1.1 基本几何定义
章节大纲
-
Geometric Definitions
::几何定义A point is an exact location in space . It describes a location, but has no size. Examples are shown below:
::点是空间中的确切位置。它描述一个位置,但没有大小。示例如下:Label It Say It A point A A line is infinitely many points that extend forever in both directions. Lines have direction and location and are always straight .
::一条线是无限多的点,在两个方向上永远延伸。 一条线有方向和位置,并且总是直的。Label It Say It line g line g ↔ PQ line P Q A plane is a flat surface that contains infinitely many intersecting lines that extend forever in all directions. Think of a plane as a huge sheet of paper with no thickness that goes on forever.
::平面是一个平面, 包含无限多的交叉线, 在所有方向都永久延伸。 将平面想象成一张巨大的纸, 没有永久的厚度 。Label It Say It Plane M Plane M Plane A B C Plane A B C We can use point , line , and plane to define new terms.
::我们可以用点、线和平面来定义新的术语。Space is the set of all points extending in three dimensions . Think back to the plane. It extended in two dimensions, what we think of as up/down and left/right. If we add a third dimension, one that is perpendicular to the other two, we arrive at three-dimensional space.
::空间是三个维度中所有点的一组。 回想到平面中。 它在两个维度中延伸, 我们称之为向上/ 向下和向左/ 向右。 如果我们加上第三个维度, 一个与其它两个维度垂直, 我们到达三维空间 。Points that lie on the same line are collinear . P , Q , R , S , and T are collinear because they are all on line w . If a point U were located above or below line w , it would be non-collinear .
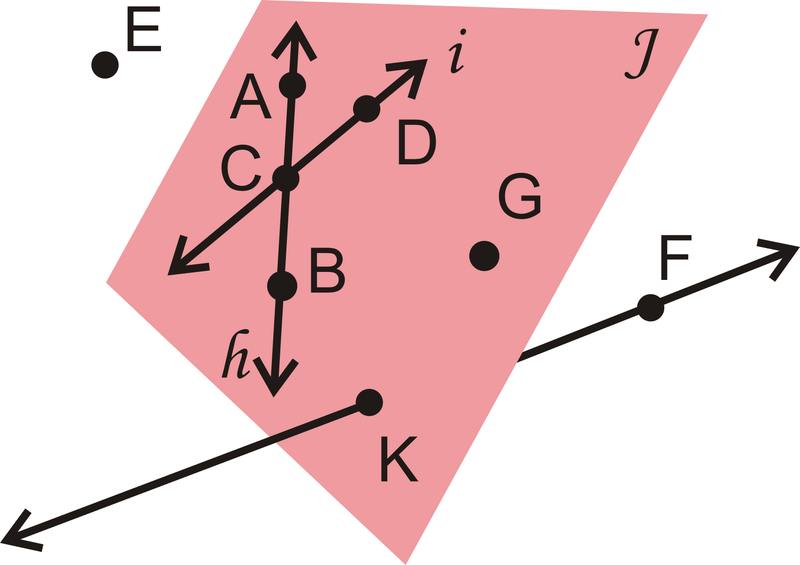
::同一线上的点是线性线性点。 P、 Q、 R、 S 和 T 是线性点, 因为它们都是线性点。 如果U点位于线上或线下, 它将是非线性点 。Points and/or lines within the same plane are coplanar . Lines h and i , and points A , B , C , D , G , and K are coplanar in Plane J . Line ↔ K F and point E are non-coplanar with Plane J .
::同一平面内的点和/或线系为共平面。 h线和i线,A线、B线、C线、D线、G线和K线系在Plane J线上的点和/或线系为共平面。An endpoint is a point at the end of a line segment . A line segment is a portion of a line with two endpoints. Or, it is a finite part of a line that stops at both ends. Line segments are labeled by their endpoints. Order does not matter.
::端点是线段结尾的点。线段是两个端点的线条的一部分。或者,是两端都停的线条的有限部分。线段按其端点贴上标签。顺序无关紧要。Label It Say It ¯ A B Segment A B ¯ B A Segment B A A ray is a part of a line. It begins with an endpoint and extends forever away from the endpoint in one direction, perfectly straight. A ray is labeled by its endpoint and one other point on the ray. For rays, order does matter. When labeling, put the endpoint under the side WITHOUT the arrow.
