子类函数的垂直垂直移位
章节大纲
-
Your knowledge of transformations, specifically vertical shift , apply directly to sinusoidal functions . In practice, sketching shifted functions requires greater attention to detail and more careful labeling than other functions. Can you describe the following transformation in words?
::您对变换的知识,特别是垂直转换的知识,直接适用于正弦函数。实际上,草图变换函数需要比其他函数更加关注细节和更加谨慎的标签。您能否用文字描述以下的变换?
::f(x) =sinxg(x) 3sinx- 4In what order do the reflection, stretch and shift occur? Is there a difference?
::反射、伸展和转移的顺序如何?有区别吗?Vertical Shift of Sinusoidal Functions
::子类函数的垂直垂直移位The general form of a sinusoidal function is:
::类象功能的一般形式是:
:xxx)+d)+(b(x+c)+(d)+(xx)+(xx)+
Recall that controls and the controls reflection. Here you will see how controls the vertical shift.
::回顾控件和 控件反射。 您可以在这里看到 d 如何控制垂直移动 。The most straightforward way to think about vertical shift of sinusoidal functions is to focus on the sinusoidal axis , the horizontal line running through the middle of the sine or cosine wave. At the start of the problem identify the vertical shift and immediately draw the new sinusoidal axis. Then proceed to graph amplitude and reflection about that axis as opposed to the axis.
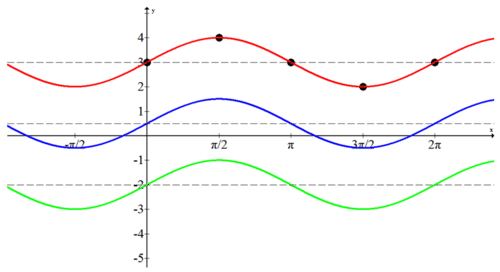
::思考正弦值函数垂直移动的最直接的方法是聚焦于正弦或正弦波中贯穿正弦或正弦波的水平线的正弦轴。在问题开始时确定垂直移动,并立即绘制新的正弦值轴。然后对正弦轴进行图解振幅和反射,而不是 X 轴。The graphs of the following three functions are shown below:
::以下三个函数的图表如下:
::f(x) =sinx+3g(x) =sinx-2h(x) =sinx+12To draw these graphs, the new sinusoidal axis for each graph is drawn first. Then, a complete sine wave for each one is drawn. Note the five important points that separate each quadrant to help to get a clear sense of the graph. There are no reflections in these graphs and they all have an amplitude of 1. Right now every cycle starts at 0 and ends at but this will not always be the case.
::要绘制这些图, 将先为每个图绘制新的正弦轴。 然后为每个图绘制完整的正弦波 。 注意五个重要点, 将每个象限分隔开来, 以帮助获得对图的清晰感 。 这些图中没有反射, 它们都有1的振幅 。 现在每个周期开始于 0 , 结束于 2+ , 但情况并非总是如此 。Watch the portions of the following video focused on vertical translations:
::观看以下视频中以垂直翻译为重点的部分:Examples
::实例Example 1
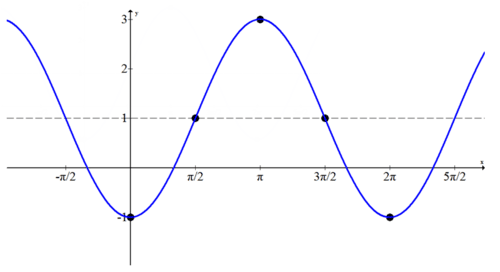
::例1Earlier, you were asked which order vertical shift and reflection should be performed in and if it matters. The following transformation can be described as follows .
::早些时候,有人问您在哪个顺序下垂直转换和反射应该进行,如果重要的话。 以下的转换可描述如下。
::f(x) =sinxg(x) 3sinx- 4D escribe the stretching and reflecting first and then the vertical shift. This is the most logical way to discuss the transformation verbally because then the numbers like 3 and -4 can be explicitly identified in the graph.
::首先描述伸展和反射,然后描述垂直变化。这是口头讨论变换的最合乎逻辑的方式,因为这样就可以在图表中明确标明3和4等数字。The order in describing the transformation matters. When describing vertical transformations it is most intuitive to simply describe the transformations in the same order as the order of operations.
::描述转换事项的顺序。 描述垂直转换时, 最直观的办法是简单地描述与操作顺序相同的转换顺序。Example 2
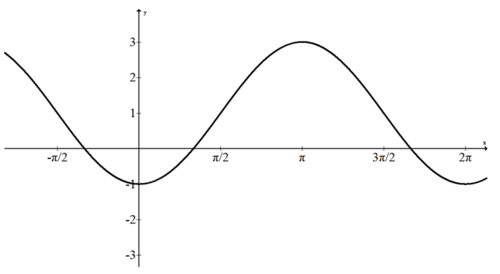
::例2Identify the equation of the following transformed cosine graph.
::标明下列已转换的余弦图的方程式。Since there is no sinusoidal axis given, you must determine the vertical shift, stretch and reflection. The peak occurs at and the trough occurs at (0, -1) so the horizontal line directly between +3 and -1 is . Since the sinusoidal axis has been shifted up by one unit . From this height, the graph goes two above and two below which means that the amplitude is 2. Since this cosine graph starts its cycle at (0, -1) which is a lowest point, it is a negative cosine. The function is .
::由于没有给定正弦轴, 您必须确定垂直移动、 伸展和反射。 峰值在3 处发生, 顶部在 0, -1 处发生, 因此+3 和 - 1 之间的水平线直接为 Y= 1 。 由于正弦轴被一个单位 d=1 移动了 。 从此高度, 图表显示振幅在2 以上, 下图显示振幅为 2 。 由于此正弦图以最低点 0, - 1 开始循环, 它是一个负余弦。 函数为 f( x) 2cos *x+1 。 函数为 f( x) 2cosx+1 。
Example 3
::例3Transform the following sine graph in two ways. First, transform the sine graph by shifting it vertically up 1 unit and then stretching it vertically by a factor of 2 units. Second, transform the sine graph by stretching it vertically by a factor of 2 units and then shifting it vertically up 1 unit.
::以下正弦图以两种方式转换。 首先, 将正弦图垂直向上移动1个单位, 然后垂直向上拉展2个单位。 其次, 将正弦图垂直向上拉展2个单位, 然后将正弦图垂直向上移动1个单位。When doing ordered transformations it is good to show where you start and where you end up so that you can effectively compare and contrast the outcomes. See how both transformations start with a regular sine wave. The two columns represent the of transformations that produce different outcomes.
::当进行定序变换时,很好的做法是显示从何开始和从何结束,以便有效地比较和对比结果。看看两种变换是如何从正正弦波开始的。两列代表产生不同结果的变换。Example 4
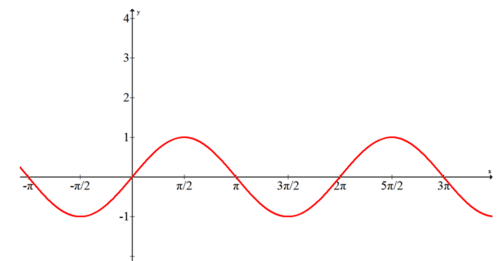
::例4What equation models the following graph?
::下图是什么样的方程式模型?
:xx) = 3sinx- 1)
Example 5
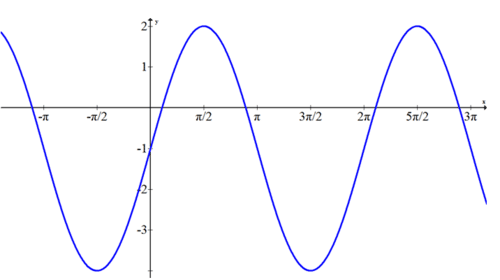
::例5Graph the following function: .
::如下函数图解 : f( x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ x+1 。First draw the horizontal sinusoidal axis and identify the five main points for the cosine wave. Be careful to note that the amplitude is 2 and the cosine wave starts and ends at a low point because of the negative sign.
::首先绘制水平正弦轴, 并确定余弦波的五个主要点。 请注意, 振幅为 2 , 余弦波因负符号而以低点开始和结束 。Summary -
For the general form of the sinusoidal function
the constant
represents the vertical shift which moves the entire function up or down.
::对于正弦函数f(x)asin(b(x+c)+d)的一般形式,恒定 d 表示将整个函数上下移动的垂直移动。 -
To understand vertical shift, focus on the sinusoidal axis, the horizontal line running through the middle of the sine or cosine wave.
::要了解垂直移动,请关注正弦轴和正弦轴, 横线贯穿正弦或余弦波的中间。
Review
::回顾Graph each of the following functions that have undergone a vertical stretch, reflection, and/or a vertical shift.
::下列各函数中经过垂直伸展、反射和/或垂直移动的每个函数图。1.
::1. f(x)%2sinx+42.
::2. g(x) = 12cos=x-13.
::3. h(x)=3sinx+24.
::4. j(x)1.5cosx+125.
::5. k(x) = 23sinx-3Find the minimum and maximum values of each of the following functions.
::查找以下每个函数的最小值和最大值。6.
::6. f(x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ x+1\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\7.
::7. g(x)=2cosx-48.
::8. h(x) = 12sinx+19.
::9. j(x) cosx+510.
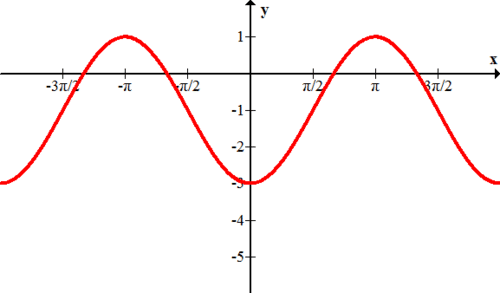
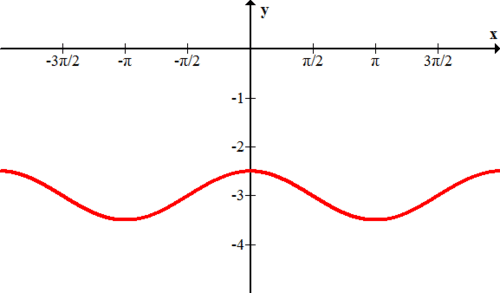
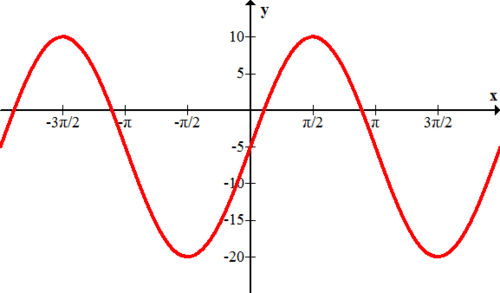
::10. k(x) =sin(x)- 1Give the equation of each function graphed below.
::给出以下图表显示的每个函数的方程式 。11.
12,
13.
14.
15.Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
For the general form of the sinusoidal function
the constant
represents the vertical shift which moves the entire function up or down.