双倍、半分和减功率
章节大纲
-
Introduction
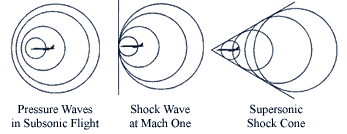
::导言A Mach number is the speed of a supersonic aircraft named for Austrian physicist Ernst Mach. The sonic boom cone represents the sound waves created by a sonic boom caused by aircraft flying faster than the speed of sound. The relationship between the cone's vertex angle, θ, and the Mach speed, M, can be represented by the formula sin θ 2 = 1 M .One very useful goal of developing trigonometric identities is to create tools to be able to solve equations. Like angles, trigonometric functions can take many forms. Being able to change a trigonometric expression from form to form helps to complete that task.
::开发三角特征的一个非常有用的目标就是创造能够解答方程式的工具。 像角度一样,三角函数可以有多种形式。 能够将三角表达形式从形式改变为形式有助于完成这项任务。The final set of identities are less geometrically intuitive than earlier identities. But practicing and working with these advanced identities will increase your toolbox for calculus. Each identity in this concept is aptly named. Double-angle identities can be used to find sin 80 ∘ when sin 40 ∘ is known . Half-angle identities are used to find sin 15 ∘ when sin 30 ∘ is known . Power-reducing identities can be used to find ( sin 15 ∘ ) 2 when the of 30 ∘ are known .
::最后一套身份与以前的身份相比,不那么具有几何直观性。 但是, 练习和操作这些先进的身份将会增加您的计算工具箱。 这个概念中的每个身份都有适当的名称。 当已知有罪40\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Double-Angle Identities
::双角特性The double-angle identities are proved by applying the sum and difference identities.
::通过使用总和和差异身份来证明双重身份。
::例如,正弦函数的总和特性为 sin( x+y) =sinxcosy+cosxsiny。 假设两个角度是相同的度量。 然后, 和特性变成
::exin(x+x)=sinxcosxx+cosxsinxsin(2x)=2sinxxxx。
::同样,正切函数的总和身份为 tanx( x+y) = tanx+tanx+tanny1 - tanxtany。当两个角度相同时, 相切函数的总和身份就会变成
::tan(x+x) = tanx+tanx1-tanxtan(2x) = 2tanx1-tan2x。The double-angle proof for the cosine function is left as an exercise. Notice there are three versions of the double-angle identity for the cosine function. The other two are derived from using a Pythagorean Trigonometric Identity .
::余弦函数的双角证明留作练习。 注意余弦函数的双角身份有三个版本。 其他两个来自使用 Pythagoren Trigonology 身份 。Double-Angle Identities
::双角特性sin 2 x = 2 sin x cos x
::exin2x=2sinxcosxcos 2 x = cos 2 x − sin 2 x = 1 − 2 sin 2 x = 2 cos 2 x − 1
::CO2x=cos2x-sin2x=1-2sin2x=2cos2x-1tan 2 x = 2 tan x 1 − tan 2 x
::tan2x=2tanx1 - tan2xExamples using the double-angle identities can be seen in the following video:
::使用双角身份的例子可见于以下视频:Half-Angle Identities
::半角特征The half-angle identities can be proved by applying the double-angle identities.
::半角身份可以通过使用双角身份来证明。
::例如,余弦函数的双角特性之一是 COs2x=1 -2-2sin2x。 假设角度大小为 0. 5, 例如 x2 。 然后双角特性变成
::cos( 2x2) =1-2sin2x2x2cosx=1-2sin2x2x2。
::解决罪恶2。
::2sin2x2=1-cosxsin2x2=1-cosx2x2=1-cosx2sinx2_Q_1-cosx2
::同样,对余弦函数 cos2x=2cos2x- 1 和 x2 使用双角身份来解析余弦函数的半角身份。正弦函数的半角证据留作练习。Half-Angle Identities
::半角特征sin x 2 = ± √ 1 − cos x 2
::exinx2\\\\\\ cosx2cos x 2 = ± √ 1 + cos x 2
::COsx21+cosx2tan x 2 = ± √ 1 − cos x 1 + cos x
::tanx2\1 - cosx1+cosxPower-Reducing Identities
::降低功率The power-reducing identities allow you to write a trigonometric function that is squared in terms of smaller powers. These identities come directly from the double-angle and half-angle identities. The proofs are left as an example and in the exercises.
