双投影镜
章节大纲
-
Refracting telescopes, such as the one shown here, use to focus the image. The telescope in this picture is one of the largest refracting telescopes in the world, and can be found in the Lick Observatory in San Jose, California.
::折射望远镜, 如此处显示的望远镜, 用来聚焦图像。 图片中的望远镜是世界上最大的折射望远镜之一, 可以在加利福尼亚州圣何塞的Lick天文台找到 。Images in Double Convex Lenses
::双投影镜头中的图像Lenses are made of transparent material such as glass or plastic with an index of refraction greater than that of air. At least one of the faces is a part of a sphere; a convex lens is thicker at the center than the edges, and a concave lens is thicker at the edges than the center. Convex lenses are called converging lenses, because they refract parallel light rays so that they meet. They are one of the most useful and important parts of all optical devices, and are found in eyeglasses, telescopes, microscopes, magnifying glasses, cameras and many other objects.
::镜头由透明材料组成, 如玻璃或塑料, 其折射指数大于空气。 至少一张脸是球体的一部分; 锥形透镜在中间比边缘厚, 锥形透镜在边缘厚。 锥形透镜在边缘更厚。 锥形透镜被称为聚合镜, 因为它们对平行光线进行折射, 以便相撞。 它们是所有光学设备中最有用和最重要的部分之一, 并且存在于眼镜、 望远镜、 显微镜、 放大镜、 相机和许多其他物体中 。Both the mirror equation and the magnification equation also apply to lenses. However, when dealing with lenses, the mirror equation is renamed the Lens Equation.
::镜像方程和放大方程都适用于镜头。 但是,当处理镜头时,镜像方程被重新命名为“镜头方程 ” 。Double convex lenses have focal points on both sides of the lens, but it is also necessary to use points at twice the focal length to locate objects and images. Therefore, along the principal axis , there are points identified as F and as 2F on both sides of the lens.
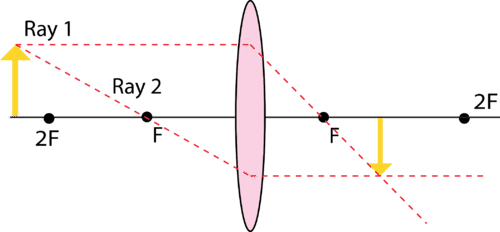
::双锥形透镜在透镜两侧都有焦点点,但也有必要使用焦距两倍的点点来定位对象和图像,因此,在主轴一带,透镜两侧都有被确定为F和2F的点点。As with , we only need to trace two rays in order to locate the image for lenses. Both rays change direction while inside the lens, and their convergence point on the opposite side of the lens is the image location. As can be seen in the figure above, Ray 1 approaches the lens parallel to the principal axis and is refracted through the focal point on the other side. Ray 2 travels through the focal point and is then refracted parallel to the principal axis. The yellow arrow on the right of the lens is the inverted image.
::和“ ” 一样, 我们只需要追踪两条线就可以定位镜头的图像。 这两条线在镜头内改变方向, 镜头对面的汇合点就是图像位置。 从上图中可以看出, Ray 1 接近主轴平行的镜头, 并通过另一边的焦点点进行反向。 Ray 2 穿过焦点点, 然后与主轴相平行。 镜头右侧的黄色箭头是反向图像 。The diagram above shows the situation when the object is outside 2F . In this situation, the image will be between F and 2F on the other side and will be inverted, diminished, and real. A real image can be projected on a screen. That is, if you placed a sheet of paper at the image position, the image would actually appear on the paper.
::上面的图表显示了对象在 2F 之外的情况。 在这种情况下, 图像在另一侧的 F 和 2F 之间, 将会被反转、 缩小和真实。 一个真实的图像可以在屏幕上放映。 也就是说, 如果您在图像位置上放一张纸, 图像将会实际出现在纸张上 。If the object is placed between 2F and F , the image will appear beyond 2F on the other side. The image will be real, inverted, and enlarged. You can do a ray tracing like the one shown to demonstrate this is true.
::如果对象位于 2F 和 F 之间, 图像将显示在另一侧的 2F 之外。 图像将会是真实的、 反转的、 扩大的。 您可以像显示的那样进行射线追踪, 以证明这是真实的 。If the object is placed inside F (between F and the lens), the image will be on the same side of the lens as the object and it will be virtual, upright, and enlarged.
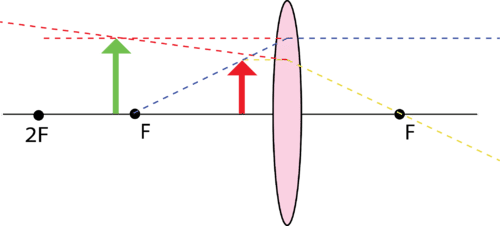
::如果对象放在F(F与镜头之间)内,图像将与对象放在镜头的同一侧,并且是虚拟的、直立的和放大的。In the sketch below, the object is red and has been placed inside F . The ray that approaches the mirror parallel to the principal axis is dotted yellow. It refracts through the focal point, also shown in dotted yellow. The ray that approaches the mirror through the focal point is dotted blue and refracts parallel to the principal axis, also shown in dotted blue. As you can see, the refracted rays diverge, so there will be no real image. If the eye is placed beyond the object around the 2F shown in the sketch, the eye will see the rays as if they have traveled in a straight line. These imaginary rays will converge at the tip of the green arrow which is the image position.
::在下面的草图中,天体是红色的,被放置在F内。 接近主轴平行的镜子的光线是点形黄色的。 它通过点形点反射, 也以点形黄色显示。 通过点形点接近镜子的光线是点形蓝色的, 折形点与主轴平行, 也以点形蓝色显示。 正如您可以看到的, 变形的射线是不同的, 因此没有真实的图像。 如果眼睛被置于画图中显示的2F对象之外, 眼睛会看到射线, 仿佛这些射线是直线穿行的。 这些想象中的射线将聚集在绿箭尖上, 而绿箭尖就是图像位置。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1An object is 40.0 cm to the left of a convex lens of +8.00 cm focal length. Determine the image .
::对象在+8.00厘米焦距的曲线透镜左侧为40.0厘米。确定图像。plugging in values
::1 do+1di=1f 插入值 140.0+1x=18.00Multiplying both sides by yields so and .
::将两边乘以 40x 产值 x+40=5x, 4x=40 和 x= 100.0 厘米。Example 2
::例2An object 1.00 cm high is 8.00 cm to the left of a convex lens of 6.00 cm focal length. Find the image location and image height.
::对象 1.00 cm 高度在 6. 00 cm 焦距 6 cm 焦距的曲线镜片左侧为 8.00 cm 厘米。 查找图像位置和图像高度 。plugging in values
::1 do+1di=1f 插入值为 18. 00+1x=16.00Multiplying both sides by yields so .
::将两侧乘以 24x 3x+24=4xxxxxxx=240.0厘米。Since the image distance is three times the object distance, the image height will be three times the object height or 3.00 cm.
::由于图像距离是对象距离的三倍,图像高度将是对象高度的三倍或3.00厘米。Launch the Magnifying Glass simulation below to investigate how this double convex lens causes the image of a candle to appear larger, smaller, and upside down:
::开始下面的放大镜模拟 来调查这个双阴道透镜 如何使蜡烛的图像看起来更大 较小 颠倒Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要-
Lenses are made of transparent materials, such as glass or plastic, with an index of refraction greater than that of air.
::镜头由透明材料,如玻璃或塑料制成,折射指数大于空气折射指数。 -
One or both of the lens faces is part of a sphere and can be concave or convex.
::一个或两个镜头的面孔是球体的一部分,可以是圆锥体或圆锥体。 -
A lens is called a convex lens if it is thicker at the center than at the edges.
::透镜如果在中间比边缘厚,则称为曲线透镜。 -
Both the mirror equation and the magnification equation apply to lenses. Generally, when dealing with lenses, the mirror equation is renamed the Lens Equation.
::镜像方程和放大方程都适用于镜片。 一般来说, 在处理镜片时, 镜像方程被重新命名为“ 镜头方程 ” 。 -
Double convex lenses have focal points on both sides of the lens; these and the points at twice the focal length are used to locate objects and images.
::双孔式透镜在透镜两侧都有焦点点;这些焦点点和焦距为焦距两倍的点点被用来定位物体和图像。 -
When the object is outside
2F
, the image will be between
F
and
2F
on the other side and will be inverted, diminished, and real.
::当对象在 2F 外时, 图像在另一侧的 F 和 2F 之间, 将被反转、 缩小和真实 。 -
If the object is placed between
2F
and
F
, the image will appear beyond
2F
on the other side. The image will be real, inverted, and enlarged.
::如果对象位于 2F 和 F 之间, 图像将出现在另一侧的 2F 以外。 图像将真实、 反转和放大 。 -
For convex lenses, when the object is placed inside
F
, the image will be on the same side of the lens as the object and it will be virtual, upright, and enlarged.
::对于卷发镜,当对象被放置在F内部时,图像将与对象在镜头的同一面,并且将是虚拟的、直立的和放大的。
Review
::回顾-
An object is placed to the left of a 25 cm focal length convex lens so that its image is the same size as the object. Determine the object and image locations.
::对象被放在25厘米焦距斜面镜片左侧,使其图像与对象的大小相同。确定对象和图像位置。 -
A lens is needed to create an inverted image twice as large as the object when the object is 5.00 cm in front of the lens. What focal length lens is needed? Hint:
::当对象在镜头前为 5. 00 厘米时, 需要一个镜头来创建反向图像, 其大小是对象的两倍。 需要哪个焦距透镜? 提示: 1di+1do=1f -
If you have a convex lens whose focal length is 10.0 cm, where would you place an object in order to produce an image that is virtual?
::如果您有一个光谱镜,其焦距为10.0厘米,您会在哪里放置一个对象来生成虚拟图像? -
Describe how a convex lens could be used to make a magnifying lens.
::说明如何利用阴道透镜放大镜。 -
Determine the image distance and image height for a 5.00 cm tall object placed 45.0 cm from a double convex lens with a focal length of 15.0 cm.
::确定一个5.00厘米高的物体的图像距离和图像高度,将45.0厘米的焦距从焦距为15.0厘米的双锥形透镜中定位。 -
Determine the image distance and image height for a 5.00 cm tall object placed 30.0 cm from a double convex lens with a focal length of 15.0 cm.
::确定一个5.00厘米高的天体的图像距离和图像高度,该天体的焦距为15.0厘米,从双锥形透镜中放置30.0厘米。 -
Determine the image distance and image height for a 5.00 cm tall object placed 20.0 cm from a double convex lens with a focal length of 15.0 cm.
::确定一个5.00厘米高的物体的图像距离和图像高度,该物体从焦距为15.0厘米的双锥形透镜上放置20.0厘米。 -
Determine the image distance and image height for a 5.00 cm tall object placed 10.0 cm from a double convex lens with a focal length of 15.0 cm.
::确定一个5.00厘米高的物体的图像距离和图像高度,从焦距为15.0厘米的双锥形镜片上放置了10.0厘米。
Explore More
::探索更多Use this resource to answer the questions that follow.
::使用此资源回答下面的问题 。-
What four points are marked on the principal axis of a lens?
::在镜头主轴上标出什么四点? -
A ray of light from the object that passes through the focal point on the same side of the lens as the object will refract ___________.
::透过镜头同一侧的焦点的物体的一线光线与该物体的反射 。 -
Under what circumstances will a convex lens form a virtual image?
::阴道透镜在什么情况下将形成虚拟图像?