营养营养营养
章节大纲
-
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
::自发性与血化性之比Living organisms obtain chemical energy in one of two ways.
::活生物体以两种方式之一获得化学能量。Autotrophs , shown in Figure , store chemical energy in carbohydrate food molecules they build themselves. Food is chemical energy stored in organic molecules. Food provides both the energy to do work and the carbon to build bodies. Because most autotrophs transform sunlight to make food, we call the process they use photosynthesis . Only three groups of organisms - plants, algae, and some bacteria - are capable of this life-giving energy transformation. Autotrophs make food for their own use, but they make enough to support other life as well. Almost all other organisms depend absolutely on these three groups for the food they produce. The producers , as autotrophs are also known, begin food chains which feed all life. Food chains will be discussed in the “ Food Chains and Food Webs ” concept.
::食品是有机分子中储存的化学能量; 食品既提供工作所需的能量,也提供建造身体所需的碳; 由于大多数自发性能改变阳光以制造食物,我们称之为光合作用过程; 只有三组生物——植物、藻类和某些细菌——能够进行这种给生命的能量转换; 自发性能使食物供自己使用,但它们足以养活其他生命; 几乎所有其它生物都绝对依赖这三类生物来生产食物。 生产者,如已知的自发性也开始食物链,为所有生命提供食物。 食物链将在“食物链和食物网”的概念中讨论。Heterotrophs cannot make their own food, so they must eat or absorb it. For this reason, heterotrophs are also known as consumers . Consumers include all animals and fungi and many protists and bacteria. They may consume autotrophs or other heterotrophs or organic molecules from other organisms. Heterotrophs show great diversity and may appear far more fascinating than producers. But heterotrophs are limited by our utter dependence on those autotrophs that originally made our food. If plants, algae, and autotrophic bacteria vanished from earth, animals, fungi, and other heterotrophs would soon disappear as well. All life requires a constant input of energy. Only autotrophs can transform that ultimate, solar source into the chemical energy in food that powers life, as shown in Figure .
::食用或吸收食物。因此,食用或吸收食物也被称为消费者。消费者包括所有动物和真菌以及许多原生生物和细菌。他们可能消耗其他生物的自发性或其他血化营养分子或有机分子。强生营养表现出极大的多样性,比生产者更令人着迷。但是,由于我们完全依赖最初制造食物的自发性食物,因此,强生营养受到限制。如果植物、藻类和自发性细菌从地球、动物、真菌和其他热营养物质中消失,那么植物、藻类和自发性细菌也会很快消失。所有生命都需要不断的能源投入。只有自发性营养能才能将最终的、太阳能源化为能,如图所示,在生命的食品中,这种化学能源才能转化为最终的、太阳能。Photosynthetic autotrophs, which make food using the energy in sunlight, include (a) plants, (b) algae, and (c) certain bacteria.
::光合成自养养分使食物使用阳光下的能量,包括(a)植物、(b)藻类和(c)某些细菌。Photosynthesis provides over 99 percent of the energy for life on earth. A much smaller group of autotrophs - mostly bacteria in dark or low-oxygen environments - produce food using the chemical energy stored in inorganic molecules such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, or methane. While photosynthesis transforms light energy to chemical energy, this alternate method of making food transfers chemical energy from inorganic to organic molecules. It is therefore called chemosynthesis , and is characteristic of the tubeworms shown in Figure . Some of the most recently discovered chemosynthetic bacteria inhabit deep ocean hot water vents or “black smokers”. There, they use the energy in gases from the Earth’s interior to produce food for a variety of unique heterotrophs: giant tube worms, blind shrimp, giant white crabs, and armored snails. Some scientists think that chemosynthesis may support life below the surface of Mars, Jupiter's moon, Europa, and other planets as well. Ecosystems based on chemosynthesis may seem rare and exotic, but they too illustrate the absolute dependence of heterotrophs on autotrophs for food.
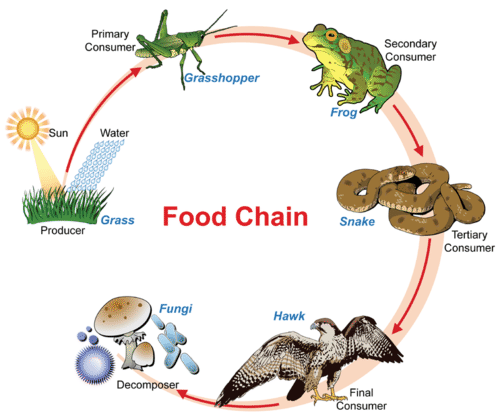
::光合作用将光能转化为化学能量,而这种使食物能从无机分子向有机分子转移化学能量的替代方法。因此,它被称为化学合成,是图中显示的管虫的特征。最近发现的化学合成细菌中有些位于深海热水喷口或“黑烟者”中。 在那里,它们利用地球内部气体中的能量生产食物,用于各种独特的外壳营养学:巨型管状虫、盲虾、巨型白蟹和装甲蜗牛。一些科学家认为,化学合成可能支持火星表面、木星月、欧罗巴和其他行星下的生命。 以化学合成细菌为基础的生态系统可能看起来很稀有,也非常具有外来性,但是它们也表明其对于食物的绝对依赖性。A food chain shows how energy and matter flow from producers to consumers. Matter is recycled, but energy must keep flowing into the system. Where does this energy come from? Though this food chains “ends” with decomposers, do decomposers, in fact, digest matter from each level of the food chain? (see the “Flow of Energy” concept.)
::食物链显示了能源与物质如何从生产者流向消费者。 物质是再循环的,但能源必须不断流入系统。 能源来自何处? 尽管食物链与分解者“末端 ” , 但分解者实际上是否在食物链的每个层次都对消化物有影响? (见“能源花”概念)。Tubeworms deep in the Galapagos Rift get their energy from chemosynthetic bacteria living within their tissues. No digestive systems needed!
::加拉帕戈斯裂谷深处的管虫从组织内的化学合成细菌获得能量,不需要消化系统!Making and Using Food
::食品的制作和使用The flow of energy through living organisms begins with photosynthesis. This process stores energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of glucose. By breaking the chemical bonds in glucose, cells release the stored energy and make the ATP they need. The process in which glucose is broken down and ATP is made is called cellular respiration .
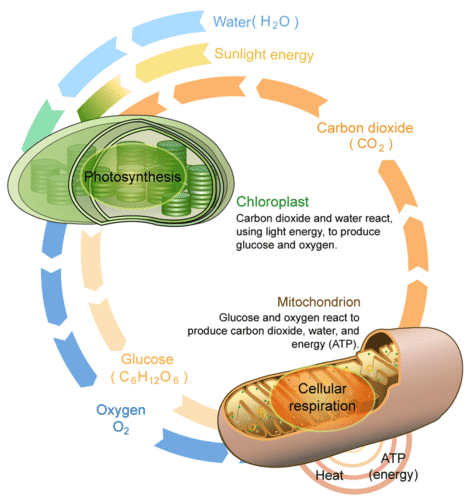
::活生物体的能量流动始于光合作用。 这一过程将阳光的能量储存在葡萄糖的化学链条中。 通过打破葡萄糖的化学链条,细胞释放了储存的能量,并使得它们需要ATP。 将葡萄糖分解并制造ATP的过程被称为细胞呼吸。Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are like two sides of the same coin. This is apparent from Figure . The products of one process are the reactants of the other. Together, the two processes store and release energy in living organisms. The two processes also work together to recycle oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere.
::光合作用和细胞呼吸就像同一枚硬币的两面。从图中可以看出这一点。一个过程的产物是另一个过程的反作用物。两个过程共同储存和释放活生物体中的能量。这两个过程还共同工作,在地球大气层中回收氧气。This diagram compares and contrasts photosynthesis and cellular respiration. It also shows how the two processes are related.
::该图比较和对比了光合作用和细胞呼吸,还显示了这两个过程之间的关系。Photosynthesis
::光合作用Photosynthesis is often considered to be the single most important life process on Earth. It changes light energy into chemical energy and also releases oxygen. Without photosynthesis, there would be no oxygen in the atmosphere. Photosynthesis involves many chemical reactions, but they can be summed up in a single chemical equation:
::光合作用通常被认为是地球上最重要的生命过程。 它将光能改变为化学能量, 并释放氧气。 没有光合作用, 大气中就不会有氧气。 光合作用包含许多化学反应, 但可以用一个化学方程式来概括:6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + Light Energy → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 .
::6CO2 + 6H2O + 轻能 + C6H12O6 + 6O2。Photosynthetic autotrophs capture light energy from the sun and absorb carbon dioxide and water from their environment. Using the light energy, they combine the reactants to produce glucose and oxygen, which is a waste product. They store the glucose, usually as starch, and they release the oxygen into the atmosphere.
::光学合成自生养分从太阳中捕捉光能,吸收二氧化碳和环境中的水。使用光能,它们结合反应剂,生产葡萄糖和氧气,这是废物产物。它们储存葡萄糖,通常是淀粉,并将氧气释放到大气中。Cellular Respiration
::细胞呼吸Cellular respiration actually “burns” glucose for energy. However, it doesn’t produce light or intense heat as some other types of burning do. This is because it releases the energy in glucose slowly, in many small steps. It uses the energy that is released to form molecules of ATP. Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions, which can be summed up with this chemical equation:
::细胞呼吸实际上“燃烧”葡萄糖作为能量。 但是,它不会像其他燃烧类型那样产生光或高热。 这是因为它以许多小步缓慢地释放葡萄糖中的能量。 它使用释放的能量形成ATP的分子。 细胞呼吸涉及许多化学反应,可以用化学方程式来概括:C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + Chemical Energy (in ATP)
::C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6O2 + 6CO2 + 6H2O+ 化学能源(在ATP中)Cellular respiration occurs in the cells of all living things. It takes place in the cells of both autotrophs and heterotrophs. All of them burn glucose to form ATP.
::细胞呼吸发生在所有生物的细胞中。它发生在自养和血化的细胞中。所有细胞都燃烧葡萄糖形成ATP。Summary
::摘要-
Autotrophs store chemical energy in carbohydrate food molecules they build themselves. Most autotrophs make their “food” through photosynthesis using the energy of the sun.
::自发性将化学能量储存在它们自己制造的碳水化合物食品分子中。 大多数自发性通过光合作用太阳的能量制造“食物 ” 。 -
Heterotrophs cannot make their own food, so they must eat or absorb it.
::血富症患者不能自己做食物,所以他们必须吃或吸收食物。 -
Chemosynthesis is used to produce food using the chemical energy stored in inorganic molecules.
::化学合成用于利用储存在无机分子中的化学能量生产食品。
Explore More
::探索更多Use this resource to answer the questions that follow.
::使用此资源回答下面的问题 。-
Autotroph vs. Heterotroph
at
.
::自发性活体变异 血化在...
1. Define autotroph and heterotroph.
::1. 定义自养和内分泌。2. What position do autotrophs fill in a food chain?
::2. 在食物链中,自发性能填充什么位置?3. Give examples of autotrophs and heterotrophs.
::3. 举二氧化物和血化物的例子。4. Describe energy production in photoautotrophs.
::4. 描述光氧化物的能源生产情况。5. What is a chemoheterotroph?
::5. 什么是化学老化?Review
::回顾1. Compare autotrophs to heterotrophs, and describe the relationship between these two groups of organisms.
::1. 将自发性与血化性相比,并描述这两组生物之间的关系。2. Name and describe the two types of food making processes found among autotrophs. Which is quantitatively more important to life on earth?
::2. 列举和描述在自养过程中发现的两类食品生产过程,在数量上哪些对地球上的生命更为重要?3. Describe the flow of energy through a typical food chain (describing “what eats what”), including the original source of that energy and its ultimate form after use.
::3. 描述能源通过典型食物链的流动情况(说明 " 什么吃什么 " ),包括这种能源的原始来源及其使用后的最终形式。2.1 Nutrition in Plants
::2.1 植物营养What is Photosynthesis?
::什么是光合作用?Photosynthesis is the way plants make sugar/food and oxygen with the use of sunlight. If you break down the name, the name explains exactly what it is.
::光合作用是植物利用阳光制成糖/食物和氧的方式。 如果您打破了名称, 名称可以解释它到底是什么 。Photo - Synthesis
::照片 - 合成(light) (to make)
:光)(制造)
The equation for photosynthesis is:
::光合作用方程式是:6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + Sunlight → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2
::6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 阳光 + C6H12O6 + 6 O2What do Plants Need for Photosynthesis?
::植物需要什么 相片合成?There are three raw materials needed for photosynthesis and they include:
::光合作用需要三种原材料,其中包括:-
Water (which is why we water plants)
::水(这就是为什么我们水厂) -
Sunlight (which is why we place plants by a window)
::阳光(所以我们把植物放在窗边) -
Carbon Dioxide.
::二氧化碳。
What do Plants Make From Photosynthesis?
::植物从相片合成中产生什么?Plants produce two products from photosynthesis. Both plants and animals (INCLUDING YOU!) need:
::植物生产两种光合作用的产品。 植物和动物( 包括你! ) 都需要 :-
Glucose (Sugar)
::甘糖(糖) -
Oxygen
::氧
Where Does Photosynthesis Occur?
::相片合成物在哪里?Photosynthesis occurs in the leaf.
::在叶子中出现光合作用。-
Leaves are broad and flat so they can absorb sunlight like a solar panel.
::叶子宽、平坦,可以吸收阳光,像太阳能电池板一样。

-
Leaves are FILLED with photosynthetic machines called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are green organelles inside the cells that produce glucose. There are many chloroplasts located on the inside of the leaf.
::叶子用称为叶板的光合机发光。氯甲醚是产生葡萄糖的细胞中的绿色有机体。叶子内部有许多叶片。

-
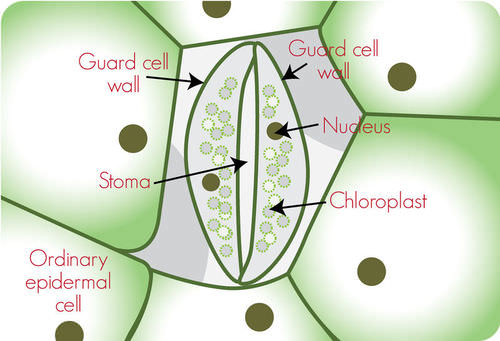
Leaves also have openings called stoma that allow the entry of carbon dioxide into the leaf. They also release of oxygen into the atmosphere.
::叶子中还存在被称为气态的孔口,允许二氧化碳进入叶子,还释放氧气到大气中。
-
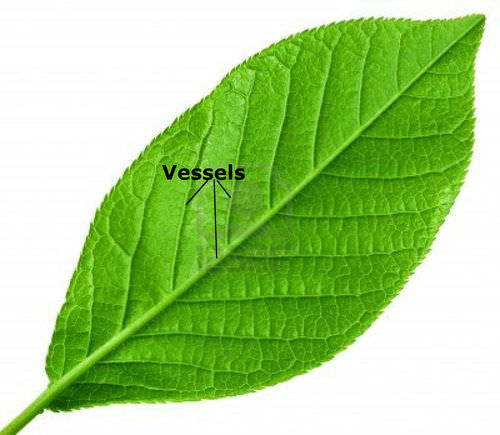
Lastly, leaves have
vascular tissue
(vessels) that deliver materials such as water to the leaf. Vessels also take away materials like glucose away from the leaf to distribute glucose to the rest of the plant.
::最后,叶子有血管组织(血管),可以将水等材料送到叶子上,船也将葡萄糖等材料从叶子上取走,以便向植物的其余部分分配葡萄糖。
How Is The Leaf Structured for Photosynthesis?
::《叶子结构》是如何为相片合成而设计的?
-
Mesophyll:
The middle layer of the leaf that makes up most of the leaf’s interior. This is where photosynthesis occurs. The mesophyll is composed of:
-
Palisades Layer:
A densely packed part of the leaf that have the majority of chloroplasts needed for photosynthesis.
::帕利萨德图层:一片密布的叶叶片 大部分叶片是光合作用所需的叶片 -
Spongy Layer:
A loosely packed layer that allows the diffusion of gas through out the leaf for photosynthesis.
::海绵层:一个松散的层层,允许气体从叶子中扩散,用于光合作用。
::美索菲利尔: 构成叶子大部分内部的叶的中间层。 这是光合作用发生的地方。 光合作用由以下部分组成: Palisades 层: 密布的叶子中大部分是光合作用所需的叶片。 海绵层: 松散的层, 允许气体通过叶子扩散, 用于光合作用。 -
Palisades Layer:
A densely packed part of the leaf that have the majority of chloroplasts needed for photosynthesis.
-
Vascular Tissue:
are made primarily of:
-
Xylem:
Vessels that transports water to the leaves for photosynthesis.
