4.10 通过保理公司解决-interactive
章节大纲
-
The Purpose of this Lesson
::本课程的目的In this lesson, you will model scenarios with quadratic functions in standard form. You'll learn to convert quadratic functions with linear and constant terms to factored form and determine characteristics of the functions from this form.
::在此课中, 您将以标准格式模拟二次函数的情景。 您将学会将二次函数转换成线性、 恒定的线性函数, 以元素化的形式, 并确定此格式函数的特性 。
Activity 1: Finding the Equation for Velocity from Standard Form
::活动1:从标准表格中寻找速度等同Previously, you created models for objects subject to a constant acceleration, an initial velocity, and an initial position. The general function for the distance of such an object as a function of time is:
::以前,您为受恒定加速度、初始速度和初始位置影响的物体创建了模型。作为时间函数,该对象距离的一般函数是:
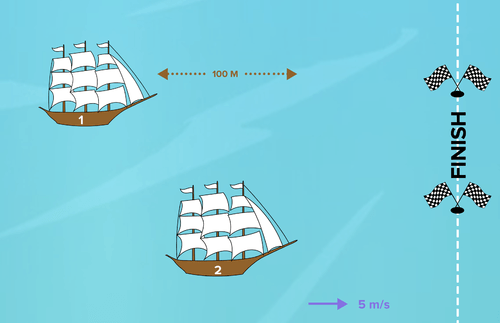
::d(x) = 12ax2+v0x+d0Two boats are racing down a river. Create a function that models the distance of each as a function of time. Example 1-1
::例1-1Two boats are racing down a river. The river is flowing at 5 meters per second. Both boats are accelerating at 8 meters per second per second. One gets a head start of 100 meters. Create a function that models the distance of each as a function of time. Do both quadratics have a linear term ? Do both have a constant term? Given the rate of acceleration of each, and the underlying velocity of the river, create equations for the velocity of each as a function of time. Explain their components. Use the equation for velocity to determine how fast they are each going at 10 seconds. Does the second boat ever pass the first? Why or why not?
::两艘船在沿河奔跑。 河流每秒5米。 两艘船都在加速速度, 每秒8米。 每艘船头的起点是100米。 每艘船头的起点是100米。 创建一个函数, 以时间的函数来模拟每艘船的距离。 两种四方形都有线性条件吗? 两者是否都有一个不变条件? 考虑到每艘船的加速速度和河底速度, 以时间的函数来为每个船只的速度创建方程式。 解释它们的组成部分。 使用速度方程式来决定它们每艘的速度是10秒。 第二艘船是否经过第一艘船? 为什么? 为什么没有?Solution: The equations for the distance each boat has traveled as a function of time are shown below. They both have linear terms, and the second has a constant term:
::解答: 每艘船舶因时间函数而行驶的距离的方程式如下所示。它们都有线性条件,而第二条则有一个常数条件:
::f(x)=4x2+5xg(x)=4x2+5x+100If each boat is accelerating at 8 meters per second, per second, its velocity at seconds is meters per second.
::如果每艘船加速速度为每秒8米,每秒8米,其x秒速度为每秒8x米。Each boat also gets the added velocity of the river, 5 meters per second.
::每艘船也得到增加的河速,每秒5米。The head start of the second boat does not influence its velocity.
::第二艘船的船头起首并不影响其速度。The function for the velocity of each boat is:
::每艘船速度的函数为:
::v(x)=8x+5At 10 seconds, each boat is traveling meters per second.
::10秒时,每艘船舶每秒行驶5-10=8-10+5=85米。Both boats have the same velocity at any given time. This means the second boat will never pass the first.
::这两艘船在任何特定时间的速度都一样,这意味着第二艘船不会通过第一艘船。The Acceleration Model
::加速加速模式If an object is subject to constant acceleration, an initial velocity, and an initial position , the equation in standard form for the object's position as a function of time is:
::如果一个对象受到恒定加速度、初始速度和初始位置的制约,该对象位置按时间函数的标准方程式的方程式为:d(x)=12ax2+v0x+d0。The equation for the velocity of the object at a given time is
::特定时间天体速度的方程式是 v(x) = ax+V0 。Example 1-2
::例1-2In the last example, there was an advantage to working with these quadratics in standard form . Given the following quadratic model for the distance of an object as a function of time, find the corresponding rates of acceleration and the initial velocity. Then write the equation for the velocity of the object as a function of time. Explain how the equation for velocity is derived from the quadratic equation for distance. What type of function is the equation for the velocity?
::在最后一个例子中,用标准形式处理这些二次方程有一个优势。根据以下关于物体距离的二次方程模型作为时间函数,可以找到相应的加速率和初始速度。然后将对象速度的方程写成时间函数。解释速度的方程是如何从距离的二次方程中衍生出来的。速度的方程是哪种函数?
::a.y= 3x2+7xb.y= 3x2+7xb.y= 6x2+4xc.y= 5x2+8x-12d.y= 12x2+x50Solution: The general equation for the position of an accelerating object as a function of time is:
::解决办法:加速物体按时间函数位置的一般方程式是:
::d(x) = 12ax2+v0x+d0Notice that the Because of this, the coefficient of the leading term is always half the rate of acceleration. If the rate of acceleration is 10, then the coefficient is 5. The reverse is also true. If the coefficient is 5, then the rate of acceleration is 10. The initial velocity is the coefficient of the linear term, and the constant term isn't relevant when finding the equation for velocity.
::注意x2 值乘以 12a。 因此, 前一术语的系数总是加速率的一半。 如果加速率是 10, 那么系数是 5 。 如果系数是 5, 则加速率是 10 。 初始速度是 线性术语的系数, 而当找到速度方程式时, 常数则无关紧要 。The equations for velocity as a function of time for each of the quadratic functions above is shown below. These functions give you the rate of change of the original function at any given time. The original functions were quadratic, these functions are linear.
::速度方程式是上述每个二次函数的时间函数。这些函数为您提供了任何特定时间的原始函数变化率。最初的函数是二次函数,这些函数是线性函数。
::a.v(x)=6x+7b.v(x)=6x+7b.v(x)=12x+4c.v(x)=10x+8d.v(x)=x+1Standard Form for a Quadratic Function
::二次曲线函数的标准格式Standard form for a quadratic function is:
::二次函数的标准窗体为: y=ax2+bx+c。The function for the rate of change of the original quadratic at a given time is
::函数是 v(x)=2ax+c。Interactive
::交互式互动Use the following interactive to change the parameters for a boat accelerating on a river with a head start. Summarize the relationship between the quadratic and the equation for the rate of change, that is, the velocity, at any given time. Units for distance are meters and units for time are seconds.
::使用以下交互效果来改变在一条河上加速的、头起动的船舶的参数。 总结二次和变化速度的方程之间的关系, 即速度, 在任何特定时间。 距离单位是米, 时间单位是秒。Work it Out
::工作出来For each of the following quadratics, determine the equation for the rate of change. Determine the rate of change at
::对于以下方形中的每一方形,确定变化率的方程。确定 x=3 的变动率。
::yy=4x2+6xb.y=3x2-2-2xc.y=15x2+4x-17d.y=34x2+12x-55
Activity 2: Using the Area Model to Distribute a Binomial to a Binomial
::活动2:使用区域模型将二子体分配成二子体The above examples and problems showed the advantages of standard form. Sometimes a quadratic can be given in factored form:
::上述例子和问题显示了标准形式的优点。
::参数格式 = 3x( 4x+5) 蛋白质乘以二进制。 y = (x-2)( x+3) 二进制乘以二进制。 y = 10( 3x+4)( - 2x+6) a 常数乘以二进制乘以二进制。Example 2-1
::例2-1Each of the quadratics above can be converted from factored form to standard form, using the area model you used earlier. Convert each of the above to quadratics in standard form.
::以上每个二次方形都可以使用先前使用的面积模型,从因数式形式转换为标准形式。以上每个二次方形都可以以标准形式转换为二次方形。Solution:
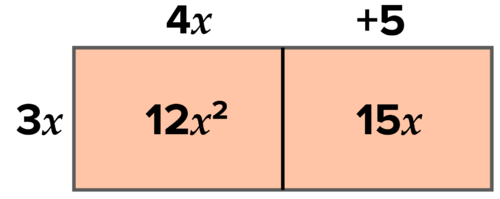
::解析度: 3x( 4x+5) = 12x2+15xUsing an area model to help organize the multiplication :
::使用区域模型帮助组织乘法 :Use an area model to organize the multiplication
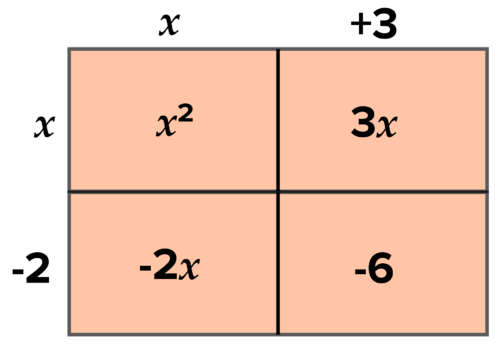
::使用区域模型来组织乘法
:x-2(x+3)=x2+x-6)
Use an area model to organize the multiplication
::使用区域模型来组织乘法
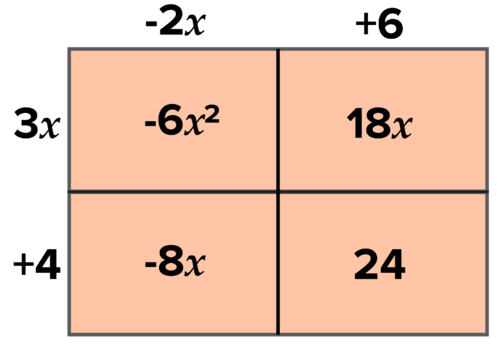
::最后的二次方块,首先乘以两个二元体, 然后分配 10 :
::10( - 6x2+10x+24) __60x2+100x+240Use an area model to organize the multiplication
::使用区域模型来组织乘法You might recall that i n the lesson on Distribution and Factoring , the quadratic term was in the bottom-left of the area model. W hen multiplying binomials using area models , the result does not depend on the order of the terms in the binomial . However, it is customary in math to write the highest term in the top-left.
