收入:税收经济学
章节大纲
-
Revenue: The Economics of Taxation
::收入:税收经济学Every government collects taxes in order to generate money to pay for the operation of the government, to fund programs, and to pay for interest on its debt. So where does the money come from? How do taxes affect individuals and businesses? Economists examine how taxes and other government revues influence productivity, growth, consumers, and resource allocation. Taxes are considered a burden since it can change the incentives to save, invest, and work. The people or companies being taxed, or the incidence of a tax, can be predicted by supply and demand. In effect, the tax on a good or service will either be absorbed by the producer or passed on to the consumer. Taxes can either encourage or discourage consumer activities. A positive aspect of a tax would be that homeowners are allowed to use interest payments on their mortgages as a tax deduction, while a sin tax is a high tax individuals pay on a socially undesirable product such as tobacco. The simplest effect is that taxes raise the final cost of a good or service and consumers will react by purchasing less of the product.
::每个政府都征税,以产生钱来支付政府的运作,资助方案,并支付其债务的利息。 因此,这些钱来自何处? 税收如何影响个人和企业? 经济学家审查了税收和其他政府复苏如何影响生产力、增长、消费者和资源分配。 税收被视为一种负担,因为它可以改变储蓄、投资和工作的激励机制。 被征税的人或公司,或税收的发生率,可以按供求预测。 事实上,对货物或服务的税收要么由生产者吸收,要么转给消费者。 税收可以鼓励或阻止消费者活动。 税收的一个积极方面是,允许房主使用抵押贷款的利息付款作为减税,而罪恶税则是高额的税收,个人对烟草等社会上不受欢迎的产品支付。 最简单的效果是,税收会提高货物或服务的最终成本,消费者会通过减少购买产品的反应。Universal Generalizations
::普遍化-
Taxes influence the economy by affecting resource allocation, consumer behavior, and the nation’s productivity and growth.
::税收影响经济,影响资源分配、消费者行为和国家生产力和增长。 -
Taxes are the single most important way for the government to raise revenue.
::税收是政府增加收入的最重要的唯一方法。 -
Government economic policies at all levels influence levels of employment, output, and price levels.
::各级政府的经济政策影响就业、产出和价格水平。
Guiding Questions
::问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问-
What does the government do with the tax money it collects?
::政府用它所收的税款做什么? -
How do government policies of taxing and spending affect the economy at the national, state, and local levels?
::政府税收和开支政策在国家、州和地方各级对经济有何影响?
All three levels of government within the United States require an enormous amount of money to run its programs and institute its policies. According to the U.S. government, all three levels (federal, state, local) collected nearly $6 trillion dollars in revenues for the fiscal year 2015. Since the end of World War II, revenues have grown exponentially. When adjusted for inflation and population, revenues have grown by more than 800%. Taxes can influence the economy by affecting various aspects of consumer behavior, resource allocation, growth, and productivity, as well as saving and spending, since the burden of taxes can be transferred to others.
::美国所有三级政府都需要巨额资金来实施其方案和制定政策。 据美国政府称,所有三级(联邦、州、地方)在2015财政年度都收集了近6万亿美元的收入。 自二战结束以来,收入急剧增长。 如果按通胀和人口进行调整,收入增长超过800 % 。 税收可以通过影响消费者行为、资源分配、增长和生产率以及储蓄和支出等各个方面影响经济,因为税收负担可以转移到其他人身上。Video: Basics of U.S. Income Tax Rate Schedule
::录像:美国所得税税率表基础-
Source: Khan Academy, Basics of US Income Tax Rate Schedule,
Elasticity and Tax Incidence
::弹性和税收发生率The example of cigarette taxes showed that because demand is inelastic, taxes are not effective at reducing the equilibrium quantity of smoking, and they are mainly passed along to consumers in the form of higher prices. The analysis, or manner, of how the burden of a tax is divided between consumers and producers is called tax incidence. Typically, the incidence, or burden, of a tax falls both on the consumers and producers of the taxed good, but if one wants to predict which group will bear most of the burden, all one needs to do is examine the elasticity of demand and supply. In the tobacco example, the tax burden falls on the most inelastic side of the market.
::香烟税的例子表明,由于需求是无弹性的,因此税收在减少吸烟的均衡数量方面并不有效,税收主要以较高价格的形式传递给消费者,对消费者和生产者之间如何分担税收负担的分析或方式被称为税收负担。 通常,税收的发生率或负担既落在消费者身上,也落在纳税商品的生产者身上,但如果人们想预测哪个群体将承担大部分负担,那么,需要做的就是检查供求的弹性。 在烟草方面,税收负担落在市场最无弹性的一边。If demand is more inelastic than supply, consumers bear most of the tax burden, and if supply is more inelastic than demand, sellers bear most of the tax burden.
::如果需求比供应更具弹性,消费者承担大部分税收负担,如果供应比需求更具弹性,卖方则承担大部分税收负担。The intuition for this is simple. When the demand is inelastic, consumers are not very responsive to price changes, and the quantity demanded remains relatively constant when the tax is introduced. In the case of smoking, the demand is inelastic because consumers are addicted to the product. The government can then pass the tax burden along to consumers in the form of higher prices, without much of a decline in the equilibrium quantity.
::这一点的直觉很简单。 当需求没有弹性时,消费者对价格变化的反应并不十分积极,而当税收引入时,要求的数量仍然相对稳定。 就吸烟而言,需求是无弹性的,因为消费者对产品上瘾。 然后,政府就可以以高价格的形式将税收负担传给消费者,而不会大量均衡数量下降。Similarly, when a tax is introduced in a market with an inelastic supply, such as, for example, beachfront hotels, and sellers have no alternative than to accept lower prices for their business, taxes do not greatly affect the equilibrium quantity. The tax burden is now passed on to the sellers. If the supply was elastic and sellers had the possibility of reorganizing their businesses to avoid supplying the taxed good, the tax burden on the sellers would be much smaller. The tax would result in a much lower quantity sold instead of lower prices received. 1 illustrates this relationship between the tax incidence and elasticity of demand and supply.
::同样,如果在供应无弹性的市场,例如海滨旅馆等市场实行税收,而卖方除了接受较低的商业价格之外别无选择,税收不会大大影响平衡数量,税收负担现在转嫁给卖方,如果供应有弹性,卖方有可能重组其企业以避免提供已征税货物,卖方的税收负担将小得多,税收将导致销售数量少得多,而不是收取的价格低得多。 1 税收支出与供求弹性之间的关系说明了。- Elasticity and Tax Incidence
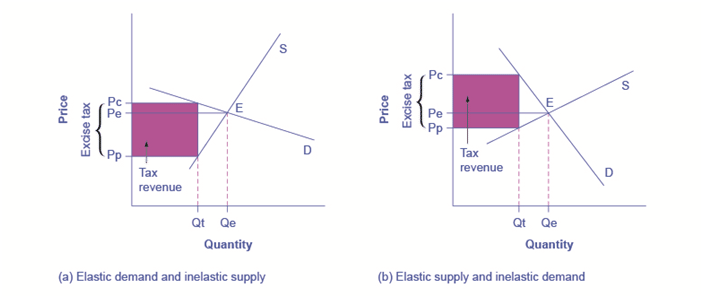
An excise tax introduces a wedge between the price paid by consumers (Pc) and the price received by producers (Pp). (a) When the demand is more elastic than supply, the tax incidence on consumers Pc – Pe is lower than the tax incidence on producers Pe – Pp. (b) When the supply is more elastic than demand, the tax incidence on consumers Pc – Pe is larger than the tax incidence on producers Pe – Pp. The more elastic the demand and supply curves are, the lower the tax revenue.
::消费税引入了消费者支付的价格(Pc)与生产者收到的价格(Pp)之间的差额。 (a) 当需求比供应更具弹性时,消费者的税额(Pc)比生产者的税额(Pe)要低。 (b) 当供应比需求更具弹性时,消费者的税额(Pc)比生产者的税额(Pp)要高。 供需曲线的弹性越大,税收就越低。In 1 (a), the supply is inelastic and the demand is elastic, such as in the example of beachfront hotels. While consumers may have other vacation choices, sellers can’t easily move their businesses. By introducing a tax, the government essentially creates a wedge between the price paid by consumers Pc and the price received by producers Pp. In other words, of the total price paid by consumers, part is retained by the sellers and part is paid to the government in the form of a tax. The distance between Pc and Pp is the tax rate. The new market price is Pc, but sellers receive only Pp per unit sold, as they pay Pc-Pp to the government. Since a tax can be viewed as raising the costs of production, this could also be represented by a leftward shift of the supply curve, where the new supply curve would intercept the demand at the new quantity Qt. For simplicity, 1 omits the shift in the supply curve.
::在1(a)项中,供应是无弹性的,需求是弹性的,例如海滨酒店等。消费者可能还有其他的度假选择,但卖主无法轻易地移动自己的生意。 通过引入税收,政府在消费者Pc支付的价格和生产商Pp收到的价格之间基本上形成了一种平衡。 换句话说,在消费者支付的总价格中,一部分由卖主保留,一部分以税收的形式支付给政府。 Pc和Pp之间的距离是税率。 新的市场价格是Pc,但卖主只得到每售一单位的PPP,因为他们向政府支付Pc-Pp。 由于税收可以被视为提高生产成本,这也可以由供应曲线的左倾转移来代表。 新的供应曲线在新数量Qt中截住需求。 为了简单起见,1省略了供应曲线的转变。The tax revenue is shown by the shaded area, which is obtained by multiplying the tax per unit by the total quantity sold Qt. The tax incidence on the consumers is given by the difference between the price paid Pc and the initial equilibrium price Pe. The tax incidence on the sellers is given by the difference between the initial equilibrium price Pe and the price they receive after the tax is introduced Pp. In 1(a), the tax burden falls disproportionately on the sellers, and a larger proportion of the tax revenue (the shaded area) is due to the resulting lower price received by the sellers than by the resulting higher prices paid by the buyers. The example of the tobacco excise tax could be described by 1(b) where the supply is more elastic than demand. The tax incidence now falls disproportionately on consumers, as shown by the large difference between the price they pay, Pc, and the initial equilibrium price, Pe. Sellers receive a lower price than before the tax, but this difference is much smaller than the change in consumers’ price. From this analysis one can also predict whether a tax is likely to create a large revenue or not. The more elastic the demand curve, the easier it is for consumers to reduce quantity instead of paying higher prices. The more elastic the supply curve, the easier it is for sellers to reduce the quantity sold, instead of taking lower prices. In a market where both the demand and supply are very elastic, the imposition of an excise tax generates low revenue.
::税收收入以阴影区为表,以每单位税乘以售出总量获得的税额乘以售出量总量获得。消费者的税额比付价Pc和最初平衡价格Pe之间的差额来表示。卖方的税额由最初平衡价Pe与税收开始后收到的价格之间的差额来表示。 在1(a)项中,卖方的税收负担不成比例地下降,而税收收入的更大比例(隐蔽区)是由于卖方收到的价格低于买方支付的较高价格。烟草消费税的例子可以1(b)项描述,因为供应弹性大于需求。现在,消费者的税额不成比例地下降,正如他们支付的价格、Pc和最初的平衡价格之间的巨大差额所显示的那样,卖主得到的价格比税前低得多,但这一差额比消费者价格的变化要小得多。从这一分析中可以预测税收是否会产生巨额收入,而消费税额则比较容易,而销售商的销售额则要降低价格。Excise taxes tend to be thought to hurt mainly the specific industries they target. For example, the medical device excise tax, in effect since 2013, has been controversial for it can delay industry profitability and therefore hamper start-ups and medical innovation. But ultimately, whether the tax burden falls mostly on the medical device industry or on the patients depends simply on the elasticity of demand and supply.
::税收税往往被认为主要伤害了它们所针对的特定行业。 比如,2013年生效的医疗设备消费税一直引起争议,因为它可能延缓行业盈利,从而阻碍新企业和医疗创新。 但最终,税收负担主要落在医疗设备行业还是病人身上,仅仅取决于供求的弹性。Consumer Behavior
::消费者行为行为In 1998 American tobacco companies were sued by the states. Tobacco companies agreed to pay annual sums of money to the states to compensate them for health-care costs related to smoking and the states increased "sin taxes" to reduce consumer consumption. A sin tax can increase the cost of the product to help off set the economic cost to others and to decrease a particular behavior. Efforts to tax tobacco in the U.S. have generated several million dollars of excess revenues for the states, however, it has not impacted current tobacco users. Tobacco is an inelastic product and the taxes have not significantly affected consumption.
::1998年,美国烟草公司被各州起诉。 烟草公司同意每年向各州支付一笔钱,以补偿他们与吸烟有关的保健费用。 各州增加了“soin税 ” , 以减少消费消费。 罪恶税可以增加产品成本以帮助抵消他人的经济成本并减少特定行为。 美国烟草税的努力为各州创造了数百万美元的超额收入,但并没有影响当前的烟草使用者。 烟草是一种无弹性产品,税收并没有严重影响消费。
Taxes on the purchase of packs of cigarettes in each state States are shaded on a continuous color scale where Less than $2 excise tax per pack $2 excise tax per pack $4 excise tax per packFor more information on taxes and consumption see: .
::有关税收和消费的更多信息见: 。In addition to sin taxes, there are taxes that can encourage certain types of activities, such as adding solar power to a house can earn a homeowner a tax credit. Home ownership is encouraged, so the federal government will allow homeowners to use interest payments on mortgages as a tax deduction.
::除了罪责税之外,还有一些税可以鼓励某些类型的活动,比如为房屋增加太阳能发电可以让房主获得税收抵免。 家庭所有权受到鼓励,因此联邦政府将允许房主将抵押贷款的利息付款用作减税。Resource Allocation
::资源分配Whenever a tax is levied, it will affect production. That is because a tax placed on a good will increase the price of that product when it is sold. This tax can shift the supply curve to the left, and the cost of the tax will eventually be passed on to the consumer. When a product increases in price, consumer reaction is predictable --- they buy less. When sales fall, the producer may have to cut back on production or cut labor costs to cover the decrease in product sales. If sales fall and do not rebound, it may impact the other factors of production. If this occurs, then labor, capital, or entrepreneurs may have to move to other industries and be "reallocated". If the products are "elastic" then consumers generally will purchase substitutes if they are less expensive, or they will not purchase the more costly items until the market readjusts. If the product is inelastic, then the consumer may have no choice but to purchase it, while adjusting spending in other areas to offset the increase in prices.
::当税收被征收时,它就会影响生产。 这是因为对货物征税会提高产品售出时的价格。 该税可以将供应曲线向左转移,而税收的成本最终将转嫁给消费者。 当产品价格上涨时,消费者的反应是可预测的 -- -- 它们买得更少。 当销售下降时,生产者可能不得不削减生产或削减劳动力成本以弥补产品销售的下降。 如果销售下降而不反弹,它可能会影响其他生产要素。 如果发生这种情况,劳动力、资本或企业家可能不得不转移到其他行业,并被“变卖 ” 。 如果产品“弹性”那么,消费者一般会购买替代物,如果价格较低的话,或者在市场调整之前不会购买更昂贵的物品。 如果产品是无弹性的,那么消费者可能别无选择,只能购买它,同时调整其他领域的支出以抵消价格的上涨。Productivity and Growth
::生产力和增长Lastly, taxes can impact both productivity and economic growth. There is a theory that if taxes go up, people will be less inclined to work hard to earn more money since they will need to pay more in taxes. It is hard to quantify if this theory is, in fact, valid. If people work hard, earn extra money, then pay more in taxes, will they really decide that the extra money they have made is not worth it since they had to pay more in taxes at the end of the year? It is doubtful. The extra amount of taxes paid are indexed and because the taxes are taken out of a person's pay before he or she ever sees it, there should be no negative consequences. Of course, a person may be upset at how much has been taken out for the purposes of paying taxes, but the additional earnings should off-set any reasonable amount paid in taxes. There is probably a level at which too many taxes, or too high of taxes, can affect productivity and growth, and this is therefore why people want lower taxes.
::最后,税收可以同时影响生产率和经济增长。 有一种理论认为,如果税收上升,人们就会不太愿意努力挣更多的钱,因为他们需要缴纳更多的税金。 如果这一理论是有效的,那么很难量化。 如果人们努力工作,挣更多的钱,然后缴纳更多的税,那么他们真的会决定他们多挣的钱是不值得的,因为他们在年底必须缴纳更多的税?这是值得怀疑的。所付的税额被指数化了,而且由于税收在人们发现之前就从一个人的薪水中扣除了,因此不应该产生消极的后果。 当然,一个人可能会对为纳税目的拿出多少钱而感到不满,但额外的收入应该抵消任何合理的纳税额。 可能有一个水平,太多的税收,或者过高的税收,会影响生产力和增长,因此人们想要降低税收。Effective Taxes
::有效税收Taxes must meet three criteria for people to be willing to pay them: efficient, simple, and equitable. Effective taxes must be efficient so that they are easy to administer and successful at generating enough revenue. Depending on the tax it may be very efficient, like individual income taxes, or less efficient such as toll road taxes. Individual income taxes are withheld from a person's paycheck and sent directly to the Internal Revenue Service. At the end of the year, the employee has paid his or her taxes, and now the paperwork must be completed to verify the total amount that should have been withheld from the employee's income. Since payroll taxes are computerized, there is no burden for either the employer nor the employee, to have the taxes withheld.
::个人所得税必须满足三种标准,才能让人们愿意支付税收:高效、简单和公平。有效的税收必须高效,以便他们易于管理和成功地创造足够的收入。取决于税收的效率,比如个人所得税,或者收费道路税等效率较低。个人所得税从个人工资支票中扣税,直接送往国内税收局。年底,雇员已经缴纳了税费,现在必须完成文书工作,以核实本应从雇员收入中扣税的总额。由于工资税是电脑化的,雇主和雇员都没有义务扣税。On the other hand, a less effective tax such as the toll road tax is collected as people use the roads. The reason that the tax is less efficient is due to the high cost of collecting the tax such as building toll booths, hiring workers to man the booths, and the cost the consumer pays to use the road, as well as the stop and go traffic on the road. States have toll roads to offset the cost of the construction and maintenance of the roads, but the burden of the toll roads do not always generate the revenue needed, and therefore states try to find other ways to create revenues, such as renewing license plates or having automobiles pass state inspections each year.
::另一方面,在人们使用公路时,征收诸如道路收费税等效果较差的税收,因为税收效率较低,原因是收取诸如建筑收费亭、雇用工人到工棚、消费者支付使用道路的费用以及公路的中途和上路交通费用等税费高昂,国家必须支付道路收费,以抵消修建和维护道路的费用,但收费道路的负担并不总是产生必要的收入,因此,国家试图寻找其他创收方式,如更新牌照或每年由汽车通过州检。The taxes also need to generate enough revenue. If the government institutes a tax that does not generate money, it may have a negative impact on the industry that it is taxing.
::税收也需要产生足够的收入。 如果政府征收的税不会产生金钱,那么它可能会对其征税的行业产生负面影响。Taxes should be fair. In fact, most people believe that they only way taxes can be effective is if everyone pays their fair share. The question arises as to what is fair? Should only the wealthy pay taxes? Should everyone pay the same amount in taxes? Should people pay taxes in proportion to what they make? There is a concern that tax loopholes allow some people to avoid paying taxes, or at least not as much in taxes as they should. Such loopholes are opposed on the grounds of fairness, but there is an argument that if you knew of a loophole that was to your benefit, you may use it yourself. In conclusion, taxes would be considered more fair if there were fewer exceptions.
::税收应该公平。 事实上,大多数人认为税收只有在每个人都支付公平份额的情况下才能有效。 问题是,什么是公平? 是否应该公平? 是否应该只征收富裕的税收? 是否每个人都应该缴纳相同的税额? 是否应该按照税收比例缴纳税收? 人们担心税收漏洞允许一些人避免纳税,或者至少不要像他们应该缴纳的税额那样多。 这些漏洞以公平为由遭到反对,但有观点认为,如果你知道有利于你的漏洞,你可以自己使用。 总之,如果有更少的例外,税收会被认为是更公平的。Taxes and the subsequent tax law should be simple and easy to understand by those paying the taxes and those creating the taxes. People are more willing to pay their taxes if they understood them. The tax code for the United States is very long and difficult to understand. Each year the Congress adds, deletes, and changes tax laws and tax brackets. Tax preparers, as well as taxpayers, must attempt to keep up with the changes or be penalized. Many people are unhappy with the current tax laws and have called for changes to not only how taxes are assessed (flat tax), but also changes to tax brackets. An example of a simple tax is a sales tax. This tax is assessed at the time of a purchase and the taxes are based on the total price of the product being taxed. The current sales tax rate for El Paso, Texas, is 8.25%.
