2.12 多元性实际零
章节大纲
-
In the real world, problems do not always easily fit into quadratic or even cubic equations. Financial models, population models, fluid activity, etc., all often require many degrees of the input variable in order to approximate the overall behavior. While it can be challenging to model some of these more complex interactions, the effort can be well worth it. Mathematical models of stocks are used constantly as a way to "look into the future" of finance and make the kinds of educated guesses that are behind some of the largest fortunes in the world.
::在现实世界中,问题并不总是容易地融入二次方程甚至立方方程。 金融模型、人口模型、流动活动等等都往往需要不同程度的投入变量才能接近总体行为。 虽然模拟其中某些更复杂的互动可能具有挑战性,但这种努力却值得。 股票的数学模型被不断用来“展望未来”金融,并进行世界上一些最大财富背后的有教育的猜测。What benefits can you think of to modeling the behavior of large populations? Can you think of other useful applications not mentioned here?
::你能想到什么好处来模拟大量人口的行为?你能想到这里没有提到的其他有用的应用吗?Finding Real Zeros of Polynomials
::寻找真正的多元体零数There are three theorems and a rule that we will be referring to during this lesson in order to help make the discovery of the roots of polynomial functions easier. You should review them and be prepared to refer to them often during the practice problems.
::我们在这个课程中将提到三个理论和一条规则,以便帮助更容易发现多元功能的根源,你应该审查这些理论和规则,并准备在实践问题期间经常提到它们。The Remainder Theorem
::遗物定理If a polynomial of degree is divided by , then the remainder is a constant and it is equal to the value of the polynomial when is substituted for . That is
::如果以 x - c 除以一多边f(x) 度 n >0 的 f(x) 度除以 x > 0, 那么其余的 R 是一个常数, 当 c 取代 x 时, 它等于多数值 。
:c) =R
The Factor Theorem
::因数定理If is a polynomial of degree and , then is a factor of the polynomial . Further, if is a factor, then is a zero of .
::如果 f(x) 是一等n > 0 和 f(c) = 0, 那么 x- c 是一等 f(x) 的一个系数。 此外, 如果 x- c 是一因数, 那么c 是 f 0 。The Rational Zero Theorem
::理性的零定理Given the polynomial
::以多面体为背景
:x) = anxn+an - 1xn - 1xn - 1a1x+a0
and is a positive integer . If the coefficients are integers and is a rational zero in lowest terms , then is a divisor of and is a divisor of .
::an0和 n 是一个正整数。如果系数是整数,而pq是最低值的合理零,那么p是a0的差数,q是a的差数。Descartes' Rule of Signs
::笛卡尔的标志规则Given any polynomial, ,
::考虑到任何多面性, p( x) ,-
Write it with the terms in descending order, i.e. from the highest degree
term
to the lowest degree term.
::以降序顺序,即从最高学位到最低学位,用术语写成。 -
Count the number of sign changes of the terms in
. Call the number of sign changes
.
::计数 p(x) 中术语的符号修改次数。 调用符号修改次数 n 。 -
Then the number of
positive
roots of
is
less than or equal to
.
::然后p(x) 正根数小于或等于n。 -
Further, the possible number of positive roots is
::此外,可能的积极根源是n,n - 2,n - 4,... -
To find the number of
negative
roots of
, write
in descending order as above (i.e. change the sign of all terms in
with odd powers), and repeat the process above. Then the
maximum
number of negative roots is
.
::要找到 p(x) 的负根数, 请按上述降序写p( x) (即用奇数更改 p(x) 中所有词的符号) , 并重复上述进程 。 那么负根的最大数是 n 。
Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked if you could identify some valuable real-world uses for modeling higher-degree .
