函数转换
章节大纲
-
Learning Objectives
::学习目标-
Identify the effect on the
graph of a function
after a transformation
.
::识别转换后函数图图中的影响。 -
Identify the parent
function
given the graph or
equation
of a transformed function.
::给已转换函数的图形或方程式指定父函数。 -
Identify how a function has been translated given the graph or equation.
::确定根据图形或方程式,函数是如何被翻译的。 -
Construct a function to model a linear relationship between two quantities from a description.
::构造一个函数以模拟描述中两个数量之间的线性关系。 -
Identify even and odd functions from their graphs.
::从图表中识别偶数和奇数函数 。
Introduction: Transforming the World Around Us
::导言:改变我们周围的世界In this graph of overlapping parent functions, which function overlaps the other half of g(x)=|x|? T he absolute value function is a basic absolute value function (you may recognize it from the prior lesson, ). The function is a transformation of the parent function A parent function is the simplest function that preserves a specific shape. All transformations of a parent function are known as the function family . Function transformations are commonly used to manipulate a parent function to model a real-world object, context, or relationship.
::绝对值函数 f(x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\基本绝对值函数( 您可以从上一个课程中识别它) 。 函数 f( x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\F\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\可以转换父函数父函数。 父函数是保存特定形状的最简单函数。 父函数的所有转换都被称为函数家族。 函数转换通常用于操作父函数来模拟真实世界对象、 对象、 或关系。Use the interactive below to explore the transformations which take place when modeling an object in the real world.
::使用下面的互动来探索在真实世界中模拟物体时发生的变异。Discussion : How does each variable affect the model? Use the point at the center of the v-shape, called the vertex , as a reference point for your explanation.
::讨论: 每个变量如何影响模型? 使用 v 形状中心点, 称为顶点, 作为您解释的参考点 。
Activity 1: Reviewing Transformations
::活动1:审查转型The following table provides a summary of the transformations explored above and derived in Algebra 1.
::下表汇总了上文所探讨和从代数1中得出的变换。Transformation Notation Condition 1 Condition 2 Points Vertical Shift Shift up if Shift down if Horizontal Shift Shift right if Shift left if Vertical Reflection Horizontal Reflection Vertical Stretch/Shrink Shrink if Stretch if Horizontal Stretch/Shrink Stretch if Shrink if Understanding these rules can help quickly graph and write function models for real-world situations.
::理解这些规则可以帮助快速地为现实世界局势绘制和写出功能模型。Use the interactive below to practice deriving and transforming a parent function.
::使用以下互动方式来实践产生和改变父函数的做法。
Activity 2 : Modeling With Transformations
::活动2:随着变革而建模While the examples above are focused on using transformations to manipulate the graph of a parent function, transformations can be used to fit a function to a context. In this case, the linear parent function will be used.
::上述示例侧重于使用变换来操纵父函数的图形,但变换可以用来适应上下文的函数。在这种情况下,将使用线性母函数f(x)=x。Example
::示例示例示例示例The commission * , in dollars, that a salesperson receives for x dollars in monthly sales can be modeled by the function This very basic (parent) version of the function states that for every $1 the salesperson sells, they make $1 in commission (a commission that high would make a very happy salesperson).
::佣金* 以美元计, 销售人员每月得到的x美元销售额可以通过函数 f(x)=x来模拟。 这个功能的基本( 母) 版本表示, 每售出一美元, 销售人员就拿出一美元佣金( 如此高的佣金会让销售人员非常快乐 ) 。*A commission is money that is paid to an employee often as the result of selling a certain amount of goods or services. This amount is usually given as a percentage of the revenue earned from the goods sold.
::* 佣金是指通常因出售一定数量的货物或服务而支付给雇员的金钱,通常按从所售货物所得收入的百分比给予这一数额。Consider this (more realistic) commission-based scenario:
::考虑这一(更现实的)基于委员会的设想:a ) A salesperson makes 5%, or 5 cents per dollar, on his or her total monthly sales in commission. Transform the function to model this scenario.
:a) 销售人员按其每月佣金销售总额计算5%,即每美元5美分。
The input of the function is the number of sales, and the output is the commission. The 5% only applies to the input, the sales made .
::函数的输入是销售数量, 产出是佣金。 5%仅适用于投入, 即销售量 。Notice that t he salesperson is earning his or her commission at a slower rate from the parent function. This change can be seen on a graph as a decrease in the steepness of the function.
::注意销售者从父函数中以较慢的速度挣取佣金。 在图表中可以将这一变化视为该函数的陡峭性降低。Answer:
::答复:g(x)=0.05(x)This transformation can also be represented as
::这种转换也可以以0.05(f(x))表示。b ) A salesperson makes 5% commission on total monthly sales over $2,000. Transform the function to model this scenario.
:b) 销售人员每月总销售额超过2 000美元的佣金占5%。
The 5% will have the same effect on the parent function as in part A. However, by only applying it to sales over $2,000, a change is being made to the input. The commission is only being applied to the sales after removing $2,000. By decreasing the input, this will have the visual effect of moving the function to the right on a graph.
::5%对母体功能的影响与A部分相同。 但是,仅对超过2 000美元的销售适用5%。 但是,对输入进行修改。 只有在删除2 000美元之后,才对销售适用委员会。 通过减少输入,这将产生将函数在图中移到右侧的视觉效果。Answer:
::答复:h(x)=0.05(x-2 000)This can also be represented as
::也可以以0.05(f(x)-2 000)表示。
Activity 3 : Putting It All Together
::活动3:将 " 团结在一起 "Use the interactive below to practice applying multiple transformations.
::使用下面的交互操作操作, 应用多个变换 。
Activity 4 : Even and Odd Functions
::活动4:偶数和奇数函数There are many ways to describe a function. One such example of this is continuous or discrete , seen in Functions. Another way to describe a function is as being even or odd. An even function is a function that is symmetric about the y-axis .
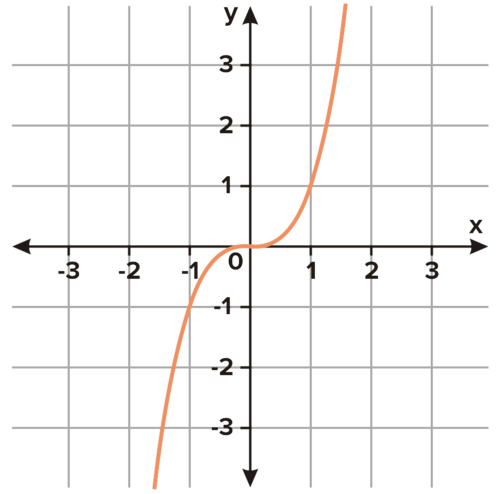
::函数的描述有很多种方式。其中一个例子是连续的或离散的,在函数中可以看到。另一种描述函数的方式是偶数或奇数。一个偶数函数是对 Y 轴的对称函数。An odd function is a function that is symmetric about the origin.
::奇数函数是对源代码的对称函数。A function is neither even nor odd if neither of the conditions above is satisfied.
::3⁄4 ̄ ̧漯B
Wrap-Up : Review Questions
::总结:审查问题
Extension : Interactive Practice
::扩展:交互式做法Use the interactive below to review vertical and horizontal shifts.
::使用下面的交互数据来审查纵向和横向变化。Use the interactive below to review stretches and reflections .
::使用下面的交互效果来审查伸展和反省。Summary
::摘要-
A
parent function
is the simplest function that preserves a specific shape.
::父函数是保存特定形状的最简单的函数。 -
All transformations of that function are known as the
function family
.
::此函数的所有变换都称为函数族。 -
A change to the output will result in a vertical transformation. A change to the input will result in a horizontal transformation.
::产出的改变将导致垂直转换。输入的改变将导致横向转换。 -
An
even function
is a function that is symmetric about the y-axis. An
odd function
is a function that is symmetric about the origin.
::even 函数是对 Y 轴的对称函数。奇数函数是对原函数的对称函数。
-
Identify the effect on the
graph of a function
after a transformation
.