保利排除原则
章节大纲
-
Can you name one thing that easily distinguishes you from the rest of the world?
::你能说出一件很容易区分你 和世界其他地方的东西吗?And we’re not talking about DNA – that’s a little expensive to sequence. For many people, it is their email address. My email address allows people all over the world to contact me. It does not belong to anyone else, but serves to identify me. Electrons also have a unique set of identifiers in the that describe their location and spin.
::我们不是在谈论DNA — — 这对序列来说有点昂贵。 对于许多人来说,这是他们的电子邮件地址。 我的电子邮件地址允许世界各地的人与我联系。 它不属于其他人,而是用来识别我。 电子在描述其位置和旋转时也有一套独特的识别资料。Pauli Exclusion Principle
::保利排除原则When we look at the possibilities for a given , we see that there are different arrangements of electrons for each different type of atom. Since each must maintain its unique identity, we intuitively sense that the four quantum numbers for any given electron must not match up exactly with the four quantum numbers for any other electron in that atom.
::当我们审视给定的可能性时,我们看到每个不同原子类型都有不同的电子安排。 由于每个原子必须保持其独特的特性,我们直觉地感到,任何特定电子的四量子数字一定不能与该原子中任何其他电子的四量子数字完全匹配。For the hydrogen atom, there is no problem since there is only one electron in the H atom. However, when we get to helium we see that the first three quantum numbers for the two electrons are the same: same energy level, same spherical shape. What differentiates the two helium electrons is their spin. One of the electrons has spin while the other electron has spin. So the two electrons in the 1s orbital are each unique and distinct from one another because their spins are different. This leads to the Pauli exclusion principle , which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. The energy of the electron is specified by the principal, angular momentum, and magnetic quantum numbers. If those three numbers are identical for two electrons, the spin numbers must be different in order for the two electrons to be differentiated from one another. The two values of the spin quantum number allow each orbital to hold two electrons. The figure below shows how the electrons are indicated in a diagram.
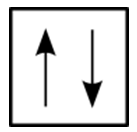
::对于氢原子来说,由于H原子中只有一个电子,所以没有问题。然而,当我们到达氦时,我们看到两个电子的前三个量子数是相同的:相同的能量水平,相同的球形。区别于两个氦电子的是它们的旋转。一个电子有一个+12旋转,而另一个电子有1-12旋转。因此,1号轨道中的两个电子由于各自的旋转不同而彼此独特和不同。这导致鲍里排除原则,该原则指出一个原子中没有两个电子可以有相同的四个量子数。电子的能量由主数、角动量和磁量数来指定。如果这两个数字是相同的,那么两个电子的旋转数字必须不同,以便两个电子相互区别。两个旋转量子数的两种值允许每个轨道保持两个电子。下图显示电子在图表中的位置。In an orbital filling diagram, a square represents an orbital, while arrows represent electrons. An arrow pointing upward represents one spin direction, while an arrow pointing downward represents the other spin direction.
::在轨道填充图中,方形代表轨道,箭头代表电子。向上箭头代表一个旋转方向,向下箭头代表另一个旋转方向。Summary
::摘要-
The Pauli exclusion principle specifies limits on how identical quantum numbers can be for two electrons in the same atom.
::保利排除原则对同一原子中两个电子的量数如何相同规定了限制。
Review
::回顾-
What is the difference between the two helium electrons?
::两枚氦电子有什么区别? -
What does the Pauli exclusion principle state?
::保利排除原则说明什么? -
What does the two values for the spin quantum number allow?
::旋转量子数字的两个值允许什么 ?
-
The Pauli exclusion principle specifies limits on how identical quantum numbers can be for two electrons in the same atom.