::更早之前,有人问过你,你能否找出 某些有价值的现实世界用途 来模拟高度的模型。Here are a few possibilities:
::以下是几种可能性:-
Identifying what times of the day people are most likely to want coffee (market research like this is key to running your own business)
::确定人们最可能想要咖啡的时段(像这样的市场研究是经营自己的企业的关键) -
Predicting population growth in a particular neighborhood or area of town (useful for identifying a good location to start a small business)
::预测特定街区或城镇地区的人口增长(用于确定开办小企业的好地点) -
Identifying which stocks are likely to
rise
or fall based on weather or season
::确定哪些储存量可能因天气或季节天气或季节而上升或下降 -
Forecasting the weather
::天气预报 -
Calculating the right head start to give a slower car to make a drag race exciting
::右头计算右头 开始给一辆慢慢的车 来让拖动赛跑刺激
There are many, many more.
::还有很多,还有更多。Example 2
::例2Use synthetic division and the remainder and factor theorems to find the quotient and the remainder if is divided by .
::使用合成分割和剩余和系数定理来找到商数Q(x),如果f(x)=2x3-3x2+6除以x-5,则其余R则除以x-5。Hence
::因此
::2x3-3x2+6=(2x2+7x+35)(x-5)+181Notice that the remainder is 181 and it can also be obtained if we simply substituted into ,
::通知其余为181,如果我们简单地将x=5改为f(x),也可以获得,
::f(5)=2(5)3-3(5)2+6=250-75+6=181Example 3
::例3Use the rational zero theorem and synthetic division to find all the possible rational zeros of the polynomial
::使用理性的零定理和合成的分解 来找到所有可能的 多元的理性零点
:xx) =x3 - 2x2 - x2+2
From the rational zero theorem, is a rational zero of the polynomial . So is a divisor of 2 and is a divisor of 1. Hence, can take the following values: -1, 1, -2, 2 and can be either -1 or 1. Therefore , the possible values of are
::从理性的零理论中, pq 是多元 f. 的理性零。 所以 p是 2 的 divisor, q 是 1 的 divisor。 因此, p 可以采取以下值: - 1, 1, 1, 2, 2 和 q 可以是 - 1 或 1 。 因此, pq 的可能值是 1 。
::q:p:-1,1,2-2,2So there are four possible zeros. Of these four, not more than three can be zeros of because is a polynomial with degree 3. To test which of the four possible candidates are zeros of , we use the synthetic division. Recall from the remainder theorem if , then is a zero of . We have
::因此有四个可能的零。 在这四个中, 最多不超过三个是f的零, 因为f是具有第3级的多元性。 为了测试四个可能的候选者中哪一个是f的零, 我们使用合成分区。 如果f(c)=0, 那么c是f的零, 那么从其余的理论中回顾一下。Hence, 2 is a zero of . Further, by the division algorithm,
::因此,2是f的零。 此外,根据分部算法,
:xx) =(x-c) Q(x) Q(x) +R(x) =(x) =(x-2)(x2) (x2-1) +0
The remaining zeros of are simply the zeros of which is easier to manipulate,
::F的其余零只是Q(x)=x2-1的零,更容易操作,
::Q(x)=x2-1=(x-1)(x+1)and thus the remaining zeros are -1 and 1. Thus the rational zeros of are -1, 1, and 2.
::因此,剩下的零是-1和1。 F的理性零是-1、1和2。Example 4
::例4Graph the polynomial function .
::图解多边函数 h( x) = 2x3- 9x2+12x-5。Notice that the leading term is , where odd and . This tells us that the end behavior will take the shape of a power function with an odd exponent .
::请注意, 前一学期为 2x3, 其中 n=3 奇数和 an=2>0 。 这告诉我们, 最终行为将使用 奇数的推力函数形状 。Here, as you can see, there is no straight-forward way to find the zeros of . However, with the use of the factor theorem and the synthetic division, we can find the rational roots of .
::这里,如你所见,没有直接前进的方法可以找到h(x)的零。然而,通过使用系数定理和合成分解,我们可以找到h(x)的理性根。First, we use the rational zero theorem and find that the possible rational zeros are
::首先,我们使用理性零理论论,发现可能的理性零是
::pq:-1,1,1,-2,2,-5,5,5,-52,52testing all these numbers by the synthetic division,
::由合成组测试所有这些数字,-1 is not a root . Now let's test .
