被动传输
章节大纲
-
Can any molecule move freely through your ?
::任何分子能通过你自由移动吗?The cell regulates most molecules that pass through the cell membrane. If a molecule is charged or very big, it won't make it through the cell membrane on its own. However, small, non-charged molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water, can pass through the cell membrane freely.
::细胞控制着大部分通过细胞膜的分子。 如果一个分子充电或非常大, 它将无法单独通过细胞膜。 但是, 小型的、 不充电的分子, 如氧、 二氧化碳和水, 可以自由地通过细胞膜。Passive Transport
::被动运输Recall that the cell membrane is semipermeable . It does not allow everything to pass through. Some molecules can pass easily through your cell membranes, while others have more difficulty. Sometimes molecules need the help of special transport proteins to move across the cell membrane. Some molecules even need an input of energy to help get them across the cell membrane. The movement of molecules across a membrane without the input of energy is known as passive transport . When energy (ATP) is needed, the movement is known as . Active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient , from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
::提醒注意细胞膜是半可移动的。 它不允许所有东西通过。 有些分子很容易通过你的细胞膜, 而另一些分子则比较困难。 有时分子需要特殊的迁移蛋白来帮助穿透细胞膜。 有些分子甚至需要输入能量来帮助他们跨过细胞膜。 分子在没有能量投入的情况下穿越细胞膜的移动被称为被动迁移。 当需要能量( APT) 时, 移动就被称为 。 主动迁移分子会随其浓度梯度移动, 从低浓度地区到高浓度地区。Simple Diffusion
::简单传播One example of passive transport is , when molecules move from an area of high concentration (large amount) to an area of low concentration (low amount). Molecules are said to naturally flow down their concentration gradient. This type of diffusion proceeds without an input of energy. In simple diffusion , molecules that are small and uncharged can freely diffuse across a cell membrane. They simply flow through the cell membrane. Simple diffusion does not require energy or need the assistance of a transport protein. Other larger or charged molecules that diffuse across a membrane may need assistance from a protein .
::被动迁移的一个例子是,当分子从高浓度地区(大)转移到低浓度地区(低量)时,分子据说会自然地向下流动其浓度梯度。这种扩散在没有投入能量的情况下进行。在简单的扩散中,小分子和未充电的分子可以在细胞膜之间自由扩散。它们只是通过细胞膜流动。简单的扩散不需要能量或需要运输蛋白的帮助。其他在膜之间扩散的较大或充电分子可能需要蛋白的帮助。Oxygen is a molecule that can freely diffuse across a cell membrane. For example, oxygen diffuses out of the air sacs in your lungs into your bloodstream because oxygen is more concentrated in your lungs than in your . Oxygen moves from the high concentration of oxygen in your lungs to the low concentration of oxygen in your bloodstream. Carbon dioxide, which is exhaled, moves in the opposite direction - from a high concentration in your bloodstream to a low concentration in your lungs.
::氧是一种分子,可以自由扩散到细胞膜中。例如,通过肺部空气囊中的氧扩散到你的血液中,因为氧在你的肺部中比在你的肺部中更加集中。氧从你的肺中的高氧浓度移动到血液中的低氧浓度。吸入的二氧化碳朝着相反的方向移动,从血液中的高浓度移动到肺部中的低浓度。Passive Transport using Membrane Proteins
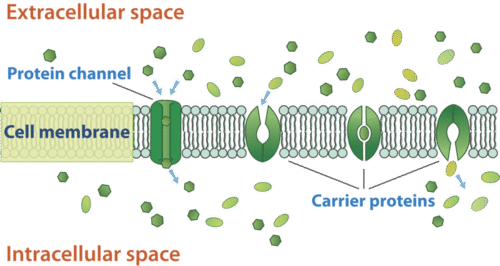
::使用薄膜蛋白进行被动运输Sometimes, molecules cannot move through the cell membrane on their own. These molecules need special transport proteins to help them move across the membrane, a process known as facilitated diffusion . These special proteins are called channel proteins or carrier proteins ( Figure ), and they are attached to the cell membrane. In fact, they go through the cell membrane, from the inside of the cell to the outside.
::有时,分子无法单独通过细胞膜。这些分子需要特殊的迁移蛋白来帮助他们通过细胞膜,这是一个被称为促进扩散的过程。这些特殊蛋白被称为通道蛋白或载体蛋白(图示 ) , 它们与细胞膜相连。 事实上,它们通过细胞膜,从细胞内部到外。Channel proteins provide an open channel or passageway through the cell membrane for molecules to move across. Many channel proteins allow the diffusion of ions. Ions are charged atoms. The charge makes it difficult to cross the cell membrane without assistance. Channel proteins are specific for the molecule they transport. For example a sodium ion crosses the membrane through a channel protein specific for sodium ions.
::通道蛋白质为分子通过细胞膜移动提供了一个开阔通道或通道。 许多通道蛋白允许离子扩散。 电离原子充电。 电荷使得在没有帮助的情况下难以跨过细胞膜。 通道蛋白度是针对其传输的分子的。 例如, 离子钠通过专门用于钠离子的通道蛋白穿过膜。Carrier proteins bind and carry the molecules across the cell membrane. These proteins bind a molecule on one side of the membrane, change shape as they carry the molecule across the membrane, and deposit the molecule on the other side of the membrane. Even though a protein is involved in both these methods of transport, neither method requires energy. Therefore these are still types of passive transport.
::载体蛋白质结合并携带分子穿过细胞膜。这些蛋白质将分子粘合在细胞膜的一边,随着分子携带到膜的两侧而改变形状,并将分子嵌入膜的另一侧。尽管这两种迁移方法都涉及蛋白质,但这两种方法都不需要能量。因此,这些仍然是被动迁移的类型。Protein channels and carrier proteins are involved in passive transport. Summary
::摘要- Passive transport does not require energy input.
::被动运输不需要能源投入。
- An example of passive transport is diffusion, the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
::被动迁移的一个例子是扩散,分子从高浓度地区转移到低浓度地区。
- Carrier proteins and channel proteins are involved in facilitated diffusion.
::承运人蛋白质和渠道蛋白质参与促进传播。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。- Cell Membrane Passive Transport at (4:41)
::4:41时(4:41)的细胞膜被动运输
- What does selectively permeable mean?
::有选择地渗透意味着什么?
- Can a membrane control the direction of diffusion? Explain your reasoning fully.
::膜能控制扩散的方向吗?
- Give two examples of phospholipid soluble molecules? How can these molecules move across a cell membrane? What affects the direction of their movement?
::举两个可以溶解的磷素分子的例子?这些分子如何移动到细胞膜上?它们的移动方向会受到什么影响?
- What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? What are two types of facilitated diffusion?
::简单与便利传播之间有什么区别?促进传播的两种类型是什么?
Review
::回顾- Explain two ways materials can enter the cell through passive transport.
::解释材料通过被动运输进入细胞的两种方式。
- Does passive transport involve an expenditure of much energy? Why or why not?
::被动运输是否需要花费大量能源?为什么或为什么不是?
- How does oxygen move across the membrane?
::氧气如何穿过膜?
- Passive transport does not require energy input.