超曲函数的衍生物和综合物
章节大纲
-
When an object, initially at rest, is dropped from a height and free-falls it can be slowed down by air resistance (drag) that is proportional to the square of its speed. In this case, Newton’s second law can be written as the differential equation , where is the speed of the falling object as a function of time, is the mass of the object, is the acceleration of gravity , and is a coefficient that accounts for the density of air, the surface area of the object and its drag coefficient. Can you show that is the solution to the differential equation? What is the terminal velocity of the object, i.e., the speed attained when gravitational and air resistance forces are balanced? What is the equation for the distance , , the object falls as a function of time?
::当对象从高度和自由落下时, 最初在休息时会从高度和自由落下, 它会因与其速度平方成比例的空气阻力( 拖动) 而放慢速度。 在这种情况下, 牛顿的第二项法律( F=ma) 可以写成差异方程式 mddtv( t) = mg- kv2, 其中 v( t) 是坠落对象作为时间函数的速度, m 是物体的质量, g 是重力加速度 (9. 8 m/ s2) , k 是计算空气密度、 物体表面面积及其拖动系数的系数的系数 。 您可以显示 v( t) =mgktanh( gkmkm}t) 是差异方程式的解决方案吗? 对象的终端速度是多少, 即当引力和空气阻力平衡时所达到的速度? 距离的方程式是多少, s( t) 对象会随着时间的函数而下降?Derivatives and Integrals of Hyperbolic Functions
::超曲函数的衍生物和综合物Recall from the previous concept that the hyperbolic functions are defined as:
::回顾以前的概念,即双曲函数的定义是:Definitions of the Hyperbolic Functions Derivatives of Hyperbolic Functions
::超曲函数的衍生物Finding the derivative of each of the functions is just a matter of differentiating the exponential expressions. If we let the argument of each be , then the generalized of the hyperbolic functions are:
::查找每个函数的衍生物只是区分指数表达式的问题。如果我们让每个函数的参数为 u(x),那么双曲函数的普遍化就是:Derivatives of the Hyperbolic Functions These derivatives can be used to find the linearization of a function. For example, find the linearization (tangent line) of the following functions at :
::这些衍生物可用于查找函数的线性化。例如,在 x=0 找到下列函数的线性化(切线) :-
::sinh 5x 和 sinh=5x -
::tanh $%23x
The linearization of a function at is .
::x=0时函数 f(x) 的线性化为 f(x)\\\\f(0)+f*(0)x=f*(0)x+f*(0)x+f*(0)x+f(0)0。For :
::对于sinh5x:
::f( 0) =sinh @ @ 0=e0 - 02=02=02=0f}( 0) =ddxsinh @5x @5x @0=5cosh @5x @0=5cosh=0=5chosh=0=5x0+e0+e0=02=5_22=5)Therefore the linearization is
::因此线性化是sinh5x5xFor :
::坦纳23x:
::f( 0) = tanh= 230= e0 - e- 0e0+e-0= 02= 0f_( 0) = ddxtanh= 23x= 0= 23sech 223x= 0= 23sech 223x= 0= 23_ 230= 23_2e0+e-0=23Therefore the linearization is .
::因此,线性化是 tanh23x23x。Integrals of Hyperbolic Functions
::双曲函数的元件As expected, the integrals involving the six hyperbolic follow from the derivatives and are stated below:
::如预期的那样,六双曲的积分由衍生物产生,如下所示:Integrals of the Hyperbolic Functions Use the formulas above to evaluate the integral
::使用上面的公式来评价 {0ln}\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\dx dxUsing u-substitution: let , then
::使用 u- 替代: let u=2x, then du=2dx
::=12sinhu02224=12[sinh(ln4)-sinh0=12(eln4-e-n42-e0-e-02)=12(4-142)=1516Therefore, .
::因此,#0ln2coosh2x dx=1516。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked if you can show that is the solution to the differential equation . This differential equation governs the speed of an object as it free-falls and is slowed down by air resistance proportional to the square of its speed.
::早些时候, 有人询问您是否可以显示 v( t) = mgkktanh( gkmt) 是 mddtv( t) = mg- kv2 的差别方程式的解决方案。 这个差别方程式在天体自由坠落时控制着物体的速度, 并且由于与其速度正方形成比例的空气阻力而放慢速度 。Since ,
::自 mddt[mgktanh(gkmt)] =mmgkägkmsech2(gkmt) =mgçsech2(gkmt) 以来,and
::和,
::毫克-kv2=mg-k[mgkktanh(gkmt)]2=mg[1-tanh2(gkmt)]=mg-sech2(gkmt)],then is the solution.
:t) =mgktanh(gkmt) 是解决方案 。
You were also asked what is the terminal velocity of the object in free-fall, i.e., the speed attained when gravitational and air resistance forces are balanced?
::有人还问你,物体在自由降落时的终端速度是多少,即当引力和空气抵抗力量平衡时达到的速度是多少?The terminal speed occurs when reaches a maximum so that . Because , gives the terminal velocity.
::当 v( t) 达到最大时, 终端速度会发生, 这样 ddtv( t) =0。 因为 limx @ tanh*x=1, limtv( t) =mgk, 终端速度会加快 。Finally, you were asked what the equation for the distance, , the object falls as a function of time is.
::最后,有人问您距离的方程是多少, s(t), 对象会随着时间的函数而掉落。The distance, , is given by , which means
::S( t) 的距离由 s( t) % 0tv( 4/) d0tmgktanh* (gkm) d_ 表示, 这意味着.
:t) 0tmgktanh(gkm)dmgkln[cosh(gkmt)]。
Example 2
::例2Evaluate the derivative of at .
::以 x=ln @% 2 来评估 Yosh23x 的衍生物 。Find :
::查找 dydx :
::dx [ - osh2\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Now evaluate the derivative at :
::现在在 x=ln @% 2 上评价衍生物 :
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}(8+82) {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}(8+82) {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080} {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080} {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080} {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080} {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}The derivative of at is approximately -96.0.
::以x=ln2为单位的yosh23x的衍生物大约96.0。Example 3
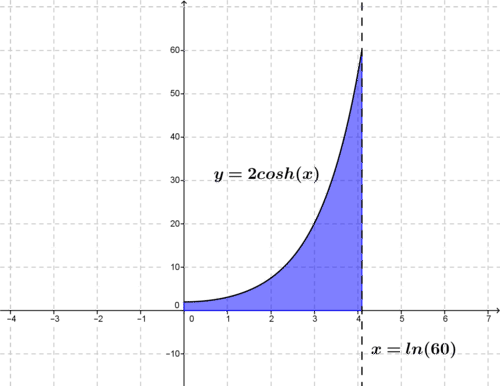
::例3Find the volume of the solid of revolution formed by the region , the -axis, the -axis, and the line revolved about the -axis.
::查找由区域y=2coshx、x轴、y轴和X=ln60围绕x轴线组成的革命固体体积。The figure above shows the disk method can be used to determine the volume: .
::上图显示了可用于确定体积的磁盘方法:Vab*f2(x)dx。
::{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}}2ddx}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}}}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}}}}}}}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}}。。Review
::回顾For #1-7, evaluate the derivatives.
::对于1 -7,评估衍生物。-
::sinh=% 4x3 内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内,内 -
::COshx22sinhx -
::sinh2 4x -
::sinh3x+2coosh(x+7) -
::- (cosh3x)2 -
::tanhx 塞克xx -
::3coth( 2x+1)
For #8-15, evaluate the integrals.
::815,评估整体体。-
::========================================================================================================================================= ======================================================================================================================= -
::========================================================================================================================================== ======================================================== -
Hint: use exponential definition of
and
-substitution
::4tanh3x dx hint: 使用 tanhx 和 u 替代的指数定义 -
::dx( ex+e- x) 2 -
:ex+e-xex-e-x)2dx
-
:ex- e- x) 2dx
-
::* * * * * * (ln*xx) dx * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * -
::================================================================================================================================= ========================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -