科士法
章节大纲
-
relates the three sides of a right triangle by .
::a2+b2=c2 右三角形的三边相连接。Observe the changes in the relationship between the sides for different values of measure of angle
::以不同角度C的计量值观察双方关系的变化。When is a right angle, the Pythagorean Theorem applies, and so the relationship is
::当 C 是 右角时, 应用 Pythagorean 理论, 所以关系是 a2+b2=c2 。When you increase the measure of above the length of the opposite side increases. Th is results in a new relationship between the sides of the triangle:
::当您将 C 的量度提高到 90o 以上时, 反面的长度会增加。 这导致三角形两侧之间出现新的关系 : a2+b2 < c2 。Similarly, when you decrease the measure of below the length of the opposite side decreases. This results in yet another new relationship between the sides of the triangle:
::同样,当您将 C 的度量降低到 90o 以下时,对面的长度会下降。这导致三角形两侧之间又出现一种新的关系:a2+b2>c2。The Law of Cosines takes these relationships one step further. It uses the measure of angle to provide an equation that relates the three sides of the triangle with angle
::科辛斯定律将这些关系再进一步一步。它使用角度C的量度来提供一个方程式,将三角形的三面与角度C联系起来。Law of Cosines:
::科斯定律:a2+b2-2abcos=C=c2T he Pythagorean Theorem applies to missing sides in right triangles.
::皮达哥里安理论适用于右三角形的缺失侧。With the Law of Cosines, you can find missing sides and angles in any type of triangle.
::有了科辛斯定律 你可以在任何三角形中 找到缺失的侧面和角度
Proving the Law of Cosines
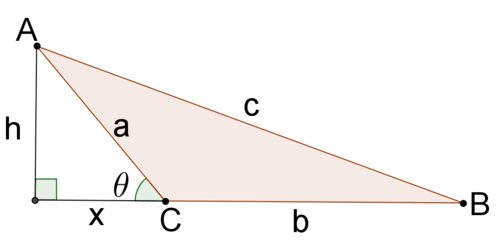
::证明科斯定律1. Given with lengths and , find in terms of and . Then, use the Pythagorean Theorem twice to come up with two equations that relate with the sides of .
::1. 以a、b和c长度的 ABC 表示,用 x 和 a 表示DB。 然后,使用 Pythagorena 理论两次得出两个方程,该方程与 ABC 的两边有关。and , so . You can use the Pythagorean Theorem with both and .
::CB=a 和 CD=x, 所以 DB=a-x。 您可以使用 Pythagoren 理论, 包括 QADC 和 QADB 。
::对于 ADC:CD2+AD2=AC2x2+h2=b2For ADS:BD2+AD2=AB2(a-x)2+h2=c22. Use the given triangle and equations to derive the Law of Cosines.
::2. 利用给定三角形和方程来得出《科辛定律》。From the first problem , you have two equations that you can solve for .
::从第一个问题, 你有两个方程式, 您可以解决 h2 。
::x2+h2=b2_h2=b2_x2(a-x)2+h2=c2_h2=c2-(a-x)2Set the new equations equal to each other, expand and simplify:
::设定对等的新方程式, 扩大和简化 :
::b-2-x2=c2-2-(a-x)2b2-2-x2+(a-x)2-2=c2b2-2-x2+a2-2-A2-2x2+x2+x2=c2a2+b2-2-2x2=c2=c2You can now consider in terms of . Within , is adjacent to . Side is the hypotenuse. This is a cosine relationship.
::您现在可以考虑 x 的 QC 值。 在 QADC 范围内, x 与 QC 相邻。 侧 b 是下限。 这是一个余弦关系 。
::COS=CDACcos=C=xbx=bcos=C =CDACcos=xbx=bcos=C =CCC=CCC=CDACC=CDACcocos=xbx=bcos=bcos*C=ccc=ccc=ccc=ccc=cc=cc=cxxx=cx=bx=bcoscos*C=ccc=ccc=ccc=cc=cc=cc=cc=cc=cc=cc=cc=c=c=cc=c=cc=cc=c=cc=cc=c=cc=cc=c=c=cc=cc=cc=c=c=cc=c=c=cc=c=c=c=cc=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=c=Substitute this equation for into the earlier equation:
::将 x 的这个方程式替换为前一个方程式 :
::a2+b2-2a2+b2-2ax=c2a2+b2-2a(bcosC)=c2a2+b2-2abcos=c2Here you have derived the Law of Cosines for acute angles . Just like the sine ratio, the cosine ratio is actually a function that takes any angle measure as an input (not just angles between and ).
::这里您已经为急性角度 C 得出了科辛斯定律。 就像正弦比一样, 余弦比实际上是一个函数, 以任何角度测量作为输入( 不只是 0 和 90 o 之间的角 ) 。One property of the cosine function is that the cosine of supplementary angles will always be opposites. In other words, In the practice exercises, you will use this fact to show that the Law of Cosines works even if is a right or obtuse angle.
::余弦函数的一个属性是补充角度的余弦总是对立的。 换句话说, coscos( 180) 。 在练习中, 您会使用这个事实来显示 Cosines 定律是有效的, 即使 C 是右角度或斜角 。Note: You will study the cosine function in much more detail in future courses!
::注意: 您将在未来的课程中更详细地研究余弦函数 !Using the Law of Cosines, when =15 , =20 and what is the value of
::如果a=15,b=20和mC=73o,c的价值是什么?The value of is
::c 值为 。
Examples
::实例实例实例实例Example 1
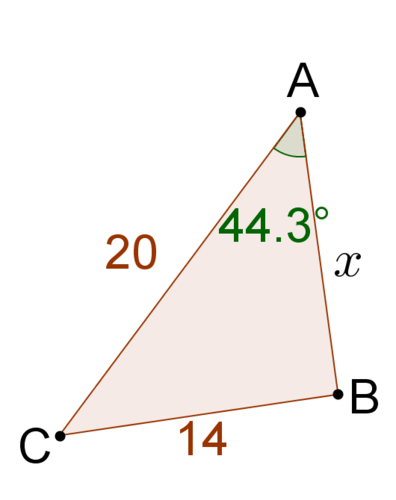
::例1You know how to use trigonometric ratios to find missing sides in right triangles. You also know how to use the to find missing sides in non-right triangles given certain information. What about the triangle below? Can you solve for
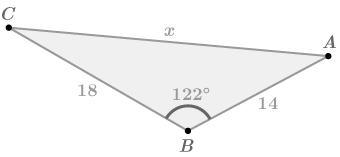
::您知道如何使用三角比在右三角形中找到缺失的边。 您也知道如何在非右三角形中找到缺失的边, 并给出某些信息 。 下面的三角形如何 ? 您能解答 x 吗 ?Notice that in this triangle, the included angle is obtuse. As was explained earlier, the Law of Cosines works for acute, right and obtuse angles. The names of the sides do not match and from the Law of Cosines exactly. What is important is that the angle you choose for is the included angle of the two sides you choose for and . Side is opposite .
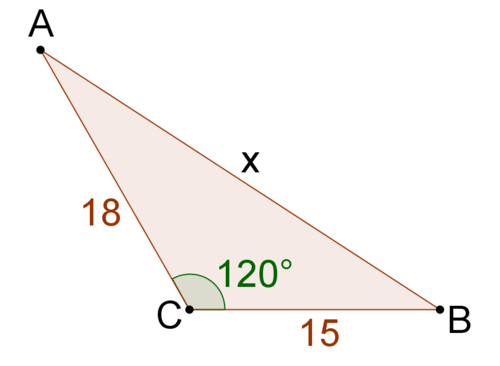
::请注意在这个三角形中, 包含的角度是模糊的。 正如前面所解释的, 科辛斯定律用于急性、 右和隐性角度。 侧边的名称与《 科辛斯定律》中的 a、 b 和 c 不完全吻合。 重要的是您选择的 QC 角度是您选择的 a 和 b 的两边的包含角度。 侧 c 是对的 QC 。In this triangle, the sides 18 and 14 have an included angle of Side is opposite the angle. Use the Law of Cosines to relate these 4 values.
::在此三角形中, 侧面 18 和 14 的角为 122o。 侧面 x 在 122 方形对面 。 使用 Cosines 法则连接这 4 个值 。Example 2
::例2Solve for .
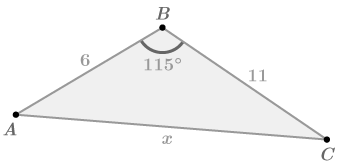
::解决x。The Law of Cosines states that . Remember that the names of your sides might not match and exactly. What is important is that is the included angle of sides and . Side is opposite .
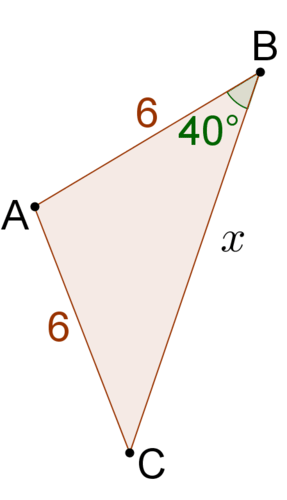
::《科辛斯法》规定,a2+b2-2abcosC=c2. 记住,你的侧面名称可能与a、b和c不完全吻合。 重要的是,C是a和b的侧角。 侧C是对的。In this triangle, the sides 11 and 6 have an included angle of Side is opposite the angle. Use the Law of Cosines to relate these 4 values.
::在此三角形中, 侧面 11 和 6 的角为 115o。 侧面 x 与 115oangle 相对。 使用 Cosines 法则来连接这 4 个值 。
::a2+c2-2accosB=b2112+62-22(11)(6)cos(115o)=x2121+36+55.8=x2212.8=x2x14.6Example 3
::例3Solve for .
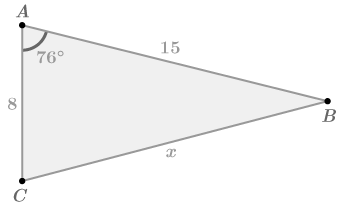
::解决x。In this triangle, the sides 8 and 15 have an included angle of Side is opposite the angle. Use the Law of Cosines to relate these 4 values.
::在此三角形中, 侧面 8 和 15 的角为 76o 。 侧面 x 与 76oangle 相对。 使用 Cosines 法则连接这 4 个值 。
::b2+c2-2bccosA=a282+152-2(8)(15)cos(76o)=x264+225-58.06=x2230.94=x2x15.2Example 4
::例4Solve for .
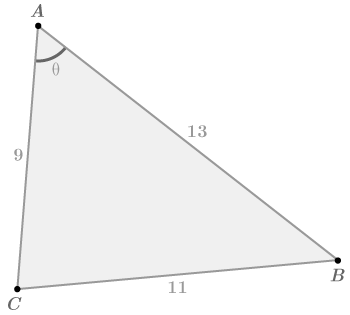
::解决... . .In this triangle, the sides 9 and 13 have an included angle of . 11 is opposite the angle . Use the Law of Cosines to relate these 4 values.
::在这个三角形中,9面和13面的括角为11。 11面与Q角相反。 使用《科辛斯定律》将这4个值联系起来。Note that you can use the Law of Cosines to solve for missing angles as well as missing sides.
::请注意,您可以使用《科辛斯定律》来解决缺失的角度以及缺失的侧面。CK-12 PLIX Interactive
::CK-12 PLIX 交互式互动Summary -
Law of Cosines:
::科斯定律:a2+b2-2abcos=C=c2
Review
::审查审查审查审查1. What is the Law of Cosines?
::1. 什么是《科辛斯定律》?2. When using the Law of Cosines, how do you decide on the values for and ?
::2. 在使用《科辛斯定律》时,如何决定a、b、c和C的数值?3. Show that the Law of Cosines is identical to the Pythagorean Theorem when is a right angle.
::3. 显示当C为正确角度时,Casines定律与Pythagorean定理相同。Use the Law of Cosines to solve for or .
::使用 Cosines 法则解决 x 或 。4.
5. The following triangle is isosceles. Solve for by first figuring out the measure of .
::5. 以下三角形为等分形。先找出 A 的度量,然后解决 x 。6.
7.
8. Attempt to solve for and round to two decimal places. Explain why you get two solutions.
::8. 试图解决 x 位数和四舍五入到小数点后两位位数的问题,解释为什么你有两个解决方案。9.
In problems 10-12, you will investigate the relationship between the cosine of supplementary angles.
::在问题10 -12中,你将调查补充角度的余弦关系。10. Find and What do you notice?
::找到Cos 30o和Cos 150o,你注意到什么了?11. Find and What do you notice?
::去找科斯80和科斯100,你注意到什么了?12. Make a conjecture based on the last two problems. How are the cosine of supplementary angles related? Note: You will prove this conjecture in future courses!
::12. 根据最后两个问题作出推测:补充角度的余弦关系如何? 注意:你将在今后的课程中证明这一推测!In problems 13-16, you will prove that the Law of Cosines works even if is an obtuse angle.
::在问题13 -16中,你会证明 科辛斯定律是有效的 即使C是一个隐蔽的角度。13. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to write an equation relating and . Then, use the Pythagorean Theorem again to write an equation relating and .
::13. 利用毕达哥里安神话来写一个与h、a和x有关的方程式。 然后,再用毕达哥里安神话来写一个与h、x、b和c有关的方程式。14. Use algebra and your work from #13 to show that the following equation is true:
::14. 使用代数和您在 #13 中的工作来显示以下方程式是真实的: a2+b2+2bx=c2。15. Find an equation that relates and and . Show that your equation is equivalent to . Solve for and substitute this quantity into the equation from #14.
::15. 找到一个关联和 ,x 和 a 的方程。 显示您的方程相当于 os( 180- C) =xa。 溶解 x , 从 # 14 将此数量替换为方程 。16. The cosine of supplementary angles are opposites. Substitute for . Show that the result is the Law of Cosines.
::16. 补充角度的余弦是相反的,COs(180-C)的替代-cosC。 显示结果为Cosines定律。17. This chapter has explored many different tools that can be used to find sides or angles in triangles. List the tools and the conditions under which they are best applied. (For example, the Pythagorean Theorem is particularly useful when there is a right triangle with two known sides, and the third side is unknown.)
::17. 本章探讨了许多可以用来在三角形中找到侧面或角的不同工具,列出工具及其最佳应用条件。 (例如,当右三角形有两个已知的侧面,而第三方未知时,Pytagoren Theorem特别有用。 )18. The law of sines showed us that we can take the sine of an obtuse angle, and the law of cosines showed us that we can take the cosine of an obtuse angle. How are the results different? Justify the difference in terms of the two laws.
::18. 成文法告诉我们,我们可以从隐蔽的角度出发,而共犯法则告诉我们,我们可以从隐蔽的角度出发,结果如何不同?从两种法律的角度来说,这是有区别的。19. If the sign of the sine of an obtuse angle is positive, and the sign of the cosine of an obtuse angle is negative, what is the sign of the tangent of an obtuse angle? Why?
::19. 如果隐性角度的正弦值是正的,而隐性角度的余弦值是负的,那么隐性角度的正弦值是什么? 为什么?Review (Answers)
::审查(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Law of Cosines: