中中和粘结细胞
章节大纲
-
Life as Art
::艺术生活This colorful picture could be an abstract work of modern art. You might imagine it hanging in an art museum or art gallery. In fact, the picture illustrates real life — not artistic creation. It is a micrograph of human nervous tissue . The neon green structures in the picture are neurons. The neuron is one of two basic types of in the . The other type is the glial cell .
::这幅丰富多彩的图片可能是现代艺术的抽象作品。 你可以想象它挂在艺术博物馆或艺术画廊中。 事实上,图片展示的是真实生活,而不是艺术创作。 它是人类神经组织的缩微图。 图片中的亮光绿色结构是神经元。 神经元是其中的两种基本类型之一。 另一种是闪光细胞。Neurons
::中中Neurons — also called nerve cells — are electrically excitable cells that are the main functional units of the nervous system. Their function is to transmit , and they are the only type of human cells that can carry out this function.
::神经中子——也称为神经细胞——是作为神经系统主要功能单元的电振动细胞,其功能是传输,是能够履行这一功能的唯一类型的人类细胞。Neuron Structure
::中中结构The figure shows the structure of a typical neuron. The main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below.
::图中显示了典型神经元的结构。图中标注了神经元的主要部分,下文对此作了说明。-
The
cell body
is the part of a neuron that contains the cell
and other cell
. It is usually quite compact, and may not be much wider than the nucleus.
::细胞体是包含细胞和其他细胞的神经元的一部分。 它通常非常紧凑, 可能不会比核大得多 。 -
Dendrites
are thin structures that are extensions of the cell body. Their function is to receive nerve impulses from other cells and to carry them to the cell body. A neuron may have many dendrites, and each dendrite may branch repeatedly to form a dendrite “tree” with more than
one thousand
“branches.” The end of each branch can receive nerve impulses from another cell, allowing a given neuron to
communicate
with tens of thousands of other cells.
::Dendrites是属于细胞体延伸的薄体结构。 它们的作用是接收其他细胞神经脉冲并将其携带到细胞体中。 神经元可能有许多外衣,每个外衣都可能反复分支,形成一个有一千多个“树”的 dendrite “树 ” 。 每个分支的末端都可以从另一个细胞中接收神经脉冲,让给定的神经元能够与其他数万个细胞进行交流。 -
The
axon
is a long, thin
extension
of the cell body. It transmits nerve impulses away from the cell body and toward other cells. The axon branches at the end, forming multiple
axon terminals
. These are the points where nerve impulses are transmitted to other cells, often to dendrites of other neurons. An area called a
occurs at each axon terminal. Synapses are complex membrane junctions that transmit signals to other cells. An axon may branch hundreds of times, but there is never more than one axon per neuron.
::轴是细胞体的长细延伸。 它会将神经脉冲从细胞体向其他细胞传播出去。 尾端的轴形分支形成多个轴形终端。 这些是神经脉冲传输到其他细胞的点, 通常被传送到其他神经元的分形中。 每个轴形终端都会出现一个叫做“ 一个”的区域。 合成是复杂的膜交叉点, 将信号传输到其他细胞。 轴形分形可以分数百次, 但每个神经元的轴数以百倍为限。 -
Spread out along axons — especially the long axons of nerves — are many sections of
myelin sheath
.
These are
layers that cover sections of the axon.
The m
yelin sheath is a very good electrical insulator, similar to the plastic or rubber that encases an electrical cord.
::散落在斧子上——特别是神经的长斧子——是米林牛群的许多部分,这些是覆盖斧子各部分的层,密林牛群是一种非常好的电绝缘器,类似于塑料或橡胶,将电线嵌入其中。 -
Regularly spaced gaps between sections of myelin sheath occur along the axon. These gaps are called
nodes of Ranvier
, and they allow transmission of nerve impulses along the axon. Nerve impulses skip from node to node, allowing nerve impulses to travel along the axon very rapidly.
::轴两端之间有固定间距的间隔。 这些间距被称为兰维尔节点,它们允许轴心神经冲动的传播。 神经冲动从节点跳到节点,允许神经脉冲快速沿着轴心移动。 -
A
Schwann cell
(also on an axon) is a type of glial cell. Its function is to produce the myelin sheath that insulates axons in the
. In the
, a different type of glial cell (called an oligodendrocyte) produces the myelin sheath.
