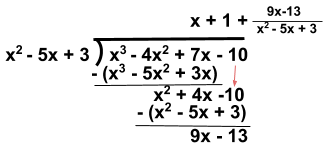合理函数的特征
章节大纲
-
Lesson Objectives
::经验教训目标-
For a
function
that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in
terms
of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a verbal description of the relationship.
::用于模拟两个数量之间的关系的函数,根据数量解释图表和表格的关键特征,以及显示关键特征的草图,以口头描述关系。 -
Rewrite simple rational expressions in different forms
::以不同形式重写简单的理性表达式
Introduction: Bright Lights Revisited
::导言:重新审视亮光Much like there isn't a specific parent polynomial function , but instead a parent function for each power, there isn't a specific parent rational function .
::就像没有特定的父函数, 而不是每个权力的父函数, 没有一个特定的母函数。The function B = L 4 π d 2 allows you to determine the apparent brightness of a light source based on distance from it. T he numerator of the function represents the luminosity, or light energy, of the light source, and the denominator represents the surface area of the light photons as they travel in all directions in 3 dimensions . The denominator takes on the formula for the surface area of a sphere, 4 π r 2 , where the radius of the sphere is the distance of the light from the source.
::函数 B=L4d2 允许您根据距离确定光源的亮度。 该函数的分子数代表光源的光度或光能,而分母则代表光光光光子在3维范围内向方移动时的表面面积。 分母以球表面面积的公式( 4r2) 为基础, 球的半径是光与源的距离。This function has a parent function of f ( x ) = 1 x 2 . Not only does the structure of a rational function affect the graph, but transformations can affect the graph like they would any other function.
::此函数有 f( x) =1x2. 的父函数。 不仅理性函数的结构会影响图形, 变换也会像影响其他函数一样影响图形 。Use the interactive below to examine how the structure of a rational function affects its graph.
::使用下面的交互功能来检查合理函数的结构如何影响其图。
Activity 1: Vertical Asymptotes
::活动1:垂直单位数A rational function is undefined at the vertical asymptote(s). Since a fraction cannot be divided by zero, the vertical asymptotes will be at values that result in the denominator being zero. Find these values by setting the denominator equal to zero and solving the equation . Recall that a rational function can be defined as r ( x ) = f ( x ) g ( x ) given that f ( x ) and g ( x ) are polynomial functions. The vertical asymptotes are the zeroes of g ( x ) . Since it is possible for a function to have unlimited zeroes, a rational function can have unlimited asymptotes .
::垂直 asymptote (s) 未定义一个合理函数。 由于分数不能除以 0, 垂直 asymptotes 将位于导致分母为零的值。 通过将分母设为 0 和解析方程式来查找这些值。 提醒注意, 如果 f( x) = f( x) g( x) 和 g( x) 是多元函数, 合理函数可以定义为 r( x) =f( x) g( x) 。 垂直 asymptotes 是 g( x) 的零。 由于函数有可能有无限的零, 理性函数可以有无限的 asymptotes 。Example
::示例示例示例示例Find the vertical asymptotes of the function r ( x ) = x x 2 − 9
::查找函数 r( x) =xx2- 9 的垂直单位数The first step in finding the vertical asymptote(s) is to set the denominator equal to zero.
::寻找垂直零位数的第一步是将分母设为零。x 2 − 9 = 0
::x2- 9=0Solving this equation will result in the following zeroes:
::解决这一方程式将产生以下零:x 2 − 9 = 0 ( x − 3 ) ( x + 3 ) = 0 x = 3 and x = − 3
::x2- 9=0(x-3)(x+3)=0x=3和 x3Answer: The vertical asymptotes are at x = 3 and x = − 3.
::答复:垂直微粒为 x=3 和 x=3 3 。
Activity 2: Horizontal Asymptotes
::活动2:水平单数represent a value that the output of a function approaches but never reaches as the x value increases or decreases without bound. When observing different rational functions, notice patterns in the values they approach as the input increases and decreases.
::表示函数处理的输出值,但值从未达到,因为 x 值的增减没有约束。在观测不同的理性函数时,它们随着输入的增减而使用的数值通知模式。Use the interactive below to look for these patterns.
::使用下面的交互式模式查找这些模式。Use the interactive below for more practice finding horizontal asymptotes.
::使用下面的交互功能, 以获得更多的实践, 找到水平的空位 。
Activity 3: Oblique Asymptotes
::活动 3: 重点零时数When the degree of the leading term in the numerator is greater than the degree of the leading term in the denominator, there is no horizontal asymptote . In this case, there is an instead of a horizontal asymptote. An oblique asymptote is a slanted line that a function approaches but never touches.
::当分子中领先术语的大小大于分母中领先术语的大小时,就不会有横向的静态。 在此情况下, 会有一个而非水平的静态。 倾斜的静态是一条倾斜的线, 函数会接近但不会触动 。To find the equation of an oblique asymptote, divide the numerator by the denominator. In the previous activity, the equations for horizontal asymptotes were derived based on the outputs approached by the function as the value of x increased or decreased. A similar approach can be used to derive the equation of an oblique asymptote.
