15.3 确定界限的图表
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言To ship a package overnight, a delivery service charges $18 for the 1st pound, and $2 for each additional pound or portion of a pound. The total cost can be represented by the function where is the number of pounds of the package . If the package weighs 5 pounds, what is the limit of the cost function ?
::在夜间装运包件时, 送货服务费为1磅18美元, 每增加1磅或1磅部分为2美元。总成本可以用函数( f(x) =180 <xxx}1美元=180 <xxxx}1201 <x=2...x>2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx2x2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx2x2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxOne-sided Limits
::片面限制A one-sided limit can be evaluated either from the left or from the right. Since left and right are not absolute directions, a more precise way of thinking about direction is from the negative side or from the positive side. The notation for these is
::单向限制可以从左侧或从右侧评价。由于左右不是绝对方向,对方向的更精确的思考方法是从负面或从正面进行。The negative superscript on is not an exponent, but rather it indicates from the negative side . Likewise, the positive superscript is not an exponent, but rather it indicates from the positive side . When evaluating one-sided limits, consider only what value the function is approaching on the one side of the -value, regardless of what the function is doing at the actual point or on the other side of the number.
::limxa- f(x) 和 limxa+f(x) 。 a 上的负上标不是引号,而是从负面表示。 同样,正上标不是引号,而是从正面表示。在评价单面限制时,只考虑函数在 x 值的一边接近的值,不管函数在实际点或数字的另一边做什么。One-sided Limits
::片面限制The limit of as approaches from the left side is
::左侧 x 接近 a 的 f( x) 限制为 L1:
::limxa-f(x)=L1。The limit of as approaches from the right side is
::从右侧接近 x 的 f( x) 限制为 L2: limxa+f( x) = L2 。Graphing to Find a Limit
::用于查找限制的图形One method of finding the limit of a function is by graphing. When evaluating the limit of a function from its graph, you need to distinguish between the function evaluated at the point, and the limit approaching the point.
::找到函数极限的方法之一是图形化。在从图形中评价函数极限时,需要区分点点上评价的函数和接近点的极限。Functions like the one above with discontinuities, asymptotes, and holes require you to have a very solid understanding of how to evaluate and interpret limits.
::类似上面的功能,有不连续、无症状和洞的功能,需要您对如何评估和解释限制有非常扎实的了解。When you evaluate limits graphically, your main goal is to determine whether the limit exists. The limit exists only when the left and right one-sided limits are equal . The f unction value at that point is irrelevant in respect to the limit at that point. A function could be defined or undefined at that point, but the limit of the function at that point exists only if the one-sided limits are equal.
::当您图形化地评估限制时,您的主要目标是确定限制是否存在。限制只在左侧和右侧的单向限制相等时才存在。该点的函数值与该点的限制无关。该点的函数值可以定义或未定义,但该点的函数值只有在单向限制相等时才存在。Existence of a Limit
::存在限制The limit of as approaches exists if
::f(x) 作为 x 方法的 f(x) 限值存在
::立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺 = 立方公尺For instance, for the graph above, the limit of the function as from the left is -2.4, and from the right is -2.4. E ven though the function has a discontinuity in the form of a hole at , the two one-sided limits equal -2.4, so the limit of the function as is -2.4. Note that w hen you evaluate the function at 0, the function value is the actual -value on the graph, .
::例如,对上图来说,左向 x 接近 0 的函数限值为 -2.4,右向函数限值为 -2.4。即使该函数以x=0的洞的形式具有不连续性,但两个单向限制等于 -2.4,因此,以x 接近 0 的函数限值为 -2.4。请注意,当您将函数值评价为 0 时,函数值是图形上的实际 y 值, (0, 1) 。
::limbx0f(x)2.4 和 f(0)=1At , the limit of the function from the left is 1, and the limit of the function from the right is 1.8. Since these one-sided limits are not equal, the limit does not exist . The function value at is 1, because the closed dot at indicates that the function is defined at this point.
::在 x=b 上,左侧函数的限值为 1, 右侧函数的限值为 1. 8。 由于这些单向限制不相等, 限制并不存在。 x=b 的函数值为 1, 因为(b, 1) 上的关闭点表示此函数是在此点定义的 。
::limxbf(x) = DNE 和 f(b) = 1Similarly, the two one-sided limits at are not equal, so the limit does not exist. T he function is defined at with a function value of -3.
::同样, x=c 的两面限制并不相等,因此该限制不存在。函数在 x=c 下定义,函数值为 -3。
:x)=DNE和f(c)________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
At , the function is undefined because there is a vertical asymptote. Since the function approaches different values from the left and from the right of , the limit does not exist.