::A Schwann 细胞( 也位于轴上) 是一种滑翔细胞。 它的功能是生成弥叶林树脂, 将斧子隔绝在 。 在 . 中, 另一种类型的滑翔细胞( 称为 寡头龙细胞) 产生。
Neurogenesis
::神经起源Fully differentiated neurons, with all their special structures, cannot divide and form new daughter neurons. Until recently, scientists thought that new neurons could no longer be formed after the brain developed prenatally. In other words, they thought that people were born with all the brain neurons they would ever have, and as neurons died, they would not be replaced. However, new evidence shows that additional neurons can form in the brain, even in adults, from the division of undifferentiated neural cells found throughout the brain. The production of new neurons is called neurogenesis. The extent to which it can occur is not known, but it is not likely to be very great in humans .
::完全有区别的神经元及其所有的特殊结构无法分割和形成新的女儿神经元。直到最近,科学家认为新的神经元在大脑产前发育后无法再形成。换句话说,他们认为人出生时拥有他们曾经拥有的所有脑神经元,随着神经元的死,他们不会被替换。然而,新的证据表明,更多的神经元可以在大脑中形成,即使是在成年人中,从整个大脑发现的无区别的神经细胞的分裂中产生。新神经元的产生被称为神经发源。新神经元的产生程度并不为人所知,但在人类中可能不是很大。Neurons in Nervous Tissues
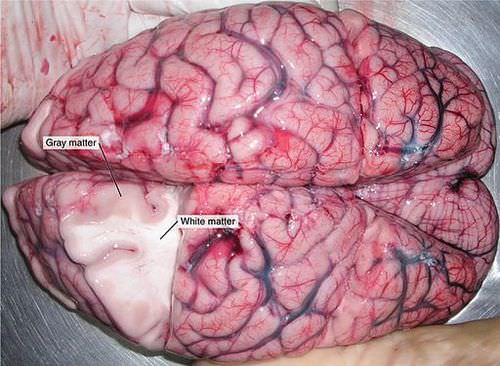
::神经组织中的神经元The nervous tissue in the brain and spinal cord consists of gray matter and white matter. Gray matter contains mainly non-myelinated structures, including the cell bodies and dendrites of neurons. It is gray only in cadavers. Living gray matter is actually more pink than gray (see image ). White matter consists mainly of axons covered with myelin sheath, which gives them their white color. White matter also makes up nerves of the peripheral nervous system. Nerves consist of long bundles of myelinated axons that extend to , organs , or glands throughout the body. The axons in each nerve are bundled together like wires in a cable. Axons in nerves may be more than a meter long in an adult. The longest nerve runs from the base of the spine to the toes.
::大脑和脊髓的神经组织由灰物质和白物质组成。灰物质主要包含非线性结构,包括细胞体和神经元的分层。它只在地籍上是灰色的。活灰物质实际上比灰色物质更粉色(见图 ) 。 白物质主要包括被髓灰质和脊椎覆盖的斧子,这给他们带来了白色的颜色。 白色物质也构成外围神经系统的神经。 神经部分包括长长的线性轴,它延伸到全身的器官或腺。 每根神经的轴像一根电缆的线条一样被捆绑在一起。 神经中的斧子可能长于一米长。 最长的神经从脊椎底一直跑到脚趾。You can see the layers of (pinkish) gray matter and white matter in this photo of a brain from a recently deceased human patient.
::您可以看到(pinkish)灰质和白质的层层(pinkish),Types of Neurons
::中子类型There are hundreds of different types of neurons in the human nervous system that exhibit a variety of structures and functions. Nonetheless, m any neurons can be classified functionally based on the direction in which they carry nerve impulses.
::人类神经系统中有数百种不同的神经元,这些神经元有着各种各样的结构和功能。 尽管如此,许多神经元可以按照携带神经冲动的方向进行功能分类。-
Sensory
(also called afferent)
neurons
carry nerve impulses from
sensory receptors
in
tissues
and organs to the central nervous system. They change physical
stimuli
(such as touch, light, and sound) into nerve impulses.
::感官神经元(也称为“感官”神经元)携带神经脉冲,从组织和器官中的感官受体到中神经系统,它们将身体刺激(如触摸、光和声音)转化为神经脉冲。 -
Motor
(also called efferent)
neurons,
like the one in the diagram
, carry nerve impulses from the central nervous system to muscles and glands. They change nerve signals into the activation of these structures.
::运动(也称“抽动”)神经元,像图表中的神经元一样,将神经冲动从中枢神经系统带到肌肉和腺。它们将神经信号转化为这些结构的激活。 -
Within the spinal cord or brain,
interneurons
carry nerve impulses back and forth often between sensory and
motor neurons
.
::在脊髓或脑内,中中子会背负神经脉冲,通常在感官神经元和运动神经元之间。
The axon in this diagram is part of a motor neuron. It transmits nerve impulses from the central nervous system to a skeletal muscle, causing it to contract.
::本图中的轴是运动神经元的一部分,它将神经脉冲从中枢神经系统传播到骨骼肌肉,导致骨骼肌肉萎缩。Glial Cells
::感光室In addition to neurons, nervous tissues also consist of glial cells (also called neuroglia). The word glial comes from a Greek word meaning “glue,” which reflects earlier ideas about the role of glial cells in nervous tissues. Glial cells were thought to be little more than “glue” holding together the all-important neurons. Glial cells are no longer thought be just “glue.” They are now known to play many vital roles in the nervous system. There are several different types of glial cells, each with a different function. You can see six types in the figure .
::除了神经元之外,神经组织也包含螺旋细胞(也称为神经球 ) 。 螺旋来自希腊语中的“胶”一词,它反映了早先关于螺旋细胞在神经组织中的作用的想法。 粘结细胞被认为比将所有重要的神经元放在一起的“胶”小得多。 粘结细胞不再被认为是仅仅是“胶 ” 。 它们现在在神经系统中扮演着许多关键角色。 有一些不同类型的滑翔细胞,每个都有不同的功能。 您可以看到数字中的六种类型 。Different types of glial cells (neuroglia) are found in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
::在中枢神经系统和外围神经系统中可以发现不同类型的螺旋细胞(中子体)。In general, glial cells provide support for neurons and help them carry out the basic function of nervous tissues, which is to transmit nerve impulses. For example, oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system generate the lipids that make up myelin sheaths, which increase the speed of nerve impulses' transmission . Functions of other glial cells include holding neurons in place, supplying neurons with nutrients , regulating the repair of neurons, destroying , removing dead neurons, and directing axons to their targets. Glial cells may also play a role in the transmission of nerve impulses, but this is still under study. Unlike mature neurons, mature glial cells retain the ability to divide by undergoing .
::一般来说,滑翔细胞为神经元提供支持,帮助他们实现神经组织的基本功能,即传播神经脉冲。例如,中枢神经系统的寡头催化细胞和外围神经系统的Schwann细胞产生构成髓灰质细胞的脂质,这增加了神经脉冲的传播速度。其他滑翔细胞的职能包括:保持神经元、供应神经元营养素、监管神经元的修复、摧毁、清除死亡神经元并将斧子引向目标。 滑翔细胞也可能在神经脉冲的传播中发挥作用,但这一作用仍在研究中。 与成熟的神经元不同,成熟的滑翔细胞通过经历保持分裂的能力。In the human brain, there are generally roughly equal numbers of neurons and glial cells. If you think intelligence depends on how many neurons you have, think again. Having a relatively high number of glial cells is actually associated with higher intelligence. When Einstein’s brain was analyzed, researchers discovered a significantly higher-than-normal ratio of glial cells to neurons in areas of the brain associated with mathematical processing and language. On an evolutionary scale, as well, an increase in the ratio of glial cells to neurons is associated with greater intelligence in .
::在人类大脑中,一般而言,神经元和滑翔细胞的数量大致相等。如果你认为智能取决于你有多少神经元,再想一想。 拥有相对多的滑翔细胞实际上与更高的智能有关。 当分析爱因斯坦的大脑时,研究人员发现在数学处理和语言相关联的大脑地区,滑翔细胞与神经细胞的比例明显高于正常水平。 在进化规模上,光滑细胞与神经细胞的比例的提高也与神经元的智能程度的提高相关。Feature: My Human Body
::特质:我的人体Would you like your brain to make new neurons that could help you become a better learner? W hen it comes to learning new things, w hat college student wouldn’t want a little more brain power? If research about rats applies to humans, then sustained aerobic (such as running) can increase neurogenesis in the adult brain, and specifically in the hippocampus, a brain structure important for learning temporally and/or spatially complex tasks, as well as memory. Although the research is still at the beginning stages, it suggests that exercise may actually lead to a “smarter” brain. E ven if the research results are not ultimately confirmed for humans, though, it can’t hurt to get more aerobic exercise. It is certainly beneficial for your body, if not your brain!
::是否希望你的大脑能制造新的神经元来帮助你成为更好的学习者? 在学习新事物时,哪个大学生不会想要更多的大脑力量? 如果关于老鼠的研究适用于人类,那么持续的有氧运动(如跑步)可以增加成人大脑神经的产生,特别是河马,一个脑结构对于学习时间和/或空间上复杂的任务以及记忆非常重要。 尽管研究仍处于初级阶段,但它表明,这种练习实际上可能导致“更聪明”的大脑。 即使研究结果最终没有被证实对人类来说,但获得更多的有氧锻炼也无妨。 这当然有益于你的身体,如果不是你的大脑的话!Summary
::摘要-
Neurons are one of two major types of nervous system cells. They are electrically excitable cells that transmit nerve impulses.
::中微子是神经系统细胞的两大类之一,它们是导出神经脉冲的电动振动细胞。 -
Glial cells are the other major type of nervous system cells. There are many types of glial cells, and they have many specific functions. In general, glial cells function to support, protect, and nourish neurons.
::粘结细胞是神经系统细胞的另一种主要类型。 有很多类型的滑翔细胞,它们有许多特定的功能。 一般来说,滑翔细胞功能支持、保护和营养神经元。 -
The main parts of a neuron include the cell body, dendrites, and axon. The cell body contains the nucleus. Dendrites receive nerve impulses from other cells, and the axon transmits nerve impulses to other cells at axon terminals. A synapse is a complex membrane junction at the end of an axon terminal that transmits signals to another cell.
::神经元的主要部分包括细胞体、 dendrites 和 axon 。 细胞体包含核。 Dendrites 接收其他细胞的神经脉冲, 轴将神经脉冲传输到轴终端的其他细胞。 突触是一个复杂的膜交叉点, 位于轴终端的尾端, 将信号传输到另一个细胞 。 -
Axons are often wrapped in an electrically-insulating myelin sheath, which is produced by glial cells. Electrical
signals
occur at gaps in the myelin sheath, called nodes of Ranvier, which speeds the conduction of nerve impulses down the axon.
::轴心往往被包裹在由滑翔细胞生成的电绝缘弥丁叶草丛中。 电子信号出现在被称作兰维尔节点的弥叶林草丛的缝隙中,它加速了轴心下神经脉冲的传导。 -
Neurogenesis, or the formation of new neurons by cell division, may occur in a mature human brain, but only to a limited extent.
::神经起源,或细胞分裂形成新的神经元,可能发生在成熟的人类大脑中,但程度有限。 -
The nervous tissue in the brain and spinal cord consists of gray matter (which contains unmyelinated cell bodies and dendrites of neurons) and white matter (which contains mainly myelinated axons of neurons). Nerves of the peripheral nervous system consist of long bundles of myelinated axons that extend throughout the body.
::大脑和脊髓的神经组织由灰质(包括未灭的细胞体和神经元的外形)和白质(主要包括神经元的近距离轴)和白质(主要是神经元的近距离轴)组成。 外围神经系统的神经系统由长捆的近距离轴组成,贯穿整个身体。 -
There are hundreds of types of neurons in the human nervous system, but m
any
can be classified on the basis of the direction in which they carry nerve impulses. Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses away from the body and toward the central nervous system, motor neurons carry them away from the central nervous system and toward the body, and interneurons often carry them between sensory and motor neurons.
::人类神经系统有数百种神经元,但许多神经元可以按照携带神经脉冲的方向进行分类。 感官神经元携带神经脉冲离开身体,进入中枢神经系统,动脉神经元携带神经脉冲离开中枢神经系统,动脉神经元将神经神经元从中枢神经系统和身体转移到中枢神经系统,而中中枢经常携带神经神经元和运动神经元。
Review
::回顾1. Identify the three main parts of a neuron, as well as their functions.
::1. 确定神经元的三个主要部分及其功能。2. Describe the myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier. How does their arrangement allow nerve impulses to travel very rapidly along axons?
::2. 描述一下Ranvier的 myelin树丛和结点:它们的安排如何允许神经冲动在轴心上快速行走?3. What is a synapse?
::3. 什么是突触?4. Define neurogenesis. What is the potential for neurogenesis in the human brain?
::4. 界定神经发源:人类大脑神经发源的潜力是什么?5. Relate neurons to different types of nervous tissues.
::5. 将神经元与不同类型的神经组织联系起来。6. Compare and contrast sensory and motor neurons.
::6. 比较和对比感官和运动神经元。7. Identify the role of interneurons.
::7. 确定中中子的作用。8. Identify four specific functions of glial cells.
::8. 确定圆柱细胞的四个具体功能。9. What is the relationship between the proportion of glial cells to neurons and intelligence?
::9. 滑翔细胞与神经元的比例与智力之间有什么关系?10. For each type of neuron below, identify whether it is a sensory neuron, motor neuron, or interneuron.
::10. 对于以下每一种类型的神经元,确定它是感官神经元、运动神经元还是中中子。a. a neuron in the spinal cord that receives touch information and then transmits that information to another spinal cord neuron that controls movement of an arm muscle
::a. 脊髓神经元,该神经元接收触摸信息,然后将该信息传递给另一个控制手臂肌肉运动的脊髓神经元b. a neuron that takes taste information from your tongue and sends it to your brain
::b. 从舌头获取品味信息的神经元,并传给大脑的神经元c. a spinal cord neuron that stimulates a muscle to contract
::c. 刺激肌肉收缩的脊髓神经元11. The myelin sheath is made by ______________.
::11. myelin 草皮由______ 制成。a. sensory neurons
::a. 感官神经元b. white neurons
::b. 白白神经元c. peripheral nervous system neurons
::c. 外围神经系统神经元d. glial cells
::d. 圆球细胞12. True or False: Synapses often exist where a dendrite and an axon terminal meet.
::12. 真实的或假的:在装饰和斧头终端碰头时,往往会发生合成。13. True or False: There is only one axon terminal per neuron.
::13. 真实或假:每个神经元只有一个xon终端。Explore More
::探索更多Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a progressive degenerative disease caused by demyelination of axons in the central nervous system. When myelin degrades, conduction of nerve impulses along the nerve can be impaired or lost, and the nerve eventually withers. Watch this TED talk, in which the speaker shares how being diagnosed with MS changed her life and inspired her to become an MS nurse.
::多发性硬化症(MS)是中枢神经系统斧子去失密引起的一种渐进性退化性疾病。 当髓灰素降解时,神经神经脉冲的传导会受损或丢失,神经最终衰竭。 观看本次TED演讲, 演讲者分享被诊断为MS如何改变了她的生活, 并激励她成为MS护士。After his death in 1955, Albert Einstein's brain was studied by scientists worldwide — all wanting to gain insight into the anatomy of a genius. It wasn't until the 1980s, however, that Dr. Marian Diamond noticed that Einstein had more glial cells than average. Glia, stemming from Greek for "glue", was previously thought to perform a strictly support role for neurons. Now it is clear that glia may play a more active, non-electrical role in brain activity.
::在1955年死亡后,阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦的大脑被全世界的科学家所研究,他们都想深入了解天才的解剖。然而,直到1980年代,马里安·戴蒙德博士才发现爱因斯坦的毛细胞比一般人多。Glia,以希腊语写成的“glue ” ( glue ) , 曾被认为是神经元的严格支持作用。现在,Glia显然可以在脑活动中发挥更活跃、非电的作用。 -
The
cell body
is the part of a neuron that contains the cell
and other cell
. It is usually quite compact, and may not be much wider than the nucleus.