::Xylem: 将水输送到叶子上进行光合作用的船只。 -
Phloem:
Vessels that carries away sugar from the leaf.
::将糖从叶子上移走的船
::血管组织:主要来自:Xylem:将水运到叶子上进行光合作用的船只。Phloem:将糖从叶子上运走的船只。 -
Xylem:
Vessels that transports water to the leaves for photosynthesis.
-
The
epidermis
is a layer of cells that makes up the:
-
Upper Epidermis:
A top layer of tightly-packed dermal cells. They secrete waxy layer called the
cuticle
to prevent evaporation of water from the leaf.
::上层冰球:一顶层的严格包装的皮肤细胞。它们秘密的蜡状层叫做切片,以防止叶子中的水蒸发。 -
Lower Epidermis:
A bottom layer of tightly-packed dermal cells. This layer has openings called stomata that allow CO
2
to enter the leaf and O
2
to exit the leaf.
::下流行病: 底部一层是 严格包装的皮肤细胞。 这个层有叫做 stomata 的开口, 允许二氧化碳进入叶子, 允许O2 进入叶子 。
::上皮层是构成以下细胞的细胞层:上皮尔米斯:一顶层是严格包装的皮肤细胞。它们隐蔽了被称作切片的蜡层,以防止从叶子中蒸发水。下皮尔米斯:一底层是严格包装的皮肤细胞层。这个层有称为stomata的孔口,允许二氧化碳进入叶叶中,O2进入叶中。 -
Upper Epidermis:
A top layer of tightly-packed dermal cells. They secrete waxy layer called the
cuticle
to prevent evaporation of water from the leaf.
How Do The Layers Of The Leaf Carry Out Photosynthesis.
::叶子图层如何执行相片合成。Watch the video at:
::观看影片在:Events involved in Photosynthesis
::涉及相片合成事件1. Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
::1. 叶绿素吸收光能。2. Conversion of light energy into chemical energy.
::2. 将光能转化为化学能源。3. Photolysis of water into hydrogen and oxygen.
::3. 将水光解成氢和氧。4. Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrate.
::4. 将二氧化碳减少至碳水化合物。Readers are advised to contribute activities to show that light is necessary for photosynthesis not found.
::建议读者提供活动,以显示光线对于找不到光合作用是必要的。2.2 Nutrition in Animals
::2.2 动物营养What can photosynthesize AND hunt for food?
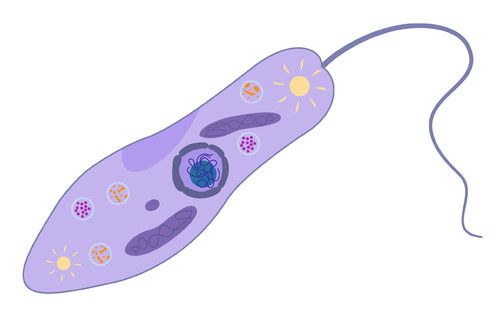
::光合作用和捕猎什么食物?No, there are no man-eating plants or leaf-growing animals. The idea of an organism both photosynthesizing and hunting for food might seem strange, but this isn't science fiction. These organisms, examples of Euglena , are protists that can feed like an animal or use the energy of the sun to make food like a plant.
::不,没有吃人植物或种植叶子的动物。生物体的光合和捕食可能看起来很奇怪,但这不是科幻小说。这些生物体,如欧格伦娜,是可以像动物一样喂养的原生生物,或者利用太阳的能量来制造像植物一样的食物。Protists Nutrition
::营养The cells of protists need to perform all of the functions that other cells do, such as grow and reproduce, maintain homeostasis, and obtain energy. They also need to obtain “ food ” to provide the energy to perform these functions.
::原生细胞需要发挥其他细胞的所有功能,如生长和繁殖、保持顺从和获得能量。 它们也需要获得“食物 ” , 以提供履行这些功能的能量。Recall that protists can be plant-like, fungi-like, or animal-like. That means that protists can obtain food like plants, fungi, or animals do. There are many plant-like protists, such as algae, that get their energy from sunlight through photosynthesis. Some of the fungus-like protists, such as the slime molds ( Figure ), decompose decaying matter. The animal-like protists must “ eat ” or ingest food.
