级?14. Explain why the following problem is not strictly a permutation or combination problem: The local ice cream shop has 12 flavors. You decide to buy 2 scoops in a dish. In how many ways could you do this if you are allowed to get 2 of the same scoop?
::14. 解释为什么以下问题不是严格意义上的变异或组合问题:当地冰淇淋店有12种口味。您决定在一个盘子里买2个勺子。如果允许您在同一勺子中买2个,您可以用多少种方式这样做?15. Your graphing calculator has the combination and permutation formulas built in. Push the MATH button and scroll to the right to the PRB list. You should see n P r and n C r as options. To use these: 1) On your home screen, type the value for n ; 2) Select n P r or n C r ; 3) Type the value for k ( r on the calculator). Use your calculator to verify that 10 C 5 = 252 .
::15. 您的图形计算器有组合和排列公式。 按下 MATH 按钮并滚动到 PRB 列表右侧。 您应该将 nPr 和 nCr 作为选项。 要使用这些选项1) 在主屏幕上输入 n;(2) 选择 nPr 或 nCr;(3) 键入 k (r 在计算器上)。 使用您的计算器验证 10C5=252 。
Review (Answers )
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
A teacher choosing a group to make a presentation is a
problem, because
order does not matter.