4.11 完成广场-interactive
章节大纲
-
The Purpose of this Lesson
::本课程的目的In this lesson, you will develop a method for converting quadratic functions from standard form to vertex form. You'll use this method to solve equations and to develop a general formula for the zeroes of a quadratic.
::在此课中, 您将开发一种方法, 将二次函数从标准格式转换为顶点格式。 您将使用此方法解析方程式, 并为二次方块的零开发一个通用公式 。
Activity 1: Finding Roots and Solving Equations in Vertex Form
::活动1:找出根和静脉式溶解等式The vertex form for a quadratic function may be useful in many situations.
::二次函数的顶部形态在许多情况下可能有用。Example 1-1
::例1-1Create quadratic functions that model the height of each rocket described below, as a function of time. Describe the graph of each, especially the vertex.
::创建二次函数, 以以下描述的每枚火箭的高度为模型, 作为时间函数。 描述每个火箭的图形, 特别是顶点 。-
Rocket A accelerates upwards at 8 meters per second per second.
::火箭A加速上升,每秒8米。 -
Rocket B has the same acceleration but starts from a height of 10 meters.
::火箭B的加速度相同 但从高度10米开始 -
Rocket C has the same acceleration but starts moving 3 seconds later than the
first
rocket.
::火箭C的加速度相同 但比第一枚火箭晚3秒开始移动 -
Rocket D has the same acceleration, starts from a height of 10 meters, and starts 3 seconds later than the first rocket.
::火箭D的加速度相同,从10米高度开始,比第一枚火箭晚3秒。
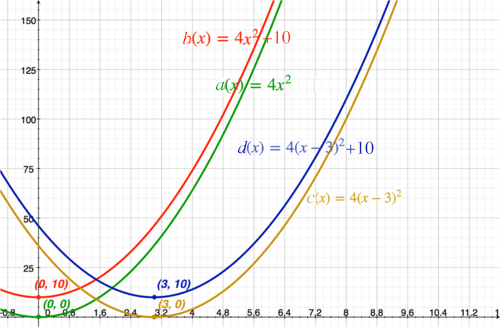
Solution: The function for rocket A is a ( x ) = 4 x 2 . The vertex is (0,0).
::解析度: A号火箭的函数为a(x)=4x2. 顶点为( 0,0) 。The function for rocket B is b ( x ) = 4 x 2 + 10. This represents a vertical shift of A by 10 units. The vertex is (0,10).
::火箭 B 的函数为 b(x)=4x2+10。 表示 A 的垂直转换为 10 个单位。 顶点为 (0, 10) 。The function for rocket C is c ( x ) = 4 ( x − 3 ) 2 . This represents a horizontal shift of A by 3 units to the right. The vertex is (3,0).
::火箭C的函数是 c(x)=4(x-3)2。这意味着 A 向右水平移动 3 个单位。顶点是 (3,0) 。The function for rocket D is d ( x ) = 4 ( x − 3 ) 2 + 10. This represents a translation of A by shifting 10 units up and 3 units to the right. The vertex is (3,10).
::火箭 D 的函数是 d(x)=4(x-3)2+10。 这是 A 的翻译, 将 10 个单位向上移动, 3 个单位向右移动。 顶点是 (3, 10) 。Four rockets - Position over time Example 1-2
::例1-2Consider the last rocket above. When does this rocket achieve a height of 100 meters? Find the answer using graphing technology. Then w rite and solve an equation to determine the answer.
::考虑上方最后一枚火箭。 这枚火箭何时达到100米的高度? 使用图形化技术找到答案。 然后写入并解析一个方程式来确定答案 。Solution: In the last lesson, you converted quadratic equations from standard form to factored form to solve them. Factoring is an effective method for finding rational zeroes , also known as rational roots . But not every quadratic can be factored, because not every solution to a quadratic equation is rational. Vertex form can help us here. When a quadratic is in vertex form, inverse operations and the properties of equality lead you to one or two rational solutions, two irrational solutions, or no solution.
::解答 : 在最后一课中, 您将二次方程从标准形式转换为因素化形式来解答它们。 乘法是找到理性零的有效方法, 也称为理性根。 但并不是每个二次方程都可以被计算在内, 因为对于二次方程, 并不是每个解决方案都是理性的。 灭蚁灵形式可以帮助我们在这里。 当二次方程为顶点形式、 逆向操作和平等特性时, 您可以找到一两个合理的解决方案, 两个不合理解决方案, 或者没有解决方案 。Equation Explanation 4 ( x − 3 ) 2 + 10 = 100 Equation to determine when the rocket reaches 100 meters. 4 ( x − 3 ) 2 = 90 Subtraction. ( x − 3 ) 2 = 45 2 Dividing both sides by 4. x − 3 = ± √ 45 2 The inverse operation of squaring is square rooting. x = 3 ± √ 45 2 Adding 3 to both sides. x = 3 ± 3 √ 5 √ 2 Simplifying. x = 3 ± 3 √ 10 2 Rationalizing the denominator. x ≈ − 1.7 or x ≈ 7.7 Approximations. x ≈ 7.7 seconds Only positive solutions make sense in the scenario.
::平方蒸发4(x-3)2+10=100等分量,以确定火箭何时达到100米4(x-3)2=90减量。 (x-3)2=452将两侧分开4.x-3452Work it Out
::工作出来-
Each of the following equations is built from a quadratic function in vertex form, equal to a
constant
function. Sketch a rough graph of each. Solve each equation and interpret the solution graphically. State if the solution is rational or irrational. Some will have no solution.
::以下方程式中的每一方程式都是从顶部函数的二次函数构建的,等于一个不变函数。 绘制每个方程式的粗图。 解析每个方程式并用图形解释解决方案。 如果解决方案合理或不合理, 请说明国家。 有些方程式没有解决方案 。
a. ( x − 3 ) 2 − 2 = 7 b. ( x + 4 ) 2 − 5 = 4 c. x 2 + 5 = 5 d. x 2 + 5 = − 3 e. ( x − 3 ) 2 = 4 9 f. − 2 ( x − 4 ) 2 + 7 = 10
::a. a. (x-3-3)2 - 2=7b. (x+4)2 - 5=4c.x2+5=5d.x2+5=5d.x2+5=3e.(x-3)2=49f.-2(x-4)2+7=10-
Identify the form for each quadratic. The options are standard form, factored form, and vertex form. Some may be in more than one form at once.
Give
one characteristic of the quadratic that can be easily gathered from the form.
Some
examples of characteristics:
::指定每个二次方形的窗体。 选项是标准形式、 系数形式和顶点形式。 有些可能同时以不止一种形式出现。 给出可以从窗体中轻松收集的二次方形的一个特征。 一些特性示例 :
-
the equation for
rate of change
a
s a function of
x
::x 函数乘以变化率的方程 -
the zeroes
::零位数 -
the
::直线 -
::顶部 -
::Y 界面 -
::x 接近正无穷度时,二次方度是增加还是减少 -
::特定 x 值的函数值 -
::确定根根是否合理, 根是非理性的, 或者没有根
a. y = 4 x 2 − 10 x + 2 b. y = 3 ( x − 8 ) 2 + 7 c. y = ( 2 x − 4 ) ( x − 5 ) d. y = x ( x − 5 ) e. y = 5 x 2 f. y = 5 ( x − 3 ) 2 g. y = 4 ( x − 20 ) ( 5 x + 4 ) h. y = 6 x 2 + 7 i. y = 6 x 2 + 7 x
::ay=4x2-10x-10x+2b.y=3(x-8)2+7c.y=2x-4(x-5)(x-5)(x-5)d.y=x(x-5)e.y=5x2f.y=5(x-3)2g.y=4(x-20)(5x+4)h.y=6x2+7i.y=6x2+7x7x-
Discuss and record the advantages and disadvantages of each form for a quadratic.
::讨论并记录每种二次方形的利弊。
Forms for a Quadratic Function
::二次曲线函数表格式格式Standard: y = a x 2 + b x + c
::标准:y=ax2+bx+c-
Advantages: Good for finding the equation for the rate of change. Good for arithmetic with other
polynomial
functions.
