函数图截取
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言The revenue collected by an apartment manager is given by where is the number of $20 rent increases:
::公寓经理收取的收入由R(x)=(580+20x)(50-x)提供,其中x是增加的20美元租金:
In another section we used this example to discuss . Now, notice the points and on the graph. These points convey special information. The first represents the revenue from rent of $29,000 per month before increasing the rent. The second point says that after fifty $20 increases (or an increase of $1000), all tenants will move and the rent revenue will be $0 per month. These special points are called intercepts .
::我们在另一节中用这个例子来讨论。现在,请注意图表上的点数(0,29000美元)和(50,0美元),这些点表示特殊信息。第一个点表示在增加租金之前每月租金收入29,000美元。第二个点表示在增加50美元(或增加1,000美元)之后,所有租户都将搬家,租金收入为每月0美元。这些特殊点被称为拦截。Intercepts
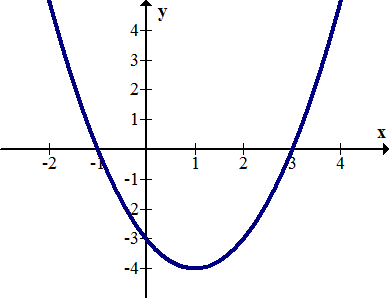
::拦截An intercept in mathematics is the point where a function crosses the - or - axis. For example, identify the intercepts for the following graph:
::数学截取是函数通过 x 或 y 轴的点。例如,为下图标明截取次数:The -intercepts are and . The -intercept is approximately .
::x 拦截是 (-2,0) 和 (3,0) 。 y 拦截大约是 (0,-1.1)。Zeros and roots are synonyms for the -values where a function crosses or touches the -axis. In order for a relation to pass the vertical line test and thus be a function, it must have only one -intercept. However, it may have multiple -intercepts.
::零和根是函数交叉或触摸 x 轴的 x 值的同义词。要通过垂直线测试从而成为函数,它必须只有一个 y 界面。 但是, 它可能有多个 x 界面 。-intercept
::x 拦截The -intercept is the point where the function crosses or touches the -axis. The -values of these points are also called roots and zeros of a function. They are found algebraically by setting and solving for .
::x 界面是函数交叉或接触 x 轴的点。这些点的X 值也称为函数的根和零。它们通过设置 y=0 和为 x 解析而找到代数。-intercept
::y 界面The -intercept is the point where the function crosses or touches the -axis. This point is found by setting to zero and solving for .
::y 界面是函数交叉或接触 y 轴的点。此点通过将 x 设置为零和为 y 解析找到。Play, Learn, Interact, and Explore Intercepts:
::玩耍、学习、互动和探索拦截:Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1What are the zeros and -intercept for the parabola ?
::参数 y=x2-2x-3 的零和 Y 界面是什么 ?Solution:
::解决方案 :Method 1: Solution using a graph:
::方法1:使用图表的解决方案:The zeros are at . The -intercept is at (0, -3).
::零位值为 x1,3。 Y 拦截值为 0, - 3 。Method 2: Solution using algebra:
::方法2:用代数解析:When , substitute 0 for to find zeros.
::当 Y=0 时, 以 0 代替 y 找到零 。
::0=x2-2-2x-3=(x-3)(x+1)
::y=0,x=3,-1The zeros are -1 and 3 and can be found at the -intercepts (-1, 0) and (3, 0).
::零为-1和3,可在X-截取器(-1,0)和(3,0)中找到。When , substitute 0 for to find the -intercept.
::当 x=0 时, 以 0 代替 x 查找 Y 接口 。
::y=(0)2-2-2(0)-33
::x=0,y3The -intercept is at (0, -3).
::y 界面为 0, - 3 。Example 2
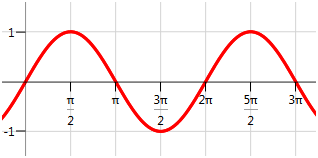
::例2Identify the zeros and -intercepts for the sine function:
::识别正弦函数的零和 Y 界面 :Solution:
::解决方案 :The -intercept is (0, 0). There are four zeros visible on this portion of the graph. The sine graph is periodic and repeats in both directions. In order to capture every -intercept, a pattern for the zeros should be identified.
::y 界面是 (0, 0) 。 图形的这一部分有 4 个零 可见 。 正弦图是周期性的, 双向重复 。 为了捕捉每个 x 界面, 需要为零确定一个模式 。The visible zeros are and . The pattern is that there is an -intercept every multiple of , including negative multiples. The matching zero values can be described in this way:
::可见零是 0, , 2, 和 3。 模式是 X 拦截 的 倍数, 包括负倍数。 匹配的零值可以这样描述 :The zeros are , where is an integer .
::零是 n, n是整数 {0, 1, 2,...} 。Example 3
::例3Identify the intercepts and zeros of the function .
::识别函数 f( x) = 1100( x-3) 33( x+2) 的拦截数和零 。Solution:
::解决方案 :To find the value of for the -intercept, substitute 0 for :
::要找到 Y 的 Y 值, 以 x 0 代替 x :
::y=1100(0-3)3(0+2)2=1100(-27)(4)1081001.08To find the -intercepts, substitute 0 for :
::要找到 X 界面, 替换 0 替换 y :
::0=1100(x-3-3)3(x+2)2By the zero product property , which states that if the product of a set of factors equals zero then one or more of the factors must equal zero, or .
::根据零产品属性,该属性规定,如果一组因数的产值等于零,则一个或多个因数必须等于零,x-3=0或x+2=0。
::x=3,-2,x=3,-2Thus, the -intercept is (0, -1.08), and the zeros are 3 and -2, which can be found at the -intercepts: (3, 0) and (-2, 0).
::因此, Y 界面是 (0, -1.08) , 零是 3 和 -2, 可在 x 界面中找到 : (3, 0) 和 (2, 0) 。Example 4
::例4Determine the -intercepts and -intercept of the following function, using algebra: .
::使用代数( f( x) = (x+3) 2(x-2) 确定下列函数的 x 界面和 Y 界面: f( x) = (x+3) 2(x-2) 。Solution:
::解决方案 :To find the -intercept, substitute 0 for :
::要找到 Y 接口, x 的替代值 0 :
::y= (0+3) 2(0-2) = 32(-2) = 9(-2) 18The -intercept is (0, -18).
::Y 拦截是 (0, -18) 。To find the -intercepts, substitute 0 for :
::要找到 X 界面, 替换 0 替换 y :
::0=(xx+3)2(x-2)By the zero product property, or .
::按零产品属性, x+3=0 或 x-2=0 。
::x3,2The -intercepts are (-3, 0) and (2, 0).
::x 界面是 (3, 0) 和 (2, 0) 。Example 5
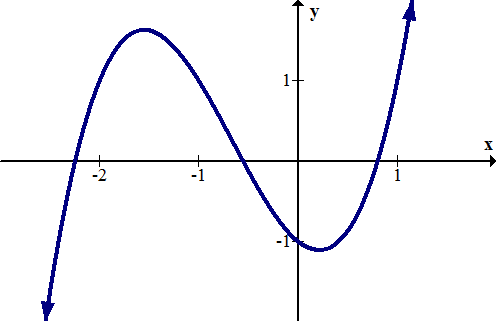
::例5Determine the roots and -intercept of the following function, using algebra or a graph:
::使用代数或图表确定以下函数的根和 Y interview:
:x) =x4+3x3- 7x2- 15x+18
Solution:
::解决方案 :To find the -intercept, substitute 0 for :
::要找到 Y 接口, x 的替代值 0 :
::y=04+303-702-15°0+18=18The -intercept is (0, 18).
::Y 界面是 (0, 18) 。By graphing the -intercepts are (2, 0), (1, 0) and (-3, 0), so the roots are 2, 1, and -3.
::通过图形 f(x) =x4+3x3- 7x2- 15x+18, x- 截取为(2, 0) (1, 0) 和 (3, 3, 0) , 所以根是 2, 1 和 - 3 。Example 6
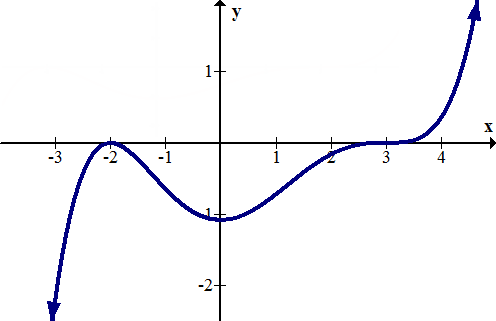
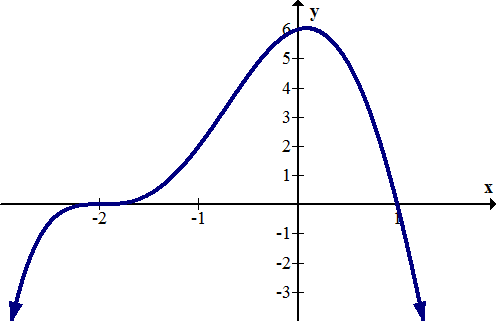
::例6Determine the intercepts of the following function graphically:
::以图形方式确定以下函数的拦截量:Solution:,
::解决方案:The -intercept is approximately (0, -1). The -intercepts are approximately (-2.3, 0), (-0.6, 0) and (0.8, 0). When finding values graphically, answers are always approximate. Exact answers need to be found analytically.
::y 界面大约为 0, - 1 。 x 界面大约为 (- 2.3, 0, 0, 0) 和 (-0.6, 0) 和 (0. 8, 0) 。 以图形方式查找数值时, 答案总是大致的。 精确答案需要用分析方式找到 。Summary
::摘要-
Zeros
and
roots
are synonyms
for the
-values where a function crosses the
-axis.
::零和根是函数交叉 x 轴的 x 值的同义词。 -
An
-intercept
i
s the point where the graph of a function crosses or touches the
-axis.
::x 界面是函数图形交叉或触碰 x 轴的点 。 -
A
-intercept
is the point where the graph of a function crosses or touches the
-axis.
::y 界面是函数图形交叉或触碰 y 轴的点。 -
Note that in order for a function to pass the vertical line test and thus be a function, it should only have one
-intercept. However, it may have multiple
-intercepts.
::请注意,为了让函数通过垂直线测试并因此成为函数,它只应有一个 Y 接口。但是,它可能有多个 x 接口。
Review
::回顾1. Determine the zeros and -intercept of the following function algebraically:
::1. 确定下列函数代数的0和Y中间值:
:xx) = (x+1) 3(x- 4)
2. Determine the roots and -intercept of the following function using algebra or a graph:
::2. 使用代数或图表确定下列函数的根和 Y 界面:
::g(x) =x4- 2x3- 7x2+20x- 123. Determine the intercepts of the following function graphically:
::3. 以图形方式确定以下函数的拦截量:Find the intercepts for each of the following functions:
::查找以下每个函数的拦截功能:4.
::4. y=x25.
::5. y=x36.
::6.y=logx7.
::7.y=1x8.
::8. y=2x9.
::9.y=x 9y=x10. Are there any functions without a -intercept? Explain.
::10. 是否有任何功能没有y-intermissions?解释。11. Are there any functions without an -intercept? Explain.
::11. 是否有任何功能没有 X 拦截?解释。12. Explain why it makes sense that an -intercept of a function is also called a “zero” of the function.
::12. 解释为什么一个函数的X拦截也称为函数的 " 零 " 是有道理的。Determine the intercepts of the following functions using algebra or a graph:
::使用代数或图表确定以下函数的截取次数:13.
::13. h(x) =x3 - 6x2+3x+1014.
::14. j(x)=x2-6x-715.
::15. kk(x)=4x4-20x3-3-3x2+14x+5Review (Answers )
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
Zeros
and
roots
are synonyms
for the
-values where a function crosses the
-axis.