::光线是线条的一部分。 它从端点开始, 并且永远从端点向一个方向延伸, 完全直线。 光线用端点和射线上的另一点贴上标签。 对于射线, 命令很重要 。 在标签时, 将端点置于侧面下, 不使用箭头 。Label It Say It → C D Ray C D ← D C Ray C D An intersection is a point or set of points where lines, planes, segments, or rays overlap.
::交叉点是指线条、平面、段或射线重叠的点或一组点。Postulates
::假设A postulate is a basic rule of geometry. Postulates are assumed to be true (rather than proven), much like definitions. The following is a list of some basic postulates.
::假设是几何学的基本规则。 假设假设是真实的( 而不是经过验证的 ) , 非常相似的定义 。 以下列出一些基本假设 。Postulate #1: Given any two distinct points, there is exactly one (straight) line containing those two points.
::假设 # 1: 鉴于任何两个不同的点, 完全有一个包含这两个点的直线( 直线) 。Postulate #2: Given any three non-collinear points, there is exactly one plane containing those three points.
::假设2:鉴于任何三个非两极点, 精确地说有一架飞机含有这三个点。Postulate #3: If a line and a plane share two points, then the entire line lies within the plane.
::假设3:如果一线和一平面共有两点,则整线就位于该平面内。Postulate #4: If two distinct lines intersect, the intersection will be one point.
::4: 如果两条不同的线交叉, 十字路口将是一个点 。Lines l and m intersect at point A .
::A点的I线和m线交叉。Postulate #5: If two distinct planes intersect, the intersection will be a line.
::5: 如果两个不同的平面交叉, 十字路口将是一条线 。When making geometric drawings, be sure to be clear and label all points and lines.
::在绘制几何图画时,一定要清楚,标出所有点和线条。What if you were given a picture of a figure or object, like a map with cities and roads marked on it? How could you explain that picture geometrically?
::如果有人给了你一张图象或物体的照片,比如一张有城市和道路标注的地图呢?你怎么用几何方式解释这个图象呢?Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1What best describes San Diego, California on a globe: point, line, or plane?
::加州圣迭戈 球体上的最佳描述是什么: 点、线或飞机?A city is usually labeled with a dot, or point, on a globe.
::一个城市通常被贴上一个点或点的标签 在全球。Example 2
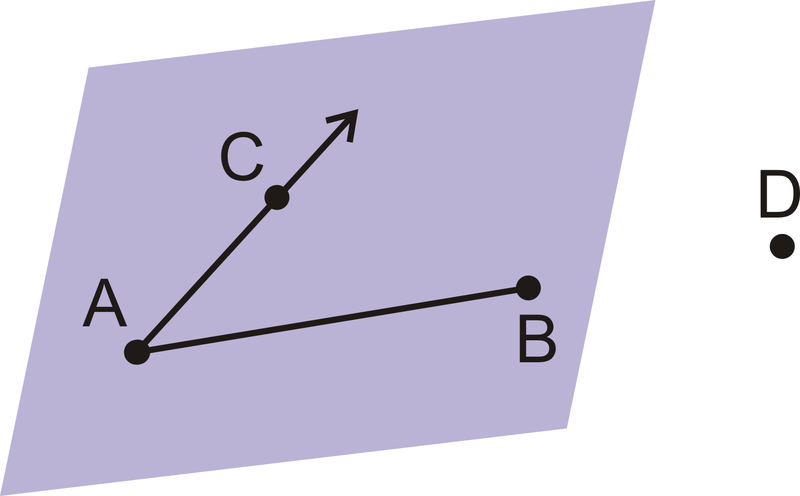
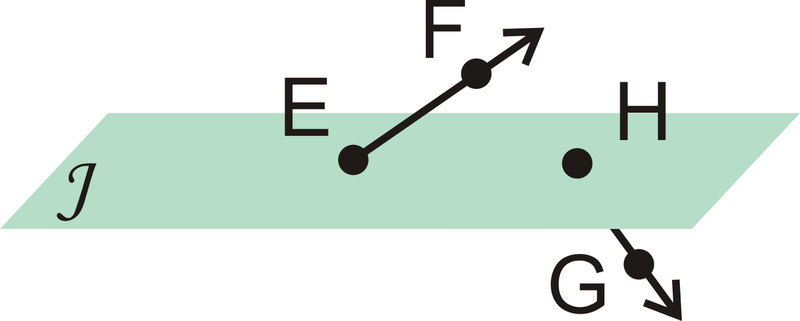
::例2Use the picture below to answer these questions.
::用下图解这些问题。-
List another way to label Plane
J
.
::列出标签为 Plane J 的另一种方式 。
Plane B D G is one possibility. Any combination of three coplanar points that are not collinear would be correct.
::3个非圆线共平板点的任何组合都是正确的。-
List another way to label line
h
.
::列出标签行 h 的另一种方式 。
↔ A B . Any combination of two of the letters A , B , or C would also be correct.
::AB. 任何两个字母A、B或C的组合也是正确的。-
Are
K
and
F
collinear?
::K和F是山线吗?
Yes, they both lie on ↔ K F .
::是的,他们都躺在KF上-
Are
E
,
B
and
F
coplanar?
::E,B和F是双平面吗?
Yes, even though E is not in Plane J , any three points make a distinct plane. Therefore, the three points create Plane E B F .
::是的,尽管E不是在Plane J中,但任何三点就是一个不同的平面。 因此,这三点就形成了Plane EBF。Example 3
::例3What best describes a straight road that begins in one city and stops in a second city: ray, line, segment, or plane?
::什么是最能描述一条直路,这条直路始于一个城市,在第二个城市停留:雷、线、线、段或飞机?The straight road connects two cities, which are like endpoints. The best term is segment.
::直路连接了两个城市,就像终点一样, 最好的用词是分路段。Example 4
::例4Answer the following questions about the picture.
::回答以下关于图片的问题。-
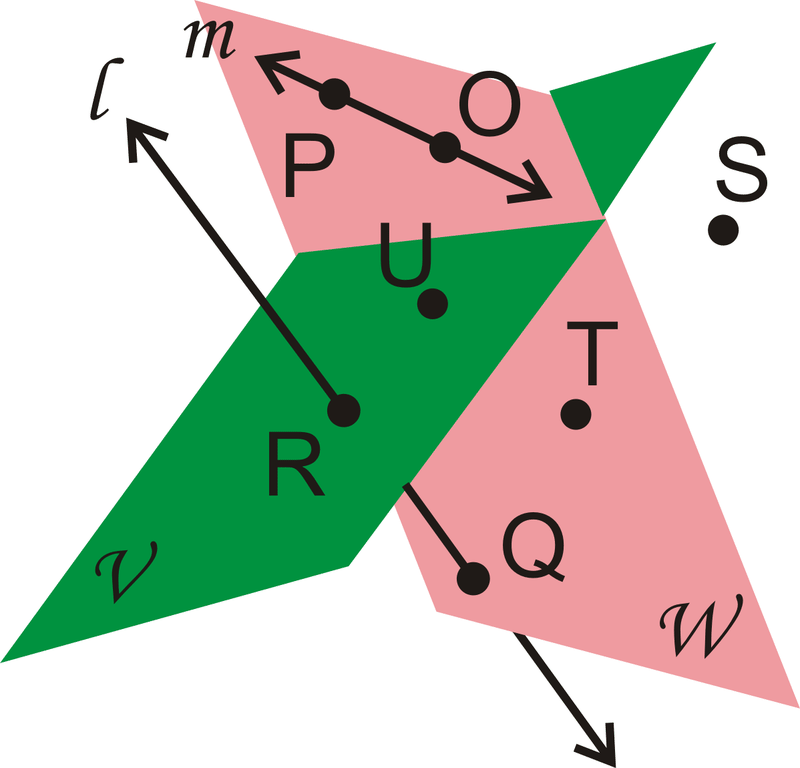
Is line
l
coplanar with Plane
V
, Plane
W
, both, or neither?
::L线与五号平面、W号平面或两者兼而有之吗?
Neither
::中 无-
Are
R
and
Q
collinear?
::R和Q是圆线吗?
Yes
::是 是-
What point belongs to neither Plane
V
nor Plane
W
?
::第五号计划或W号计划都不属于哪个点?
S
::S S 级-
List three points in Plane
W
.
::W. Plane W.中列出三点。
Any combination of P , O , T , and Q would work.
::任何P、O、T和Q的组合都会有效Example 5
::例5Draw and label a figure matching the following description: Line ↔ A B and ray → C D intersect at point C . Then, redraw so that the figure looks different but is still true to the description.
::绘制并标签一个符合以下描述的图 : 线 AB 和 ray CD 在 C点交叉。 然后, 重新绘制, 使图看起来不同, 但仍符合描述 。Neither the position of A or B on the line, nor the direction that → C D points matter.
::无论是A或B在线上的位置,还是 " CD点点 " 的重要方向。For the second part, this is one way to draw the diagram differently:
::对于第二部分,这是以不同方式绘制图表的一种方法:Review
::回顾For questions 1-5, draw and label a figure to fit the descriptions.
::对于问题1至5,绘制和标出一个符合描述的数字。-
→
C
D
intersecting
↔
A
B
and Plane
P
containing
↔
A
B
but not
→
C
D
.
::CD 交叉 AB 和 plane P , 包含 AB , 但不包含 CD 。 -
Three collinear points
A
,
B
,
and
C
.
B
is also collinear with points
D
and
E
.
::A、B和C.B三个山丘线点也是D和E点的山丘线点。 -
→
X
Y
,
→
X
Z
,
and
→
X
W
,
such that
→
X
Y
and
→
X
Z
are coplanar, but
→
X
W
is non-coplanar with both of the other rays.
::XY, XZ, 和XW, 如此一来, XY 和XZ 是共平板, 但XW 与另外两种射线是非相平面的。 -
Two intersecting planes,
P
and
Q
, with
¯
G
H
,
where
G
is in plane
P
and
H
is in plane
Q
.
::两架交错的飞机,P和Q,G在G和H在G和Q之间。 -
Four non-collinear points
I
,
J
,
K
,
and
L
,
with line segments connecting all points to each other.
::4个非两极点I、J、K和L,各线段将所有点相互连接。 -
Name this line in five ways.
::以五种方式命名此行 。 -
Name the geometric figure in three different ways.
::以三种不同的方式列出几何数字。 -
Name the geometric figure in two different ways.
::以两种不同的方式命名几何图。 -
What is the best possible geometric model for a soccer field? Explain your answer.
::足球场的最佳几何模型是什么? -
List two examples of where you see rays in real life.
::列举两个例子, 说明您在现实生活中看到光线的地方 。 -
What type of geometric object is the intersection of a line and a plane? Draw your answer.
::线和平面的交叉点是哪一类几何物体? 请绘制您的答案 。 -
What is the difference between a postulate and a theorem?
::假设和定理之间有什么区别?
For 13-16, use geometric notation to explain each picture in as much detail as possible.
::对于13-16,使用几何符号来尽可能详细地解释每一张照片。For 17-25, determine if the following statements are true or false.
::17-25时,确定以下陈述是真实的还是虚假的。-
Any two points are collinear.
::任何两个点都是共线的。 -
Any three points determine a plane.
::任何三点都决定飞机的位置。 -
A line is two rays with a common endpoint.
::一线是两线,有共同的终点。 -
A line segment is infinitely many points between two endpoints.
::线段是两个终点之间无限多的点。 -
A point takes up space.
::一个点占上空间。 -
A line is one-dimensional.
::一条线是一维的。 -
Any four points are coplanar.
::任何四个点都是共同平面的 -
→
A
B
could be read “ray
A
B
” or “ray
B
A
.”
::AB可以是“射线AB”或“射线BA”。 -
↔
A
B
could be read “line
A
B
” or “line
B
A
.”
::AB可以是“线性AB”或“线性BA”。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
List another way to label Plane
J
.