::优点: 有利于找到变化率的方程式。 有利于算术和其他多面函数 。 -
Disadvantages: Zeroes, line of symmetry, and vertex not readily apparent.
::缺点:零,对称线和顶部不明显。
Factored: y = a ( x − p ) ( x − q )
::乘以: y=a( x- p)( x- q)-
Advantages: Good for finding the zeroes. Good for solving quadratic equations.
::优点:有利于找到零。有利于解决二次方程。 -
Disadvantages: Quadratics that don't have rational roots cannot be factored.
::缺点:没有合理根基的四方不能被考虑在内。
Vertex: y = a ( x − h ) 2 + k
::vertex: y=a(x-h)2+k-
Advantages: Vertex immediately visible. Equations featuring this structure can be solved for rational and irrational solutions,
or
no solution. Written as a transformation of
y
=
x
2
.
::优点 : Vertex 立即可见。 以此结构为特点的公式可以解答为合理和不合理的解决方案, 或者没有解决方案 。 以 y=x2 的转换写成 y=x2 。 -
Disadvantages: If the function is given in standard form and the roots are rational, factoring is generally easier than converting to vertex form.
::缺点:如果函数以标准形式给出,而根部是理性的,则乘数一般比转换为顶点形式容易。
-
Factor
each of the following. Two are
perfect squares
. Which two? How do you know?
::两个是完美的方形 哪一个是? 你怎么知道的?
a. y = x 2 b. y = x 2 + 10 x c. y = x 2 + 10 x + 25
::a.y=x2b.y=x2+10xc.y=x2+10x+25
Activity 2: Creating Perfect Squares
::活动2:创造完美的广场Read the advantages of vertex form above. The most substantial of these is the ability to solve for irrational roots. Up to this point, you were frequently given an equation whose solution was irrational, and you were instructed to approximate the solution using graphing or solving technology. Vertex form is a tool you can use to find exact solutions to such equations.
::读取上面顶点形式的优点。 其中最实质性的是解决非理性根根的能力。 到此点, 您经常得到一个不合理的方程式, 其解决方案是非理性的, 并指示您使用图形化或解析技术来接近解决方案。 Vertex 窗体是一个工具, 您可以用来找到这些方程式的精确解决方案 。Frequently you are given quadratics in standard form. You need to learn how to convert from standard to vertex form to gather information about a quadratic, or solve equations.
::通常您会以标准格式获得二次方程。 您需要学习如何从标准形式转换为顶点形式, 以收集关于二次方程或解析方程的信息 。Example 2-1
::例2-1A quadratic in vertex form features a perfect square as part of its structure. Identify the perfect square in the quadratic y = ( x − 3 ) 2 + 5. Expand the perfect square and write the polynomial in standard form.
::顶点形态的二次方形具有一个完美的正方形,作为结构的一部分。在二次方形 y = (x-3)2+5 中指定一个完美的正方形。扩大正方形,以标准格式写入多面形。Solution:
::解决方案 :Equation Explanation y = ( x − 3 ) 2 + 5 Vertex form. ( x − 3 ) 2 This is the perfect square. ( x − 3 ) ( x − 3 ) Definition of squaring. x 2 − 6 x + 9 Expanding. y = x 2 − 6 x + 9 + 5 Replacing the perfect square in vertex form. y = x 2 − 6 x + 14 Simplifying.
::EquationExplationy=(x-33)2+5Vertex形态。 (x-3)2 这是完美的正方形 。 (x-3) (x-3) (x-3) (x-3) 定义 方圆.x2-6x+9 Expanding.y=x2-6x+9+5) 将正方形替换为 y=x2-6x+14 简化 。In the last example , you saw that every quadratic in vertex form features a perfect square as part of its structure. Given a quadratic in standard form, the first step to converting it to vertex form is finding this perfect square.