::降低功率身份允许您写入一个以较小功率平方表示的三角函数。 这些身份直接来自双角和半角身份。 证据作为例子和练习中留下。Power-Reducing Identities
::降低功率sin 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x 2
::exi2x=1-cos2x2cos 2 x = 1 + cos 2 x 2
::CO2x=1+cos2x2tan 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x 1 + cos 2 x
::tan2x=1 - cos2x1+cos2xExamples
::实例Example 1
::例1Rewrite sin 4 x as an expression without powers greater than one.
::重写 sin4x 是一个表达式, 没有大于 1 的功率 。Solution:
::解决方案 :While sin x ⋅ sin x ⋅ sin x ⋅ sin x is one correct answer, applying another identity will produce a sum:
::虽然 sinxíxísinxíxísinxísinx是一个正确的答案,sin 4 x = ( sin 2 x ) 2 = ( 1 − cos 2 x 2 ) 2 = 1 − 2 cos 2 x + cos 2 2 x 4 = 1 4 ( 1 − 2 cos 2 x + 1 + cos 4 x 2 )
::exin4x= (sin2x) 2= (1 - cos2x2) 2= 1 - 2cos2x+cos22x4=14(1 - 2cos2x+1+cos4x2)Example 2
::例2Write the following expression with only sin x and cos x : sin 2 x + cos 3 x .
::仅用 sinx 和 cosx 写下以下表达式: sin2x+cos3x 。Solution:
::解决方案 :sin 2 x + cos 3 x = 2 sin x cos x + cos ( 2 x + x ) = 2 sin x cos x + cos 2 x cos x − sin 2 x sin x = 2 sin x cos x + ( cos 2 x − sin 2 x ) cos x − ( 2 sin x cos x ) sin x = 2 sin x cos x + cos 3 x − sin 2 x cos x − 2 sin 2 x cos x = 2 sin x cos x + cos 3 x − 3 sin 2 x cos x
::sin2x=2sinxxxxxxxx+2sinxxxx+2sinxxxx+2sinxxxxxx=2sinxxxxx+(cos2xxx-sin2xxxx)cosx-(2sinxxxxxx)=2sinxxxxx+2sinxxxxxxxx-2xxxxxxx-2xxxxxx=2sinxxxxxx=2sinxxxxxxxx=2sxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx2sinxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx2sinxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxExample 3
::例3Use the following half-angle identity to find an exact value of tan 22.5 ∘ without using a calculator. tan x 2 = ± √ 1 − cos x 1 + cos x
::使用以下半角身份来查找 tan22.5 的准确值, 而不使用计算器 。 tanx2\\\\\ 1 - cosx1+cosxSolution:
::解决方案 :tan 22.5 ∘ = tan ( 45 ∘ 2 ) = √ 1 − cos 45 ∘ 1 + cos 45 ∘ = √ 1 − √ 2 2 1 + √ 2 2 = √ 2 2 − √ 2 2 2 2 + √ 2 2 = √ 2 − √ 2 2 + √ 2 = √ 2 − √ 2 2 + √ 2 ⋅ 2 − √ 2 2 − √ 2 = √ 4 − 4 √ 2 + 2 4 − 2 = √ 6 − 4 √ 2 2 = √ 3 − 2 √ 2
::-2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2Example 4
::例4Return to the problem in the Introduction: Determine sin 2 15 ∘ .
::回到导言中的问题:确定 sin215__________________________________________________________________________________________________________Solution:
::解决方案 :Use the power-reducing identities to determine sin 2 15 ∘ .
::使用减能身份 确定sin215___。sin 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x 2 sin 2 15 ∘ = 1 − cos 30 ∘ 2 = 1 2 − √ 3 4
::exic2x=1 - cos2x2sin215\\1 - cos30\2=12}34Example 5
::例5Prove the power-reducing identity for sine.