::您可能记得,在分配和保理课中, 二次词位于区域模型的左下角。 当使用区域模型乘以二进制时, 其结果并不取决于二进制词的顺序。 然而, 在数学中, 通常会写上一个左侧最高词 。Work it Out
::工作出来-
David and Toni are making squares in the sand.
David
makes his square with a side length of
units, Toni makes her square with a side length of
units. How much greater is the area of Toni's square than
David's
? Write your answer as a function of
Determine how much greater the area of Toni's square is than
David's
when David's has a side length of 6 meters.
::大卫和托尼在沙地上建方形。 大卫用侧长的x单位建方形, 托尼用侧长的x+1单位建方形。 托尼的方形面积比大卫的方形大多少? 写下答案作为x的函数。 确定当大卫的侧长为6米时, 托尼的方形面积比大卫的方形大多少。 -
Determine the
difference
between each pair of quadratics below as a function of
by subtracting the second from the first.
::通过从第一组中减去第二组,确定下方每组四方形之间的差数,以乘以 x 的函数。
::ay= (x+3)(x- 4)y= (x+2)(x+7) b.y= 3x(x- 7)y= (2x- 3)(x+4) c.y= 2(x-2)(x- 1)y= 6(x+2)(4x+1) d.y= 5x2+4xy=4x2e.y=3x(x+1)y=x2f.y=(x+3)(x- 3)y=(x+3)2-
Gloria and Veronica are both farmers, and their farms are growing. Their farms are rectangles whose
dimensions
are in kilometers. Gloria's farm has dimensions 2 by 1, and Veronica's farm has dimensions 3 by 4. The dimensions increase by 1 kilometer every year. Write equations for the area of each farm as a function of the year. Convert them to standard form. Write an equation for the rate of growth, that is, the rate of change, for the area of each farm as a function of time. Determine how fast each farm is growing at the 10-year mark. Determine the area of each farm at this time.
::格洛丽亚和维罗妮卡都是农民,他们的农场正在成长。他们的农场是方形,面积在几公里之内。格洛丽亚的农场有2乘1, 维罗妮卡的农场有3乘4, 维罗妮卡的农场有3乘4, 维罗妮卡的农场每年增加1公里。 将每个农场面积的方程式作为一年的函数写成方程式。 将其转换为标准格式。 将每个农场的增长率, 即变化率, 写一个方程式, 将每个农场的增长率作为时间函数。 确定每个农场在10年的生长速度。 确定每个农场在这个时候的面积 。 -
The path of a baseball from the origin is described by the function
and
represent the horizontal and
vertical
distance in meters from the origin.
Factor
the quadratic to find the
zeroes
. Find the line of
and the
vertex
. Interpret the meaning of each in the context of the scenario.
::函数 y 12x2-20x. x 和 y 描述棒球起源的路径。 函数 y 12x2 - 20x. x 和 y 代表从起源起的公米的水平和垂直距离。 乘四边形以找到零。 查找线条和顶点。 在假设情景中解释每个词的含义 。
The previous examples and problems showed you how standard form can be used to find the equation for the rate of change of a quadratic and to compare two quadratic functions. The factored form also communicates vital information about a quadratic function.
::先前的例子和问题向您展示了如何使用标准格式来寻找二次方程变化速度的方程式,并比较两个二次方程函数。因子形式还传递关于二次函数的重要信息。Advantages of Standard and Factored Form for a Quadratic
::二次曲线的标准和计数表格的优点Standard Form:
::标准表格:-
Enables comparison of two quadratics.
