7.13 自我统一
章节大纲
-
Self-Similarity
::自我团结When one part of an object can be enlarged (or shrunk) to look like the whole object it is self-similar .
::当一个对象的一部分可以放大(或缩放)到看起来像整个对象时,它就会自相类似。To explore self-similarity, we will go through some examples. Typically, each step of a process is called an iteration . The first level is called Stage 0 .
::为了探索自我相似性, 我们将尝试一些例子。 通常, 一个过程的每个步骤都被称为迭代。 第一个级别被称为第 0 阶段 。What if you were given an object, like a triangle or a snowflake, in which a part of it could be enlarged (or shrunk) to look like the whole object? What would each successive iteration of that object look like?
::假若你们获得一个物体,如三角形或雪花,其中一部分可以放大(或缩放),而看起来像整个物体,那么它会变成什么样?该物体的相继迭代会是什么样子呢?Examples
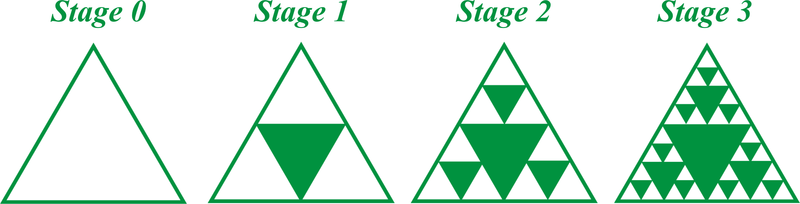
::实例Example 1 (Sierpinski Triangle)
::例1 (Sierpinski三角)The Sierpinski triangle iterates a triangle by connecting the midpoints of the sides and shading the central triangle (Stage 1). Repeat this process for the unshaded triangles in Stage 1 to get Stage 2.
::Sierpinski三角形通过连接两边的中点和阴影中三角形(Stage 1)将三角形复制成三角形(Sierpinski三角形),为第一阶段的未阴影三角形重复此进程,以获得第2阶段。Example 2
::例2Determine the number of shaded and unshaded triangles in each stage of the Sierpinkski triangle. Determine if there is a pattern.
::确定Sierpinkski 三角形每个阶段的阴影和未阴影三角形数。确定是否有模式。Stage 0 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Unshaded 1 3 9 27 Shaded 0 1 4 13 The number of unshaded triangles seems to be powers of . The number of shaded triangles is the sum the number of shaded and unshaded triangles from the previous stage. For Example, the number of shaded triangles in Stage 4 would equal 27 + 13 = 40.
::未阴影三角体的数目似乎是3:30、31、32、33的功率。阴影三角体的数目是前一个阶段的阴影三角和未阴影三角体的数目之和。例如,第四阶段的阴影三角体的数目等于27+13=40。例如,第四阶段的阴影三角体的数目等于27+13=40。Example 3 (Fractals)
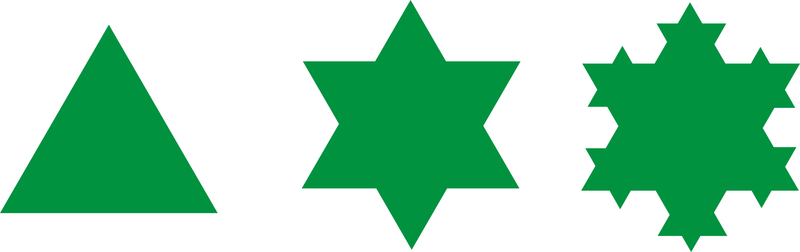
::例3(事实)Like the Sierpinski triangle, a fractal is another self-similar object that is repeated at smaller scales. Below are the first three stages of the Koch snowflake.
::与Sierpinski三角形一样,折形是另一个在较小尺度上重复的自我相似对象。下面是Koch雪花的前三个阶段。Example 4
::例4Determine the number of edges and the perimeter of each snowflake shown in Example 3. Assume that the length of one side of the original (stage 0) is 1.
::确定例3所示每片雪花的边缘数和周界,假定原(第0阶段)的一侧长为1。Stage 0 Stage 1 Stage 2 Number of Edges 3 12 48 Edge Length 1 Perimeter 3 4 Example 5 (The Cantor Set)
::例5 ( " 罐件集 " )The Cantor set is another example of a fractal. It consists of dividing a segment into thirds and then erasing the middle third.
::Cantor 集是分形的又一个例子。 它包括将一段分割成 3 /3, 然后删除中间的 3 3 个 。Review
::回顾-
Draw Stage 4 of the Cantor set.
::绘制 Cantor 集的第四阶段 。 -
Use the Cantor Set to fill in the table below.
::使用 Cantor 设置来填充以下表格 。
Number of Segments Length of each Segment Total Length of the Segments Stage 0 1 1 1 Stage 1 2 Stage 2 4 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 -
How many segments are in Stage
?
::有多少部分处于第n阶段? -
Draw Stage 3 of the Koch snowflake.
::绘制 Koch 雪花的第 3 阶段 。 -
A variation on the Sierpinski triangle is the Sierpinski carpet, which splits a square into 9 equal squares, coloring the middle one only. Then, split the uncolored squares to get the next stage. Draw the first 3 stages of this fractal.
::Sierpinski三角形上的一个变异是Sierpinski地毯,它将方形分割成9等方形,仅以中间方形为颜色。然后,将非彩色方形分割为下一个阶段。绘制此分形的前三个阶段 。 -
How many colored vs. uncolored square are in each stage?
::每个阶段有多少色对非色方形? -
Fractals are very common in nature. For example, a fern leaf is a fractal. As the leaves get closer to the end, they get smaller and smaller. Find three other examples of fractals in nature.
::分形在自然界中非常常见。 例如, 青叶是分形。 当叶子接近尾端时, 它们越来越小。 找到自然界中另外三个分形的例子 。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Draw Stage 4 of the Cantor set.