关系
章节大纲
-
A transformation is a function that takes points in the plane as inputs and gives other points as outputs. You can think of a transformation as a rule that tells you how to create new points from old points.
::变换是一个函数, 将平面中的点作为输入, 并给出其他点作为输出。 您可以将变换视为一个规则, 告诉您如何从旧点创建新点 。Reducing and Enlarging
::减少和增加A dilation is a transformation that grows or shrinks a figure, but keeps the same overall shape. Since a dilation does not retain distance between points, it is not a rigid transformation . Instead, it is known as a similarity transformation because the shape of the figure is retained during dilation, so the image (after the dilation) is similar to the original figure, not congruent .
::膨胀是一种变形,它会增长或缩小一个数字,但保持相同的整体形状。由于膨胀不会保持点数之间的距离,它不是硬质变形。相反,它被称为相似变形,因为数字的形状在变形时会保留下来,所以图像(在变形后)与原始数字相似,而不是一致。-
A dilation that creates a larger image is called an enlargement (growing the figure).
::产生更大图像的放大( 增加数字) 。 -
A dilation that creates a smaller image is called a reduction (shrinking the figure).
::产生较小图像的放大法称为减缩( 缩略图) 。
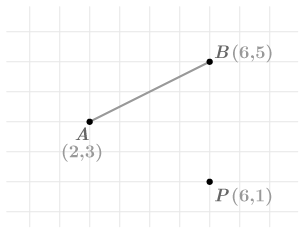
The figure below has been dilated about point by a scale factor of 2 . Notice that and are all collinear . Similarly, and are collinear and and are collinear. and The scale factor of this dilation is 2, because
::下图 ABC 被扩大至 P 点, 比例系数为 2 。 注意 P、 A 和 A 均为 collinear, 类似地, P、 B 和 B 是 collinear , P、 C 和 C 。 PC= 3andPC 。 6 此比值系数为 2, 因为 PC= 63= 2 。If you calculate and you will find that as well.
::如果你计算PA,PA,PA,PB,PB,和PB,你会发现PA=PBB=2。
A Dilation is not a Rigid Transformation
::膨胀不是僵硬的转变A dilation is not a rigid transformation because it does not preserve distance . In the dilation above, is larger than Dilations do, however, preserve angles .
::膨胀不是僵硬的变形, 因为它无法保持距离。 在上文的膨胀中, A_B_C_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_C_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_BAR_-
A shape and its image after a dilation
are
similar, meaning they
are
the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
::一个形状及其在放大后的形象相似, 意思是它们是相同的形状, 但不一定是相同的大小 。
Fractional Scale Factor Dilation
::小数比例系数A shape is dilated by a scale factor of . How does the image relate to the original shape?
::形状被12 的缩放因子放大 12 。 图像与原始形状的关系如何 ?If the scale factor is less than 1, the image will be smaller than the original shape.
::如果比例系数小于1,图像将小于原始形状。
Whole Number Scale Factor Dilation
::整个数字缩缩系数1. Dilate the line segment below about point by a scale factor of 3. Make at least two conjectures about how relates to .
::1. 将P点下方的线段除以3的比值因数,至少对AB与A`B'的关系作出两个猜想。To dilate the line segment, draw a ray starting at point through each end point . Use the grid lines to help you find points on these rays that are three times the distance from point as the original endpoints were. Mark these points as and , where and are all collinear. Join and to complete the dilation.
::要扩大线条段, 请从端点Prough每个端点开始绘制一线。 使用网格线来帮助您找到这些线条上的点数, 这些点数是P点与最初端点的距离的三倍。 将这些点标为 A 和 B 点, P- A- A- A- 和 P- B- B- B 均为圆线。 加入 A 和 B 以完成扩展 。Two conjectures you might make are that or
::你可能得出两个猜想 是AB3AB还是ABABAB2. Show that and for the dilation in the previous problem.
::2. 显示A'B'3AB和A'B'A'B'A'B 用于前一个问题的放大。To find the lengths of the segments, consider the segments as the hypotenuses of the right triangles .
::为了找到各段的长度,将各段视为右三角形的下限。Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the hypotenuses.
::利用毕达哥里安定理词来寻找下层的长度 。Therefore:
::因此:A_B______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Two line segments are parallel if they have the same slope.
::如果两条线段具有相同的斜坡,则两条线段是平行的。Therefore: .
::因此:A'B'''''A'B'B'A'B'A'B'。
Dilation
::关系Adjust the slider to change the scale factor and drag the vertex to change the shape. Point represents the center of dilation. Observe the transformed shape being dilated and note the effects of moving the center of dilation.
::调整滑动器以修改缩放系数,拖动顶点以改变形状。 O点代表放大中心。 观察变形变形放大, 并注意移动放大中心的效果 。Triangle
::三角三角形
CK-12 PLIX Interactive
::CK-12 PLIX 交互式互动
Examples
::实例实例实例实例Example 1
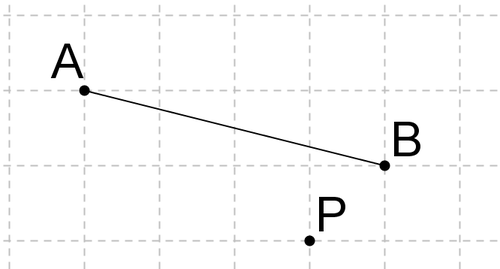
::例1When you dilate a line segment, how is the original line segment related to the image?
::当放大线段时,原始线段与图像的关系如何?When you dilate a line segment, the original line segment will always be parallel to (or on the same line as) the image. Also, if the length of the original line segment is and the scale factor is the length of the image will be
::当您扩大线段时,原始线段将始终与图像平行(或与图像的线条相同)。此外,如果原始线段的长度为L,而缩放系数为k,则图像的长度为kL。Example 2
::例2A shape is dilated by a scale factor of 1. How does the image relate to the original shape?
::形状由 1 的缩放因子放大 。 图像与原始形状的关系如何 ?If the scale factor is 1, the shape does not change size or move at all. The image will be equivalent to the original figure.
::如果缩放系数为 1, 则形状不会改变大小或移动。 图像将相当于原图 。Example 3
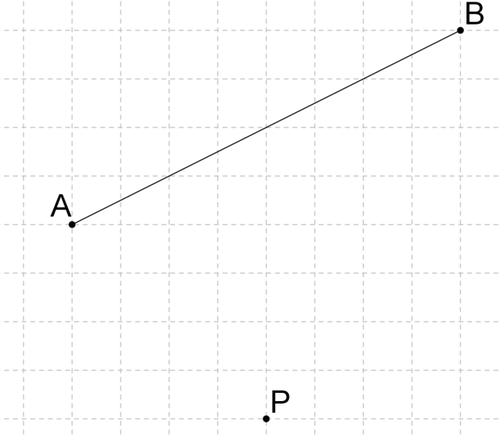
::例3Dilate the line segment below about point by a scale factor of .
::将P点的线段下方的线段扩大12个比例系数。If the scale factor is , the distance from to should be half the distance from to . Similarly, the distance from to should be half the distance from to
::如果比额表系数为12,则P至A的距离应为P至A的距离的一半。 同样,P至B的距离应为P至B的距离的一半。Notice that is the midpoint of and is the midpoint of .
::注意A是PA的中点,B是PB的中点。Example 4
::例4Using your answer to Example #3, show that and .
::使用您对例3的答复, 显示 A'B12AB 和 A'B' 和 A'B'。Use the Pythagorean Theorem to compare the lengths of the two segments.
::使用毕达哥里安定理词比较两个部分的长度。
::d= d= (x2-x1)2+ (y2-y1)2+ (y2-y1)2\ AB=6-2)2+(5-3)2AB=(4)2+(2)2AB=16+4=20=25Similarly,
::同样,
::A_B(6-4)2+(3-2)2A_B(2)+(1)2A_B4+1=5Therefore : .
::因此:A_B12AB。Two line segments are parallel if they have the same slope.
::如果两条线段具有相同的斜坡,则两条线段是平行的。
::斜坡 = y2 -y1x2 - x1 的换换 AB 5 - 36 - 2= 24= 12 的换换 AB 3 - 26 - 4= 12 的换换 。Therefore : .
::因此:A'B'''''A'B'B'A'B'A'B'。Summary -
A
dilation
is a transformation that grows or shrinks a figure, but keeps the same overall shape.
::膨胀是一种变形, 生长或缩小一个数字, 但保持相同的整体形状。 -
A dilation is known as a
similarity transformation
because the shape of the figure is retained during dilation,
::放大法被称为相似性变异,因为数字的形状在变相时会保留, -
A
scale factor
is a ratio of the scale model to the original or actual dimension written in simplest form.
::比额表系数是比额表模型与原始或实际尺寸之比,以最简单的形式写成。 -
Three or more points are
collinear
when they lie on the same line.
::3个或3个以上点在同一线上时为共线。
Review
::审查审查审查审查1. Describe how to perform a dilation.
::1. 描述如何进行放大。2. Explain why a dilation is not an example of a rigid transformation.
::2. 解释为何放大不是僵硬变形的例子。3. True or false: angle measures are preserved in a dilation.
::3. 真实的或虚假的:用放大法保留角度措施。4. A shape is dilated by a scale factor of . How does the image relate to the original shape?
::4. 形状因32的尺度因子而膨胀。 图像与原始形状的关系如何?5. In general, if the scale factor will the image be larger or smaller than the original figure?
::5. 一般而言,如果比例系数k>1大于或小于原图,图像是否会大于或小于原图?6. In general, if the scale factor will the image be larger or smaller than the original figure?
::6. 一般而言,如果比例系数k<1,图像会大于还是小于原图?7. Dilate the line segment below about point by a scale factor of 2.
::7. 将P点下方的线段除以比例因数2。8. Using your answer to #7, show that .
::8. 使用你对7号的答复,显示AB2AB。9. Using your answer to #7, show that .
::9. 使用你对7号的回答,显示A'B'`A'B'。10. If one of the points of your figure IS the center of dilation, what happens to that point when the dilation occurs?
::10. 如果你的身材有一个点是放大中心,那么当放大发生时,该点会怎样?11. Dilate the line segment below about point by a scale factor of .
::11. 将P点下方的线段除以14的比值系数。12. Using your answer to #11, show that .
::12. 使用您对 #11的回答, 显示 A_B_B_14AB 。13. Using your answer to #11, show that .
::13. 利用你对11号的回答,显示A'B'`A'B'。You can perform dilations using interactive geometry software just like you can perform other transformations. Start by creating your figure and the point for your center of dilation. Then, select "Dilate an Object from Point by Factor", then your figure, and then the center of dilation.
::您可以使用交互式几何软件进行比喻, 就像您可以执行其他变换一样。 从创建您的图形开始, 以及您放大中心的点 。 然后选择“ 按因子对对象进行比喻 ” , 然后用您的图形, 然后用比喻中心 。Enter the scale factor into the pop up window and your figure will be dilated.
::在弹出窗口中输入比例系数,然后您的数字将会扩大。14. Create a triangle with interactive geometry software and dilate it about the origin by a scale factor of 2.
::14. 建立一个带有交互式几何软件的三角形,将其来源扩大为2个比例系数。15. Dilate the same triangle about a different point by a scale factor of 2.
::15. 将同一三角形向另一点上拉动为2的尺度因数。16. Compare and contrast the two images from #13 and #14.
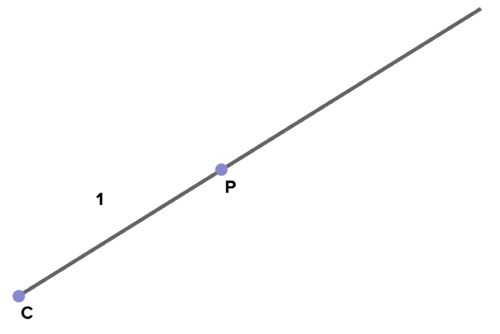
::16. 比较和对比13号和14号两张图片。17. Below is a diagram of a center of dilation C and a point P. Create your own version of this diagram. The length of is 1. Dilate point P around center C by a scale factor of 2 to get to point P'. (You can use a compass to do this by capturing the length of and making an arc from P that crosses What is the length of ? What is the ratio ? If we dilated point P by a scale factor of 3, how would these lengths and ratios change?
::17. 下面是放大中心C和点P的图表。 创建您自己版本的这个图表。 CP的长度是 1 。 CP 的长度是 C 中心周围的点P 乘以 2 比例乘以 2 来达到点P 。 ( 您可以使用一个指南针来做到这一点, 捕捉 CP 的长度, 并用 P 的弧从 C 的对面交叉射线 。 ) PP 的长度是多少? 比率是多少 CP ? 如果我们将点P 乘以 3 比例乘以 3 , 这些长度和比率会怎样变化 ?A diagram of point P and center of dilation C 18. Sketch a line containing the points A and B, with a center of dilation not on the line. This part of the diagram is shown below. Dilate the line by a scale factor of 2. What is the image of the line after dilation? What is its relationship with the original line? Does the same observation apply for a ray? Explain.