::要找到倾斜的瞬间方程式, 将分子数除以分母。 在先前的活动中, 水平小数方程式的公式是根据函数所选择的数值增加或减少的输出而得出的。 类似的方法可以用来计算斜斜的瞬间方程式的等式 。Example
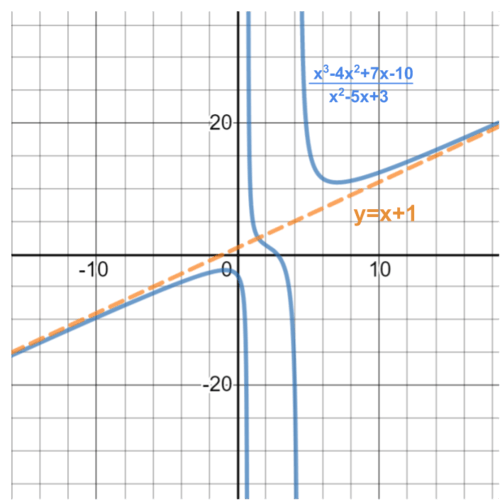
::示例示例示例示例Find the oblique asymptote of the function g ( x ) = x 3 − 4 x 2 + 7 x − 10 x 2 − 5 x + 3 .
::查找函数 g( x) =x3- 4x2+7x- 10x2- 5x+3 的斜体星位As the value of x increases, the value of g ( x ) will approach infinity. Consider the leading terms in both the numerator and denominator. The value of x 3 will increase faster than the value of x 2 by a rate of x . Furthermore, it can be stated that the value of x 3 − 4 x 2 + 7 x − 10 will increase faster than x 2 − 5 x + 3 by a factor of x 3 − 4 x 2 + 7 x − 10 x 2 − 5 x + 3 .
::随着x值的增加, g(x) 的值将接近无穷。 考虑分子和分母中的主要值。 x3 的值将以x的速率比x2的值增长更快。 此外, 可以指出, x3-4x2+7x- 10的值将比x2-5x+3的速率增长更快, 乘以 x3-4x2+7x- 10x2- 5x+3。D ividing the numerator by the denominator will produce the oblique asymptote.
::将分子分解为分母 将产生倾斜无序U se t he quotient x + 1 + 9 x − 13 x 2 − 5 x + 3 to find the equation of the asymptote. The remainder portion of the quotient can be removed because as the value of x increases, the value of the remainder will approach 0 (a result of the degree of the numerator being less than the degree of the denominator).
::使用 商数 x+1+9x- 13x2- 5x+3 查找无线方程式的方程。 商数的剩余部分可以删除, 因为随着 x 值的增加, 剩余部分的值将接近 0 (由于分子的程度小于分母的程度)。Answer: The equation of the asymptote is y = x + 1.
::回答:小数方程式的方程式是y=x+1。All asymptotes thus far have been linear ; however, polynomial division could produce a quadratic function , a cubic function, etc. Consider the function h ( x ) = x 4 + 1 x 2 − 1 . The quotient of x 4 + 1 x 2 − 1 is x 2 + 1 + 2 x 2 − 1 . Since the remainder approaches 0 as the value of x increases, the result will be an oblique asymptote of y = x 2 + 1. How does the equation y = x 2 + 1 relate to the function h ( x ) ?
::到目前为止,所有微粒都是线性的; 但是, 多式分裂可以产生二次函数、 立方函数等。 考虑函数 h( x) =x4+1x2 - 1。 x4+1x2 - 1 的商数是 x2+1+2x2 - 1 。 由于其余值随着x值的增加而接近 0, 其结果将是 y=x2+1 的倾斜性, y=x2+1 。 公式 y=x2+1 与函数 h( x) 有何关系?Use the interactive below to explore this relationship.
::使用下面的交互方式来探索这种关系。
Activity 4: Using Characteristics to Graph Rational Functions
::活动4:利用特征来图形有理函数Using your knowledge of asymptotes coupled with your knowledge of intercepts , you can quickly graph a rational function. Recall that the x - intercept is the value of x when f ( x ) = 0. Additionally, the y-intercept is the value of f ( x ) when x = 0.
::使用您对小点数的知识以及您对拦截的知识, 您可以快速绘制一个合理的函数。 提醒注意, 当 f( x) =0 时, x 界面是 x 的值。 此外, y 界面是当 x=0 时 f( x) 的值 。Example
::示例示例示例示例Graph the function below after f inding the asymptotes, domain , x-intercepts, and y-intercept.
::在找到小数点、 域、 x 界面和 y 界面后, 图形显示下面的函数 。f ( x ) = 3 x x 2 − 3 x − 4
:xx) = 3x22 - 3x- 4
a. Asymptotes
::a. 微粒The vertical asymptote can be found with any value of x that makes the denominator undefined once the fraction is fully simplified. Since this function cannot be simplified, set the denominator to 0 and solve for x.
::以任何 x 值可以找到垂直的单点, 使分母在分数完全简化后没有定义 。 由于此函数无法简化, 将分母设为 0 并解析 x 。x 2 − 3 x − 4 = 0 ( x − 4 ) ( x + 1 ) = 0
::x2- 3x- 4=0(x- 4)(x+1)=0The vertical asymptotes are x = 4 and x = − 1.
::垂直的单位数为 x=4 和 x1 。The following are the rules for finding the horizontal asymptote for a function of the form r ( x ) = a x n + . . . b x d + . . . , derived in the previous activity.
::以下是从上一个活动中生成的 r( x) = oxn+...bxd+... 的窗体函数的横向末位值的查找规则 。If n < d The horizontal asymptote is y = 0. If n = d The horizontal asymptote is y = a b . If n > d There is no horizontal asymptote. In this case, the degree of the numerator is less than the degree of the denominator. The horizontal asymptote will be y = 0.
::在此情况下, 分子的度小于分母的度。 水平衰减将是 y=0 。b. Domain
::b. 域域The domain of a rational function will be all real numbers except for any holes or vertical asymptotes. These values will result in an undefined output. Since this function has no holes and the vertical asymptotes are at x = 4 and x = − 1 , the domain will be all real numbers except 4 and -1. This can be written using set notation as { x | x ∈ ℝ , x ≠ − 1 , 4 } or interval notation as
::理性函数的域将全部为真实数字, 除了任何孔或垂直的单点数之外。 这些值将导致未定义的输出。 由于此函数没有洞, 垂直的单点数为 x=4 和 x\\\\ 1, 域数将全部为真实数字, 除了 4 和 - 1 。 这可以使用设置的标记来写入 {xxR, x1,4} 或间距标记 (,- 4)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ 4,\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ 。c. x-intercept
::c. x 接口Since the y-value of the x-intercept is 0, the x-intercept can be found by setting f ( x ) equal to 0 and solving for x.
::由于 X 界面的 Y 值为 0, 通过设定 f( x) 等于 0 和为 x 解析, 可以找到 x 的 y 值 。0 = 3 x x 2 − 3 x − 4
::0=3x22-3x-4From here, multiply both sides by x 2 − 3 x − 4 to cancel the denominator , leaving you with only the numerator. Another approach could be putting 0 over 1 and cross multiplying.
::从这里, 将两边乘以 x2 - 3x - 4 来取消分母, 只留给您一个分子。 另一种方法可能是将 0 乘以 1 并交叉倍增 。( x 2 − 3 x − 4 ) ⋅ 0 = 3 x x 2 − 3 x − 4 ⋅ ( x 2 − 3 x − 4 )
:x2-3x-4)0=3x2-3x-4(x2-3x-4)0=3x2-3x-4(x2-3x-4)0=3x-3x-4=3x_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
::3⁄4 ̄ ̧漯B
::d. y 界面
::在 f( 0) 时可以找到 y 界面 。 对于 y 轴上降落的点, 它必须 x 值为 0 。
::f( 0) = 3( 0)( 0) 2 - 3( 0) - 4( 0) - 4= 0 - 4=0
::y- interview 也会在 0,0 点, 你本可以在没有找到 f (0) 的情况下发现这一点, 因为 x- interview 是在 y 轴上 。
::e. 图f(x)
::绘制理性方程式的快速方法包括先绘制小点图。一旦获得这些方程式,你只需要知道函数接近小点图的方向。要更好地了解图形如何适合小点图,请绘制 X 界面和 y 界面图。要获取更多细节,请绘制其他点图。
::另一种快速的图形分析方法是使用您对正数和负数的知识。一旦分子和分母都得到充分的计算,您可以将您选择的输入替换为每个系数,如果系数是正数或负数,则只记录。数值f(-4)将用来演示。
:x) = 3xx2-3x-4-4= 3xx(x-4)(x+1)f(-4) = (34)(-4)-4(-4)-4(-4+4)(-4)-(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(-)(+)(-)(-)(-)
If there are an even number of negative lines in that section, the graph of the original function will be posi tive.
::由于负除以两个负数因素为负数,f(x)至f(-4)的f(x)将是负数。较快的方法是逐个绘制分子和分母中的系数。X调之间的每一部分是正数或负数,取决于该节中每个系数的图表是正数还是负数。如果该节中出现奇数的负数行,原函数的图将是负数。如果该节中出现偶数的负数行,原始函数的图表将是正数。如果该节中出现偶数的负数,则原始函数的图表将是正数。Use the interactive below to explore how this would work on the function f ( x ) .
::使用下面的交互方式来探索如何在 f(x) 函数上运行 。Summary -
Vertical asymptotes
happen when the denominator of a rational function equals zero.
::当一个理性函数的分母等于零时, 垂直会发生空位 。 -
Horizontal asymptotes
happen when the degree of the numerator is less than or equal to the degree of the denominator.
::当分子的程度小于或等于分母的程度时,水平的微粒就会发生。 -
Oblique asymptotes
happen when the degree of the numerator is greater than the degree of the denominator.
::当分子的程度大于分母的程度时,就会出现简单微弱的微粒。 -
To find the equation of an oblique asymptote, divide the numerator by the denominator.
::要找到倾斜的瞬间方程式, 将分子除以分母 。
Wrap-Up: Review Questions
::总结:审查问题 -
For a
function
that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in
terms
of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a verbal description of the relationship.