::在最后一个例子中,你看到每个顶端形态的二次体都有一个完美的正方形作为其结构的一部分。鉴于标准形态的二次体,将其转换为顶端形态的第一步就是找到这个完美的正方形。Example 2-2
::例2-2The following quadratic is not a perfect square. It features a linear term but no constant term. What constant term is required to make this quadratic a perfect square? Add this constant term to both sides of the equation. Factor the right side, then isolate y . What do you observe?
::下面的二次曲线不是一个完美的正方形。 它包含一个线性术语, 但没有常态术语 。 要将二次曲线变成一个完美的正方形, 需要哪个常态术语? 在方程的两侧添加这个常态术语 。 乘以右侧, 然后孤立 y 。 您观察了什么 ?y = x 2 + 12 x
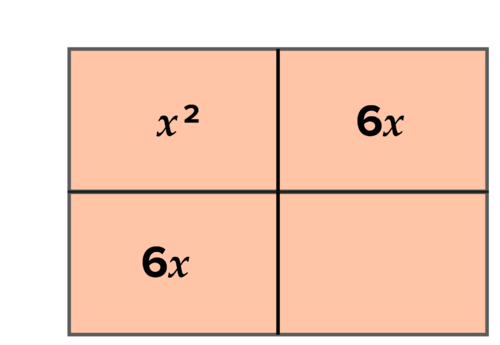
::y=x2+12x y=x2+12xSolution: The area model is useful here. You know the contents of the top-left region, that's x 2 . In order for the entire rectangle to be a perfect square, the two regions for the linear term must have the same area. So each must be 6 x :
::解决方案 : 区域模型在此有用 。 您知道左上角区域的内容, 即 x2 。 要让整个矩形成为完美的正方形, 线性词的两个区域必须拥有相同的区域 。 所以每个区域必须是 6x :Use an area model to assist with factoring
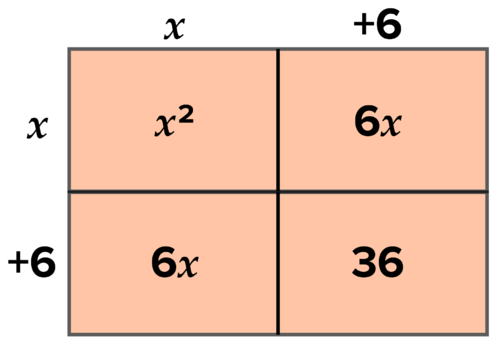
::使用区域模型协助保理业务Can you see the dimensions now? Can you find the value of the unknown region, the constant term? Here's the solution:
::您现在能看到维度吗? 您能找到未知区域的价值吗? 恒定值? 以下是解决方案:Use an area model to help organize factoring
::使用区域模型帮助组织计数Now, write that algebraically, in the context of the given function:
::在给定函数的上下文中写此代数 :Equation Explanation y = x 2 + 12 x Given quadratic. y = x 2 + 6 x + 6 x Divide the linear term equally into its two regions. y + 36 = x 2 + 6 x + 6 x + 36 Add the constant term to both sides. y + 36 = ( x + 6 ) 2 Factor. y = ( x + 6 ) 2 − 36 Isolate x .
::赤道Explationy=x2+12xFelenden quadritic.y=x2+6x6+6xDivide 线性术语平等进入其两个区域。y+36=x2+6x+6x+36Add 双侧的常数术语为y+36=(x+6)2Factor.y=(x+6)2-36Isoltate x。Work it Out
::工作出来-
Identify the perfect square in each of the following. Expand the perfect square and write the polynomial in standard form.
::在以下各处指定完美的正方形。 展开完美的正方形, 并以标准格式写入多面形 。
a. y = ( x + 4 ) 2 − 7 b. y = ( x + 2 ) 2 c. y = − 5 x 2 − 10 d. y = − 2 ( x + 1 2 ) 2 + 3 4
::ay=(x+4)2-7b.y=(x+2)2c.y=5x2-10d.y=2(x+12)2+34-
The method of transforming a quadratic from standard form to vertex form is called
. Complete the square to convert each of the following from standard form to vertex form. If there is already a constant term present, subtract it from both sides so the right side is quadratic with only a linear term.