::18. 绘制一条包含点A和点B的线条,图图的这一部分显示在下方。将线条的大小乘以2. 比例乘以2. 比例乘以线条的图象?线条与原线条有何关系?同一观察结果是否适用于射线?解释。A line containing points A and B, with a center of dilation not on the line. Can you dilate the line by a scale factor of 2? 19. Sketch and a center of rotation not on the angle. Dilate the angle by a scale factor of your choice. How does the image of the angle after translation compare to the original angle? Why? Prove it.
::19. Spetch ABC 和一个不在角度上的旋转中心。 按您选择的尺度因子将角度扩大。 翻译后角度的图像如何与原始角度进行比较? 为什么? 证明它 。20. Sketch a triangle and a center of dilation not on the triangle as shown below. Draw straight lines from the center of dilation through each vertex as shown. Dilate the triangle by a scale factor of 2. What are the similarities and differences between the image and the original? Dilate by a scale factor of 3. Measure the angles and compare with the original. Find the ratio of the lengths of corresponding sides by measuring and dividing, then summarize your results.
::20. 在三角形上绘制三角形和放大中心,而不是如下所示的三角形。从放大中心通过显示的每个顶点绘制直线。将三角形扩大为2. 比例系数;图像和原始图像之间的相似和差异是什么?将比例系数扩大为3. 度度系数,度量角度并与原始角进行比较。通过测量和分隔查找相应边的长度比,然后总结结果。A triangle with a center of dilation not on the triangle. 21. Using interactive geometry software , di late a segment around a point on the segment by a scale factor of 2. Explain the results. Place the center of dilation outside the segment, but on the line. Explain the results.
::21. 使用交互式几何软件,将部分上的一个点周围的一段段扩大为比例因数2. 解释结果。将放大中心置于部分外,但放在线上。解释结果。22. Using interactive geometry software , dilate a segment around a center of dilation not on the line containing the segment. Are the segments parallel? Why or why not? Construct rays from the center of dilation through the endpoints of segment. Identify two triangles. Describe the ratios of the sides in the two triangles. Explain these results.
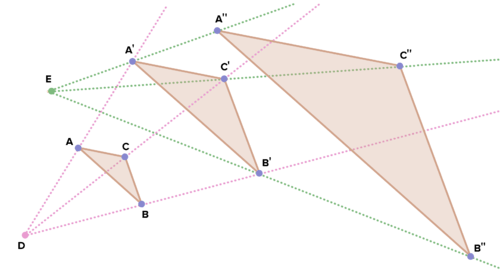
::22. 使用交互式几何软件,在包含该段的线条上没有扩展的外延中心周围扩大一个段。这些段是平行的吗?为什么或为什么不是?从扩展中心到断段的端点的构造射线。确定两个三角。描述两个三角形的两边比例。解释这些结果。23. The triangle below has undergone a sequence of dilations. Describe the sequence. Find a single dilation that would transform the original into the image in one step. Explain how you found the center of dilation. What's the scale factor? Explain. Try your own version of this experiment on paper or with interactive geometry software .
::23. 下面的三角形经历了一个演算序列。 描述序列。 找到一个能将原形一步转换成图像的单一演算。 解释你是如何找到演算中心的。 缩放因素是什么? 解释。 请在纸面或交互式几何软件上尝试您自己的实验版本 。A triangle undergoing a sequence of dilations. 24. Graph a polygon on the coordinate plane. Dilate it around the origin by a scale factor of 2. How will the coordinates of each point change? Explain. On another set of coordinate axes graph a polygon and dilate it around a point not on the origin. Follow these steps: Translate the object and its center of dilation so that the center is on the origin. Perform the dilation. Move the resulting image and center of dilation so that the center is back to its original location. Explain how this can be accomplished without graphing if you are given the coordinates of the center and the vertices of the polygon.
::24. 在坐标平面上绘制多边形图,在原点周围以 2 的尺度系数进行比对。每个点的坐标如何变化? 解释。 在另一组坐标轴上绘制一个多边形,然后在非原点上将其放大。 跟随这些步骤: 翻译对象及其放大中心, 以便中心在原点上。 执行放大。 将产生的图像和放大中心移动到原点, 以便中心回到原点。 如果您得到多边形中心及其顶点的坐标, 解释如何在不绘制图形的情况下完成这项工作 。Review (Answers)
::审查(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
A dilation that creates a larger image is called an enlargement (growing the figure).