人权机构
章节大纲
-
How is the human body similar to a well-tuned machine?
::人的身体如何 类似于一个运转良好的机器?Many people have compared the human body to a machine. Think about some common machines, such as drills and washing machines. Each machine consists of many parts, and each part does a specific job, yet all the parts work together to perform an overall function. The human body is like a machine in all these ways. In fact, it may be the most fantastic machine on Earth.
::许多人把人体比作机器。 想想一些普通机器, 比如钻孔和洗衣机。 每台机器由许多部件组成, 每个部件都做一个特定的工作, 但是所有部件都一起工作 来履行一个整体功能。 人体在所有这些方面都像一台机器。 事实上, 它可能是地球上最神奇的机器。Organization of Your Body: , Tissues, Organs
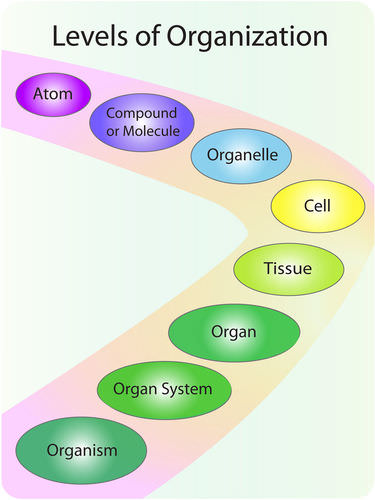
::贵机构的组织: 组织、组织、机关The human machine is organized at different levels, starting with the and ending with the entire organism (see Figure ). At each higher level of organization, there is a greater degree of complexity.
::人类机器在不同层次上组织,从整个有机体开始和结束(见图 )。在每一个更高的组织层次上,都存在着更大程度的复杂性。The human organism has several levels of organization. Cells
::单元格单元格The most basic parts of the human machine are cells—an amazing 100 trillion of them by the time the average person reaches adulthood! Cells are the basic units of structure and function in the human body, as they are in all living things. Each cell carries out basic life processes that allow the body to survive. Many human cells are specialized in form and function, as shown in Figure . Each type of cell in the figure plays a specific role. For example, nerve cells have long projections that help them carry electrical messages to other cells. Muscle cells have many that provide the energy they need to move the body.
::人体机器的最基本部分是细胞——在普通人成年时,细胞是惊人的100万亿个。细胞是人体结构和功能的基本单位,如同所有生物一样。每个细胞都进行基本的生命过程,使身体得以生存。许多人类细胞在形式和功能上是专门的,如图所示。图中的每类细胞都发挥一个具体的作用。例如,神经细胞有很长的预测,可以帮助他们将电文传送到其他细胞。肌肉细胞有许多能提供移动身体所需的能量。Different types of cells in the human body are specialized for specific jobs. Do you know the functions of any of the cell types shown here? (a) blood cells, (b) surface skin cells, (c) bone cell, (d) smooth muscle cells, (e) neuron, (f) columnar epithelial and goblet cells, (g) cardiac muscle cells, skeletal muscle cells.
Tissues
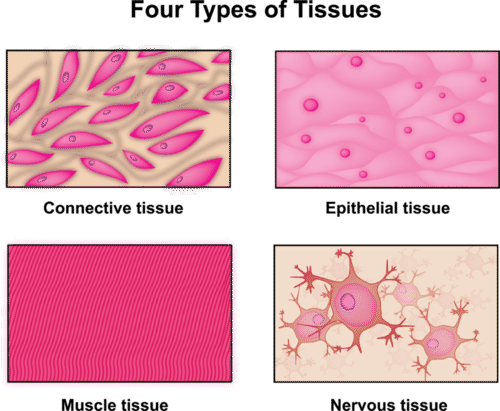
::组织组织After the cell, the tissue is the next level of organization in the human body. A tissue is a group of connected cells that have a similar function. There are four basic types of human tissues: epithelial, muscle, nervous, and connective tissues . These four tissue types, which are shown in Figure , make up all the organs of the human body.
::在细胞之后,组织是人体的下一个层次组织。组织是一组具有类似功能的相连细胞。有四种基本的人的组织类型:上皮、肌肉、神经和连接组织。图中显示的这四种组织类型构成人体的所有器官。The human body consists of these four tissue types. -
Connective tissue
is made up of cells that form the body’s structure. Examples include
and
cartilage
.
::连接组织由构成身体结构的细胞组成,例如软体和软体。 -
Epithelial tissue
is made up of cells that line inner and outer body surfaces, such as the skin and the lining of the digestive tract. Epithelial tissue protects the body and its internal organs, secretes substances such as
, and absorbs substances such as
nutrients
.
::动物组织由细胞组成,细胞在身体的内外表面,如皮肤和消化道的衬里。 动物组织保护身体及其内部器官,秘密物质,如.和吸收物质,如营养物质。 -
Muscle tissue
is made up of cells that have the unique ability to contract, or become shorter.
attached to bones enable the body to move.
::肌肉组织由细胞组成,这些细胞具有独特的结合能力,或变短。 骨骼与骨骼相连,使身体能够移动。 -
Nervous tissue
is made up of
, or nerve cells, that carry electrical messages. Nervous tissue makes up the
brain
and the nerves that connect the brain to all parts of the body.
::神经组织是由携带电子信息神经细胞组成的神经组织。神经组织由大脑和神经组成,将大脑与身体各个部位连接在一起。
Organs and Organ Systems
::和机关和机关系统After tissues, organs are the next level of organization of the human body. An organ is a structure that consists of two or more types of tissues that work together to do the same job. Examples of include the brain, heart, lungs , skin, and . Human organs are organized into organ systems , many of which are shown in Figure . An organ system is a group of organs that work together to carry out a complex overall function. Each organ of the system does part of the larger job.
::在组织之后,器官是人体的下一个层次组织。器官是由两种或两种以上的组织组成的结构,它们一起工作,从事同样的工作。例如,大脑、心脏、肺、皮肤和。人体器官被组织成器官系统,其中有许多在图中显示。器官系统是一组合力履行复杂的整体功能的器官。系统的各个器官都从事更大的部分工作。Many of the organ systems that make up the human body are represented here. What is the overall function of each organ system? Your body’s 12 organ systems are shown below ( Table ). Your organ systems do not work alone in your body. They must all be able to work together. For example, one of the most important functions of organ systems is to provide cells with oxygen and nutrients and to remove toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. A number of organ systems, including the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, all work together to do this.
::您身体的12个器官系统如下表所示(表 ) 。 您的器官系统并非在身体中单独运作,它们必须能够一起工作。 比如,器官系统最重要的功能之一是为细胞提供氧气和营养,以及清除二氧化碳等有毒废物。 许多器官系统,包括心血管和呼吸系统,都为此共同努力。Organ System Major Tissues and Organs Function Cardiovascular Heart; ; Transports oxygen, hormones, and nutrients to the . Moves wastes and carbon dioxide away from cells. Lymphatic Lymph nodes ; lymph vessels Defend against infection and disease, moves lymph between tissues and the blood stream. Digestive Esophagus ; stomach ; ; Digests foods and absorbs nutrients, minerals , vitamins , and . Endocrine Pituitary gland , hypothalamus ; adrenal glands ; ovaries ; testes Produces hormones that communicate between cells. Integumentary Skin, hair, nails Provides protection from injury and water loss, physical defense against infection by microorganisms, and temperature control. Muscular Cardiac muscle; ; smooth muscle ; tendons
Involved in movement and heat production. Nervous Brain, spinal cord ; nerves Collects, transfers, and processes information. Reproductive Female: uterus ; vagina ; fallopian tubes ; ovaries
::女性:子宫;阴道;输卵管;卵巢Male: penis ; testes; seminal vesicles
::男性:阴茎;睾丸;精细囊Produces gametes (sex cells) and sex hormones . Respiratory Trachea , larynx , pharynx , lungs Brings air to sites where gas exchange can occur between the blood and cells (around body) or blood and air (lungs). Skeletal Bones, cartilage; ligaments Supports and protects soft tissues of body; produces blood cells; stores minerals. Urinary Kidneys; urinary bladder Removes extra water, salts, and waste products from blood and body; controls pH; controls water and salt balance . Immune Bone marrow ; spleen ; white blood cells Defends against diseases. Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要-
The human body is organized at different levels, starting with the cell.
::人体由不同层次组织,从细胞开始。 -
Cells are organized into tissues, and tissues form organs.
::细胞组织成组织,组织形成器官。 -
Organs are organized into organ systems such as the skeletal and muscular systems.
::器官组织成器官系统,如骨骼和肌肉系统。
Review
::回顾-
What are the levels of organization of the human body?
::人体的组织水平如何? -
Which type of tissue covers the surface of the body?
::哪类组织覆盖身体表面? -
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
::骨骼系统的功能是什么? -
Which organ system supports the body and allows it to move?
::哪个器官系统支持身体并允许它移动? -
Explain how form and function are related in human cells. Include examples.
::解释人体细胞的形式和功能是如何关联的, 包括示例 。 -
Compare and contrast epithelial and muscle tissues.
::对比和对比上皮和肌肉组织
-
Connective tissue
is made up of cells that form the body’s structure. Examples include
and
cartilage
.