::将二次曲线从标准窗体转换为顶点窗体的方法被称为 。 完成方形, 将以下各位从标准窗体转换为顶点窗体。 如果已有一个常数, 请从两边减去它, 右侧是二次曲线, 只有线性词 。
a. y = x 2 + 2 x b. y = x 2 − 2 x c. y = x 2 − 22 x + 14 d. y = x 2 + 5 x e. y = x 2 − x f. y = x 2 + b x
::a.y=x2+2xb.y=x2-2xxxc.y=x2-22x+14d.y=x2+5xe.y=x2-xf.y=x2+bxCompleting the Square
::完成广场Given a quadratic of the form: y = x 2 + b x :
::给定窗体的二次方: y=x2+bx:-
Divide the linear term into two equal
terms
. The
coefficient
of each
term
will be
b
2
.
::线性术语除以两个等值术语。 每个任期的系数为 b2 。 -
Add
(
b
2
)
2
to both sides of the equation. This will create a perfect square on the right.
::将(b2) 2 添加到等式的两侧。 这将在右侧创造一个完美的平方 。 -
Factor the right, then isolate
y
.
::以右键乘数,然后隔断 y。
PLIX Interactive
::PLIX 交互式互动
Activity 3: Completing the Square When the Leading Coefficient Isn't 1
::活动3:当领导系数不是1时完成广场Look at all the problems you completed in number 6. What was the leading coefficient in all cases? How do we convert a quadratic from standard form to vertex form when the leading coefficient isn't 1? The example below shows you.
::看看你们在6号中完成的所有问题,在所有情况中,主要系数是什么?当主要系数不是1时,我们如何将二次曲线从标准形式转换为顶点形式?下面的例子向你们展示。Example 3-1
::例3-1Pay close attention to the third line, and the explanation for it.
::密切注意第三行及其解释。Equation Explanation y = 3 x 2 + 30 x − 1 Given quadratic in standard form. y + 1 = 3 ( x 2 + 10 x ) Factoring out the leading coefficient. y + 1 + 75 = 3 ( x 2 + 10 x + 25 ) Completing the square in the parenthesis. Adding 25, which is multiplied by 3, is adding 75. This can be confirmed by distributing the the 3 again. y + 76 = 3 ( x + 5 ) 2 Simplifying on the left, factoring on the right. y = 3 ( x + 5 ) 2 − 76 Isolating y .
::公式Explationy = 3x2+30x- 1Felenden 二次方位数, 以标准格式表示 y+1= 3 (x2+10x) 。 显示主系数 y+1+75= 3 (x2+10x+25) 完成括号中的方位数 。 添加 25, 乘以 3 。 添加 25, 乘以 3 将 75 。 这可以通过在左侧再分配 3 .y+76 = 3 (x+5) 3 来确认 简化, 以 右 y= 3 (x+5) 2 - 76 孤立 y 来确认 。Completing the square can also be used to solve equations directly.
::完成方形也可以用于直接解析方程式 。Example 3-2
::例3-2Equation Explanation 0 = 4 x 2 + 32 x − 1 Given equation in standard form. 1 = 4 x 2 + 32 x The right side is now quadratic with a linear, but no constant, term. 1 4 = x 2 + 8 x Dividing both sides by 4 to make the leading coefficient 1. 1 4 + 16 = x 2 + 8 x + 16 Completing the square. 65 4 = ( x + 4 ) 2 Simplifying on the left and factoring on the right. x + 4 = ± √ 65 4 Square rooting. x = − 4 ± √ 65 2 Isolating x and simplifying.