::能够比较两个二次方位 。 -
The equation for the rate of change of the function at a given time can be found.
::可找到特定时间函数变化率的方程式 。
Factored Form
::计数表-
Enables location of zeroes, the line of symmetry, and vertex.
::启用零的位置、对称线和顶点。 -
Enables solving
some
equations involving quadratics.
::能够解决一些涉及二次方程的方程。
Activity 3: Factoring Quadratics
::活动3:保理四方Example 3-1
::例3-1In the prior problem, you factored a quadratic with a linear term and no constant term. Use the area model to factor the following quadratic and find the zeroes.
::在前一个问题中,您用线性术语和无常值术语来计算二次方位值。使用区域模型来计算以下二次方位值并找到零。
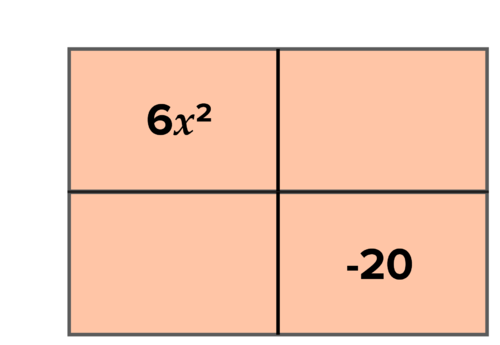
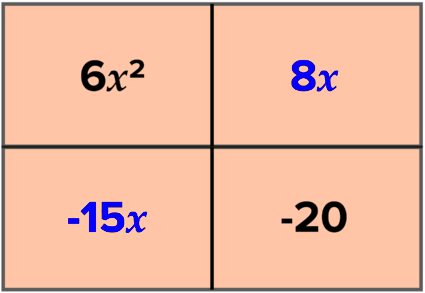
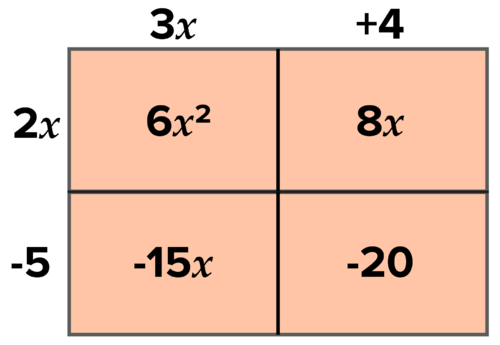
::y= 6x2 - 7x - 20Solution: To factor a trinomial to the product two binomials, draw a 2 by 2 area model . As we saw in the previous activity , multiplying binomials resulted in the quadratic term in the top-left and the constant term in the bottom-right.
::解决方案 : 要将产品两个二进制三进制乘以两个二进制, 请绘制一个 2 乘以 2 区域模型 。 正如我们在先前的活动中看到的那样, 乘以二进制导致左上方的四进制词和底端的常态词 。Start by filling in the quadratic term and constant. We know that the sum of the other two boxes must equal the linear term. Additionally, the product of the diagonals in the area model are always equal. Set up an X problem to find the two terms that add to the linear term, and multiply to the product of the quadratic and constant term,
::我们知道其他两个框的总和必须等于线性术语。 此外,区域模型中的对角学产物总是相等的。 设置一个 X 问题, 以找到线性术语中增加的- 7x 和乘以二次和恒定术语的产物( 6x2)( -20) 的两个词 。What two terms multiply to the top and add to the bottom? After c hecking some factor pairs of -120, we find that -15 and 8 multiply to -120 and add to -7, so the other two boxes of the area model are and
::在检查了1-120的几组因子之后,我们发现 -15和8乘以 -120,加到 -7,所以区域模型的其他两箱是-15x和8x。Next find the sides of the area model by factoring out the greatest common factor of each row and column :
::接下来通过将每一行和列的最大共同系数乘以下列因素,找到区域模型的两边:Factor out the greatest common factor to find the sides of the area model. Factored form of the quadratic is
::梯度的乘数形式为 Y=( 2x-5)( 3x+4)。To find the zeroes, set the equation equal to zero:The zero product property tells us that if the product of two factors equals 0, one of the factors must be 0. This allows us to write and solve two equations to determine when each factor equals 0:The zeroes ofExample 3-2
::例3-2FactorSolution: Another method to factor quadratics is guess and check . You know that the sides of the area model will be factors of the quadratic and constant terms of the quadratic. Systematically experiment with factors of both:
::解答: 另一种因子二次方位法是猜测和检查。 您知道, 区域模型的侧面是二次方位法和二次方位法的常数参数。 系统实验两种因素 :
::3x(x) 3x3x和x是3x2(3x-5)(x+2)-5和2是-10.3x2+6x-5x-10-10的因数。Note that the first two steps require experimentation, and the process will require testing and experimentation with factors that do not work. This method should only be used when there are few possible factors of the quadratic and constant terms.
