蛋白质合成
章节大纲
-
How do you build a protein ?
::你怎么制造蛋白质的?Your body needs proteins to create , regulate chemical reactions , transport oxygen, and perform other important tasks in your body. But how are these proteins built? They are made up of units called amino acids . Just like there are only a few types of blocks in a set, there are a limited number of amino acids. But there are many different ways in which they can be combined.
::您的身体需要蛋白质来创造、调节化学反应、运输氧和在您的身体中执行其他重要任务。 但是这些蛋白质是如何构建的呢? 它们由称为氨基酸的单位组成。 就像在一组中只有几类区块一样, 氨基酸的数量也有限。 但是可以用多种不同的方式将其组合在一起。Introduction to Protein Synthesis
::蛋白综合介绍A monomer is a molecule that can bind to other monomers to form a polymer. Amino acids are the monomers of a protein. The sequence contains the instructions to place amino acids into a specific order .
::单体是一种可与其他单体结合形成聚合物的分子。氨酸是蛋白质的单体。序列包含将氨基酸置于特定顺序的指令。When the amino acid monomers are assembled in that specific order, proteins are made, a process called protein synthesis. In short, DNA contains the instructions to create proteins. But DNA does not directly make the proteins. Proteins are made on the ribosomes in the cytoplasm , and DNA (in an eukaryotic cell) is in the . So the cell uses an intermediate to produce proteins.
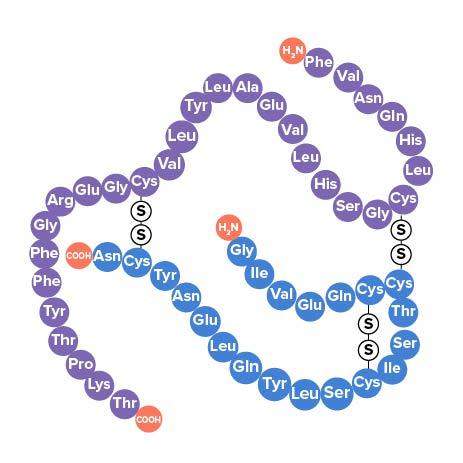
::当氨基酸单体按此特定顺序组装时,就会产生蛋白质,一个叫蛋白质合成的过程。简言之,DNA包含创造蛋白质的指示。但DNA并不直接产生蛋白质。蛋白质是用细胞细胞内的血清制成的,而DNA(在乳胶细胞中)在细胞中。所以细胞使用中间体来生产蛋白质。Each strand of DNA has many separate sequences that code for a specific protein. Insulin is an example of a protein made by your cells ( Figure ). Units of DNA that contain code for the creation of a protein are called genes .
::每条DNA都有许多不同的序列,这些序列为特定蛋白质编码。胰岛素是细胞(图示 ) 所制作蛋白质的例子。 含有蛋白质生成代码的DNA单位被称为基因。Insulin. Each blue (Chain B) or purple (Chain A) bead represents a different amino acid. Just 20 different amino acids are arranged in many different combinations to make thousands of proteins. Cells Can Turn Genes On or Off
::单元格可以打开或关闭基因There are about 22,000 genes in every human cell. Does every human cell have the same genes? For the most part, yes. Does every human cell make the same proteins? No. In a multicellular organism , such as us, cells have specific functions because they have different proteins. They have different proteins because different genes are expressed in different cell types (which is known as gene expression ).
::每个人类细胞中大约有22,000个基因。每个人类细胞有相同的基因吗?大部分是。每个人类细胞都有相同的蛋白质吗?没有。在像我们这样的多细胞生物体中,细胞有特定的功能,因为它们有不同的蛋白质。它们有不同的蛋白质,因为不同的基因以不同的细胞类型表达(被称为基因表达方式 ) 。Imagine that all of your genes are "turned off." Each cell type only "turns on" (or expresses) the genes that have the code for the proteins it needs to use. So different cell types "turn on" different genes, allowing different proteins to be made. This gives different cell types different functions.
::想象一下, 您所有的基因都是“ 关闭 ” 。 每个细胞类型只“ 启用 ” ( 表达式) 。 因此不同的细胞类型“ 启用 ” 不同的基因, 允许生成不同的蛋白质。 这给不同的细胞类型提供了不同的功能 。Once a gene is expressed, the protein product of that gene is usually made. For this reason, gene expression and protein synthesis are often considered the same process.
::因此,基因表达和蛋白质合成往往被视为同一过程。Summary
::摘要-
DNA contains the instructions to assemble amino acids in a specific order to make protein.
::DNA含有将氨基酸组装成蛋白质特定用途的指示。 -
Each cell type only "turns on" (or expresses) the genes that have the code for the proteins it needs to use.
::每个细胞类型只“打开”(或表示)具有需要使用的蛋白质编码的基因。 -
Gene expression and protein synthesis are usually considered the same molecular process.
::基因表达和蛋白合成通常被视为相同的分子过程。
Review
::回顾-
What is a gene?
::什么是基因? -
What is an amino acid?
::什么是氨基酸? -
If every human cell has the same genes, how can they look and function so differently?
::如果每个人类细胞都有相同的基因, 它们如何看起来和功能如此不同? -
What is the relationship between DNA and proteins?
::DNA和蛋白质之间的关系是什么?
-
DNA contains the instructions to assemble amino acids in a specific order to make protein.