::提醒人们,原生者可以是植物类、真菌类或动物类。 这意味着原生者可以获得植物类、真菌类或动物类等食物。 许多植物类原生者,如藻类,通过光合作用从阳光中获取能量。 某些像真菌类原生者,如粘泥模型(Figure ) , 腐烂物质分解。 动物类原生者必须“吃 ” 或食食 。Some animal-like protists use their “ tails ” to eat. These protists are called filter-feeders . They acquire nutrients by constantly whipping their tails, called flagellum , back and forth. The whipping of the flagellum creates a current that brings food into the protist.
::一些像动物一样的先锋主义者用他们的“尾巴”来吃饭。 这些先锋主义者被称为过滤器。 他们通过不断鞭打尾巴获得营养素,即所谓的旗鼓、前后。 鞭打旗鼓制造了一种能给先锋带来食物的洋流。Other animal-like protists must “ swallow ” their food through a process called endocytosis . Endocytosis happens when a cell takes in substances through its membrane. The process is described below:
::其他动物类先质学家必须通过一个叫做内分泌中毒的过程“吞噬”他们的食物。 当细胞通过膜吸收物质时,内分泌中毒就会发生。1. The protist wraps around its prey, which is usually bacteria.
::1. 蛋白质环绕猎物,通常是细菌。2. It creates a food vacuole , a sort of “ food storage compartment, ” around the bacteria.
::2. 它在细菌周围制造一种食物真空,一种 " 食物储藏区 " 。3. The protist produces toxins which paralyze its prey.
::3. 蛋白质产生毒素,使猎物麻痹。4. Once digested, the food material moves through the vacuole and into the cytoplasm of the protist.
::4. 食物材料一旦消化,就会穿过真空体,进入原生体的细胞托盘。Also, some of the animal-like and fungi-like protists are parasitic and absorb nutrients meant for their host, harming the host in the process.
::此外,有些动物类和真菌类原生者是寄生虫,吸收寄生虫宿主的养分,在此过程中损害宿主。Slime molds live on decaying plant life and in the soil.
::石质模具靠腐烂的植物生命和土壤中腐烂而生存。Summary
::摘要-
Some protists are plant-like and photosynthesize.
::一些原生者是植物类和光合体。 -
Some protists absorb nutrients from decaying matter like a fungus.
::一些原生生物吸收了腐烂物质的养分 像真菌一样 -
Some protists hunt their food or act as parasites.
::一些原生者猎食或充当寄生虫。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the following questions.
::使用以下资源回答下列问题。-
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
at
(1:54)
:1:54)时的内分泌中毒和异分症
1. Why do some protista need endocytosis to take in nutrition?
::1. 为何某些蛋白质需要内分泌硬化来获取营养?2. What are the three types of endocytosis?
::2. 三种内分泌疾病是什么类型?3. What differentiates the three types of endocytosis?
::3. 是什么区分这三类内分泌疾病?4. What process is used by a protist to ingest a bacterial cell. Be specific in your response.
::4. 前体者用什么程序来摄取细菌细胞,请在答复中具体说明。Review
::回顾1. How do algae obtain food?
::1. 藻类如何获得食物?2. How do animal-like protists “swallow” their prey?
::2. 象动物一样的原生者如何 " 吞咽 " 他们的猎物?3. What is a filter-feeder?
::3. 什么是过滤器?4. How do slime molds get their energy?
::4. 粘土模具如何获得能量?2.3 Nutrition in Humans
::2.3 人类营养Digestive System Organs
::消化系统机关Specifically, our energy comes from what?
::具体地说,我们的能量来自什么?The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to provide cells with the oxygen they need for cellular respiration. Cells also need glucose for cellular respiration. Glucose is a simple sugar that comes from the food we eat. To get glucose from food, digestion must occur. This process is carried out by the digestive system.
::呼吸和循环系统共同为细胞提供细胞呼吸所需的氧气。细胞也需要葡萄糖进行细胞呼吸。葡萄糖是一种简单的糖,来自我们吃的食物。要从食物中获取葡萄糖,就必须进行消化。这一过程由消化系统进行。Overview of the Digestive System
::消化系统概览The digestive system consists of organs that break down food and absorb nutrients such as glucose.
::消化系统由分解食物和吸收葡萄糖等养分的器官组成。Do you know when you're digesting food?