::平方Explation0=4x2+32x-1Inspenden 方程式,标准格式为1=4x2+32x 右侧现在是四方形,具有线性,但没有恒定的线性。 14=x2+8x 双侧除以 4 使主要系数 1. 14+16=x2+8x+16 完成正方形654=(x+4)2 左侧简化和右侧的保理。x+4654Square根化.x4652Isoltization x和简化。Work it Out
::工作出来-
Complete the square to convert each of the following from standard form to vertex form:
::完成正方形, 将以下各位从标准表单转换为顶点表单 :
a. y = x 2 − 9 x + 2 b. y = 2 x 2 − 4 x c. y = 3 x 2 + 12 x − 5 d. y = − 2 x 2 + 20 x − 6 e. y = 2 x 2 + x f. y = 3 x 2 − x
::ay=x2-9x+2b.y=2x2-4xc.y=3x2+12x-5d.y=2x2+20x-6e.y=2x2+xf.y=3x2-x-
Complete the square to solve each of the following equations. State if the solutions are rational or irrational, or if there is no solution.
::填写正方形以解答以下方程式中的每一个方程式。 如果解决方案是合理或不合理的, 或者没有解决方案, 请声明 。
a. 0 = x 2 − 14 x b. 0 = x 2 − 8 x + 5 c. 7 = 2 x 2 − 10 x − 1 d. 10 = 2 x 2 − 5 x − 2 e. 3 x + 4 = x 2 − 7 x + 1 f. x 2 + x + 5 = 0
::a.0=x2-14xb.0=x2-8x+5c.7=2x2-8x+5c.7=2x2-10x-1d.10=2x2-5x-5x-2e.3x+4=x2-7x+1f.x2+5=0
Activity 4 : Completing the Square to Create General Formulas
::活动4:完成广场以创建通用公式The Quadratic Formula
::二次曲线公式The process you've practiced above can be applied to a quadratic of the general form y = a x 2 + b x + c . The zeroes will be in terms of the coefficients a , b , and c .
::以上练习的过程可以应用到 y= ax2+bx+c 的一般形态的二次方位。 零将用系数a、b和c表示。Equation Explanation 0 = a x 2 + b x + c Given equation. − c = a x 2 + b x The right side is quadratic with a linear, but no constant, term. − c a = x 2 + b a x Dividing both sides by a so the leading coefficient is 1. − c a + ( b 2 a ) 2 = x 2 + b a x + ( b 2 a ) 2 Completing the square. Half the coefficient of the linear term is b 2 a . To complete the square we add ( b 2 a ) 2 to both sides. − c a + b 2 4 a 2 = x 2 + b a x + ( b 2 a ) 2 Simplifying on the left. − 4 a c 4 a 2 + b 2 4 a 2 = x 2 + b a x + ( b 2 a ) 2 Getting common denominator on the left. b 2 − 4 a c 4 a 2 = x 2 + b a x + ( b 2 a ) 2 Adding fractions on the left. b 2 − 4 a c 4 a 2 = ( x + b 2 a ) 2 Factoring on the right. x + b 2 a = ± √ b 2 − 4 a c 4 a 2 Square rooting. x + b 2 a = ± √ b 2 − 4 a c 2 a Simplifying. x = − b 2 a ± √ b 2 − 4 a c 2 a Isolating x . x = − b ± √ b 2 − 4 a c 2 a Adding fractions on the right.
::赤道Exparation0=x2+bx++xx+cFelenden 方程式。 - c=x2+bxxx2+baxDiv 右侧均以最大系数为 1. -ca+( b2a) 2=x2+bax+2+bax+( b2a) 2 , 方形完成。 线性术语的系数是 b2a 。 要完成正方字, 我们向两边添加了 (b2a) 2。 要想完成正方字, 我们向两边都添加了 (b2a) 2。 ca+b242=xxxx(b2a) 2+b24a2+b2xxxxx+(b2a2a) 2在左方位取得共同分母。 b-2- 4a2=xx2+bax2+bx2x+bx2x2xxxxx。 在左方2b2x2-a2xa2xa2x2xa=2x a a a a a b_a_ab2_ab_ab2x2xa a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a bb2 a bb2 a a a a a a a a a a a b b b b___b2 a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a b b b b b a a a a b a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a b b b a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b b a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a aThe Quadratic Formula
::二次曲线公式Given a quadratic equation of the form a x 2 + b x + c = 0 , the solutions, if they exist, are given by the formula:
::根据x2+bx+c=0形式的四方形方程式,如果存在解决方案,则由公式给出:x = − b ± √ b 2 − 4 a c 2 a
::xbb2 - 4ac2aThe Formula for the Line of Symmetry
::对称线的公式The same process used to derive the quadratic formula results in a general formula for converting a quadratic function y = a x 2 + b x + c from standard to vertex form:
::用于得出二次公式结果的相同进程, 即用于将 y= ax2+bx+c 函数从标准形式转换为顶点形式的一般公式 :y = ( x + b 2 a ) 2 − b 2 − 4 a c 4 a 2
::y= (x+b2a) 2-b2 - 4ac4a2This formula is not typically memorized, but it does contain a useful feature. The line of symmetry is x = − b 2 a .