::At x=a, 函数没有定义, 因为有一个垂直的空点。 由于函数与左侧和 x=a 右侧的值不同, 限制不存在 。
::limxaf(x) = DNE 和 f(a) = DNEThe graph of the function appears to flatten as it moves to the left. Thus, there is a horizontal asymptote at as .
::函数的图形在向左移动时似乎会平滑。因此,在 y=0 的 x\\\ 时,会有一个水平的同位数 。
::limxf(x)=0However, t he graph of the function appears to continue to increase without bound as it moves to the right. Thus, the limit of the function does not exist as .
::然而,函数图在向右移动时似乎在不受约束的情况下继续增加。因此,函数的极限并不存在 x 。
::limxf(x) = DNEAnother example of these ideas can be found in the following video:
::这些想法的另一个例子是在以下录像中看到的:Play, Learn, and Explore One-sided Limits:
::玩耍、学习和探索单向限制:Examples
::实例Example 1
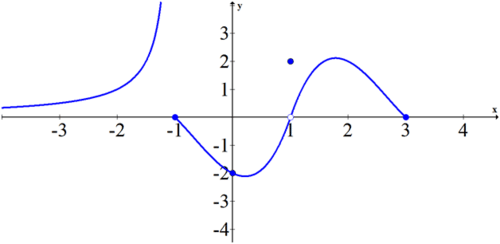
::例1Evaluate the following expressions using the graph of the function :
::使用函数 f(x) 的图形评价以下表达式:a.
::a. limxf(x)Solution:
::解决方案 :
::limxf(x)=0b.
::b. limx%1f(x)Solution:
::解决方案 :
::limx1f(x) = DNEc.
::c. 立方厘米Solution:
::解决方案 :
::立方厘米#0f( x) @%%2d.
::d. 立方厘米1f(x)Solution:
::解决方案 :
::limx% 1f( x) =0e.
::e. limx%3f(x)Solution:
::解决方案 :because only the limit from the left side exists, and therefore the two one-sided limits do not exist.
::limx}3f(x)=DNE,因为只有左侧的限制存在,因此不存在两个单方的限制。f.
::f. f. f(-1-1)Solution:
::解决方案 :
::f( - 1) =0g.
::g. f( 0) 数Solution:
::解决方案 :
:f0)%2
h.
::h. f(1)Solution:
::解决方案 :
::f(1)=2i.
::i. f. (3)Solution:
::解决方案 :
::f(3)=0
Example 2
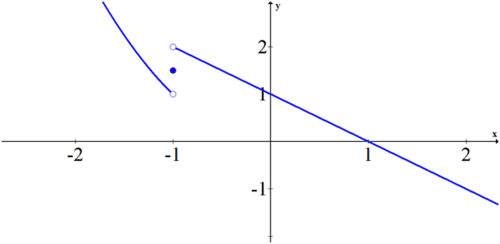
::例2Sketch a graph that has a limit at where the limit value does not match the function value .
::绘制一个在 x=2 上有限制的图形, 当限制值与此点的函数值不符时 。Solution:
::解决方案 :While there are an infinite number of graphs that fit this criteria, you should make sure your graph has a removable discontinuity at .
::虽然有无数符合此标准的图表,但您应该确保您的图表在 x=2 时具有可移动的不连续性。Example 3
::例3Sketch a graph that is defined at but does not exist.
::绘制一个在 x1 上定义的图形, 但是 limx1f(x) 不存在 。Solution:
::解决方案 :The graph must have either a jump or an infinite discontinuity at and also have a closed hole filled in somewhere on that vertical line.
::图形必须在 x1 上有一个跳跃或无限的不连续性, 并在垂直线上某个地方有一个封闭的洞。Example 4
::例4Recall the problem from the Introduction: Determine the limit of the cost function of shipping a 5-pound package overnight. The total cost is represented by where is the number of pounds of the package.
::回顾导言中的问题:确定夜间装运5磅包件的成本功能限度。总成本为f(x)$180 <xx}1$1$201 <x}2,...x>2,其中x是包件的磅数。Solution:
::解决方案 :The graph of the cost function is shown below. T he limit to the left of is 26, and the limit to the right of is 28. Since these two one-sided limits are not equal, the limit of the function as the package weighs 5 pounds does not exist.
::成本函数图如下。 x=5 左侧的限值为 26, x=5 右侧的限值为 28。 由于这两个单方的限值不相等, 包件重量为 5 磅的函数限值不存在 。
Example 5
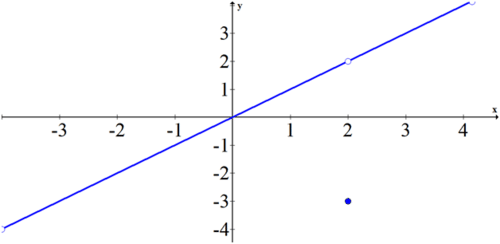
::例5Identify where t he limit exists and where the limit does not exist for the following function:
::确定存在限制的地点和不存在限制的下列职能:Solution:
::解决方案 :The limit does not exist at . The limit exists at every other point on the graph, including .
::限制不存在于 x%3, 3, -1, 2, , 。 该限制存在于图中的其他每个点, 包括 x=1 。Example 6
::例6Evaluate and explain how to find the limits as approaches 0 and 1 in the previous question.
::评估并解释在前一个问题中如何找到x 接近0和1的界限。Solution:
::解决方案 :Both of these limits exist because the two one-sided limits at these points are equal. As approaches 0 from the left and from the right, the function value approaches 2. The function value at is also defined at 2. As approaches 1 from the left and from the right, the function value approaches 1. Even though the function value is defined elsewhere for , the limit value is still 1.
::这两个限制都存在,因为这两个点的两个单向限制是相等的。作为左侧和右侧的xoproaches 0,函数值方针2。x=0的函数值也定义为 2. x=0的函数值也定义为 2. 作为左侧和右侧的x oice 1,函数值方针1。即使 x=1的函数值在别处被定义,但极限值仍然是 1 。
::limx% 0f( x) = 2 和 limx% 1f( x) = 1Example 7
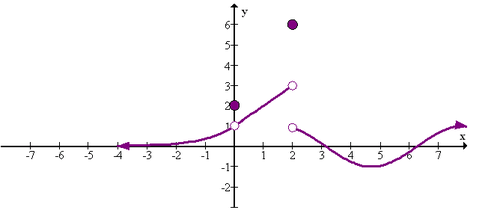
::例7Evaluate the limits of the following piecewise function at -2, 0, and 1:
::以 -2, 0 和 1 来评价以下片段函数的极限值: 2- 2, 0 和 1 :
:xx) 2x% 2x% 2- 1x% 2- 2- 2- 2 < x=0x20 < x=1-2x=1x21 <x
Solution:
::解决方案 :
::limx% 2 - f( x) = 2limx @ 2+f( x) = 0limx% 2f( x) = DNE
::limx_0- f( x) =2limx_0+f( x) = 0limx_0f( x) = DNE
::limx% 1f( x)=1Summary
::摘要-
The limit of as approaches from the left side is denoted .
::左侧 x 接近 a 的 f(x) 限制值为limxa- f(x) = L1 。
::左侧 x 接近 a 的 f(x) 限制值为limxa- f(x) = L1 。 -
The limit of as approaches from the right side is denoted .
::右侧 x 接近 a 的 f(x) 限制值表示 limxa+f(x) = L2 。
::右侧 x 接近 a 的 f(x) 限制值表示 limxa+f(x) = L2 。 -
The limit only exists when the left and right one-sided limits
are equal
.
::只有在左和右的单向限制相等时才存在限制。 limxa- f( x) =limxa+f( x) =limxaf( x) =L -
If the left and right one-sided limits are not equal, then the limit does not exist, or DNE.
::如果左侧和右侧的界限不相等,则该界限不存在,或 DNE。
Review
::回顾Use the graph of below to evaluate the expressions in 1-6.
::使用下面f(x)的图形来评价 1-6 中的表达式。1.
::1. limxf(x)2.
::2. limxf(x)3.
::3. limx%2f(x)4.
::4. limx%0f(x)5.
::5.f(0)6.
::6.f(2) 6 f(2)Use the graph of below to evaluate the expressions in 7-13.
::使用下方 g(x) 的图形来评价 7- 13 中的表达式 。7.
::7. limxg(x)8.
::8. limxg(x)9.
::9. limx%2g(x)10.
::10. limx0g(x)11.
::11. 立方4g(x)12.
::12. g(0)13.
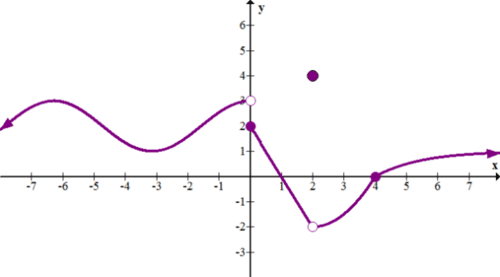
::13.g(2)14. Sketch a function such that but .
::14. 将函数 h(x) 折叠成 h(2)=4, 但 limx%2h(x) = DNE 。15. Sketch a function such that but .
::15. 绘制函数j(x),使 j(2) = 4, 但 limx%2j(x) = 3。Review (Answers )
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -