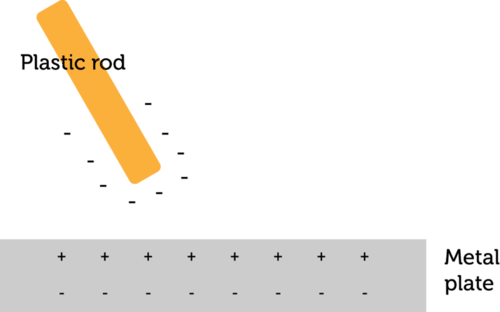电电费转电
章节大纲
-
Why is this girl's hair standing straight up? She is touching a device called a van de Graaff . The dome on top of the device has a negative electric charge . When the girl places her hand on the dome, she becomes negatively charged as well—right down to the tip of each hair!
::为什么这个女孩的头发直立起来?她触摸着一个叫范德格拉夫的装置。装置顶部的穹顶有负电荷。当那个女孩将她的手放在穹顶上时,她也变得负电荷——直到每根头发的顶部。Q: What causes the hair to stand on end?
::问题:什么原因导致头发在最后站立?A: All of the hairs have all become negatively charged, and like charges repel each other. Therefore, the hairs are pushing away from each other, causing them to stand on end.
::答:所有的头发都变成负的,就像电击一样,互相击退。因此,电击的头发互相推开,使头发最后站立。Transferring Electrons
::电子传输The girl pictured above became negatively charged because electrons flowed from the van de Graaff generator to her. Whenever electrons are transferred between objects, neutral matter becomes charged. This occurs even with individual atoms. Atoms are neutral in electric charge because they have the same number of negative electrons as positive . However, if atoms lose or gain electrons, they become charged particles called . You can see how this happens in the Figure . When an loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion, or cation. When an atom gains electrons, it becomes a negative charged ion, or anion.
::上面所描绘的女孩因为电子从范德格拉夫发电机流到她身上而变得负电。当电子在物体之间转移时,中性物质就会被电荷充电。这甚至发生在个别原子中。原子在电荷中是中性的,因为它们的负电子数量与正电子相同。但是,如果原子丢失或获得电子,它们就会成为电磁粒子。您可以看到图中是如何发生的。当电子丢失时,它就会变成正电离子或电离子。当原子获得电子时,它就会变成负电离子或电离子。Conservation of Charge
::保管费的保存Like the formation of ions, the formation of charged matter in general depends on the transfer of electrons, either between two materials or within a material. Three ways this can occur are referred to as , polarization, and . All three ways are described below. However, regardless of how electrons are transferred, the total charge always remains the same. Electrons move, but they aren’t destroyed. This is the law of conservation of charge .
::和离子形成一样,充电物质的形成一般取决于电子的转移,要么在两种材料之间,要么在一种材料之内。 三种方式可以被称为“、两极分化”和“。 所有三种方式都说明如下。 但是,不管电子是如何转移的,总电荷总是保持不变。电荷移动,但是它们并没有被摧毁。这是保护电荷的法律。Conduction
::指挥The transfer of electrons from the van de Graaff generator to the man is an example of conduction. Conduction occurs when there is direct contact between materials that differ in their ability to give up or accept electrons. A van de Graaff generator produces a negative charge on its dome, so it tends to give up electrons. Human hands are positively charged, so they tend to accept electrons. Therefore, electrons flow from the dome to the person’s hand when they are in contact.
::将电子从van de Graaff发电机转移到男人身上是行为举止的一个例子。 当不同的材料在放弃或接受电子的能力上发生直接接触时,就会发生操控。 范德拉夫发电机在其圆顶上产生负电荷,因此它倾向于放弃电子。 人手受到正面电压,因此他们倾向于接受电子。 因此,电子从穹顶流到接触时的人手。You don’t need a van de Graaff generator for conduction to take place. It may occur when you walk across a wool carpet in rubber-soled shoes. Wool tends to give up electrons and rubber tends to accept them. Therefore, the carpet transfers electrons to your shoes each time you put down your foot. The transfer of electrons results in you becoming negatively charged and the carpet becoming positively charged.
::你不需要用范德格拉夫发电机来进行导电。 当你穿着橡皮鞋走过羊毛地毯时,可能会发生这种情况。 伍尔倾向于放弃电子和橡胶,他们往往会接受。 因此,每次你放下脚,地毯就会将电子转移到鞋子上。 电子转换导致你受到负电,地毯就会受到正面电压。Polarization
::极分化Assume that you have walked across a wool carpet in rubber-soled shoes and become negatively charged. If you then reach out to touch a metal doorknob, electrons in the neutral metal will be repelled and move away from your hand before you even touch the knob. In this way, one end of the doorknob becomes positively charged and the other end becomes negatively charged. This is called polarization. Polarization occurs whenever electrons within a neutral object move because of the electric field of a nearby charged object. It occurs without direct contact between the two objects. The Figure models how polarization occurs.
::假设你穿着橡胶溶胶鞋穿过羊毛地毯,并受到负电荷。如果你再伸出手去触摸金属门把手,中性金属中的电子将被击退,并在你甚至触摸把手之前离开你的手。这样,门把手的一端就会受到正电,另一端就会受到负电荷。这被称为两极化。当中性物体中的电子由于附近一个电磁器的电场而移动时,就会发生极化。它不会在两个物体之间发生直接接触。两极化的图示模型是如何发生的。Q: What happens when the negatively charged plastic rod in the diagram is placed close to the neutral metal plate?
::问题:当图中负电荷塑料棒放在中性金属板附近时会怎样?A: Electrons in the plate are repelled by the negative charges in the rod. The electrons move away from the rod, causing one side of the plate to become positively charged and the other side to become negatively charged.
::A:电板上的电被棒子中的负电压击退,电离棒子移动,使板子的一边受到正电压,另一边受到负电压。Friction
::摩擦Did you ever rub an inflated balloon against your hair? You can see what happens in the Figure . Friction between the balloon and hair cause electrons from the hair to “rub off” on the balloon. That’s because a balloon attracts electrons more strongly than hair does. After the transfer of electrons, the balloon becomes negatively charged and the hair becomes positively charged. The individual hairs push away from each other and stand on end because like charges repel each other. The balloon and the hair attract each other because opposite charges attract.
::你曾经在头发上擦过膨胀的气球吗?你可以看到图中的情况。气球和头发之间的摩擦导致从头发到气球上的“擦掉”电子。 这是因为气球比头发更能吸引电子。 在电子转换后,气球会受到负电压,头发会受到正面电压。 个人头发会相互推开,最后会站立,因为像电击一样互相反射。 气球和头发会相互吸引,因为电击会相互吸引。Electrons are transferred in this way whenever there is friction between materials that differ in their ability to give up or accept electrons.
::每当材料之间发生摩擦时,如果它们放弃或接受电子的能力不同,电子就以这种方式转让。Q: If you rub a balloon against a wall, it may stick to the wall. Explain why.
::问题:如果你在墙上擦气球,它可能粘在墙上。解释原因。A: Electrons are transferred from the wall to the balloon, making the balloon negatively charged and the wall positively charged. The balloon sticks to the wall because opposite charges attract.
::A:电从墙上转移到气球上,使气球负电,而墙上正电。气球卡在墙上,因为反电会吸引电。Use the PLIX below to determine if the known objects are attracted-to or repulsed-by a negatively charged balloon:
::使用下面的PLIX来确定已知物体是否被负电热气球吸引或击退:Summary
::摘要-
Whenever electrons are transferred between objects, neutral matter becomes charged. For example, when atoms lose or gain electrons they become charged particles called ions.
::当电子在物体之间转移时,中性物质就会被电荷充电。例如,当原子丢失或获得电子时,它们就会成为电荷粒子,称为离子。 -
Three ways electrons can be transferred are conduction, friction, and polarization. In each case, the total charge remains the same. This is the law of conservation of charge.
::电子可被转移的三种方式是导电、摩擦和两极分化。 在每一种情况下,总电费保持不变。 这是保护电费的法律。 -
Conduction occurs when there is direct contact between materials that differ in their ability to give up or accept electrons.
::当材料在放弃或接受电子的能力上有所不同时,即发生直接接触。 -
Polarization is the movement of electrons within a neutral object due to the electric field of a nearby charged object. It occurs without direct contact between the two objects.
::极化是指由于附近一个充电物体的电场而使电子在中性物体内移动,该物体在两个物体之间没有直接接触的情况下发生。 -
Electrons are transferred whenever there is friction between materials that differ in their ability to give up or accept electrons.
::每当材料之间发生摩擦时,如果材料放弃或接受电子的能力不同,即转让电子。
Review
::回顾-
How is charge transferred by a van de Graaff generator?
::Van de Graaff发电机如何转移电费? -
Compare and contrast the formation of cations and anions.
::比较和对比 生化和阴离子的形成。 -
State the law of conservation of charge.
::国家保存指控法。 -
Explain how conduction and polarization occur, using the example of walking across a wool carpet in rubber-soled shoes and then reaching out to touch a metal doorknob.
::解释导电和两极分化是如何发生的,例如,用橡皮鞋穿过羊毛地毯,然后伸出手来触摸金属门把手。 -
Predict what will happen to the charges of a plastic comb and a piece of tissue paper if you rub the tissue paper on the comb. (
Hint
: Plastic tends to accept electrons and tissue paper tends to give up electrons.)
::如果你在梳子上擦擦组织纸,预计塑料梳子和纸纸的装药将会发生什么。 (提示:塑料倾向于接受电子,组织纸倾向于放弃电子。 )
-
Whenever electrons are transferred between objects, neutral matter becomes charged. For example, when atoms lose or gain electrons they become charged particles called ions.