::请注意,前两个步骤需要实验,而这一过程需要试验和试验无效的因素。 只有在二次和不变条件的可能因素很少的情况下,才应使用这种方法。Converting Quadratics from One Form to Another
::将四方形从一个表格转换为另一个表格To convert a quadratic from factored form to standard form, here are two options:
::要将二次曲线从因数表态转换为标准表态,这里有两个选项:-
Use the area model to distribute one binomial or
monomial
to the other.
::使用区域模型将一个二元或单元分布到另一个。 -
Multiply each term in the first binomial times each in the second.
::在第一个二进制乘以每个学期,在第二个学期乘以每个学期。
To convert a quadratic from standard form to factored form, here are two options:
::要将二次曲线从标准窗体转换为因子窗体,这里有两个选项:-
Use the area model and
X
problem
::使用区域模型和 X 问题 -
Guess and check with factors of the first and third term without drawing the rectangle.
::猜测和检查第一和第二学期的因素,而不绘制矩形。
Work it Out
::工作出来-
Factor each of the following and find the zeroes.
::以下列各点的乘数计算并找到零。
-
Julio is a geologist working in a tropical forest in Brazil. His radar equipment shows that there is an ancient crater that's been filled in over time, hidden under the forest. He is standing at the origin. His experiments show that the crater is curved in the shape of a
parabola
. The quadratic function for this curve is:
::Julio是一位在巴西热带森林工作的地质学家。 他的雷达设备显示有一个古老的火山坑, 已经填满了一段时间, 隐藏在森林下。 他站在原地。 他的实验显示火山坑的形状是抛物线。 这个曲线的二次函数是:
::y=0.01( x2 - 20x - 2400)Julio would like to investigate the edges of the crater on foot, but this form of the quadratic function does not show the zeroes. Factor to find the zeroes so that Julio can find the edges of the crater. Find the maximum depth of the crater, and determine where Julio should drill if he wants to drill to the crater's lowest point.
::Julio想调查弹坑的边缘,但这种四方形函数没有显示零。找到零的因子是为了让Julio找到弹坑的边缘。找到弹坑的最大深度,并确定Julio如果想钻到弹坑的最低点,应该在哪里钻井。-
Nuria launches a baseball from a height of 28 meters. Its initial velocity is 31 meters per second, and it's subject to acceleration due to gravity, that's -10 meters per second per second. Write an equation for the height of the baseball as a function of time. Use factoring to determine when the object hits the ground. Use the two zeroes to find the line of symmetry. Find the highest point the baseball reaches. Find the equation for the velocity of the baseball as a function of time. Determine the velocity of the baseball when it hits the ground. Determine the velocity of the baseball when it reaches its highest point.
::Nuria 从28米高度发射棒球。 最初的速度是31米/ 秒, 并会因重力而加速, 也就是每秒10米/ 秒。 写一个棒球高度的方程式作为时间函数。 使用乘数来确定物体何时撞击地面。 使用两个零来找到对称线 。 找到棒球到达的最高点 。 找到棒球到达的最高点 。 找到棒球速度的方程式作为时间函数 。 确定棒球到达地面的速度 。 确定棒球到达最高点时的速度 。 -
Re-arrange each of the equations so that one side is 0. Then
factor to solve
.
::重新排列每个方程, 使一面为 0。 然后解答因素 。
::ax2+5x6x6b.x2x6x7c.6x2-20#5xd.x2-6x-10x10xxx2-x+2e.3x2-11x2x2x2x2+10x4f.x2=9Summary
::摘要-
Standard form for a quadratic reveals certain characteristics of the quadratic and enables comparisons between quadratics.
::二次方位标准表显示二次方位的某些特点,可以对二次方位进行比较。 -
Factored form for a quadratic reveals the zeroes and gives you a method for solving certain equations involving quadratics.
::二次方块的因子表显示零, 并给了你一种方法, 解决某些涉及二次方块的方程式。 -
Two methods for factoring a quadratic are (1) using the area model and X problem and (2) guess and check.
::计算二次曲线的两种方法是1)使用区域模型和X问题;(2)猜测和检查。
-
David and Toni are making squares in the sand.
David
makes his square with a side length of
units, Toni makes her square with a side length of
units. How much greater is the area of Toni's square than
David's
? Write your answer as a function of
Determine how much greater the area of Toni's square is than
David's
when David's has a side length of 6 meters.