::此公式通常不会被记住, 但含有一个有用的特性 。 对称线是 xb2a 。The Formula for the Line of Symmetry for a Quadratic in Standard Form
::标准格式的二次曲线对称线公式Given a quadratic function of the form y = a x 2 + b x + c , the line of symmetry is given by:
::y=ax2+bx+c 窗体的二次函数为y=ax2+bx+c,对称线由 :x = − b 2 a
::xb2a xb2aWork it Out
::工作出来-
Use the quadratic formula to solve each of the following quadratic equations. For some equations, there will be no solution or one solution. Identify the conditions under which there is no solution. What component of the formula determines this, and what values must this component return for there to be no solution? Identify the conditions under which there is one solution. What component of the formula determines this, and what values must this component return for there to be one solution? This component of the equation is called the
discriminant
.
::使用二次方程来解决以下二次方程中的每一种。 对于某些方程, 将没有解决方案或一种解决方案。 确定无法解决方案的条件。 公式的哪个组成部分决定了这一点, 以及该组成部分必须返回什么值才能没有解决方案? 确定存在一个解决方案的条件。 公式的哪个组成部分决定了这一点, 以及该组成部分必须返回什么值才能找到一个解决方案 。 此方程的这个组成部分被称为“ 分歧 ” 。
a. 0 = x 2 + 2 x − 9 b. 0 = x 2 + 2 x + 9 c. 0 = x 2 + 2 x + 1 d. 3 = 2 x 2 + 5 x e. 2 x − 5 = x 2 + 4 x − 5 f. − 2 x 2 = 11
::a.0=x2+2+2x-9b.0=x2+2x-2x+9c.0=x2+2x+1d.3=2x2+5x2x-5x-5=x2+4x-5f.-2x2=11Using to Determine the Number of Solutions to a Quadratic Equation
::用于确定二次赤道的解决方案数Given a quadratic equation of the form 0 = a x 2 + b x + c :
::考虑到表0=ax2+bx+c的二次方程:The discriminant is b 2 − 4 a c .
::抗议者是b2 -4ac。If the discriminant is negative, there is no solution to the quadratic equation.
::如果对立是否定的,则二次等式就没有解决办法。If the discriminant is 0, there is one solution to the quadratic equation.
::如果对立方为0,则二次方程有一个解决办法。If the discriminant is positive, there will be two solutions.
::如果争议是积极的,就会有两种解决办法。-
Create
equations for several quadratic functions in standard form. Use the formula above to find the line of symmetry. Find the vertex. Approximately confirm your results using graphing technology.
::以标准格式为多个二次函数创建方程式。 使用上面的公式来找到对称线。 查找顶点。 大约用图形化技术来确认您的结果 。
Summary
::摘要Given a quadratic function in standard form:
::给定标准形式的二次函数 :-
It is possible it can be factored to find rational
zeroes
.
::可以考虑找到合理的零点。 -
It can be converted to vertex form by completing the square.
::通过完成正方形,它可以转换成顶部形态。 -
Rational or irrational zeroes, or a result of no solution, can be found by completing the square.
::通过完成广场,可以找到理性或非理性的零点,或任何解决办法的结果。 -
Rational or irrational zeroes, or a result of no solution, can be found with the quadratic formula.
::以二次公式可以找到理性或非理性的零,或任何解决办法的结果。
-
Rocket A accelerates upwards at 8 meters per second per second.