::纳税人和随后的税法应该简单易懂。 纳税人和纳税人应该容易理解。 人们如果理解他们,就更愿意纳税。 美国的税法非常长,很难理解。 每年国会都增加、删除和修改税法和税括。 纳税人以及纳税人必须努力跟上变化或受到惩罚。 许多人对当前的税法不满意,不仅要求改变征税方式(增税税 ) , 还要求改变税括号。 简单税的一个例子就是销售税。这种税在购买时评估,税则以所征税产品的总价格为基础。 德克萨斯州埃尔帕索目前的销售税率是8.25%。If you purchase $10.00 worth of goods, then multiply 8.25% to pay a total of $0.83 in taxes for a total of $10.83.
::如果购买价值10.00美元的货物,则乘以8.25%支付总额0.83美元的税款,共计10.83美元。If you purchase $22.00 worth of goods, then multiply 8.25% to pay a total of $1.82 in taxes for a total of $23.82.
::如果你购买价值22.00美元的商品,则乘以8.25%支付总额1.82美元的税款,共计23.82美元。Go to for a sales tax calculator.
::去一个销售税计算器那里Types of Taxes
::税 税 税 类型In the United States, there are three types of taxes: proportional, progressive and regressive.
::在美国,有三种税种:比例税、累进税和递减税。Proportional taxes : the tax rate is the same for everyone regardless of income. For example, if the tax rate is 10%, then everyone, regardless of their income pays the same rate. If a person earned $100,000 and was taxed at 10% then the tax would be only $10,000. However, if a person only made $10,000 in one year then his tax would be $1,000 -- -to this person it would be much more of a burden.
::比例税:不论收入如何,对每个人的税率都是相同的。例如,如果税率是10%,那么每个人,无论其收入如何,都支付同样的税率。如果一个人挣了10万美元,按10%征税,那么税收就只有10 000美元。然而,如果一个人在一年中只挣了10 000美元,那么他的税就是1 000美元 -- -- 对这个人来说,这将是一个更大的负担。Video: Proportional Tax
::视频:比例税Progressive taxes : the tax rate is on a sliding scale, and the more money one earns, the more he/she pays in taxes. Progressive taxes use a marginal tax rate to adjust to the various levels of income that people may earn.
::累进税:税率处于滑动规模,挣得的钱越多,他/她所付的税越多。 累进税使用边际税率来适应人们可能赚取的不同收入水平。Video: The Progressive Income Tax: A Tale
::录像:累进所得税:故事The following chart is for 2014 Tax brackets by income and is considered progressive
::下表是2014年图表,按收入分列的税括号,被视为累进式Tax rate Single filers Married filing jointly or qualifying widow/widower Married filing separately Head of household 10% Up to $9,075 Up to $18,150 Up to $9,075 Up to $12,950 15% $9,076 to $36,900 $18,151 to $73,800 $9,076 to $36,900 $12,951 to $49,400 25% $36,901 to $89,350 $73,801 to $148,850 $36,901 to $74,425 $49,401 to $127,550 28% $89,351 to $186,350 $148,851 to $226,850 $74,426 to $113,425 $127,551 to $206,600 33% $186,351 to $405,100 $226,851 to $405,100 $113,426 to $202,550 $206,601 to $405,100 35% $405,101 to $406,750 $405,101 to $457,600 $202,551 to $228,800 $405,101 to $432,200 39.6% $406,751 or more $457,601 or more $228,801 or more $432,201 or more Read more:
The last type of tax is a regressive tax which places the burden on those with lower incomes rather than those with higher incomes. For example if a person with an income of $20,000 purchases products in a state with a 4% sales tax, they will pay more of their income on products versus a person who's income is $100,000. Another example of a regressive tax is the FICA tax, which is less of a burden on someone who makes more money since the percentage declines as the income goes up.
::最后一种税是递减税,让收入较低的人而不是收入较高的人承担重担。 比如,如果收入为20,000美元的人购买产品时持有4%的销售税,他们将用产品支付更多的收入,而收入为100,000美元的人将支付更多的收入。 递减税的另一个例子是FICA税,这一税对收入较高的人来说负担较少,因为收入随着收入的增加而下降,百分比会下降。Video: Regressive Tax
::视频:递减税In the United States taxes are based on two concepts: the benefit principle of taxation and the ability-to-pay principle. The benefit principle is the idea that people who benefit from government goods should pay taxes in proportion to the number of benefits that they may receive. The basic problem with this concept is that the people who are in most needs of the government's programs are the least likely to be able to pay for those services. In addition, how can we measure those benefits? If there is a tax paid on air travel to improve the airport buildings, and the local restaurant near the airport benefits from that tax, should they have to pay for that benefit? Can there be a monetary value placed on externalities? Probably not. Therefore, the idea of the benefit principle of taxation is not a viable theory. The second concept, the ability-to-pay principle is the belief that people should pay taxes based on their ability to pay. If you make very little money, then you should pay less in taxes. If you make more money, then you should pay more in taxes. The belief is that people should pay according to how much they make or pay taxes on a marginal tax rate or a progressive tax rate.
::在美国,税收基于两个概念:税收福利原则和支付能力原则。福利原则是,从政府货物受益的人应该按照他们可能得到的收益数量来缴纳税款。这一概念的基本问题是,政府方案最需要的人最不可能支付这些服务。此外,我们如何衡量这些福利?如果对航空旅行征税以改善机场建筑,以及机场附近的当地餐厅从该税中获益,如果他们必须支付这种福利的话?有没有货币价值?也许没有。因此,税收福利原则的想法不是一个可行的理论。第二个概念,即支付能力原则是人们应该根据其支付能力纳税。如果你赚的钱很少,那么你应该少付税。如果你赚更多的钱,那么你应该支付更多的税。这个信念是,人们应该支付多少税,或者按边际税率或累进税率纳税。Video: Tax Man Max
::影片:税务员MaxAnswer the self check questions below to monitor your understanding of the concepts in this section.
::回答下面的自我核对问题,以监测你对本节概念的理解。Self Check Questions
::自查问题1. Explain how taxes can affect the economy. Give 4 examples of their impact.
::1. 解释税收如何影响经济,举4个例子说明税收的影响。2. What is the purpose of a "sin tax"? Give an example.
::2. " 辛税 " 的目的是什么?3. Research online to find out how high some sin taxes are in various states. Then research to see if the sin taxes do what they are supposed to do. What is taxed? Does it raise significant revenue? Has it changed consumer behavior?
::3. 在线研究,以了解各州的罪恶税有多高;然后研究,看看罪恶税是否照规定行事;课税是做什么的?它是否增加大量收入?它是否改变了消费者行为?4. There is a belief that taxes affect productivity and growth. How is this possible?
::4. 人们相信,税收影响生产力和增长,这怎么可能?5. What is the incidence of a tax? Who does it impact? Give an example.
::5. 税收的发生率是多少?对谁有影响?举一个例子。6. What are the 3 criteria for effective taxes?
::6. 有效征税的三项标准是什么?7. Explain the "benefit principle of taxation." Explain 2 limits of the "benefit principle of taxation."
::7. 解释“税益原则”。解释“税益原则”的2个限制。“税益原则”的2个限制。8. Explain the "ability-to-pay principle of taxation."
::8. 解释“税的可支付性原则”。9. What are the 3 types of taxes?
::9. 三种税种是什么?10. What is a proportional tax?
::10. 什么是比例税?11. What is a progressive tax? How does it work?
::11. 什么是累进税?它如何运作?12. Define regressive tax.
::12. 界定递减税。 -
Taxes influence the economy by affecting resource allocation, consumer behavior, and the nation’s productivity and growth.