6.7 极曲线的交叉体
章节大纲
-
You are working in Art Class one afternoon and decide to draw the "Olympic Rings". These are a set of rings that lock together and are the symbol of the Olympics.
::你在一个下午在艺术类工作,决定画“奥林匹克环”。这是一套环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环形环状,是奥运会的象征。You can do this on the computer by generating a circle for each of the rings using an equation in . The equations you use for the first two rings are and . Is it possible for your to find the angles where these first two rings intersect each other?
::您可以在计算机上这样做, 方法是使用 中 的公式为每个环生成一个圆。 前两个环所使用的方程式是 r=2sin 和 r=2cos 。 您能否找到前两个环相互交叉的角度 ?Intersections of Polar Curves
::极曲线的交叉点When you worked with a system of linear equations with two unknowns, finding the point of intersection of the equations meant finding the coordinates of the point that satisfied both equations. If the equations are rectangular equations for curves, determining the point(s) of intersection of the curves involves solving the equations algebraically since each point will have one ordered pair of coordinates associated with it.
::当您在两个未知的线性方程式系统中工作时, 找到方程式的交叉点意味着找到符合两个方程式的点的坐标。 如果方程式是曲线的矩形方程式, 确定曲线的交叉点需要解析方程式的代数, 因为每个点都会有一个与之相联的定数对坐标。Let's take a look at a few problems that involve intersections of polar curves.
::让我们来看看几个问题 涉及到极地曲线的交叉点1. Solve the following system of equations algebraically:
::1. 解决下列方程式代数系统:
::x2+4y2 - 36=0x2+y=3Before solving the system, graph the equations to determine the number of points of intersection.
::在解析系统之前,请绘制方程图,以确定交叉点的数目。The graph of is an ellipse and the graph represented by is a parabola. There are three points of intersection. To determine the exact values of these points, algebra must be used.
::x2+4y2-36=0的图形是一个椭圆形,以 x2+y=3 表示的图形是一个抛物线。有三个交叉点。为了确定这些点的确切值,必须使用代数。
::x2+4y2 - 36= 0x2+4y2= 36x2+4y2+0y2= 36x2+4y2+0y=36x2+y2+y=3x2+0y2+y=3-1(x2+0y2+y2+y=3)-x2-0y2+y2=3-0y2-y2=3-x2-0y2-y2+0y2=36x2+4y2+0y2=36x2+y2+y2+y=3x2+-0y2+y2+y=3-1(x2+0y2+y2+y=3)-x2--02-y2-y2=3-x2-0y2-y2-y2=33Using the quadratic formula,
::使用二次方形, a=4 b1 c33
::y( - 1) ( - 1) 2- 4(4)( - 332(4)y) y= 1+238= 3y= 1 - 2382. 75These values must be substituted into one of the original equations.
::这些数值必须替换为原始方程之一。
::x2+y=3 x2+y=3 x2+3=3x2+3=3x2+( - 2. 75)=3x2=0 x2=5. 75x=0x_ @5. 75=2.4The three points of intersection as determined algebraically in Cartesian representation are and .
::在笛卡尔代表处中确定代数的三个交叉点是A(0)、B(2.4、-2.75)和C(2.4、2.75)。If we are working with polar equations to determine the polar coordinates of a point of intersection, we must remember that there are many polar coordinates that represent the same point. Remember that switching to polar form changes a great deal more than the notation. Unlike the Cartesian system which has one name for each point, the polar system has an infinite number of names for each point. One option would be to convert the polar coordinates to rectangular form and then to convert the coordinates for the intersection points back to polar form. Perhaps the best option would be to explore some more examples. As these problems are presented, be sure to use your graphing calculator to create your own visual representations of the equations presented.
::如果我们使用极方程式来确定一个交叉点的极坐标, 我们就必须记住, 许多极坐标代表着同一个点。 记住, 转换为极形会比符号改变更多。 与每个点有一个名称的笛卡尔系统不同, 极系统每个点有无限数量的名称。 一种选择是将极坐标转换为矩形, 然后将交叉点的坐标转换为极形。 也许最好的选择是探索更多例子。 这些问题会呈现出来, 请使用您的图形计算器来创建您自己对所显示的方程式的直观表达方式 。2. Determine the polar coordinates for the intersection point(s) of the following polar equations: and .
::2. 确定下列极方程式的交叉点的极坐标:r=1和r=2cos。Begin with the graph. Using the process described in the technology section in this chapter; create the graph of these polar equations on your graphing calculator. Once the graphs are on the screen, use the trace function and the arrow keys to move the cursor around each graph. As the cursor is moved, you will notice that the equation of the curve is shown in the upper left corner and the values of are shown (in decimal form) at the bottom of the screen. The values change as the cursor is moved.
::开始使用图形。 使用本章技术部分中描述的流程; 在您的图形计算器上创建这些极方程式的图形。 一旦图形出现在屏幕上, 将使用跟踪函数和箭头键将光标移动到每个图形周围。 当光标被移动时, 您会注意到曲线的方程式在左上角显示, 并在屏幕底部显示 , x, y 的值( 以小数数格式) 。 当光标被移动时, 值会变化 。
::r= 12cos%1r= 2cosços%12cos_1(cos)=cos_112in the first quadrant and in the fourth quadrant.
::3 在第一个象限 53 在第四个象限。The points of intersection are and . However, these two solutions only cover the possible values . If you consider that is true for an infinite number of theta these solutions must be extended to include and Now the solutions include all possible rotations.
::交叉点是(1,%3)和(1,5,5,3),但是,这两个解决方案仅涵盖可能的值 02。如果您认为对于无限数量的线性来说, cos12是真实的, 这些解决方案必须扩展至包括(1,%3)和(1,5,5,13)+2k,k。 现在解决方案包括所有可能的旋转。3. Find the intersection of the graphs of and
::3. 查找 r=sin 和 r= 1-sin 的图形的交叉点Begin with the graph. You can create these graphs using your graphing calculator.
::以图形开头。您可以用您的图形计算计算器创建这些图形。
::在第一个象限中,r=sin1-sin1-sin1-sin2sin1=12r=sin6,在第二个象限中,r=sin6 交叉点为(12,6)和(12,56)r=12Another交叉点似乎是起源(0,0)。If you consider that is true for an infinite number of theta as was in #2, the same consideration must be applied to include all possible solutions. To prove if the origin is indeed an intersection point, we must determine whether or not both curves pass through (0, 0).
::如果您认为sin12 和 # 2 中的cos12 一样, 对于无限数量的theta 来说是真实的, 就必须将同样的考虑应用到包括所有可能的解决方案。 要证明源代码是否确实是一个交叉点, 我们必须确定两个曲线是否经过( 0, 0 ) 。
::r=sinr=1-sin0=sin0=1-sinr=01=sin2=0From this investigation, the point (0, 0) was on the curve and the point was on the curve . Because the second coordinates are different, it seems that they are two different points. However, the coordinates represent the same point (0,0). The intersection points are and (0,0).
::从本次调查中,点(0,0)位于曲线 r=sin,点(0,%2)位于曲线 r=1-sin。由于第二个坐标不同,它们似乎是两个不同的点。然而,坐标代表同一个点(0,0)。交叉点是(12,%6),(12,56)和(0,0)。Sometimes it is helpful to convert the equations to rectangular form, solve the system and then convert the polar coordinates back to polar form.
::有时,将方程式转换成矩形形式、解析系统、然后将极坐标转换回极形形式是有益的。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked to find the intersection of two equations.
::早些时候,你被要求找到两个方程式的交叉点。The goal is the find the place where the two equations meet. Therefore, you want the point where they are equal. Mathematically, this is:
::目标是找到两个方程式相匹配的地方。 因此, 您想要它们平等的点。 从数学角度讲, 这是:
::222222222222222222Example 2
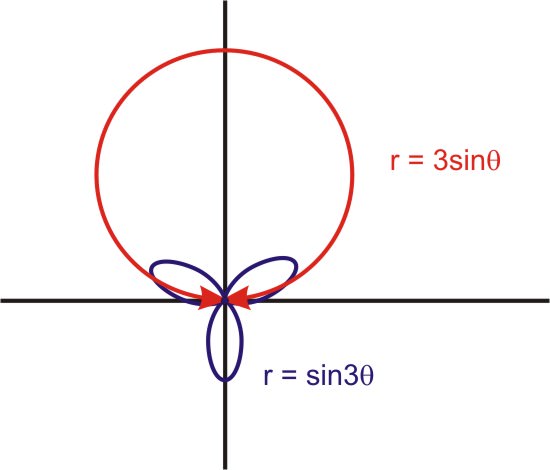
::例2Find the intersection of the graphs of and .
::查找 r=sin3和 r=3sin的图形的交叉点。There appears to be one point of intersection.
::似乎有一个交叉点。
::-======================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================The point of intersection is (0, 0)
::交叉点为( 0, 0)Example 3
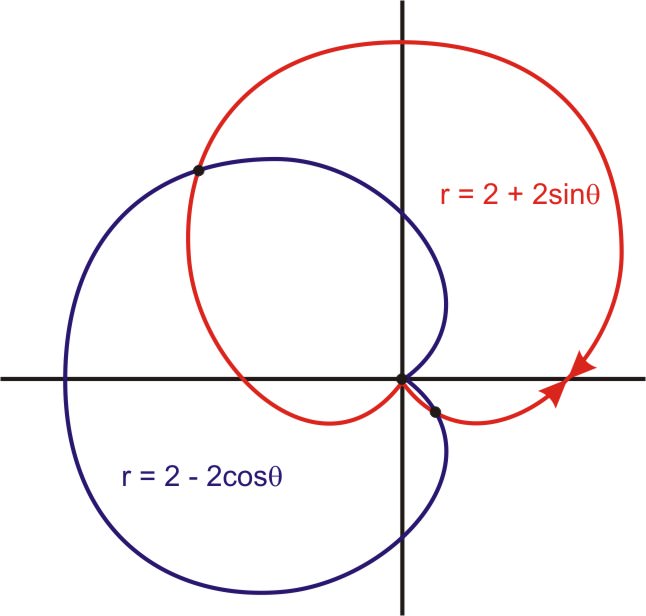
::例3Find the intersection of the graphs of and
::查找 r=2+2sin 和 r=2-2cos 的图形的交叉点
::r=2+2sinr=2+2sinr=2+2+2sin(34)r=2+2sin@74r3.4r}0.59r=2+2sinr=2-2-2cos0=2+2sin0=2-2cos1=sin=1=cos}3220=0Since both equations have a solution at , that is (0, ) and (0, 0), respectively, and these two points are equivalent, the two equations will intersect at (0, 0).
::由于两个方程式的溶液为r=0,即分别为(0,32)和(0,0),而且这两个点相等,这两个方程式在0,0时将交叉。
::r=2+2sinr=2 -2cos2+2sin2 -2cos2sin2cos2cos2cos2cos2cos2cos2cos2cos2cos}1tan}1134和74The points of intersection are and .
::交叉点是(3.4,34)(0.59,74)和(0,0)。Example 4
::例4Determine two polar curves that will never intersect.
::确定两个绝对不会交叉的极曲线。There are several answers here. The most obvious are any two pairs of circles, for example and .
::这里有几个答案。 最明显的是任何两对圆圈, 例如 r=3 和 r=9 。Review
::回顾Find all points of intersection for each of the following pairs of graphs. Answers should be in polar coordinates with .
::查找以下各对图形的所有交叉点。 答案应该与 02 的极地坐标一致 。-
and
::r=2和r=2cos -
and
::r=3和r=3sin -
and
::r=1和r=2sin -
and
::r=sin和r=1+sin -
and
::r=sin2222222222222 -
and
::r=3+3sin和r=3-3cos -
and
::r=cos 3 和r=sin 3 -
and
::r=sin=%2 和r=sin=%3 和r=sin=%2 和r=sin=%3 -
and
::r=3cos和r=2_cos -
and
::r=1 r=1 r=1 r=1 r=cos r= r= r=1 r= r=1 -
and
::r=3sin和r=2-sin -
and
::r2=sin和r2=cos -
and
::r2=sin2222222222 -
Explain why one point of intersection of polar graphs can be represented by an infinite number of polar coordinate pairs.
::解释为什么极地图的一个交叉点可以用无限数量的极地坐标对表示。 -
Explain why the point (0,0) in polar coordinates is not always found as a point of intersection when solving for points of intersection algebraically.
::解释为什么极地坐标中的点(0,0)在解决交叉代数点时并不总是作为交叉点。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
and