按跨科划分的卷数
章节大纲
-
Remember how to compute the volume of a cylinder or prism using the cross-sectional area and length (height) of the object? If the cross-sectional area is known and constant along the height, the volume calculation is easy. But, what if the cross-sectional area changes in a known manner along the line that is the height, like it does for a cone or pyramid? How could a single method in calculus be used to determine the volume of either of these types of solids?
Volumes by Cross Section
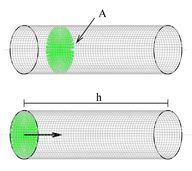
::按跨科划分的卷数A circular cylinder can be generated by translating a circular disk along a line that is perpendicular to the disk. In other words, the cylinder can be generated by moving the cross-sectional area (the disk) through a distance . The resulting volume is called the volume of solid and it is defined to be
::圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆柱体可以通过圆圆圆圆圆盘沿着与圆盘垂直的直线转换产生,换言之,圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆圆
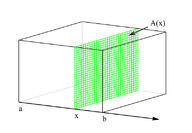
::V=Ah。 。 。The volume of solid does not necessarily have to be circular. It can take any arbitrary shape. One useful way to find the volume is by a technique called “slicing”. To explain the idea, suppose a solid is positioned on the -axis and extends from points to .
::固体体积不一定是圆形的。它可以任意形状。找到体积的一个有用方法是使用一种称为“切除”的技术。为了解释这一想法,假设固体S位于x轴上,从x=a点延伸到x=b点。Let be the cross-sectional area of the solid at some arbitrary point . Just like we did in calculating the definite integral in the previous chapter, divide the interval into sub-intervals and with widths
::让 A( x) 成为某个任意点 x 时固体的横截面区域。 就像我们在计算上一章中确定的组成部分时所做的一样, 将间隔 [a, b] 分为 n 次隔间和宽度
::x1,x2,x3,x3... xn。Eventually, we get planes that cut the solid into slices
::最终,我们得到的飞机 将固体切成n片
::S1,S2,S3,S3,SSTake one slice, . We can approximate slice to be a rectangular solid with thickness and cross-sectional area . Thus the volume of the slice is approximately
::切片一个片段, Sk。 我们可以将切片Sk 大致为长方形固体, 厚度为 xk 和横截面区域 A( xk) 。 因此切片的卷Vk 大约是
::VkáA(xk) xk(xk) 。Therefore the volume of the entire solid is approximately
::因此,整个固体的V体容量大约是
::V=V1+V2+...+Vnk=1nA(xk)xk。If we use the same argument to derive a formula to calculate the , let us increase the number of slices in such a way that . In this case, the slices become thinner and, as a result, our approximation will get better and better. That is,
::如果我们用同样的论据来得出计算 的公式,让我们增加切片数量,这样可以达到 xk0。在这种情况下,切片变薄,结果我们的近似值会变得更好。也就是说,
:xk) *xk*xk*xk*xk=1nA(xk) *xk*xk=1nA(xk) *xk*xk=1nA(xk)xk。
Notice that the right-hand side is just the definition of the definite integral. Thus
::注意右侧只是确定的整体部分的定义。
::V=limx0k=1nA(xk)xkabA(x)dx。Now, let's derive a formula for the volume of a sphere with radius centered on the point (0, 0, 0) whose cross section in the -plane is as shown using slices perpendicular to the -axis to determine .
::现在,让我们为以点( 0, 0, 0)为中心半径的球体体体积得出一个公式, 这个圆球体的横段与X轴垂直的切片相同, 以决定 A( x) 。A cross-section of the sphere in the plane is shown.
::显示Xy平面中球体的横截面。Cross-sections through the sphere that are perpendicular to the -axis are circles. Since the equation of the circle in the -plane is , the radius of the circle in the plane perpendicular to the -axis is , which means the area of each circle is
::横跨与 x 轴垂直的圆球的横截面为圆圈。由于x- 平面圆的方程式为x2+y2=r2, 圆的半径为 y=r2-x2, 这意味着每个圆圈的面积为 A(x)\\\ y2\\\(r2-x2)。If we look at the area slices from to , the volume of the sphere is given by
::如果我们查看 x=0 到 x=r 的区域切片, 球的体积由
::VabA(x)dx=20r(r2-x2)dx=2[r2x-x33]0r=2[2r33]VabA(x)dxV=43r3This is the formula we expect to see for the volume of a sphere, .
::这是我们期望看到的一个球体的体积的公式,V=43°r3。The above derivation used a cross-section perpendicular to the -axis, and therefore integration along the -axis. The next example uses integration along the -axis.
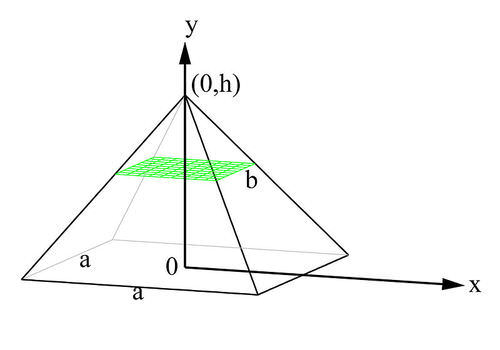
::上述推论使用了与x轴相对切的截面截面,因此沿x轴进行了整合。下一个例子使用了Y轴的集成。Now, let's derive a formula for the volume of a pyramid whose base is a square of sides and whose height (altitude) is .
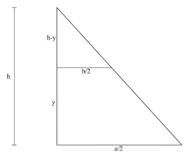
::现在,让我们为金字塔的体积 得出一个公式, 金字塔的基数是平方 a 和它的高度(高度)是h。Let the -axis pass through the apex of the pyramid, as shown above . At any point in the interval , the cross-sectional area is a square. If is the length of the sides of any arbitrary square, then, by similar triangles (Figure 7b),
::让 Y 轴通过金字塔的顶端, 如上所示。 横截面区域是一个正方形。 如果 b 是任意方形两边的长度, 那么用相似的三角形( 图 7b) 。
::12b12a=h-yh,b=ah(h-yy)。Since the cross-sectional area at is %3Db%5E2"> ,
::由于y的横截面面积为A=b2,
%3Db%5E2%3D%5Cfrac%7Ba%5E2%7D%7Bh%5E2%7D(h-y)%5E2.">
::A=b2=a2h2(h-y) 2。
Using the volume formula,
::使用音量公式,dy%20%5C%5C%0A%26%3D%5Cint%5Climits_0%5Eh%20%5Cfrac%7Ba%5E2%7D%7Bh%5E2%7D(h-y)%5E2dy%20%5C%5C%0A%26%3D%5Cfrac%7Ba%5E2%7D%7Bh%5E2%7D%20%5Cint%5Climits_0%5Eh%20(h-y)%5E2%20dy.%5C%5C%0A%26%3D%5Cfrac%7Ba%5E2%7D%7Bh%5E2%7D%20%5Cleft%5B-%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B3%7D%20(h-y)%5E3%20%5Cright%5D_0%5Eh%20%26%26%20%5Cldots%20%5Ctext%7BUsing%7D%20%5C%20u-%20%5Ctext%7Bsubstitution%20of%7D%20%5C%20u%3Dh-y%20%5C%20%5Ctext%7Band%7D%20%5C%20du%3D-dy%5C%5C%0AV%20%26%3D%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B3%7D%20a%5E2%20h%20%26%26%20%5Ctext%7Bto%20evaluate%20the%20integral.%7D">
::VcdA= 0ha2h2(h-y)2dy=a2h20h(h-y)2dy.=a2h2[-13(h-y)3,310h].Using u - 替代u=hy和dudyV=13a2hto 评估整体体。
Therefore the volume of the pyramid is , which agrees with the standard formula.
::因此,金字塔的体积是V=13a2h,这与标准公式一致。Cavalieri's Principle
::Cavalieli原则You may recall from geometry that two triangles with congruent bases and the same height have the same area regardless of what the triangle looks like. This arises from the 2-dimensional case of Cavalieri’s Principle . The 2-dimensional case states: Two regions between two parallel lines have the same area if and only if every line parallel to the two bounding lines intersects the two regions with line segments of equal length. Watch the first 1 minute and 30 seconds of the following video for a good visual explanation of the 2-dimensional case.
::从几何学上,你可能记得,两个三角形具有相同的基点和同一高度,无论三角形长长什么样,都具有相同的区域。这来自卡瓦列里尼原则的二维案例。二维案例指出:两个平行线之间的两个区域具有相同的区域,如果而且只有当两个平行线的每条线线都与两条线的线条相交,而两条线的线条长度相同。请看以下视频的前1分钟和30秒,对二维案例作一个清晰的直观解释。There is also a 3-dimensional case of Cavalieri's Principle which applies to volume. The 3-dimensional case of Cavalieri’s Principle states: The volumes of two objects are equal if the areas of their corresponding cross-sections are in all cases equal. Two cross-sections correspond if they are intersections of the figure with planes equidistant from a chosen base plane. In other words, imagine placing two figures between two parallel planes so that the bases are on the parallel planes. Now, imagine taking the cross-section of the two figures with a plane that is parallel to the plane the base is on. If the areas for both of those cross-sections are the same and that same result holds true for any plane between the base planes, then the two figures have the same volume.
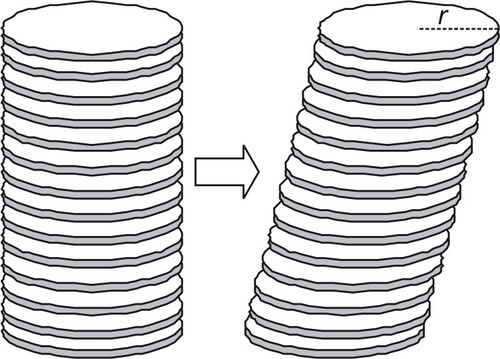
::Cavalielii原则还有一个适用于体积的三维案例。Cavalirii原则的三维案例指出:两个对象的体积是相等的,如果它们对应的横截面的面积在所有情况下都是相等的。两个横截面对应的是数字的交叉点和与选定基平面相等的平面的平面。换句话说,想象在两个平行的平面之间放置两个数字,使基面处于平行的平面上。现在,想象用一个与基座的平面平行的平面将两个数字的截面取出。如果这两个横截面的面积相同,而且对基平面之间的任何平面的结果都是一样的,那么这两个数字的体积是相同的。Visually, take a stack of coins such as in the image below.
::从视觉上看,拿一堆硬币,比如下面的图像。The stack is a cylinder and it is easy to calculate the volume because we have the formula: .
::堆叠是一个圆柱体,很容易计算体积,因为我们有公式:Vr2h。If you push the coins so that they are not all perfectly aligned like in the image below, it becomes more difficult to calculate the volume just by looking at the shape.
::如果按下硬币,使硬币不完全和下面的图像一样,那么光看形状就更难计算体积。However, since no coins were taken from or added to the stack, the overall number of coins is still the same and thus the volume of the object is the same as it was when it was a regular cylinder.
::然而,由于没有从堆叠中取出或加进硬币,硬币总数保持不变,因此对象的体积与一般圆筒时相同。Cavalieri’s principle can be proven by finding the . The volume by cross section method takes the area of all of the slices of the shape and adds them together to find the total volume. For two shapes, if the corresponding slices have the same area then the sum will be the same and the shapes will have the same volume.
::卡瓦列里(Cavaeliri) 的原则可以通过找到 来证明 。 以跨节法计算,体积的体积将形状所有切片的面积进行计算,并将其加在一起以找到总体积。 对于两种形状来说,如果相应的切片具有相同的区域,那么总和就会相同,形状的体积也会相同。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked how a single method in calculus could be used to determine the volume of a solid by knowing its cross-sectional area in any plane perpendicular along its height (length).
::早些时候,有人问,如何使用单一的微积分法,通过了解固体在任何高处(长度)垂直的平面上的横截面面积来确定固体的体积。This concept presented a method to find the volume by:
::这一概念提供了一种方法,通过下列方法查找卷号:-
Sketching the solid and a cross-section in a plane perpendicular to its height (length)
::将固体和横截面切切成与高度(长度)垂直的平面 -
Finding an expression for the cross-sectional area
(volume slice
) in the direction of the height (length).
::在高度(长度)方向的横截面区域A(片片 Adx)中查找表达式。 -
Determining the limits of integration along the direction of the height (length).
::确定沿着高度(长度)方向的融合限度。 -
Integrating to find the volume
::集成以查找音量
Example 2
::例2A solid has as it’s base the region in the -plane defined by the ellipse . Every cross-section by a plane perpendicular to the -axis is a quarter circle, with radius in the base. Find the volume of the solid.
::固态的基点是椭圆x2+4y2=4定义的X-平面区域。 与 y- 轴垂直的平面的每个横截面都是四分之一圆, 半径在基底。 查找固体的体积 。The cross section of the elliptical base in the plane is shown.
::显示xy平面的椭圆基的十字部分。Each cross-section perpendicular to the -axis through the ellipse is a quarter-circle with a radius equal to the line through the ellipse. The expression for the radius can be determined by solving the equation of the ellipse for :
::垂直于 Y 轴的每个横截面通过椭圆是一个四分之一圆圈,半径等于通过椭圆的线条。 半径的表达式可以通过解析椭圆的方程式来决定 x:, which gives the portion of the ellipse in Quadrant I.
::x=4 - 4y2=21 - y2,它给出了Quadrant I 部分的椭圆。The radius of any quarter-circle section in the upper half of the ellipse is:
::椭圆上半部任何四分之一圆圈的半径是:%3D2x%3D2%20%5Cleft%5B2%20%5Csqrt%7B1-y%5E2%7D%20%5Cright%5D%3D4%20%5Csqrt%7B1-y%5E2%7D.">
::r=2x=2[21-y2]=41-y2。
This means that the area of any quarter-circle section in the upper half of the ellipse is
::这意味着,椭圆上半部任何四分之一圈圈的面积是:%20%26%3D%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B4%7D%20%5Ccdot%20%5Cpi%20r
%5E2%3D%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7B4%7D%20%5Ccdot%20%5Cpi%20%5Cleft%5B4%20%5Csqrt%7B1-y%5E2%7D%20%5Cright%5D%5E2%2C%20%5C%20or%20%5C%5C%0AA
%20%26%3D4%20%5Cpi(1-y%5E2)">
::A=14r
2=14[41-y2/2),或A
=4(1-y2)
The volume of the solid can now be evaluated as follows:
::固体的体积现在可以评估如下:dy%20%5Cldots%20%5C%20%5Ctext%7BAccount%20for%20the%20upper%20and%20lower%20portions%20of%20the%20ellipse%7D%20%5C%5C%0A%26%3D2%20%5Cint%5Climits_0%5E1%204%20%5Cpi(1-y%5E2)dy%20%5C%5C%0A%26%3D8%20%5Cpi%5Cleft%5By-%20%5Cfrac%7By%5E3%7D%7B3%7D%20%5Cright%5D_0%5E1%20%5C%5C%0AV%20%26%3D%5Cfrac%7B16%7D%7B3%7D%20%5Cpi%20">
::V=2cdAdy... 计算椭圆的上下部分=2014(1-y2)dy=8[y-y33]01V=163
The volume of the solid is cubic units.
::固体的体积是163立方厘米。Example 3
::例3The base of a solid is in the -plane, and is defined by the equation . Each cross-section defined by a plane perpendicular to the -axis is an isosceles triangle, with height 5 inches. The side of the triangle that is not congruent to the other two is the base in the -plane. Find the volume of the solid.
::固态的底部位于xy-plane, 由方程式 x2+y2=36 定义。 与 x 轴垂直的平面所定义的每个横截面为等骨三角形, 高度为5 英寸。 三角形的侧面与其它两个不相容的侧面是 x- 平面的底部。 查找固体的体积 。The base of the solid in the -plane is shown below.
::x-平面上的固体底部如下所示。
The equation is a circle of radius 6. Each cross-section perpendicular to the -axis through the circle is an isosceles triangle whose base is determined to be:
::方程式 x2+y2=36 是半径的圆形 6. 圆形中与 x 轴相垂直的每个横截面是一个等分三角形,其基数被确定为:
::B(x)=2[36-x2],从x=0到x=6。This means that the area of any isosceles section in Quadrants I & IV of the circle is
::这意味着圆的 Quadrants I & IV 中的任何等距区域是
::A(x)=12B(x)=5=536-x2。The volume of the solid can now be evaluated as follows:
::固体的体积现在可以评估如下:
::V=2abA(x)dx... 圆圈左侧部分(二次和三次二次二次夸轮)和右侧部分(第一次和第四次二次夸轮)的计数值。=20636-x2dxx... 集成可以通过(1) 使用图形计算器 OR=100636-x2dx... (2) 进行以下变量替换,然后进行评估: V=2abA(x)x...x=6sinu,dx=6cosçudu, 和整合限制 u=0至u2V=100236cos2udu=36000212(1+cos2u)du=180[u+sin2u]02V=903V=282.7英寸3The volume of the solid is cubic units.
::固体的体积是90立方单位。Review
::回顾-
Find the volume of a pyramid whose base is a square with sides of length 20 and whose height is 15.
::找到一个金字塔的体积,其底部是方形,方形长20,身高15。 -
Find the volume of a cone of height 4 and base diameter 10.
::查找高4和直径10的锥体体的体积。 -
A 12 by 15 swimming pool has a depth that changes along its longer side as the function
. Find its volume.
::A 12+ 15 游泳池的深度随着函数 f(x) = 6+2cos( 20x) 的功能而变化。 查找其体积 。 -
Use the method of slicing to find the volume of a pyramid of height two whose base is an equilateral triangle with sides of length two.
::使用切片方法查找高高2的金字塔的体积,其底部是双边三角形,两边长。 -
Use the method of slicing to find the volume of an object of length 5 whose cross sections are triangles of height 4 and width given by
,
.
::使用切除方法查找长度为5的物体的体积,其横段为高度4的三角形,宽度由 w(x)=1+x, 0x=5给定。 -
There is a solid lying on the Cartesian plane between
and
whose cross sectional area is given by the function
. What is its volume?
::在X=0和x=1之间的笛卡尔平面上有一个实心,函数A(x)=x3+x给定了该平面的横段区域。其体积是多少? -
There is a solid lying on the Cartesian plane between
and
whose cross sectional area is given by the function
. What is its volume?
::在X=5和x=6之间的笛卡尔平面上有一个实心,函数A(x)=1x给定了该方块的横段区域。其体积是多少? -
There is a solid lying on the Cartesian plane between
and
whose cross sectional area is given by the function
. What is its volume?
::函数 A( x) =xcos =( x2) 给定的横段区域在 x1 和 x=1 之间的笛卡尔平面上有一个实心,其体积是多少? -
There is a solid lying on the Cartesian plane between
and
whose cross sectional area is given by the function
. What is its volume?
::在X=2和x=4之间的笛卡尔平面上有一个实心,函数A(x)=ln(x)x给定了横截段区域。其体积是多少? -
There is a solid lying on the Cartesian plane between
and
whose cross sectional area is given by the function
. What is its volume?
::函数 A( x) =sin( x) cos ( x)+1 给定的横段区域在 x=10 和 x=20 之间,在笛卡尔平面上有一块固体。 其体积是多少? -
State Cavalieri’s principle.
::国家卡瓦列里原则。 -
Consider a cross sectional cut of a sphere, taken parallel to and
units above the sphere’s “equator.” What is the radius of this cut, in terms of
, the radius of the sphere, and
?
::考虑一个球体的跨区块切除,与球体的“赤道”的“赤道”值平行和以y单位为单位。 从R、球体的半径和y的角度来说,这一切除的半径是多少? -
Say that a cylinder of height
is drilled into a sphere along a line that intersects the sphere’s center. What is the radius of this cylinder, in terms of
, the radius of the sphere, and
?
::说高度的气瓶 h 被钻入球体, 沿着横交球体中心线。 这个气瓶的半径是多少, 以R 、 球体半径和 h 表示? -
Say that a cylinder of height
is drilled into a sphere along a line that intersects the sphere’s center. What is the volume of what remains of the sphere? What term does this surprisingly not rely on? This is commonly known as the napkin ring problem.
::说高度的气瓶 h 被钻入球体中, 球体的中间线交叉。 球体的剩余体积是多少? 令人惊讶的是, 这个词不依赖什么? 这通常被称为餐巾环问题 。 -
How does the above napkin ring result relate to Cavalieri’s principle?
::上述餐巾环结果与卡瓦列里尼原则有何关系?
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Sketching the solid and a cross-section in a plane perpendicular to its height (length)