::- 1 不是根。 现在让我们测试 x=1 。we find that 1 is a zero of and so we can re-write ,
::我们发现1是h的零, 所以我们可以重写h(x),
::h(x) = (2x2-7x+5)(x-1)Looking at quadratic part,
::看着二次方形部分,
::2x2-7x+5=(2x-5)(x-1)and so
::如此,如此,如此,如此
::h(x) = (2x-5)(x-1)2Thus 1 and are the intercepts of . The intercept is
::因此,1和52是h(x)的 x- 截取。 y(x) 截取
:0)5
Further, the synthetic division can be also used to form a table of values for the graph of :
::此外,合成分数也可以用来组成h(x)图的数值表:
::2523h(x)-28-50-104We choose test points from each interval and find .
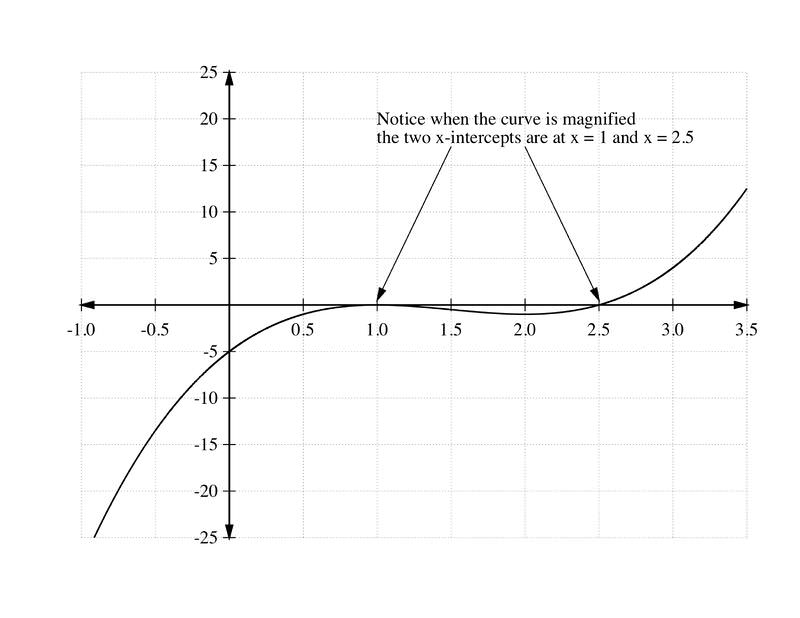
::我们从每个间隔选择测试点并找到 g(x) 。Interval Test Value Sign of Location of points on the graph -1 -28 - below the axis - below the axis 3 4 + above the axis From this information, the graph of is shown in the two graphs below. Notice that the second graph is a magnification of in the vicinity of the axis.
::在此信息中, h(x) 图形在下面两个图表中显示。 请注意, 第二个图形是 x- 轴附近 h(x) 的放大值 。Example 5
::例5Use the 'rational zero' theorem and synthetic division to find all the possible rational zeros of the polynomial
::使用“ 合理零零” 理论和合成分解, 以找到所有可能的 多元数的理性零 。
:xx) =x3- 2x2- 5x+6)
Assume is a rational zero of . By the rational zero theorem, is a divisor of 6 and is a divisor of 1. Thus and can assume the following respective values
::假设pq是f的理性零。根据理性零理论,p是6的断点,q是1的断点,因此p和q可以假定以下各自的数值:andTherefore, the possible rational zeros will be
::因此,可能的理性零将达到-1,1,2,2,3,3,3,6和6q:-1,1,1,2,3,6,66。Notice that with these choices for and there could be rational zeros. But, eight of them are duplicates. For example . The next step is to test all these values by the synthetic division (we'll let you do this on your own for practice) and we finally find that
are zeros of . That is
::请注意, p和 q 的这些选择可能为 82= 16 理性零。 但是, 其中八个是重复的 。 例如 1-1\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ 下一步是用合成分解来测试所有这些值( 我们允许您自己做这个练习), 我们最终发现 1, - 2 和 3are 零 f., 即 f( x) =x3 - 2x2 - 5x+6=( x-1) (x+2) (x- 3) 。Example 6
::例6Use Descartes' Rule of Signs to identify the possible number of positive and negative roots of
::使用笛卡尔的标志规则,确定.
