鲜血船
章节大纲
-
How does travel around the body?
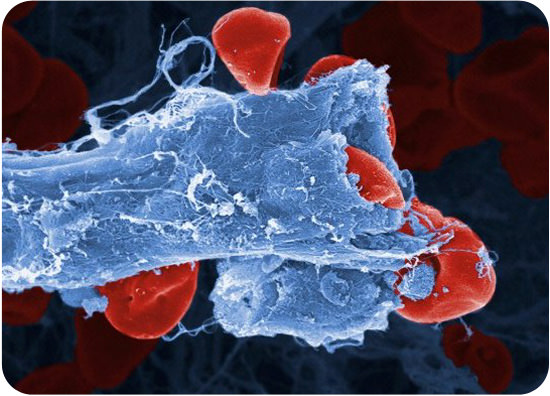
::身体周围的行踪如何?This color-enhanced image was made with an electron , so the objects it depicts are extremely small. This incredible photo shows red blood cells leaking out of a ruptured blood vessel. Blood vessels are part of the ; they are the “highway” system of the that transports materials to all of its . And the red blood cells that carry some of these materials are a little like trucks on the highway.
::这个彩色增强的图像是用电子制作的,所以它所描绘的物体是极小的。这幅令人难以置信的照片显示红血球从一个破裂的血管中渗出。血管是其中的一部分;它们就是将材料运到所有它的“高速公路”系统。而载有其中一些材料的红血细胞与高速公路上的卡车有点相似。Blood Vessels
::鲜血船The blood vessels are part of the and function to transport blood throughout the body. The two most important types are arteries and veins . Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins return blood to the heart.
::血管是整个身体输送血液的一部分和功能,其中最重要的两种是动脉和血管,动脉从心脏中取出血液,而血管则返回心脏血液。Arteries, Veins and Capillaries
::动脉、动脉和胶卷There are various kinds of blood vessels. The main types are listed below:
::各种血管种类繁多,主要类型如下:-
Arteries
are the large, muscular vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
::动脉是巨大的肌肉血管 从心脏携带血液 -
An
arteriole
is a small-diameter blood vessel that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries.
::动脉是一种小直径的血管,从动脉伸展和伸展,并导致刺骨。 -
Veins
are vessels that carry blood toward the heart. The majority of veins in the body carry deoxygenated blood from the
tissues
back to the heart.
::血管是将血液带入心脏的血管。体内大部分血管含有脱氧血液,从组织到心脏。 -
A
venule
is a small vessel that allows deoxygenated blood to return from the capillaries to veins.
::卵巢是一种小容器,可以让脱氧血液从血管中恢复到血管中。 -
Capillaries
are the smallest of the body's blood vessels. They connect arterioles and venules and are important for the interchange of gases and other substances between blood and
.
::Capillary是身体血管中最小的,它们连接动脉和静脉,对于血液和血液之间气体和其他物质的交换很重要。
Blood vessels include arteries, veins, and capillaries.
::血管包括动脉、血管和刺青。The blood vessels all have a similar basic structure. The endothelium is a thin layer of cells that creates a smooth lining on the inside surface of blood vessels. Endothelial tissue is a specialized type of epithelium, one of the four types of tissue found in the body. Endothelial cells have an important structural role in blood vessels; they line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillary. Around the endothelium there is a layer of smooth muscle , which is well developed in arteries. Finally, there is a further layer of connective tissue that surrounds the smooth muscle. This connective tissue, which is mostly made up of collagen , contains nerves that innervate the smooth muscule layer. The connective tissue surrounding larger vessels also contains capillaries to bring nutrients to the tissue. Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, are made up of a single layer of endothelium and a small amount of connective tissue.
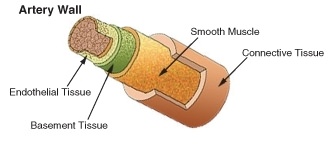
::血管基本结构相似。 内是一个细细胞层, 使血管表面表面形成光滑的衬里。 内组织是一种特殊的上皮类, 这是体内发现的四个组织类型之一。 内皮细胞在血管中具有重要的结构作用; 它们把整个循环系统从心脏到最小的毛细管都排在一起。 内膜周围有一层光滑的肌肉, 它在动脉中发育良好。 最后, 还有一层连接组织, 环绕着光滑的肌肉。 这种连接组织, 大部分由椰子组成, 内含光滑的肌肉层的神经。 大容器周围的连接组织也含有毛细的血管, 以给组织带来营养素。 最小的血管, 由单层的内衣和少量的接合组织组成。The structure of an artery wall.
::动脉墙的结构Arteries and Arterioles
::动脉和动脉The arteries carry blood away from the heart. As shown in Figure , arteries have thick walls that have three major layers: an inner endothelial layer, a middle layer of smooth muscle, and an outer layer of stretchy connective tissue (mostly collagen). The elastic qualities of artery walls allow them to carry pressurized blood from the heart while maintaining .
::动脉将血液从心脏中流出。如图所示,动脉有厚厚的墙壁,有三大层:内内皮层、中间的光滑肌肉层和外部的伸缩连接组织层(主要是科兰根 ) 。 动脉壁的弹性质能让动脉从心脏中携带压力化的血液,同时保持。The aorta is the largest artery in the body. It receives blood directly from the left ventricle of the heart through the aortic valve. The aorta branches into smaller arteries, and these arteries branch in turn, becoming smaller in diameter, down to arterioles. The arterioles supply the capillaries that carry nutrients to the body’s cells and tissues. The aorta is an elastic artery. When the left ventricle contracts to force blood into the aorta, it expands. This stretching gives the potential energy that will help maintain blood pressure during diastole, when the aorta contracts passively.
::动脉是身体中最大的动脉。 动脉直接通过动脉阀从心脏左心室直接接收血液。 动脉分泌为小动脉, 这些动脉分泌, 直径小一些, 直径小一些, 直到动脉。 动脉提供给身体细胞和组织带来营养的动脉。 动脉是一种弹性动脉。 当左心室约定将血液强制进入动脉时, 它会膨胀。 这种伸展提供了潜在的能量, 有助于保持异质期间的血压, 当动脉被动收缩时 。An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel that branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have thin, muscular walls, composed of one or two layers of smooth muscle, and are the primary site of vascular resistance. Vascular resistance is the resistance to flow that blood must overcome to be pumped through the circulatory system. Increasing vascular resistance is one way your body can increase blood pressure.
::动脉是一种小直径的血管,它从动脉中分流出来,并通向刺绣。 动脉有薄的肌肉壁,由一至两层光滑肌肉组成,是血管抵抗的主要场所。 血管抵抗是血液阻力,血液必须克服,才能通过循环系统抽出。 增加血管抵抗力是身体增加血压的一种方法。Veins and Venuoles
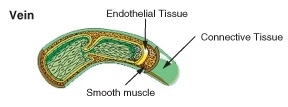
::排量和排量The internal structure of a vein.
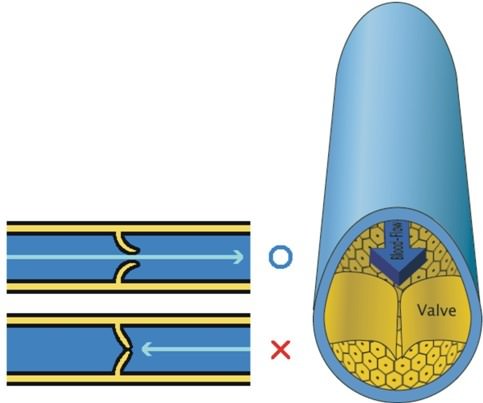
::静脉的内部结构Most veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart. The thick, outer layer of a vein is made up of collagen-containing connective tissue, as shown in Figure . The connective tissue is wrapped around bands of smooth muscle, while the interior is lined with endothelium. Most veins have one-way flaps called valves, shown in Figure , that prevent blood from flowing backward and pooling in the legs, feet, arms, or hands due to the pull of gravity. The location of veins can vary from person to person.
::大部分血管将脱氧血液还原为心脏。如图所示,血管的厚厚外层由含有钴的连接组织组成,如图所示。连接组织环绕着光滑肌肉的波段,而内部则与内相连。大多数血管有单向侧翼,称为“阀门”,如图所示,防止血液在腿部、脚部、手臂或手部向后流动,并因引力而聚集在一起。血管的位置因人而异。Valves found in veins prevent the blood from flowing backward and pooling in the lowest parts of the body such as the legs and feet.
::静脉中发现的阀门防止血液向后流,并聚集在身体的最低部位,如腿和脚。A venule is a small blood vessel that allows deoxygenated blood to return from the capillary beds to the larger blood vessels called veins. Venules have three layers: an inner endothelium composed of squamous epithelial cells that act as a membrane, a middle layer of muscle and elastic tissue, and an outer layer of fibrous connective tissue. The middle layer is poorly developed so that venules have thinner walls than arterioles.
::输血管是一种小血管,它使脱氧血液从毛虫床返回到更大的血管,称为血管。 输血管有三层:内内内皮由作为膜膜的细形上皮细胞组成,中间一层肌肉和弹性组织,外层是纤维连接组织。 中间层发育不良,因此,毒物的壁比动脉薄。Capillaries
::胶卷Capillaries are the smallest of a body's blood vessels, measuring 5-10 μm in diameter. Their size is shown in relation to body cells in Figure . Capillaries connect arterioles and venules, and they are important for the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other substances between blood and body cells.
::Capillarys是身体血管中最小的,直径为5-10微米,其大小与身体细胞的大小见图 。Capillarys连接了动脉和动脉,对于血液和身体细胞之间的氧、二氧化碳和其他物质交换非常重要。The structure of capillaries. Note their size in comparison to the cells around them.
::刺绣结构。 注意它们与周围细胞相比的大小 。The walls of capillaries are made of only a single layer of endothelial cells. This layer is so thin that molecules such as oxygen, , and can pass through them by and enter the . Waste products, such as carbon dioxide and urea, can diffuse back into the blood to be carried away for removal from the body. Capillaries are so small that the blood cells need to pass through them in a single file line. A capillary bed is the network of capillaries supplying an organ . The more metabolically active a tissue or organ is, the more capillaries it needs to get nutrients and oxygen.
::毛细膜的墙壁仅由单层内皮细胞组成。这个层是如此薄,以至于氧等分子能够通过它们,并且能够通过它们进入。 二氧化碳和尿素等废品可以再扩散到血液中,从身体中取出。 毛细膜太小,以至于血细胞需要通过单一的档案线。 毛细的床是提供器官的毛细膜网络。 一个组织或器官的代谢活性越强,它就越需要获得营养素和氧气。Blood vessels are roughly grouped as arterial or venous. This grouping is determined by whether the blood in the vessel is flowing away from (arterial) or toward (venous) the heart. In general, the term arterial blood is used to describe blood high in oxygen, although the pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood, and blood flowing in the pulmonary vein is rich in oxygen.
::血液血管大致按动脉或静脉分类。这种分类取决于血管中的血液是从(动脉)流出的还是流向(静脉)心脏的。一般而言,动脉血液一词用于描述氧气中的高血量,尽管肺动脉含有脱氧血液,而肺血管中的血液流却富含氧气。Roles of Blood Vessels
::鲜血船的作用Blood vessels are not involved in regulating the transport of blood; the endocrine and nervous systems do that. However, arteries and veins can regulate their inner diameters by contractions of the smooth muscle layer. This widening or narrowing of the blood vessels changes the blood flow to the organs of the body. This process is controlled by the autonomic nervous system ; it is not controlled consciously.
::血液血管不参与血液运输的管理;内分泌和神经系统也参与管理,但是动脉和血管可以通过光滑肌肉层的收缩来调节其内直径;血管的扩大或缩小会改变血液流向人体器官;这一过程由自主神经系统控制;它不是有意识地控制的。Vasodilation is a process by which blood vessels in the body become wider due to the relaxation of the smooth muscle in the vessel wall. This reduces blood pressure since there is more room for the blood to move through the vessel. Endothelium of blood vessels uses nitric oxide to signal the surrounding smooth muscle to relax, which dilates the artery and increases blood flow. Nitric oxide is a vasodilator.
::血管消融是一种过程,通过这个过程,由于容器壁上光滑的肌肉松动,血管中的血管会变得更宽,从而降低了血压,因为血液在容器中流动的空间更大。血管的使用氧化氮来信号周围的光滑肌肉放松,从而扩大动脉,增加血液流动。氧化氮是一种血管病。Vasoconstriction is the constriction of blood vessels (narrowing or becoming smaller in cross-sectional area) by contracting the vascular smooth muscle in the vessel walls. Vasoconstriction is controlled by substances such as some and neurotransmitters , which are called vasoconstrictors. For example, the “fight or flight” hormone epinephrine is a vasoconstrictor that is released by the adrenal glands .
::血管收缩是指通过在容器壁上绑定血管滑动肌肉来收缩血管(在横截面区域缩小或变小),使血管收缩受到某些物质和神经传导器的控制,这些物质被称为血管收缩器,例如,“战斗或飞行”激素肾上腺是肾上腺释放的血管收缩器。Permeability of the endothelium is important for the release of nutrients to the tissue. Permeability is the ability of a membrane to allow certain molecules and ions to pass through it by diffusion. Permeability of the endothelium increases during an immune response , which allows white blood cells and other substances to get to the site of injury or irritation.
::的渗透性对于向组织释放养分很重要,渗透性是指膜能够允许某些分子和离子通过扩散通过它。在免疫反应期间,的渗透性增加,使白血细胞和其他物质能够到达受伤或刺激的地点。Oxygen, which is bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells for transport through the body, is the most critical nutrient carried by the blood. In all arteries apart from the pulmonary artery, hemoglobin is highly saturated (95-100%) with oxygen. In all veins apart from the pulmonary vein, the hemoglobin is desaturated at about 70%. (The values are reversed in the pulmonary circulation .)
::与红血细胞中的血红蛋白相连的Oxygen通过身体迁移,是血液携带的最关键营养物质。除肺动脉外,所有动脉中血红蛋白都含有氧气(95-100%),除肺静脉外,所有静脉中血红蛋白的饱和度约为70%。 (在肺循环中,值出现逆向。 )Blood Vessels and Blood Pressure
::血浆和血压Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. The pressure of the circulating blood gradually decreases as blood moves from the arteries, to the arterioles, to the capillaries, and to the veins. The term "blood pressure" generally refers to arterial pressure, which is the pressure in the larger arteries that take blood away from the heart. Arterial pressure results from the force that is applied to the blood by the contracting heart. When the heart contracts, the blood “presses” against the walls of the arteries.
::血液压力是指血管壁上循环血液所施加的强度,循环血液的压力随着血液从动脉、动脉、血管和血管的移动而逐渐减少,“血压”一词一般指动脉压力,即大动脉中将血液从心脏取出的压力,动脉压力来自接触心脏对血液施压的力度。当心脏收缩时,血液“压住”动脉的墙壁。The systolic arterial pressure is defined as the peak pressure in the arteries, which occurs near the beginning of the cardiac cycle; the diastolic arterial pressure is the lowest pressure (at the resting phase of the cardiac cycle).
::循环动脉压力的定义是动脉中的峰值压力,它发生在心脏循环开始的附近;断开动脉压力是最低的压力(在心脏循环的休息阶段)。Arterial pressure is most commonly measured by a sphygmomanometer, which is shown in Figure . The height of a column of mercury indicates the pressure of the circulating blood. Although many modern blood pressure devices no longer use mercury, values are still universally reported in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
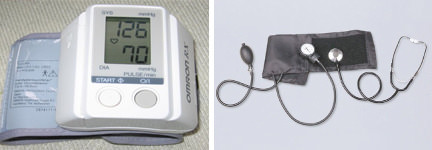
::动脉压力最常用血压计测量,如图12所示。一列汞的高度表明循环血液的压力。尽管许多现代血压装置不再使用汞,但以毫米汞(mmHg)表示的数值仍然普遍呈报。The new and the “classic” ways to measure blood pressure. A digital sphygmomanometer, shown on the left, runs on electricity or batteries and measure blood pressure automatically. The cuff, which you can see behind the digital readout, is wrapped around the upper arm, just like the cuff of the older devices. The cuff then inflates automatically and measures blood pressure as the cuff deflates. The older, mechanical sphygmomanometer with a cuff, pressure reader, and stethoscope is shown on the right. The cuff is inflated and deflated manually while a medical technician listens for related changes in the sound of blood moving through arteries in the arm.
::测量血压的新方法和“古典”方法。 左侧显示的数字血压计在电或电池上运行,并自动测量血压。 在数字读出后可以看到的手铐,就像旧装置的手铐一样,紧紧缠在上臂上方。 袖口然后自动充气,测量血压,像手铐减肥一样。 右侧显示的是带手铐、 压力读器和听诊器的更老的机械血压计。 袖口被膨胀,手动减缩,而医疗技师则聆听手臂动脉的血液声音的有关变化。Blood Pressure Ranges
::血压范围In the U.S., the healthy ranges for arterial pressure are the following:
::在美国,动脉压力的健康范围如下:-
Systolic: less than 120 mm Hg.
::控制线:低于120毫米汞。 -
Diastolic: less than 80 mm Hg.
::透析器:少于80毫米汞。
Blood pressure is usually written as systolic/diastolic mm Hg; for example, a reading of 120/80 mm Hg is said as "one hundred and twenty over eighty." These measures of arterial pressure are not static, but go through natural variations from one heartbeat to another and throughout the day (in a circadian rhythm). Factors such as age, gender, and race influence blood pressure values. Pressure also varies with , emotional reactions, sleep, stress, nutritional factors, drugs , and disease.