::证明权力减少身份是不可剥夺的。sin 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x 2
::exi2x=1-cos2x2Solution:
::解决方案 :Start with the double-angle identity for cosine.
::以余弦的双角身份开始 。cos 2 x = cos 2 x − sin 2 x = ( 1 − sin 2 x ) − sin 2 x = 1 − 2 sin 2 x
::CO2x=cos2x-sin2x=(1-sin2x)-sin2x=1-2sin2xNote this expression is an equivalent expression to the double-angle identity, and is often considered an alternate form.
::请注意,该表达式相当于双角特性的表达式,通常被视为另一种形式。2 sin 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x sin 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x 2
::2辛2x=1 - COs2x辛2x=1 - COs2x2Example 6
::例6Simplify the following identity: sin 4 x − cos 4 x .
::简化以下身份: sin4x-cos4x。Solution:
::解决方案 :sin 4 x − cos 4 x = ( sin 2 x − cos 2 x ) ( sin 2 x + cos 2 x ) = − ( cos 2 x − sin 2 x ) = − cos 2 x
:cos2x-sin2x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\
Example 7
::例7What is the period of the function below?
::下文所述职能的期限是多少?f ( x ) = sin 2 x ⋅ cos x + cos 2 x ⋅ sin x
::f(x) =sin2xxxcosx+cos2xxsinxSolution:
::解决方案 :f ( x ) = sin 2 x ⋅ cos x + cos 2 x ⋅ sin x = sin ( 2 x + x ) = sin 3 x
::f(x) = sin2xxxcosx+cos2xxxsinx=sin( 2x+x) =sin3xSince b = 3 , this implies the period is 2 π 3 .
::b=3,这意味着该期间为2_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Summary
::摘要-
Double-Angle Identities:
::双角特性 :
sin 2 x = 2 sin x cos x cos 2 x = cos 2 x − sin 2 x tan 2 x = 2 tan x 1 − tan 2 x
::辛醇/水分配系数=2xxxxxx2xxcos2xxcos2xxcos2xxxxx-辛2xxxxtan2xx=2tanx1-tan2xx-
Half-Angle Identities:
::半角特性 :
sin x 2 = ± √ 1 − cos x 2 cos x 2 = ± √ 1 + cos x 2 tan x 2 = ± √ 1 − cos x 1 + cos x
::========================================================================================================================================-
Power-Reducing Identities:
::功率下降标志:
sin 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x 2 cos 2 x = 1 + cos 2 x 2 tan 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x 1 + cos 2 x
::exin2x=1-cos2x2cos2x=1+cos2x2tan2x1-cos2x1+cos2xReview
::回顾Prove the following identities.
::证明以下身份。1. cos 2 x = cos 2 x − sin 2 x
::1. 1. CO2x=cos2x-sin2x2. cos 2 x = 1 − 2 sin 2 x
::2. CO2x=1--2sin2x3. cos 2 x = 2 cos 2 x − 1
::3. CO2x=2cos2x-14. cos 2 x = 1 + cos 2 x 2
::4. CO2x=1+CO2x25. tan 2 x = 1 − cos 2 x 1 + cos 2 x
::5. tan2x=1-cos2x1+cos2x6. tan x 2 = ± √ 1 − cos x 1 + cos x
::6. tanx21-cosx1+cosx7. csc 2 x = 1 2 csc x sec x
::7. csc2x=12cscxsecx8. cot 2 x = cot 2 x − 1 2 cot x
::8. comt2x=cot2x-12ctx9. tan x 2 = 1 − cos x sin x
::9. tanx2=1-cosxsinx10. Show that tan x 2 = sin x 1 + cos x .
::10. 显示 tanx2=sinx1+cosx。11. Rewrite cos 4 x as an expression without powers greater than one.
::11. 重写 os4x 是一个表达式,无大于1的功率。Find the value of each expression using half-angle identities.
::使用半角身份查找每个表达式的值。12. csc 22.5 ∘
::12. csc22.513. tan 15 ∘
::13. tan15______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________14. tan 22.5 ∘
::14. tan22.5_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________15. sec 22.5 ∘
::15秒22.5____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
Double-Angle Identities: