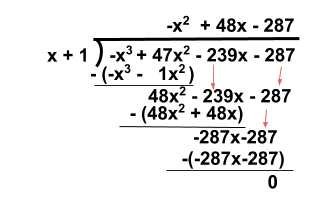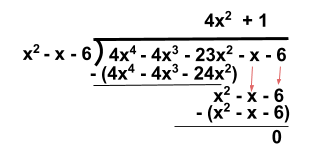多元等同根
章节大纲
-
Lesson Objectives
::经验教训目标-
Interpret the characteristics of a
polynomial
within a real-world context.
::在现实世界背景下解释多元性的特点。 -
Use the Rational
Zeros
Theorem
and
division
to find the
zeroes
and possible zeros of a polynomial with
degree
greater than
two.
::使用理性的零点理论和分解来找到一个大于2度的多元数值的零和可能的零。 -
Understand the
.
::理解这一点。 -
Identify the zeros of a polynomial given the graph.
::标记图形给出的多面体数的零。 -
Write and solve a polynomial within a real-world or mathematical context.
::在现实世界或数学背景下写并解析一个多义。
Introduction: Container Volume Problem - Thick Walls
::导言:集装箱数量问题 -- -- 厚墙壁Use the interactive below to explore how to find the volume of different size containers that have walls that are 1 inch thick.
::使用下面的交互方式来探索如何找到墙壁厚1英寸的不同尺寸集装箱的容量。+Do you want to reset the PLIX?In this lesson, you will investigate the following questions:
::在这一教训中,你将调查下列问题:-
What expressions could be used to model the side lengths?
::可使用什么表达式来模拟侧边长度? -
What polynomial could be used to model the volume the container can support?
::容器能够支撑的体积可使用何种多式模型? -
What size would the side length of the cube need to be to hold 150 cubic inches?
::立方体的侧长需要多少大小才能保持150立方英寸?
Activity 1: Factored Form
::活动1:有因数形式To solve the problem above, you will need to know more about the zeros of a polynomial function . The zeros of a polynomial function are the - intercepts . Zeroes are also called roots in the context of a polynomial equation , where the term solutions may also apply .
::要解决上述问题, 您需要了解更多关于多元函数的零。 多元函数的零是 X 截取。 在多元方程式的背景下, 零也被称为根。 在多元方程式中, 也可以使用术语解决方案 。To help visualize zeros, revisit the example from the section Using Quadratic Methods.
::为帮助直观化零,请在“使用二次曲线方法”一节中重温这个例子。Example
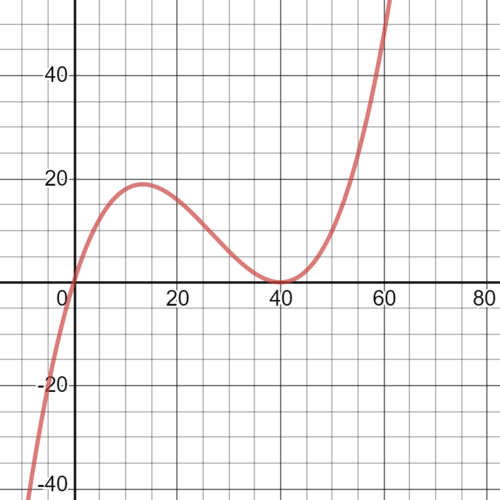
::示例示例示例示例The concentration, in parts per million, of a medicine in a patient’s bloodstream after hours can be modeled using the function given a specific domain . What are the zeros of this function ? What do they mean in context?
::病人在x小时后的血液中的药物浓度,每百万分之一的浓度,可以用功能C(x)=0.002x3-0.16x2+3.2x来模拟。根据特定域,该函数的零值是多少?在上下文中它们意味着什么?The polynomial can be factored as follows:
::多元性可考虑如下:
::0002x3-0.16x2+3.2x=0.002x(x-40)(x-40)The graph of this polynomial is:
::此多面体的图示是 :Use the graph and the factored form of the polynomial to answer the questions below.
::使用图形和多数值的因子形式回答下面的问题。Discussion Question : Write a non-linear polynomial function in factored form that has one zero . W rite a non- quadratic function in factored form that has two zeros.
::讨论问题: 以系数为零以非线性多元函数写成。 以系数为零以二为零以非线性多元函数写成。 以系数为零以二为零以非二次的二次函数写成。When the solutions or -intercepts repeat, this refers to the multiplicity of that solution. A solution that occurs once has a multiplicity of 1, a solution that occurs twice has a multiplicity of 2, a solution that occurs three times has a multiplicity of 3, etc.
::当解决方案或 X 界面重复时, 这里指的是该解决方案的多重性。 一旦出现的解决办法有多重性 1, 两次出现的解决办法有多重性 2, 三次出现的解决办法有多重性 3 等 。In the example the solutions are 0 and 40. The solution 40 has a multiplicity of 2 because it occurs twice. In the next activity, you will explore the effect that m ultiplicity has on the graph of a polynomial function.
::在C(x)=0.002x(x-40)(x-40)(40)的示例中,解决办法是0和40。40的答案是40。40的答案是2倍,因为它发生两次。在下一个活动中,你将探讨多重性对多元函数图形的影响。
Activity 2: Rational Zeroes Theorem
::活动2:理性零点理论Factoring a polynomial function can help you to easily identify the zeros because it allows you to use the zero product property .
::乘以一个多元函数可以帮助您很容易地识别零,因为它允许您使用零产品属性。Example
::示例示例示例示例A furniture company performed an analysis on one of the couches they sell.
::一家家具公司对其出售的沙发之一进行了分析。-
The
revenue
as a function of selling
couches can be modeled by the function
::销售 x 沙发的收入函数,可以用 R(x) = 47x2 - x3 函数模拟。 -
The monthly cost of selling
couches can be modeled using
::可使用C(x)=239x+287模拟出售x沙发的月成本。 -
The profit function can be modeled using the polynomial
::利润函数可使用多边 P(x) x3+47x2-239x-287模型构建。
Use algebraic methods to find the zeroes of this function.
::使用代数方法查找此函数的零。+Do you want to reset the PLIX?T here are not any quadratic methods that will work for this case. Instead, t he function can be written in factored form using the R ational F actors T heorem. The factors of the leading coefficient , -1, are ± 1. The factors of the constant , -287, are ±1, ±7, ±41, ±287. The possible rational factors are:
::不存在适用于此案例的任何二次曲线方法。 相反, 函数 P( x) x3+47x2-2-239x-287可以使用理性因素理论以系数形式写成。 主要系数-1的系数为 +1。 常数- 287的系数为 +1, +7, 41, 287, 可能的理性因素为 :
:1x+1)、(1x-1)、(1x-1)、(1x+7)、(1x-7)、(1x-7)、(1x+41)、(1x-41)、(1x+287)、(1x-287)、(1x-287)、(1x-1x+1)、(-1x-1/1)、(-1x+7)、(-1x-7)、(-1x+41)、(-1x-41)、(1x+287)、(-1x-287)
B egin by testing and continue through the list until you find a factor . Keep in mind that none of these may be factors.
::开始测试( 1x+1) , 并在列表中继续直到您找到一个系数 。 请记住, 这些要素都不是因素 。Since the remainder is 0, is a factor of Furthermore , the quotient when is divided by is Thus, the polynomial can be written as:
::由于其余为0,x+1是-x3+47x2-239x-239x-287的乘数,因此,当-x3+47x2-2-239x-287除以x+1时,多数值可以写成:
::-x3+47x2-239x-287=(x+1)(-x2+48x-287)The quadratic factor can be further factored into It is customary to factor out negative leading coefficients as well. For example, can be rewritten as so the polynomial in factored form is:
::二次系数-x2+48x-287可以进一步纳入(-1x+7)(x-41),通常也考虑负主要系数。例如,(-1x+7)可以改写为(x-7),因此,系数形式的多数值为:
::-x3+47x2-2-239x-287(x+1)(x-7)(x-41)U sing the zero product property, find the zeros of the function as follows:
::使用零产品属性,查找函数的零如下:•
•
::• x+1=0x%1•
::• x-7=0x=7•
::• x-41=0x=41Answer: The zeros of are -1, 7, and 41.
::答复:P(x)零是-1、7和41。The zeros of the profit function represent the break-even points. If the price is set to $7 or $41, the company will make $0 profit. The zero at -1 should be ignored because the price cannot be set to -$1. In general, the domain of the profit function only includes prices greater than or equal to 0, or
::利润函数的零代表平衡点。 如果价格定在7美元或41美元, 公司将产生0美元利润。 以 - 1 的零应该忽略, 因为价格不能定在 - 1 美元。 一般来说, 利润函数的域只包括大于或等于 0 或 x+0 的价格 。Since the factors of a polynomial determine the zeros ( t he factor will have a zero at the R ational F actors T heorem can be extended to zeros.
::由于多元系数的系数决定零(系数ax-b在巴巴为零),理性系数理论可以扩大到零。Rational Zeros Theorem
::理性零点定理If
Activity 3: The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
::活动3:代数的基本理论The chapter Functions explored the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra in quadratics. A ll degree 2 functions have 2 roots.
::本章“函数”探讨了二次方位代数的基本理论。所有二级函数都有2个根。From this, you might speculate that a function of degree would have roots. This conjecture is the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra .
::由此,你可能会推测, 程度 n 的函数有正根。 这个猜想是代数的基本理论 。The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
::代数基本理论Any polynomial with complex coefficients of degree has complex roots, including repeated roots.Although some roots may not be rational, they still exist as irrational or complex roots.
::虽然有些根源可能不合理,但它们作为不合理或复杂的根源仍然存在。Example
::示例示例示例示例Find the zeros of the function:
::查找函数的零: f(x)=4x4-4x4-4x3-23x2-x-6To find the zeros of a function, a n alternative to using the R ational Z eros T heorem is using a graph. Use the graph below to find any rational zeros of
::要找到函数的零, 使用理性零点理论的替代方法正在使用一个图形。 使用下方的图形来查找任何f( x) 的理性零。The graph shows two zeros: -2 and 3. However, according to the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, there should be 4 roots because this is a degree 4 polynomial.
::该图显示两个零:-2和3。 然而,根据代数的基本理论,应该有4根根,因为这是4度多义。T he missing roots are not irrational because irrational roots cross the -axis at irrational values. Since there are no other -intercepts , the missing roots must be complex.
::缺失的根不是非理性的,因为非理性的根以非理性的值跨越 X 轴。 因为没有其他的 X 拦截, 缺失的根必须复杂。To find the complex roots, start by dividing the polynomial by the known factors. The root -2 means that is a factor of and the root 3 means that is also a factor of
::要找到复杂的根根, 首先从已知因素除以多元系数开始。 根 - 2 意味着 x+2 是 f( x) 的因数, 根 3 意味着 x-3 也是 f( x) 的因数 。You could either divide by these factors one by one using synthetic division , or multiply them together and divide by the resulting product . This would be similar to how dividing 12 by 2 and then by 3 is the same as dividing 12 by 6.
::您可以用合成分裂法将这些因素一一地除以,也可以用合成分裂法将这些因素一一地相除,或者将这些因素相乘,然后用所产生的产品加以除以。这类似于12除以2,然后再除以3等于12除以6。The factors multiply to U se long division to divide by
::乘以 (x+2)(x-3) =x2-x-6) 乘以 (x2-x3) =x2-x-6 。The division problem above can be written as:
::上面的划分问题可以写为:
::4x4-4x3-23x2-x-6=(x2-x-6)(4x2+1)This can be factored since
::从 x2 - x - 6= (x+2)(x- 3) 开始可以计算。
::4x4-4x3-23x2-x-6=(x+2)(x-3)(4x2+1)Although the quadratic cannot be factored using rational numbers, t he zeros can be found using the square root method.
::虽然方形 4x2+1 无法使用合理数字进行系数计算,但可用平方根法找到零。Answer:
::答复:-2,3,12i,-12iDiscussion Question : Is it possible for a polynomial to have an odd number of complex roots?
::讨论问题:多族制是否可能有数量奇多的复杂根根?
Activity 4: The Container Problem Solved
::活动4:解决集装箱问题Answer the questions below to solve the problem asked in the introduction: What size would the sides of the cube need to be to hold 150 cubic inches?
::回答以下问题以解决导言中提出的问题:立方体的两侧需要多少尺寸才能保持150立方英寸?Recall the container problem and interactive from the introduction:
::回顾前言中的集装箱问题和互动:+Do you want to reset the PLIX?Discussion Question : How could you solve the container problem without rewriting the equation into standard form ?
::讨论问题:如果不将等式改写成标准形式,你如何解决集装箱问题?
Wrap-Up: Review Questions
::总结:审查问题Summary
::摘要-
The zeros of a polynomial function are the
intercepts.
::多面函数的零是 X 界面。 -
The Rational Zeros Theorem states that if
is a zero of the polynomial function
with integer coefficients, then
is a factor of the constant term, and
is a factor of the leading coefficient.
::理性零理论指出,如果qp是具有整数系数的多元函数p(x)的零,则q是常数的一个系数,p是主要系数的一个系数。 -
The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra states that any polynomial with complex coefficients of degree
has
complex roots, including repeated roots.
::代数的基本理论指出,任何具有复杂程度系数的多元性,都有复杂的根部,包括反复的根部。
-
Interpret the characteristics of a
polynomial
within a real-world context.