::血液压力通常被写成“双向/直径毫米汞 ” ; 比如, 120/80毫米汞的读数被称为“ 120/80 / 80 ”。 这些动脉压力的量度不是静态的,而是通过从心跳到另一个的自然变化以及整个白天(以环形节奏)的自然变化。年龄、性别和种族等因素影响血压值。 压力也因情感反应、睡眠、压力、营养因素、药物和疾病而不同。Studies have shown that people whose systolic pressure is around 115 mm Hg rather than 120 mm Hg have fewer health problems. Clinical trials have shown that people who have arterial pressures at the low end of these ranges have much better long term . For this reason, some researchers say that 115/75 mm Hg should be the ideal measurement.
::研究表明,其周期性压力约为115毫米汞而不是120毫米汞的人的健康问题较少,临床试验表明,在这些距离的低端有动脉压力的人具有更好的长期性。 为此原因,一些研究人员说,115/75毫米汞应该是理想的测量标准。Hypertension is a condition in which a person’s blood pressure is chronically high. Hypertension is said to be present when a person's systolic blood pressure is always 140 mm Hg or higher and/or their diastolic blood pressure is always 90 mm Hg or higher. Blood pressure readings between 120/80 mm Hg and 139/89 mm Hg are called prehypertension. Prehypertension is not a disease category; rather, it is a way to identify people who are at high risk of developing hypertension.
::高血压是一个人的血压长期居高不下的一个条件。 据说当一个人的静脉血压总是140毫米汞或更高和/或他们的阴道血压总是90毫米汞或更高时会出现高血压。 120/80毫米汞和139/89毫米汞之间的血压读数被称为前高血压。 前高血压不是一个疾病类别;而是一种识别高血压高危人群的方法。Arterioles and Blood Pressure
::青树和血压Arterioles have the greatest collective influence on both local blood flow and overall blood pressure. They are the primary "adjustable nozzles" in the blood system, across which the greatest pressure drop occurs. Heart output (cardiac output) and systemic vascular resistance, which refers to the collective resistance of all of the body's arterioles, are the principal determinants of arterial blood pressure at any given moment.
::青蒿素对当地血液流动和总体血压具有最大的集体影响。 青蒿素是血液系统中主要的“可调适的喷嘴 ” , 其间的压力降幅最大。 心脏输出(心力输出)和系统血管抵抗(指身体所有动脉的集体抵抗)是任何特定时刻动脉血压的主要决定因素。Summary
::摘要-
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart, while veins are blood vessels that return blood to the heart.
::动脉是血管,从心脏流出血液,而血管是血管,将血液还给心脏。 -
Blood vessels all have a similar basic structure: the endothelium forms the innermost layer, then a layer of smooth muscle, and finally a layer of connective tissue that surrounds the smooth muscle.
::血液容器的基本结构都相似:内形成最深层层,然后形成一层光滑的肌肉,最后形成一层围绕光滑肌肉的连接组织。 -
The walls of capillaries are made of only a single layer of endothelial cells, so molecules such as oxygen, water, and lipids can pass through them by diffusion and enter the body tissues.
::毛细膜的墙壁只有一层内皮细胞组成,因此,氧、水和脂质等分子可以通过扩散穿过它们,进入人体组织。 -
In all arteries apart from the pulmonary artery, hemoglobin is highly saturated (95-100%) with oxygen. In all veins apart from the pulmonary vein, the hemoglobin is desaturated at about 70%. (The values are reversed in the pulmonary circulation.)
::在除肺动脉以外的所有动脉中,血红蛋白都与氧高度饱和(95-100% ) 。在除肺静脉之外的所有静脉中,血红蛋白的饱和度约为70%。 (在肺循环中,值被逆转。 ) -
Hypertension is said to be present when a person's systolic blood pressure is always 140 mm Hg or higher and/or their diastolic blood pressure is always 90 mm Hg or higher.
::据说,当一个人的周期性血压始终为140毫米汞或更高和/或他们的异口型血压为90毫米汞或更高时,就会出现高血压。
Review
::回顾-
What small blood vessels allows deoxygenated blood to return from the capillaries to the veins?
::是什么小血管能让脱氧血液从血管里 恢复到血管里? -
What kind of specialized tissue make up the endothelium?
::哪种特殊组织构成? -
How do veins ensure that blood does not flow backwards?
::血管如何确保血液不会回流? -
How thin are capillaries?
::毛细有多细? -
Give an example of a hormone that causes blood vessels to narrow.
::举个激素的例子 激素会导致血管缩小
-
Arteries
are the large, muscular vessels that carry blood away from the heart.