DNA DNA
章节大纲
-
What Makes You...You?
::是什么让你... 你?This young woman has naturally red hair. Why is her hair red instead of some other color? In general, what gives her the specific traits she has? There is a molecule in human beings and most other living things that is largely responsible for their traits. The molecule is large and has a spiral structure in eukaryotes . What molecule is it? With these hints, you probably know that the molecule is DNA.
::这个年轻女人自然有红色头发。为什么她的头发是红色而不是其他颜色?一般而言,是什么让她有了她的特殊性格?人类和大多数其他生物中有一个分子是他们特征的主要原因。分子是巨大的,在银河菌中有一个螺旋结构。是什么分子?这些暗示,你可能知道分子是DNA。Introducing DNA
::引进DNAToday, it is commonly known that DNA is the genetic material that is passed from parents to offspring and determines our traits. For a long time, scientists knew such molecules existed — that is, they were aware that genetic information is contained within biochemical molecules. What they didn’t know was which molecules play this role specifically. In fact, for many decades, scientists thought that were the molecules that contain genetic information.
::如今,众所周知,DNA是遗传物质,从父母传给后代,决定着我们的特性。 长期以来,科学家们知道这些分子的存在 — — 也就是说,他们知道遗传信息包含在生化分子中。 他们不知道哪个分子具体扮演了这一角色。 事实上,几十年来,科学家们一直认为这些分子包含基因信息。Discovery that DNA i s the Genetic Material
::发现DNA是遗传物质Determining that DNA is the genetic material was an important milestone in biology . It took many scientists undertaking creative over several decades to show with certainty that DNA is the molecule that determines the traits of organisms . This research began in the early part of the 20th century.
::确定DNA是遗传物质是生物学中的一个重要里程碑。 数十年来,许多科学家都进行了创造性研究,肯定地表明DNA是决定生物特征的分子。 这项研究始于20世纪初。Griffith's Experiments with Mice
::格里菲斯与老鼠的实验The first important discovery was made in the 1920s. An American scientist named Frederick Griffith was studying mice and two different strains of a , called R (rough)-strain and S (smooth)-strain. He injected the two bacterial strains into mice. The S-strain was virulent and killed the mice, whereas the R-strain was not virulent and did not kill the mice. You can see these details in the diagram . Griffith also injected mice with S-strain bacteria that had been killed by heat. As expected, the dead bacteria did not harm the mice. However, when the dead S-strain bacteria were mixed with live R-strain bacteria and injected, the mice died.
::第一个重要发现发生在1920年代。一个名叫弗雷德里克·格里菲斯的美国科学家正在研究小鼠和两个不同的菌株,一个叫R(rough)-strain和S(smooth)-strain。他把这两个菌株注入小鼠体内。S-strain是毒药,杀死小鼠,而R-strain不是毒药,没有杀死小鼠。在图表中可以看到这些细节。格里菲斯也用被热杀死的S-strain细菌给小鼠注射。正如预期的那样,死细菌并没有伤害小鼠。然而,当死S-strain细菌与活的R-strain细菌混合并注射时,小鼠死亡。Griffith’s Experimental Results. Griffith showed that a substance could be transferred to harmless bacteria and make them deadly.
::格里菲斯的实验结果。 格里菲斯表明,一种物质可以转移到无害细菌,使其致命。Based on his observations , Griffith deduced that something in the dead S-strain was transferred to the previously harmless R-strain, making the R-strain deadly. What was this "something?" What type of substance could change the characteristics of the organism that received it?
::根据他的观察,格里菲斯推断,死亡的S-S-S-Srain中有些物质被转移到了先前无害的R-S-Srain中,使R-S-S-Srain致命。什么是“东西?”什么物质可以改变接受该物质的生物的特性?Avery and His Colleagues Make a Major Contribution
::艾弗里和他的同事作出了重大贡献In the early 1940s, a team of scientists led by Oswald Avery tried to answer the question raised by Griffith’s research results. First, they inactivated various substances in the S-strain bacteria. Then they killed the S-strain bacteria and mixed the remains with live R-strain bacteria. (Keep in mind that the R-strain bacteria normally did not harm the mice.) When they inactivated proteins, the R-strain was deadly to the injected mice. This ruled out proteins as the genetic material. Why? Even without the S-strain proteins, the R-strain was changed (or transformed) into the deadly strain. However, when the researchers inactivated DNA in the S-strain, the R-strain remained harmless. This led to the conclusion that DNA — and not protein — is the substance that controls the characteristics of organisms. In other words, DNA is the genetic material.
::1940年代初期,由奥斯瓦尔德·艾弗里率领的一组科学家试图回答格里菲斯的研究成果提出的问题。 首先,他们使斯丁氏菌中的各种物质停止活动。 然后,他们杀死了斯丁氏细菌,并将残留物与活的R-strain细菌混为一谈。 (记住R-strain细菌通常不会伤害小鼠。 )当他们不活化蛋白时,R-strain对被注射的老鼠是致命的。这排除了蛋白质作为遗传物质。 为什么?即使没有斯丁氏蛋白,R-strain也变了(或变了)致命菌株。然而,当研究者在斯丁氏菌中活化DNA时,R-strain的DNA仍然无害。这导致这样的结论,即DNA — 而不是蛋白质 — 是控制生物特性的物质。换句话说,DNA是遗传物质。Hershey and Chase Confirm the Results
::贺喜和大通确认结果The conclusion that DNA is the genetic material was not widely accepted until it was confirmed by additional research. In the 1950s, Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase did experiments with and bacteria. Viruses are not . Instead, they are basically DNA (or RNA) inside a protein coat. To reproduce, a virus must insert its own genetic material into a cell (such as a bacterium). Then, it uses the cell’s machinery to make more viruses. The researchers used different radioactive elements to label the DNA and proteins in DNA viruses . This allowed them to identify which molecule the viruses inserted into bacterial cells. DNA was the molecule they identified. This confirmed that DNA is the genetic material.
::DNA是基因材料这一结论直到得到进一步研究的证实后才被广泛接受。1950年代,Alfred Hershey和Martha Chase对细菌进行了实验。病毒不是。相反,它们基本上是蛋白质外衣中的DNA(或RNA ) 。要繁殖,病毒必须把自己的遗传材料插入细胞(如细菌 ) 。然后,它利用细胞的机器制造更多的病毒。研究人员使用不同的放射性元素在DNA病毒中给DNA和蛋白质贴上标签。这使得他们能够识别病毒插入细菌细胞的分子。DNA是他们识别的分子。这证实了DNA是遗传物质。Chargaff Focuses on DNA Bases
::关注DNA基点Other important discoveries about DNA were made in the mid-1900s by Erwin Chargaff. He studied DNA from many different and was especially interested in the four different nitrogen bases of DNA: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Chargaff found that concentrations of the four bases differed between species . Within any given species, however, the concentration of adenine was always the same as the concentration of thymine, and the concentration of guanine was always the same as the concentration of cytosine. These observations came to be known as Chargaff’s rules . The significance of the rules would not be revealed until the double-helix structure of DNA was discovered.
::Erwin Doffaff 于19世纪中叶发现了关于DNA的其他重要发现。 他研究了许多不同的DNA,并特别关心DNA的四个不同的氮基:adenine(A)、guanine(G)、cytosine(C)和themine(T ) 。 他发现这四个基点的浓度在物种之间有差异。 但在任何特定物种中,的浓度总是与甲状腺的浓度相同,而的浓度总是与cytosine的浓度相同。 这些观察结果被称为代名词规则。 在发现DNA的双螺旋结构之前,规则的意义是不会暴露的。Discovery of the Double Helix
::发现双螺旋After DNA was shown to be the genetic material, scientists wanted to learn more about it and its structure. James Watson and Francis Crick are usually given credit for discovering that DNA has a double helix shape like a spiral staircase, as shown in the illustrations . In fact, Watson and Crick's discovery of the double helix depended heavily on the prior work of Rosalind Franklin and other scientists, who had used X-rays to learn more about DNA’s structure. Unfortunately, Franklin and these others have not always been given credit for their important contributions to the discovery of the double helix.
::在DNA被证明是遗传物质之后,科学家们希望更多地了解DNA及其结构。 詹姆斯·沃森和弗朗西斯·克里克通常会因为发现DNA的双螺旋形状像螺旋楼梯而得到赞扬,如插图所示。 事实上,华生和克里克发现双螺旋后,严重依赖罗萨琳德·富兰克林和其他科学家以前的工作,他们曾经用X光片来了解DNA的结构。 不幸的是,富兰克林和其他人对发现双螺旋结构的重要贡献并不总是得到赞扬。The DNA molecule has a double helix shape. This is the same basic shape as a spiral staircase. Do you see the resemblance? Which parts of the DNA molecule are like the steps of the spiral staircase?
::DNA分子有双螺旋形状。 这是螺旋楼梯的基本形状。 您看到相似之处吗? DNA分子的哪个部分像螺旋楼梯的阶梯?The double helix shape of DNA, along with Chargaff’s rules, led to a better understanding of DNA. As a , DNA is made from nucleotide monomers . Long chains of nucleotides form polynucleotides , and the DNA double helix consists of two polynucleotide chains. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of the four bases (adenine, cytosine, guanine, or thymine). The sugar and phosphate molecules in adjacent nucleotides bond together and form the "backbone" of each polynucleotide chain.
::DNA的双螺旋形状,加上阿卡夫的规则,使人们更好地了解了DNA。作为一个DNA,DNA是由核糖核酸单体制成的。长链的核酸单体形成多核酸,而DNA的双螺旋体由两个多核酸链组成。 每一种核酸由糖(脱氧核糖核酸)组成,一个磷酸组,四个基体(九、细胞素、guanine或甲胺)之一组成。 相邻的核糖核酸单体联结中的糖和磷酸分子组成了每个聚核酸链的“后骨 ” 。Scientists concluded that bonds between the bases hold together the two polynucleotide chains of DNA. Moreover, adenine always bonds with thymine, and cytosine always bonds with guanine. That's why these pairs of bases are called complementary base pairs . If you look at the nitrogen bases in the figure , you will see why the bases bond together only in these pairings. Adenine and guanine have a two-ring structure, whereas cytosine and thymine have just one ring. If adenine were to bond with guanine, as well as thymine, for example, the distance between the two DNA chains would vary . When a one-ring molecule ( like thymine) always bonds with a two-ring molecule (like adenine), however, the distance between the two chains remains constant. This maintains the uniform shape of the DNA double helix. The bonded base pairs (A-T and G-C) stick into the middle of the double helix, forming the "steps" of the spiral staircase.
::科学家们得出结论, 基底之间的纽带将DNA的两个多核酸链连接在一起。 此外, 亚丁总是与甲状腺联系在一起, 细胞素也总是和guanine联系在一起。 这就是为什么这些基底配对被称为互补基底对。 如果你看一下图中的氮基底, 你会看到为什么基底连接在一起, 亚丁和guanine只有这些配对。 亚丁和guanine有双环结构, 而cytosine和Hymine只有一个环形圈。 如果亚丁和Hymine连接在一起, 比如说, 两根DNA链之间的距离就会不同。 当一环分子( 如甲状腺) 总是和两环分子( 如adenine) 连接在一起时, 两个链的距离会保持不变。 这维持了DNA双螺旋的统一形状 。 双螺旋的基底组( A- T 和 G- C) 坚持在双螺旋中间, 形成螺旋阶的“ 步骤 ” 。Nitrogen Bases in DNA. The DNA of all species has the same four nitrogen bases.
::DNA中的氮基。所有物种的DNA都有相同的四个氮基。DNA Replication
::DNA复制Knowledge of DNA’s structure helped scientists understand how DNA replicates. DNA replication is the process by which DNA is copied. It occurs during the synthesis (S) phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle. DNA must be copied so that each daughter cell will have a complete set of after occurs.
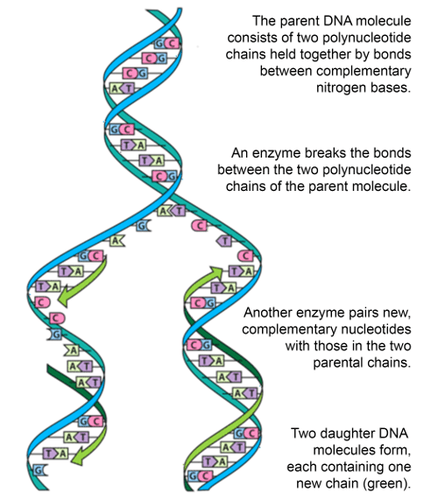
::对DNA结构的了解有助于科学家理解DNA是如何复制的。 DNA复制是复制DNA的过程。 它发生在尿液细胞循环合成(S)阶段。 DNA必须复制,这样每个女儿细胞在后天将拥有完整的数据集。DNA replication begins when an called helicase breaks the bonds between complementary bases in the molecule, as shown in the figure . This exposes the bases inside the molecule so they can be “read” by another enzyme (DNA polymerase) and used to build two new DNA strands with complementary bases. Each of the two resulting daughter molecules contains one strand from the parent molecule, as well as one new complementary strand. As a result, the two daughter molecules are both identical to the parent molecule.
::DNA复制开始于一个名为“ helicase ” 的分子间互补基点断开连接时, 如图所示。 这暴露了分子内部的基点, 这样它们就可以被另一个酶( DNA 聚合酶) “ 读” , 并用来构建两个具有互补基点的新的DNA线。 由此产生的两个女分子中, 每一个都含有母分子的一丝, 以及一个新的互补基点。 结果, 两个女分子都与母分子相同 。DNA Replication. DNA replication is a semi-conservative process. Half of the parent DNA molecule is conserved in each of the two daughter DNA molecules.
::DNA复制。DNA复制是一个半保守过程。母DNA分子的一半保存在两个女儿的DNA分子中。Summary
::摘要-
Determining that DNA is the genetic material was an important milestone in biology. The first important discovery was made in the 1920s, when Griffith showed that something in virulent bacteria could be transferred to nonvirulent bacteria, making them virulent, as well.
::确定DNA是遗传物质是生物学中的一个重要里程碑。 第一次重要发现是在1920年代发现的,当时格里菲斯表明,毒细菌中的某些物质可以转移到非病毒细菌中,使其也具有毒性。 -
In the early 1940s, Avery and colleagues showed that the "something" Griffith found in his research was DNA and not protein. This result was confirmed by Hershey and Chase, who demonstrated that viruses insert DNA into bacterial cells so the cells will make copies of the viruses.
::20世纪40年代初,艾弗里和同事们表明,在他的研究中发现的格里菲斯(Griffith)是DNA而不是蛋白质。 赫希和大通证实了这一结果,他们证明病毒将DNA插入细菌细胞,以便细胞复制病毒。 -
In the mid-1950s, Chargaff showed that, within the DNA of any given species, the concentration of adenine is always the same as the concentration of thymine, and that the concentration of guanine is always the same as the concentration of cytosine. These observations came to be known as Chargaff's rules.
::20世纪50年代中期,电源显示,在任何特定物种的DNA中,的浓度总是与甲状腺的浓度相同,而的浓度总是与乙酸的浓度相同。 这些观察结果被称为“电源规则 ” 。 -
Around the same time, James Watson and Francis Crick, building on the prior X-ray research of Rosalind Franklin and others, discovered the double-helix structure of the DNA molecule. Along with Chargaff's rules, this led to a better understanding of DNA's structure and function.
::大约在同一时间,詹姆斯·沃森(James Watson)和弗朗西斯·克里克(Francis Crick)在罗莎琳德·富兰克林(Rosalind Franklin)和其他人先前的X光研究的基础上,发现了DNA分子的双螺旋结构。 这与教官的规则一起,导致人们更好地了解了DNA的结构和功能。 -
Knowledge of DNA's structure helped scientists understand how DNA replicates, which must occur before cell division occurs so each daughter cell will have a complete set of chromosomes. DNA replication is semi-conservative because each daughter molecule contains one strand from the parent molecule and one new complementary strand.
::对DNA结构的了解有助于科学家理解DNA复制的方式,这种复制必须在细胞分裂发生之前发生,这样每个女儿细胞将拥有一套完整的染色体。 DNA复制是半保守的,因为每个女儿分子都含有母分子的一股和一个新的互补的一股。
Review
::回顾1. Outline the discoveries that led to the determination that DNA (not protein) is the biochemical molecule that contains genetic information.
::1. 概述导致确定DNA(不是蛋白质)是含有遗传信息的生化分子的发现。2. State Chargaff's rules. Explain how the rules are related to the structure of the DNA molecule.
::2. 国家工作人员规则:解释规则如何与DNA分子的结构相关。3. Explain how the structure of a DNA molecule is like a spiral staircase. Which parts of the staircase represent the various parts of the molecule?
::3. 解释脱氧核糖核酸分子的结构如何像螺旋楼梯。4. Describe the process of DNA replication.
::4. 描述DNA复制过程。5. When does DNA replication occur, and why is the process said to be semi-conservative?
::5. DNA复制何时发生,为什么据说这一过程是半保守的?6. Why do you think dead S-strain bacteria injected into mice did not harm the mice, but killed them when mixed with living (and normally harmless) R-strain bacteria?
::6. 为什么你认为注射到小鼠体内的死S-S-strain细菌没有伤害小鼠,而是在与活的(通常无害的)R-strain细菌混合时杀死它们?7. In Griffith’s experiment, do you think the heat treatment that killed the bacteria also inactivated the bacterial DNA? Why or why not?
::7. 在格里菲斯的实验中,你是否认为杀死细菌的热处理也使细菌DNA失去活性?为什么或为什么没有?8. Give one example of the specific evidence that helped rule out proteins as genetic material.
::8. 举一个具体证据的例子,帮助排除蛋白质作为遗传材料。9. True or False: Two-ring bases always bind to each other.
::9. 真实或假:双环基础总是相互约束。10. True or False: DNA replication involves the breaking of one of the polynucleotide chains into individual nucleotides.
::10. 真实或假的:DNA复制涉及将一个多核酸链破碎成个别核酸。11. True or False: In DNA, each nucleotide has a sugar.
::11. 真实或假:在DNA中,每一种核糖酸都有糖。12. What would the complementary strand of the below stretch of DNA bases be?
::12. DNA基础下层的互补部分是什么?GTTAC
::GTTAC 全球TTAC13. Which scientist(s) detected labeled DNA that was transferred from one organism to another?
::13. 哪些科学家检测到从一个生物体转移到另一个生物体的贴有标签的DNA?a. Hershey and Chase
::a. 贺西和大通b. Chargaff
::b. 股 员c. Avery
::c. 艾弗里d. Griffith
::d. Griffith14. ________ break the bonds between complementary bases and add new complementary nucleotides to the parental strands during DNA replication.
::14. 打破补充基础之间的纽带,在DNA复制过程中,在亲子之间增加新的补充核糖核酸。a. phosphates
::a. 磷酸盐b. enzymes
::b. 酶c. viruses
::c. 病毒d. RNA molecules
::d. RNA分子Explore More
::探索更多Rosalind Franklin was a British scientist who helped discover the structure of DNA. To learn more about her, check this out:
::罗莎琳德·富兰克林是一位英国科学家 他帮助发现了DNA的结构。 -
Determining that DNA is the genetic material was an important milestone in biology. The first important discovery was made in the 1920s, when Griffith showed that something in virulent bacteria could be transferred to nonvirulent bacteria, making them virulent, as well.