::你知道你什么时候消化食物吗?Unless you have an upset stomach, digestion usually happens without you even noticing. You consciously chew up your food, but most of the digestive process takes place without your conscious awareness. Long after you put down your fork, food is still passing through your stomach and small intestine. It may take over a day for a meal to pass all the way through your digestive system.
::除非胃不适,否则消化通常不会发生,甚至没有注意到。你有意吞噬食物,但大部分消化过程都是在没有意识的情况下发生的。在你放下叉子之后,食物仍然通过胃和小肠。吃一顿饭可能要花一天时间才能通过消化系统。Function of the Digestive System
::消化系统功能Nutrients in the foods you eat are needed by the cells of your body. How do the nutrients in foods get to your body cells? What organs and processes break down the foods and make the nutrients available to cells? The organs are those of the digestive system. The processes are digestion and absorption.
::您所食食物中的营养素是您身体细胞需要的。 食物中的营养素是如何进入身体细胞的? 哪些器官和过程会分解食物,并将营养素提供给细胞? 器官是消化系统。 过程是消化和吸收。How Food is Digested - Peristalsis, Storage and Excretion
::食物如何被消化-持久性、储存和排泄Watch how food is digested.
::看看食物是如何消化的。Watch the video at:
::观看影片在:Peristalsis illustration
::持久性说明Peristalsis pushes food through the GI tract.
::持久性把食物推穿GI道The digestive system is the body system that breaks down food and absorbs nutrients. It also gets rid of solid food waste. The digestive system is mainly one long tube from the mouth to the anus, known as the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). The main organs of the digestive system include the esophagus, stomach and the intestine, and are pictured below ( Figure ). The intestine is divided into the small and large intestine. The small intestine has three segments. The ileum is the longest segment of the small intestine, which is well over 10 feet long. The large intestine is about 5 feet long.
::消化系统是分解食物和吸收养分的人体系统,它也能够消除固体食品废物。消化系统主要是从嘴到肛门的一条长管,称为胃肠道(GI道)。消化系统的主要器官包括食道、胃和肠道,并在下面(图)有图象。肠分为小肠和大肠。小肠分三部分。小肠是小肠最长的部分,大大超过10英尺。大肠大约5英尺。This drawing shows the major organs of the digestive system. The liver, pancreas and gallbladder are also organs of the digestive system.
::这一图示显示了消化系统的主要器官,肝脏、胰腺和胆囊也是消化系统的器官。Digestion is the process of breaking down food into nutrients. There are two types of digestion, mechanical and chemical. In mechanical digestion , large chunks of food are broken down into small pieces. Mechanical digestion begins in the mouth and involves physical processes, such as chewing. This process continues in the stomach as the food is mixed with digestive juices. In chemical digestion , large food molecules are broken down into small nutrient molecules. This is a chemical process which also begins in the mouth as saliva begins to break down food and continues in the stomach as stomach enzymes further digest the food.
::消化过程是将食物分解成养分的过程,有两种消化、机械和化学两种。在机械消化过程中,大量食物分解成小块。机械消化始于口中,涉及物理过程,如咀嚼。这一过程在胃中持续,因为食物混合了消化汁。在化学消化过程中,大的食物分子分解成小营养分子。这个化学过程也始于口中,因为唾液开始分解食物,而胃中继续,因为胃酶进一步消化食物。Absorption is the process that allows substances you eat to be taken up by the blood. After food is broken down into small nutrient molecules, the molecules are absorbed by the blood. After absorption, the nutrient molecules travel in the bloodstream to cells throughout the body. This happens mostly in the small intestine.
::吸附是允许你吃的物质被血液吸收的过程。 在食物分解成小营养分子后, 分子被血液吸收。 吸收后, 营养分子在血液中流到整个身体的细胞中。 这主要发生在小肠中 。Some substances in food cannot be broken down into nutrients. They remain behind in the digestive system after the nutrients are absorbed. Any substances in food that cannot be digested and absorbed pass out of the body as solid waste. The process of passing solid food waste out of the body is called elimination .
::食物中的某些物质不能分解成养分,在吸收养分后仍留在消化系统中; 食物中的任何物质不能消化,不能作为固体废物从身体中吸收出来; 将固体食品废物从身体中输送出来的过程称为消除。 -
Autotrophs store chemical energy in carbohydrate food molecules they build themselves. Most autotrophs make their “food” through photosynthesis using the energy of the sun.