:xx)... 2x3+x2 -3x5+5x-1;
First, re-write in descending order
::首先,将f(x)重写为 f(x) , 依次顺序f(x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxThe number of sign changes of is 2, so the number of positive roots is either 2 or 0.
::f( x) 的符号更改数为 2, 正根数为 2 或 0 。For the negative roots, write
::负根, 写法 f( - x)\\\\\\\ 3x5+2x3+x2- 5x- 1The number of sign changes of is 2, so the maximum number of negative roots is 2.
::f( - x) 的符号更改数为 2, 因此负根的最大数为 2 。The graph of below shows that there is one negative root and two positive roots.
::F(x)下图显示有一个负根和两个正根。Review
::回顾Questions 1 - 3: Use a) long division and b) synthetic division to perform the divisions. Express each result in the form: .
::问题1 - 3: 使用(a) 长的分区和(b) 合成分区来进行分区。 表示每个结果的形式为: f(x) = D(x) (x)+R。-
by
::5x5-3x4+2x3+x2-7x+3 x-2xxxxx -
by
::-4x6-5x3+3x2+x+7 x-1xx -
by
::2x3- 5x2+5x+11xxxxx- 12xxxx -
Use synthetic division to find
and
so that
if
and
::使用合成分解来找到 Q(x) 和 f(c) , 这样f( x) = (x) Q(x) +f(c) 如果 f( x) = 3x4 - 3x3+3x2+2x4 和 c*2, 则 f(x) = (x) Q(x)+f(c) -
If
, use synthetic division to determine the following: a)
b)
c)
d)
e) What are the factors of
?
::如果f(x)=x3+2x2-10x+10,则使用合成分解来确定以下因素a) f(-1) b) f(-3) c) f(0) d) f((4) e) f(x)有哪些因素?
-
Find
so that
is a factor of
::查找 k, 这样 x- 2 是 f( x) = 3x3+4x2+kx-20 的系数 -
Use synthetic division to determine all the zeros of the polynomials: a)
b)
::使用合成分解来确定多元数的所有零: a) f(x)=3x3-7x2+8x-2b) g(x)=4x4-4x3-7x2+4x3+4x3 -
Graph the polynomial function
by using synthetic division to find the
intercepts and locate the
intercepts.
::通过合成分解查找 x- 截取器和定位 y- 截取器, 绘制多数值函数 f( x) =x3 - 2x2 - 5x+ 6 。 -
Graph the polynomial function
by using synthetic division to find the
intercepts and locate the
intercepts.
::通过合成分解查找 x- 界面和定位 y- 界面, 绘制多数值函数 h( x) =x3- 3x2+ 4 。 -
Write a 3rd degree equation of a polynomial function with the zeroes: 0, 2, and -5.
::写入一个多面函数的三度方程式, 零: 0, 2 和 - 5 。 -
Write a 7th degree equation of a polynomial function with the zeroes: 0 (multiplicity 2), 2 (multiplicity 3), and -5 (multiplicity 2)
::以零为0(多重2),2(多重3)和-5(多重2),写入多边函数的7度方程式,以0为0:0(多重2),2(多重3)和5(多重2) -
Write a quadratic equation which has 4 (multiplicity 2) as the zero and opens downward.
::写一个二次方程, 以 4 (多重 2) 为零, 向下打开 。 -
Write a 3rd degree polynomial function with the zeroes: -2, 2, and 6, passing through the point (3, 4)
::写一个三度多元函数,零为: -2, 2和6, 穿过点(3, 4) -
Let
and find the solutions: a)
b)
::Let f( x) = 2x3 - 5x2 - 4x+3 找到解决方案 : a) f( x) = 0 b) f( 2x) = 0 -
Graph and find the solution set of the inequality
.
::并找到不平等 x3 - 2x2 - 5x+6+0 的解决方案集 。 -
Use the graph of
to find the solution set of the inequality
.
::使用 f( x) =x( x- 1) (x+2) 的图形来找到不平等 x( x- 1) (x+2) > 0 的解决方案集 。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Write it with the terms in descending order, i.e. from the highest degree
term
to the lowest degree term.