水晶固体类
章节大纲
-
What are common things that we connect to wires?
::我们连接到电线的普通事物是什么?We often take a lot of things for granted. We just assume that we will get electric power when we connect a plug to an electrical outlet. The wire that comprises that outlet is almost always copper, a material that conducts electricity well. The unique properties of the solid copper allow electrons to flow freely through the wire and into whatever device we connect it to. Then we can enjoy music, television, work on the computer, or whatever other activity we want to undertake.
::我们常常认为很多事情都是理所当然的。我们只是假设当我们把插头连接到电源出口时,我们将获得电力。 包括该插头的电线几乎总是铜,这种材料能很好地进行电力生产。 固体铜的独特特性允许电子通过电线自由流动,并进入我们连接到它的任何设备中。 然后我们可以享受音乐、电视、计算机工作或我们想从事的其他活动。Classes of Crystalline Solids
::水晶固体类Crystalline substances can be described by the types of particles in them and the types of chemical bonding that takes place between the particles. There are four types of crystals: (1) ionic , (2) metallic , (3) covalent network, and (4) molecular . Properties and several examples of each type are listed in the following table and are described in Table .
::晶体物质可以按颗粒的类型和粒子之间发生的化学结合类型来描述,有四种晶体1) 离子体,(2) 金属,(3) 共价网络,(4) 分子。
Crystalline Solids – and Boiling Points Type of Crystalline Solid Examples (formulas) Melting Point (°C) Normal Boiling Point (°C) Ionic NaCl
::NaCl 纳居器CaF 2
::CAF2801
1418
1413
2533
Metallic Hg
::汞汞汞汞汞Na
::纳纳Au
::秋秋W
::西 西-39
371
1064
3410
630
883
2856
5660
Covalent network B
::BB ,BC (diamond)
::C(钻石)SiO 2
::锡O22076
3500
1600
3927
3930
2230
Molecular H 2
::H2H2I 2
::I2, I2NH 3
::NH3 NH3H 2 O
::H2O-259
114
-78
0
-253
184
-33
100
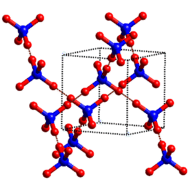
1. Ionic crystals -- The ionic crystal structure consists of alternating positively-charged and negatively-charged (see Figure ). The may either be monatomic or polyatomic. Generally, ionic crystals form from a combination of Group 1 or 2 and Group 16 or 17 or nonmetallic polyatomic ions. Ionic crystals are hard and brittle and have high melting points. do not conduct electricity as solids, but do conduct when molten or in aqueous solution .
::1. 离子晶体 -- -- 离子晶体结构由正充电和负充电交替组成(见图 ) , 可以是单子晶体或多原子体。一般而言, 离子晶体由第1组或第2组和第16组或第17组或非金属多原子离子组合形成。 离子晶体是硬的、易碎的,熔点高。 离子晶体不是作为固体进行电,而是在熔化或水溶时进行电解。NaCl crystal.
::纳氏晶体2. Metallic crystals -- Metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a “sea” of mobile (see Figure ). These electrons, also referred to as delocalized electrons , do not belong to any one , but are capable of moving through the entire crystal. As a result, metals are good conductors of electricity. As seen in Table , the melting points of metallic crystals display a wide range.
::2. 金属晶体 -- -- 金属晶体由被移动的 " 海洋 " 环绕的金属板块组成(见图)。这些电子,又称非本地化电子,不属于任何一种电子,但能够穿过整个晶体,因此,金属是良好的电力导体,如表所示,金属晶体的熔点显示的范围很广。Metallic crystal lattice with free electrons able to move among positive metal atoms.
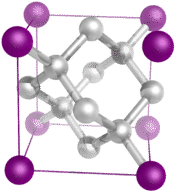
::金属晶体板,有自由电子,能够在正金属原子之间移动。3. Covalent network crystals -- A covalent network crystal consists of atoms at the lattice points of the crystal, with each atom being covalently bonded to its nearest neighbor atoms (see Figure ). The covalently bonded network is three-dimensional and contains a very large number of atoms. Network solids include diamond, quartz, many , and oxides of and metalloids. Network solids are hard and brittle, with extremely high melting and boiling points. Being composed of atoms rather than ions, they do not conduct electricity in any state.
::3. 共价网络晶体 -- -- 共价网络晶体,由晶体花边点的原子组成,每个原子都与近邻原子相连接(见图)。共价连接的网络是三维的,包含大量原子。网络固体包括钻石、石英、许多,氧化物和蛋白质。网络固体是硬的和易碎的,熔点和沸点极高。由原子而不是离子组成,它们不会在任何州用电。Diamond is a network solid and consists of carbon atoms covalently bonded to one another in a repeating three-dimensional pattern. Each carbon atom makes four single covalent bonds in a tetrahedral geometry.
::钻石是一个网络固体,由碳原子以三维的重复模式相互连接组成。 每个碳原子在四面形几何中形成四个单一的共价键。4. Molecular crystals -- Molecular crystals typically consist of molecules at the lattice points of the crystal, held together by relatively weak intermolecular forces (see Figure ). The intermolecular forces may be dispersion forces in the case of nonpolar crystals, or dipole-dipole forces in the case of polar crystals. Some molecular crystals, such as ice, have molecules held together by . When one of the is cooled and solidified, the lattice points are individual atoms rather than molecules. In all cases, the intermolecular forces holding the particles together are far weaker than either ionic or . As a result, the melting and boiling points of molecular crystals are much lower. Lacking ions or free electrons, molecular crystals are poor electrical conductors.
::4. 分子晶体 -- -- 分子晶体 -- -- 分子晶体通常由晶体花边点的分子组成,由相对弱的分子间力量合在一起(见图)。分子的中间力量可能是非极晶体的分散力量,或极晶体的二极力量,有些分子晶体,如冰,有分子在一起。当其中一种被冷却和凝固时,悬浮点是单个原子,而不是分子。在所有情况下,将粒子放在一起的中间分子力量远远弱于离子或离子或离子体。结果,分子晶体的熔点和沸点要低得多,缺乏电离子或自由电,分子晶体是贫弱的电导体。Ice crystal structure.
::冰晶结构Summary
::摘要-
Ionic crystals are composed of alternating positive and negative ions.
::离子晶体由交替的正离子和负离子组成。 -
Metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a “sea” of mobile valence electrons.
::金属晶体由金属刻板组成,周围环绕着移动价值电子的“海洋”。 -
Covalent crystals are composed of atoms which are covalently bonded to one another.
::共价晶体由原子组成,这些原子相互连接共价。 -
Molecular crystals are held together by weak intermolecular forces.
::分子晶体由微弱的分子内部力量凝聚在一起。
Review
::回顾-
What is an ionic crystal?
::什么是离子晶体? -
What type of crystal is a diamond?
::钻石是什么样的晶体? -
What forces hold molecular crystals together?
::是什么力量将分子晶体凝结在一起? -
Which type of crystal is a good conductor of electricity?
::哪种水晶是好电导体?
-
Ionic crystals are composed of alternating positive and negative ions.