血血型
章节大纲
-
A, B, AB, O, +, -. Does it really matter?
::A,B,AB,O,+,真的重要吗?It sure does. These represent blood type, which is determined by markers on the outside of red blood cells . Just like any other , if your body detects a cell with something on its outside that it does not recognize, then your body will decide it does not belong.
::确实如此。 这些代表血型, 血型由红细胞外部的标记决定。 就像任何其他的一样, 如果你的身体检测到一个细胞, 外表上的东西是它无法识别的, 那么身体就会决定它不属于它。Blood Types
::血血型Blood type (also called a blood group ) is determined by the presence or absence of certain molecules, called antigens , on the surface of red blood cells. An antigen is a molecule or substance that causes an immune response . Blood type antigens may be or , depending on the blood group system. The antigens on a person’s own are recognized by their immune system as “self” antigens, and their immune system does not attack them. However, if a person is exposed to a blood group antigen that is different from their own blood group, the person’s immune system will produce antibodies against the donor blood antigens. These antibodies can bind to antigens on the surfaces of transfused red blood cells (or other tissue cells), often leading to destruction of the cells by the immune system.
::血型(也称为血型)由红血细胞表面某些分子(称为抗原)的存在或不存在决定。抗原是一种分子或物质,引起免疫反应。血型抗原可能或取决于血型系统。一个人自己的抗原被其免疫系统确认为“自我”抗原,其免疫系统不会攻击他们。然而,如果一个人接触不同于其血型的血型抗原,那么其免疫系统将产生抗体来对抗捐赠者血型抗原。这些抗体可以与转基因红血细胞(或其他组织细胞)表面的抗原捆绑在一起,常常导致免疫系统对细胞的破坏。The erythrocyte surface antigens that have one , or a group of very closely linked genes , are collectively called a "blood group system." There are approximately 30 known blood group systems in humans, but the ABO blood group system and the Rhesus (Rh) blood group system are the most important for blood transfusions.
::红细胞表面抗原中含有一种或一组紧密相连的基因,统称为“血组系统 ” 。 人类中大约有30个已知的血组系统,但ABO血组系统和Rhsus(Rh)血组系统是输血最重要的系统。ABO Blood Group System
::ABO 血型系统In 1875, a German physiologist, Leonard Landois, reported that the blood cells of a human and an would clump together when mixed. In the early 1900s, Austrian biologist and physician Karl Landsteiner pointed out that a similar clumping reaction occurred when the blood of one person was transfused with another. He determined that this might be the cause of shock, jaundice, and the release of hemoglobin that had followed some earlier attempts at person-to-person blood transfusions.
::1875年,一位德国生理学家Leonard Landois(Leonard Landois)报告说,人类的血细胞在混合时会凝聚在一起。 1900年代初,奥地利生物学家和医生Karl Landsteiner(Karl Landsteiner)指出,当一个人的血液被与另一个人的血液混合时,也发生了类似的阻塞反应。 他确定这可能导致休克、黄玉和血红蛋白的释放,此前曾试图进行人与人之间的输血。In 1909, Landsteiner classified blood into the A, B, AB, and O groups. He also showed that transfusions between two people of the same blood group did not result in the destruction of blood cells and that clumping occurred only when a person was transfused with the blood of a person belonging to a different blood group.
::1909年,Landsteiner将血液分类为A、B、AB和O类,他还表明,同一血族中两个人的输血没有导致血细胞的破坏,只有当一个人与属于不同血族的人的血液混合时,才会出现排挤。The "A" and "B" of the ABO blood group refer to two carbohydrate antigens found on the surfaces of red blood cells. There is not an O antigen. Type O red blood cells have neither type A nor type B antigens on their surfaces, as listed in Table . Antibodies are found in the blood plasma. The blood type of a person can be determined by using antibodies that bind to the A or B antigens of red blood cells.
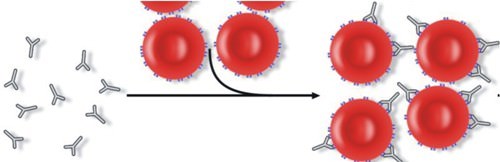
::ABO血组的“A”和“B”指红血细胞表面发现的两种碳水化合物抗原,没有O抗原,O型红血细胞在表A所列表面没有A型和B型抗原。血浆中发现了抗体。一个人的血型可以通过使用与A或B型红血细胞抗原结合的抗体来确定。Blood Types, Antigen Types, and Antibody Types Blood Type Antigen Type Serum (Plasma) Antibodies Can Receive Blood from Types Can Donate Blood to Types A A anti-B A, O A, AB B B anti-A B, O B, AB AB A and B none AB, A, B, O AB O none anti-A, anti-B O AB, A, B, O Agglutination is the clumping of red blood cells that occurs when different blood types are mixed together, as shown in Figure . It involves a reaction between antigens on the surfaces of red blood cells and protein antibodies in the blood plasma. Mixing different blood types together can cause agglutination, a process that has been used as a way of determining a person’s blood type.
::如图所示,浸泡是不同血型混合在一起时出现的红血细胞的堵塞。 它涉及红血细胞表面的抗原与血浆中的蛋白抗体之间的反应。 将不同的血型混合在一起可以造成浸泡,这个过程被用来确定一个人的血型。Antigens on the red blood cell surface. Antibodies attach to the antigens on the red blood cell, causing the blood cells to clump together. This leads to agglutination of the blood.
::红色血细胞表面的抗原,抗体附在红色血细胞上的抗原上,导致血细胞聚集在一起,从而导致血液的混入。Rhesus Blood Group System
::Rhesus血型血型系统The Rhesus system is the second most significant blood group system for human blood transfusion. The most significant Rhesus antigen is called the RhD antigen (also called Rhesus factor). A person either has or does not have the RhD antigen on the surfaces of their red blood cells. This is usually indicated by adding either a "RhD positive" (does have the RhD antigen) or a "RhD negative" (does not have the antigen) suffix to the ABO blood group (see the blood agglutination test in Figure ).
::Rhesus系统是人类输血的第二大血族系统,最重要的Rhsus抗原称为RhD抗原(又称Rhsus因子)。一个人的红血细胞表面有RhD抗原,或者没有RhD抗原。这通常通过添加“RhD阳性”(有RhD抗原)或“RhD阴性”(没有抗原)与ABO血组的后缀(见图中的血液浸泡试验)来表示。The Rhesus system is named after the Rhesus monkey, in which the antigen was first discovered by Karl Landsteiner and Alexander S. Wiener in 1937. The importance of the Rh factor was realized soon after. Dr. Phillip Levine, a pathologist who worked at a New York hospital, made the connection between the Rh factor and the incidence of a blood disease in newborn babies. The disease, called hemolytic disease of the newborn, is a condition that develops while the fetus is in the womb. If a mother is RhD negative and the father is RhD positive, the fetus may inherit the dominant RhD positive trait from the father. The RhD negative mother can make antibodies against the RhD antigens of her developing baby. This can happen if some of the fetus' blood cells pass into the mother's blood circulation or if the mother has received an RhD positive blood transfusion.
::Rhesus系统是以Rhesus 猴子命名的,其中抗原最初由Karl Landsteiner和Alexander S. Wiener于1937年首次发现;Rh因素的重要性在在纽约医院工作的一个病理学家Phillip Levine博士不久就实现;他把Rh因素与新生婴儿的血液疾病发病率联系起来;这个疾病被称为新生儿的血解疾病,是在胎儿在子宫里发育的;如果母亲为RhD阴性,而父亲为RhD阳性,胎儿可以继承父亲的主要RhD阳性特征;RhD阴性母亲可以对婴儿的RhD抗原产生抗体;如果胎儿的一些血细胞进入母亲的血液循环,或者如果母亲获得RhD阳性血液输血,这可能会发生。The fetus’ red cells are broken down and the fetus can develop anemia. This disease ranges from mild to very severe, and fetal death from heart failure can occur. Most RhD diseases can be prevented by treating the mother during or soon after childbirth. The mother is injected with anti-RhD antibodies, so that the baby’s red blood cells are destroyed before her body can produce antibodies against them. If a pregnant woman is known to have anti-RhD antibodies, the RhD blood type of the fetus can be tested by analysis of fetal in maternal plasma to assess the risk to the fetus of RhD disease.
::胎儿的红细胞被打破,胎儿可以发展出贫血症。 这种疾病从温和到非常严重不等,胎儿死于心脏衰竭。 大部分RHD疾病可以通过在分娩期间或分娩后不久对母亲进行治疗来预防。 母亲注射抗RHD抗体,这样婴儿的红细胞就会在身体产生抗体之前被摧毁。 如果孕妇已知有抗RHD抗体,那么胎儿的RHD血型可以通过对孕妇血浆中的胎儿进行血浆分析来检测,以评估RHD病对胎儿的风险。The presence or absence of the ABO group antigens and the RhD antigens is always determined for all recipient and donor blood. Figure shows a routine way in which a person’s ABO blood group is determined.
::ABO组抗原和RhD抗原的存在或不存在,总是对所有接受者和捐献者的血液进行确定。 图显示了确定一个人的ABO血组的常规方法。A bedside blood grouping card showing the agglutination of the blood with anti-A and anti-Rh(D), but not with anti-B. Therefore, the blood group is A positive. This method of blood grouping relies on seeing an agglutination reaction to determine a person’s blood group. The card has dried blood group antibody reagents fixed onto its surface. A drop of the person’s blood is placed on each area on the card. The presence or absence of visual agglutination allows a quick method of determining the ABO and Rhesus groups of the person.
::床边血层分类卡,显示血液与抗A和抗Rh(D)的分泌情况,但没有与反B的分泌情况。 因此,血层为阳性。 这种血层分类方法取决于是否看到一种分泌反应以确定一个人的血层。卡片上固定在表面的血层血层抗体试剂已经干涸。卡片上每个区域都放置了一滴人的血。由于存在或没有视觉分泌,可以快速确定一个人的ABO和Rhesus群体。Blood Products
::血血制品In order to provide maximum benefit from each blood donation and to extend shelf-life, blood banks separate some whole blood into several different products. Some of the most common of these products are packed red blood cells, plasma, platelets , and fresh frozen plasma. Units of packed red blood cells are made by removing as much of the plasma as possible from whole blood units. Clotting factors made by genetic engineering are now routinely used for the treatment of the clotting disorder hemophilia, so the risk of possible infection from donated blood products is avoided.
::为了从每次献血中获取最大利益并延长保存期,血库将一些全血分解成几种不同的产品,其中最常见的产品是包装的红血细胞、血浆、小板和新鲜的冷冻等离子体;用尽可能多地从整个血细胞中去除血浆来制造包装的红血细胞单位;现在,遗传工程造成的消化因子经常用于治疗凝聚性紊乱血友病,从而避免捐赠的血制品可能感染的风险。Universal Donors and Universal Recipients
::普遍捐助者和普遍接受者Regarding the donation of packed red blood cells, individuals with type O negative blood are often called universal donors , and those with type AB positive blood are called universal recipients . Type O red blood cells do not have the A or B antigens and can be given to people with a different ABO blood group. The blood plasma of an AB person does not contain any anti-A or anti-B antibodies, so they can receive any ABO blood type . The possible reactions between anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the donor blood and the recipient’s red blood cells are usually not a problem because only a small volume of plasma that contains antibodies is given to the recipient. Refer to Table for a complete listing of ABO antigens and antibodies that are involved in the ABO system.
::关于包装的红血球捐赠,O型阴性血型个人通常被称为普遍捐赠者,AB型阳性血型个人则被称为普遍接受者。O型红血细胞没有A型或B型抗原,可以提供给不同ABO血族的人。AB型人的血浆不含任何抗A型或B型抗体,因此他们可以得到任何ABO血型。捐赠者的血液中抗A型和B型抗体之间可能的反应通常不是问题,因为接受者只得到少量含有抗体的血浆。参考表格列出参与ABO系统的ABO抗原和抗体。In April 2007, researchers discovered a way to convert blood types A, B, and AB to O; the method uses that remove the antigens on the surfaces of the red blood cells.
::2007年4月,研究人员发现了一种将A型、B型和AB型血液转化为O型血液的方法;这种方法用于去除红细胞表面的抗原。Other Blood Group Systems
::其他血型系统You probably have heard a lot about the ABO and Rhesus (RhD) blood group systems by now, but you have probably not heard much about the other systems. Many other antigens are found on the of red blood cells. For example, an individual can be AB RhD positive while being M and N positive (MNS system), K positive (Kell system), Le a or Le b negative (Lewis system), Duffy positive or Duffy negative (Duffy system), and so on, being positive or negative for each blood group system antigen. Many of the blood group systems were named after the patients in whom the antibodies were first found.
::你可能已经听说过很多关于ABO和Rhesus(RhD)血族的系统,但你可能还没有听说过很多其他的系统。在红血细胞中还发现了许多其他抗原。例如,一个人在M和N(MNS)呈阳性(MNS系统)、K呈阳性(Kell系统)、Lea或Leb呈阴性(Lewis系统)、Duffy呈阳性或Duffy呈阴性(Duffy系统),等等,每个血族的抗原都是正的或负的。许多血族系统是以最初发现抗体的病人命名的。Some blood group systems are associated with a disease. For example, the Kell antigen is associated with McLeod syndrome, a in which the red blood cells are spiky shaped. Certain other blood group systems may affect resistance to infections, an example being the resistance to specific malaria seen in individuals who lack the Duffy antigen. The Duffy antigen is less common in ethnic groups from areas with a high incidence of malaria.
::例如,Kell抗原与McLeod综合症有关,其中红血细胞成型,某些其他血细胞系统可能会影响对感染的抗药性,一个例子是缺乏Duffy抗原的个人对特定疟疾的抗药性,Duffy抗原在疟疾高发地区的族裔群体中不太常见。Rare blood types can cause supply problems for blood banks and hospitals. For example, Duffy-negative blood occurs much more frequently in people of African origin, and the rarity of this blood type in the rest of the can result in a shortage of Duffy-negative blood. Similarly for RhD negative people, there is a risk associated with traveling to parts of the world where supplies of RhD negative blood are rare, particularly East Asia.
::罕见的血型可能会给血库和医院造成供应问题,例如,在非洲血统的人中,Duffy-阴性血液更频繁发生,其余血型的罕见可能导致Duffy-阴性血液的短缺。 同样,对于RhD负性人群来说,前往世界上很少有RhD阴性血液供应的地区,特别是东亚,也存在风险。Summary
::摘要-
Blood type (also called a blood group) is determined by the presence or absence of certain molecules, called antigens, on the surfaces of red blood cells.
::血型(也称血型)取决于红细胞表面是否存在某些分子,即所谓的抗原。 -
The antigens on a person’s own body cells are recognized by their immune system as “self” antigens, and their immune system does not attack them.
::一个人自己的身体细胞上的抗原被其免疫系统确认为 " 自我 " 抗原,其免疫系统不攻击这些抗原。 -
The "A" and "B" of the ABO blood group refer to two carbohydrate antigens found on the surfaces of red blood cells. Type O red blood cells have neither type A or type B antigens on their surfaces.
::ABO血组中的“A”和“B”指红细胞表面发现的两种碳水化合物抗原,O型红细胞表面没有A型或B型抗原。 -
A person either has or does not have the RhD antigen on the surfaces of their red blood cells. This is usually indicated by adding either a "RhD positive" or a "RhD negative" suffix to the ABO blood group.
::一个人的红细胞表面有或没有RhD抗原,通常通过在ABO血组中添加“RhD正数”或“RhD负数”后缀来表示。 -
Individuals with type O negative blood are often called universal donors, and those with type AB positive blood are called universal recipients.
::O型阴性血的人常常被称为普遍捐赠者,AB型阳性血的人被称为普遍接受者。
Review
::回顾-
How are blood group systems determined?
::血组系统是如何确定的? -
What blood group systems are most important for blood transfusions?
::哪些血组系统对输血最重要的? -
Give an example of a blood group system that is associated with disease.
::举一个与疾病有关的血型系统的例子。 -
What is a possible complication for universal recipients?
::对于普遍接受者来说,什么是可能的复杂问题? -
What causes agglutination, and what is a possible use for it?
::何为造成混凝土化? 其可能用途是什么?
-
Blood type (also called a blood group) is determined by the presence or absence of certain molecules, called antigens, on the surfaces of red blood cells.