1.8 顺弦、顺弦和相切函数
章节大纲
-
You are helping your grandfather with some repairs around the house when he mentions that he could use some help painting some boards on the staircase of his front porch. When you go out to see what he means, you notice that the stairs are supported by a set of boards that are glued together so that they are shaped like a triangle, with one extra board placed over top of them for decoration.
::你正在帮助你的祖父在房子周围做一些修理,他提到他可以使用一些帮助,在他前门门廊的楼梯上画一些板子。当你出去看看他的意思时,你注意到楼梯有一套粘在一起的板子支撑着,使楼梯的形状像三角形,再加一个板子放在上面装饰。As you are looking around for paint, you think about the situation and realize that this reminds you a lot of your math class. In your study of triangles, you are about to start a unit working with the relationships between the sides of a triangle. You begin to wonder: "How many possible relationships are there between sides of triangles, anyway?"
::当你四处寻找涂料的时候,你就会想想情况, 并意识到这提醒了你很多数学课。 在您对三角的研究中, 您即将启动一个单位, 与三角形两侧的关系合作。 您开始想 : “ 三角形两侧之间究竟有多少可能的关系? ”Sine, Cosine and Tangent Functions
::顺弦、顺弦和相切函数The first three trigonometric functions we will work with are the sine, cosine, and tangent functions.
::我们将要合作的头三个三角函数是正弦、正弦和正弦的函数。The elements of the domains of these functions are angles. We can define these functions in terms of a right triangle: The elements of the range of the functions are particular ratios of sides of triangles.
::这些函数域的元素是角度。 我们可以用右三角形来定义这些函数: 函数范围的元素是三角形侧面的特定比例 。We define the sine function as follows: For an acute angle in a right triangle, the is equal to the ratio of the side opposite of the angle over the hypotenuse of the triangle. For example, using this triangle, we have: and .
::我们给正弦函数下定义如下:对于右三角形的急性角 x , 罪过等于三角形下方角对面的侧边之比。 例如, 使用此三角形, 我们有: sinA=ac 和 sinB=bc 。Since all right triangles with the same acute angles are similar, this function will produce the same ratio, no matter which triangle is used. Thus, it is a well-defined function.
::由于所有右三角形的急性角度相同是相似的,此函数将产生相同的比例, 不论使用哪个三角形, 因此, 它是一个定义明确的函数 。Similarly, the cosine of an angle is defined as the ratio of the side adjacent (next to) the angle over the hypotenuse of the triangle. Using this triangle, we have: and .
::同样,角的余弦被定义为相邻侧(紧随)三角形下方角的比。使用此三角形,我们有:cosA=bc和cosB=ac。Finally, the tangent of an angle is defined as the ratio of the side opposite the angle to the side adjacent to the angle. In the triangle above, we have: and .
::最后,角的正切值被定义为角对面方与角对面方与角对面方之比。在以上三角形中,我们有:tanA=ab和tanB=ba。There are a few important things to note about the way we write these functions. First, keep in mind that the abbreviations , and are just like . They simply stand for specific kinds of functions. Second, be careful when using the abbreviations that you still pronounce the full name of each function. When we write it is still pronounced sine , with a long i. When we write , we still say co-sine. And when we write , we still say tangent.
::关于我们写这些函数的方式,有一些重要的东西值得注意。 首先,记住缩写sinx、cosx和tanx就像 f(x)一样。 它们只是代表特定类型的函数。 其次, 当使用您仍然念出每个函数的全名的缩写时要小心。 当我们写 sinx时, 它仍然是正弦的, 长长的 i。 当我们写cosx时, 我们仍然说共弦。 当我们写tanx时, 我们还是说正弦的。We can use these definitions to find the sine, cosine, and tangent values for angles in a right triangle.
::我们可以使用这些定义来找到右三角形角的正弦值、正弦值和正弦值。Use the definition of sine, cosine and tangent to find the values for angles in the given triangles.
::使用正弦、连弦和正切值的定义来查找给定三角形中角的值。Let's look at some example problems.
::让我们来看看一些例子问题。1. Find the sine, cosine, and tangent of :
::1. 找到A的正弦、正弦和正弦和正弦:
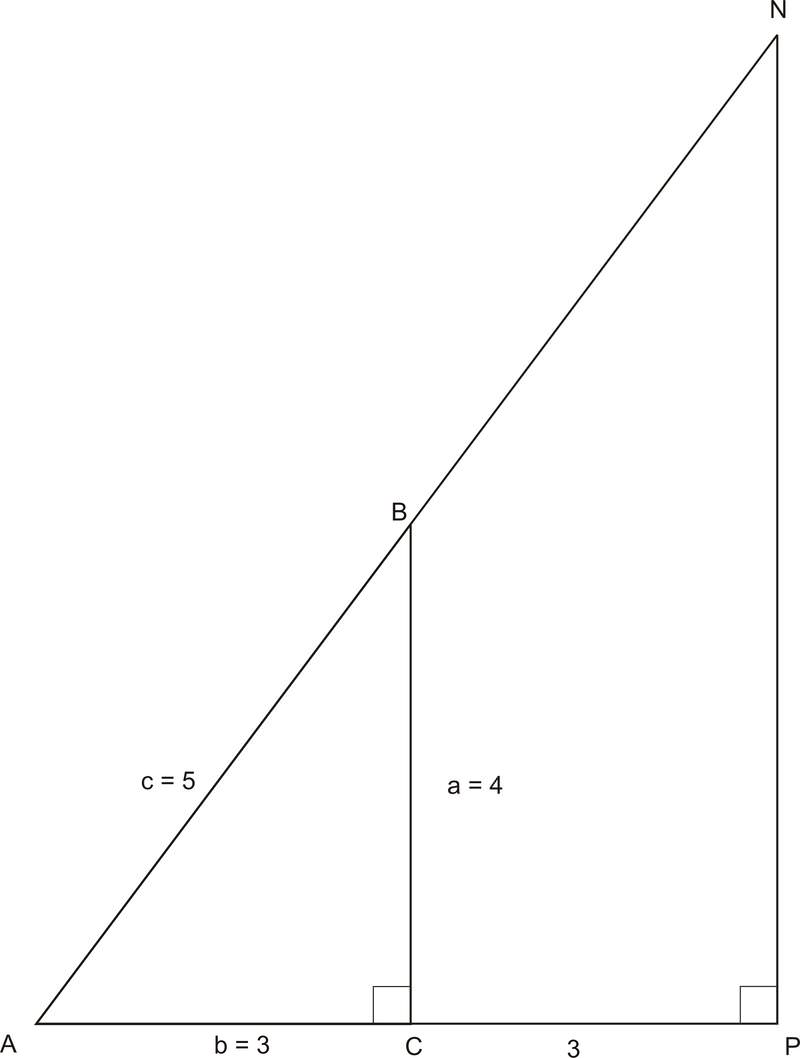
::A=对面侧对面侧对面侧对面对面侧对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面侧对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面侧对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面侧对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对面对2. Find using and
::2. 使用 " ABC " 和 " NAP " 找出罪状B。Using
::使用 @ABC:sin_B=35
Using
::使用 NAP:sinB=610=353. Find and in the triangle below:
::3. 在以下三角形中查找sinB和tanA:
::=11213tan=A=对面侧邻接面=512Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were given a problem about your grandfather's staircase.
::之前,你爷爷的楼梯出了问题We can see that there are several ways to make relationships between the sides. In this case, we are only interested in ratios between the sides, which means one side will be divided by another. If we assume that dividing a side by itself doesn't count (since the answer would always be equal to one), let's look at the number of possible combinations:
::我们可以看到,在双方之间建立关系有几种方式。在这种情况下,我们只对双方的比例感兴趣,这意味着一方会被另一方分开。如果我们假设一方自己分裂并不重要(因为答案总是等于一个 ) , 那么让我们看看可能的组合数量:If we use the angle labelled above, there is: 1) The side opposite the angle divided by the hypotenuse (the sine function) 2) The side adjacent the angle divided by the hypotenuse (the cosine function) 3) The side opposite the angle divided by adjacent side (the tangent function)
::如果我们使用上面标注的角,则有:1)对面的角除以下限(正弦函数) 2;对面的侧面是下限(余弦函数) 3;对面的侧面是相邻边的侧面(正弦函数) 3;对面的侧面是相邻边的角(正弦函数) 。You can also imagine taking the same sides, except reversing the numerator and denominator: 4) The hypotenuse divided by the side opposite the angle 5) The hypotenuse divided by the side adjacent to the angle 6) The side adjacent to the angle divided by the side opposite to the angle
::您也可以想象采取相同的两边, 除了逆转分子和分母 : 4) 倾角对面的下压值除以侧面 5) 倾角对面的下压值除以侧面 6) 角对面的侧面的下压值除以侧面 6) 角对面的侧面对面的侧面The first three functions are what we introduced in this Concept. The last three are other functions you'll learn about in a different Concept.
::前三个功能是我们在这个概念中引入的。最后三个功能是其它功能, 你会在不同的概念中学习。Using the triangle shown here:
::使用此处显示的三角形 :Example 2
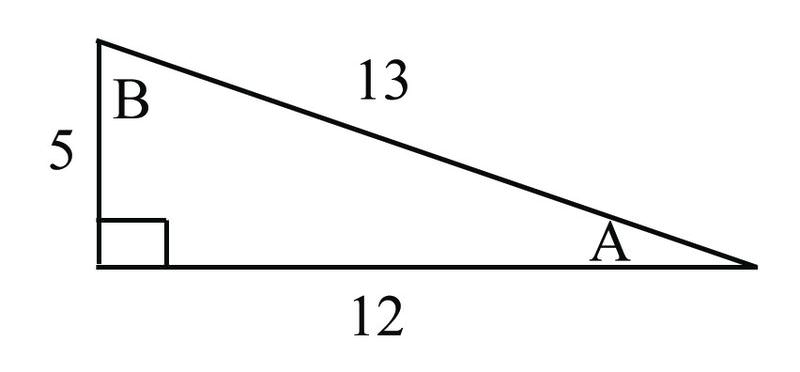
::例2Find the sine of angle
::查找角度 {A} 的正弦The sine is equal to the opposite divided by the hypotenuse.
::不可抗力等于负负分法的对立分法。
:a) 甲型六氯环己烷和乙型乙型六氯环己烷的含量为1161=18。
Example 3
::例3Find the cosine of angle
::查找角的余弦 AThe cosine is equal to the adjacent divided by the hypotenuse.
::余弦等于下限的相邻部分。
::A=邻接子体=606198Example 4
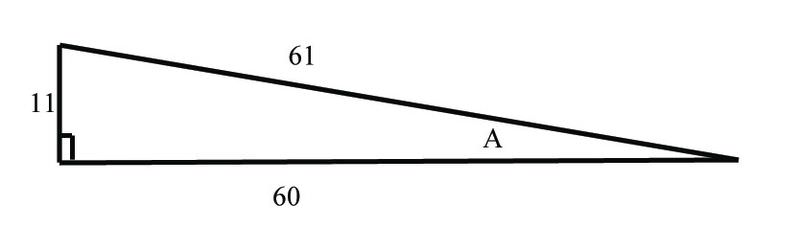
::例4Find the tangent of angle
::查找角的正切值 AThe tangent is equal to the opposite divided by the adjacent.
::相切值等于相邻方除以的对等值。
::TANA=对面近地点=61601.01Review
::回顾Use the diagram below for questions 1-3.
::问题1-3使用下图。-
Find
and
.
::找到罪和罪 -
Find
and
.
::找到CosáA和C。 -
Find
and
.
::找到塔纳和塔纳卡
Use the diagram to fill in the blanks below.
::使用图表填充下面的空白。-
::泰纳? -
::C=吗? -
::唐纳克? -
::科斯? 科斯? 科斯? -
::说错什么了? -
::A=?
From questions 4-9, we can conclude the following. Fill in the blanks.
::从问题4-9,我们可以得出以下结论。填空。-
and
.
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}我... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}我... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}我... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}我... {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080} -
and
are _________ of each other.
::塔纳和塔尼卡是彼此的一对 -
Explain why the cosine of an angle will never be greater than 1.
::解释为什么一个角度的余弦永远不会大于1。 -
Use your knowledge of 45-45-90 triangles to find the sine, cosine, and tangent of a 45 degree angle.
::使用您对 45 - 45 - 90 三角形的知识 找到45度角的正弦、正弦、正弦和正正弦。 -
Use your knowledge of 30-60-90 triangles to find the sine, cosine, and tangent of a 30 degree angle.
::使用您对 30- 60- 90 三角形的知识, 找到 30 度角的正弦、 连弦和正切值 。 -
Use your knowledge of 30-60-90 triangles to find the sine, cosine, and tangent of a 60 degree angle.
::使用您对 30- 60- 90 三角形的知识, 找到60 度角的正弦、 连弦和正切值 。 -
As the degree of an angle increases, will the tangent of the angle increase or decrease? Explain.
::随着角度的增加,角的正切度会增减吗?解释一下。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Find
and
.