2.14代数基本理论
章节大纲
-
The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra is really the foundation on which most study of Algebra is built. In simple terms it says that every polynomial has zeros . That means that every polynomial can be factored and set equal to zero (the Factorization Theorem).
That is an extremely broad statement! Every polynomial can be factored? What about functions like ? What about crazy big ones, like ?
::这是一个非常宽泛的语句 ! 每个多元性都可以被计算 。 那么 x2\\\ 4 的函数呢 ? 那么疯狂的大功能呢 , 比如 x6 - 23x5+1246x4 - 23x3 ?Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
::代数基本理论Here are four important theorems in the study of complex zeros of polynomial functions:
::以下是研究多元函数复合零的四项重要理论:The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
::代数基本理论If is a polynomial of degree , then has at least one zero in the complex number domain . In other words, there is at least one complex number such that .
::如果 f( x) 是一度 n1, 那么 f( x) 在复数域中至少有 零 。 换句话说, 至少有一个复数 c , 如 f( c) =0 。There is no rigorous proof for the fundamental theorem of algebra. Some mathematicians even believe that such proof may not exist. However, the theorem is considered to be one of the most important theorems in mathematics. A corollary of this important theorem is the factorization theorem .
::代数的基本理论没有严格的证据。 一些数学家甚至认为这种证据可能不存在。 但是,理论被认为是数学中最重要的理论之一。 这一重要理论的必然结果是因子化理论。The Factorization Theorem
::集成定理If
::如果(如果)
:x) = anxn+an - 1xn - 1xn - 1a1x+a0
where , and is a positive integer , then
::a++%0, 和 n为正整数的
:xx) = an(x-c1)(x-c2) (x-c0)
where the numbers are .
::数字 CI 的位置。The Roots Theorem
::N-Roots定理If is a polynomial of degree , where , then has, at most, zeros.
::如果 f(x) 是一等n, 其中n0, 那么f(x) 最多为 n0。Notice that this theorem does not restrict that the zeros must be distinct. In other words, multiplicity of the zeros is allowed. For example, the quadratic equation has one zero, -3, and we say that the function has -3 as a double zero or one zero with multiplicity . In general, if
::请注意此定理没有限制零必须区别。 换句话说, 允许多个零。 例如, 四方方方方程式 f( x) =x2+6x+9 中为 1 0, - 3, 并且我们说, 函数 - 3 具有 - 3 双 0 或 1 0 和 k=2 。 一般来说, 如果
:xx) = (x-c) kq(x) 和q(c) =0
then is a zero of the polynomial and of multiplicity . For example,
::然后, c 是多面性 f 和多重 k 的零。 例如,
:xx)=(x-2)3(x+5)
has 2 as one zero with and -5 as a zero with .
::2 等于 1 0, k=3 和 -5 等于 0, k= 1 。Conjugate Pairs Theorem
::共和对等理论If is a polynomial of degree , with and with real coefficients, and if , where , then . Where is the complex conjugate of .
::如果 f(z) 是一等量 n, 有n0 和真实系数, 如果 f(z0) = 0, 其中z0=a+bi, 那么 f(z0) = 0。 z0 是 z0 的复合共和值 z0 。This is a fascinating theorem! It says basically that if a complex number is a zero of a polynomial, then its complex conjugate must also be a zero of the same polynomial. In other words, complex roots (or zeros) exist in conjugate pairs for the same polynomial. For example, the polynomial function
::这是一个令人着迷的定理! 它基本上说, 如果一个复杂数字是多元数的零, 那么它的复杂共鸣也必须是同一多元数的零。 换句话说, 复杂的根( 或零) 存在于同一个多元数的组合配对中。 例如, 多元函数 。
:xx) =x2-2x+2
has two zeros: one is the complex number . By the conjugate pairs theorem (also called the conjugate root theorem), is also a zero of . We can easily prove that by multiplication :
::具有两个零: 一个是复合数 1+i。 以共生配对定理( 也称为共生根定理) , 1- i 也是 f( x) =x2 - 2x+2 的零。 我们很容易通过乘法证明:
::[x-(1+一) [x-(1-一)]=(x-1-(一)-(一)=(x-1-(一)(x-1+一)=x2-(x)-(x)-(x)-(x)-(x)-(x)-(x)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)][x-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)(一)(一)=x2-(一)-(x)-(x)-(x)-(x)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-1)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)+)-(一)+)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)+)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-)(二)-(一)-(一)-)(二)-(一)-(一)-)(一)-)(一)-(一)-)-)-)-(一)-(一)-(一)-)-)-(一)-)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一)-(一Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Write as a complex polynomial in factored form .
::将 g(x) =x2+x+1 写成因数表达式的复杂多元数 。Notice that has no real roots. You can see this in the graph of , or by looking at the discriminant , .
::注意 g( x) 没有真正的根根 。 您可以在 g( x) 图表中看到这一点, 或者通过查看 disriminant, b2 - 4ac=1 - 4 3 。Using the quadratic formula , the roots of are
::使用二次公式, g(x) 的根是
::xbb2 - 4ac2z13212+32i或- 12-32iFinally, writing in factored form,
::最后,以因数形式写g(x),
::g(x)=[x-(-12+32i)][x-(-12-32i)]Example 2
::例2What is the form of the polynomial if it has the following numbers as zeros: and ?
::如果多式f(x)的数值为零,则其形式是什么:-13、1-i和2i?Since the numbers and are zeros, then they are roots of . It follows that they must satisfy the conjugate root theorem. Thus and must also be roots of . Therefore ,
::由于数字2i和1+i为零,因此它们是f(x)=0的根。因此,它们必须满足同族根定理。因此,-2i和1-i也必须是f(x)的根。因此,
:xx)=(x)=(x+13)[x-(1-)(一)][x-(1+一)][x-(1+一)][x-(二)][x-(二)][x-(-2i)]
Simplifying,
::简化,
:xx) = (x+13) (x-1+1) (x-1) - (i) (x-2) (x+2i)
After multiplying we get,
::乘以乘以后,我们得到,
::f(x) = 13( 3x5 - 5x4+13x3 - 192+4x+4)which is a fifth degree polynomial. Notice that the total number of zeros is also 5.
::注意零的总数也是5。Example 3
::例3Find the multiplicity of the zeros of the following polynomial:
::查找下列多元数的零的多重性:
::g(x) =x4 - 6x3+18x2 - 54x+81With the help of the rational zero theorem and synthetic division , we find that is a zero of ,
::在理性零理论和合成分解的帮助下 我们发现x=3是g(x)0
::g(x) =x4-6x3+18x2-54x+81=(x-3)(x3-3x2+9x-27)Using synthetic division on the quotient, we find that 3 is again a zero:
::我们发现3还是0:or from the Roots Theorem (Theorem 3), we write our solution as
::或从 n- Roots 定理( 理论 3 ) 中, 我们写入我们的解决方案 。
::g(x) =(x-3)(x-3)(x-3)(x2+9) =(x-3)(x-3)(x-3i)(x+3i)So 3 is a double zero and and are each of .
::3是双零(k=2),3i和-3i是K=1中各一个。Example 4
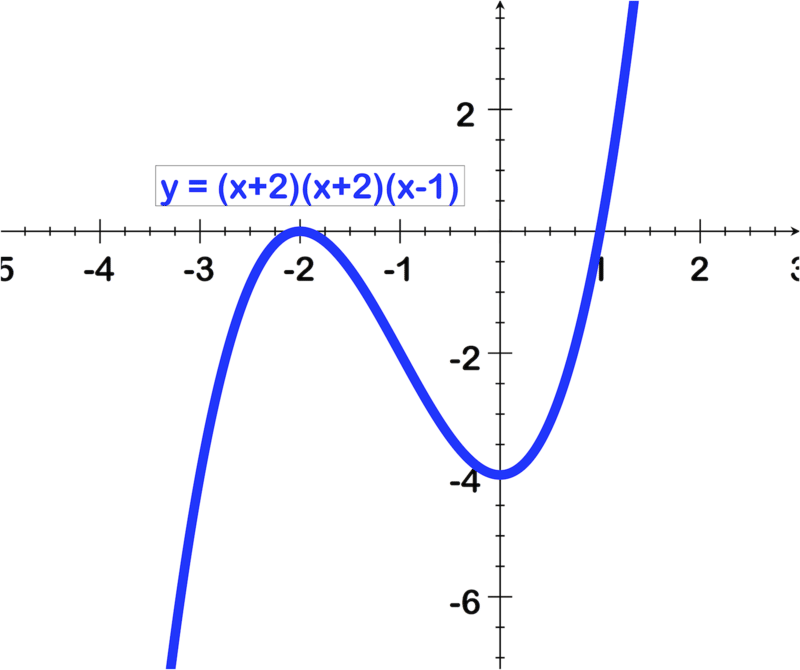
::例4Identify or estimate the values of the zeros from the following equation and state their multiplicities: .
::确定或估计以下方程式的零值,并说明其多重性:y=(x+2)2(x-1)。To identify the roots and their multiplicities:
::为了查明根源及其多重性:First, set the function equal to 0:
::首先,将函数设定为 0x+2)(x+2)(x+2)(x- 1)=0)
The roots then are and
::根为 x=1 和 x2Since the root appears twice, it has a multiplicity of 2, whereas the root appears only once, so its multiplicity is 1.
::由于 x% 2 根出现两次, 其多重性为 2, 而 x=1 根只出现一次, 因此其多重性为 1 。Note: The graph of this function (shown below) will pass through the axis at the root and bounce off the axis at the root .
::注意: 此函数的图形( 如下表所示) 将在 root x=1 处穿过轴, 并在 root x @ @% 2 处从轴中反弹 。If a root has an even multiplicity, it will "bounce" off of the axis, and if it has an odd multiplicity, it will pass through.
::如果根有偶数的倍数, 它会从轴上“ 反弹 ” , 如果它有奇数的倍数, 它会通过 。Example 5
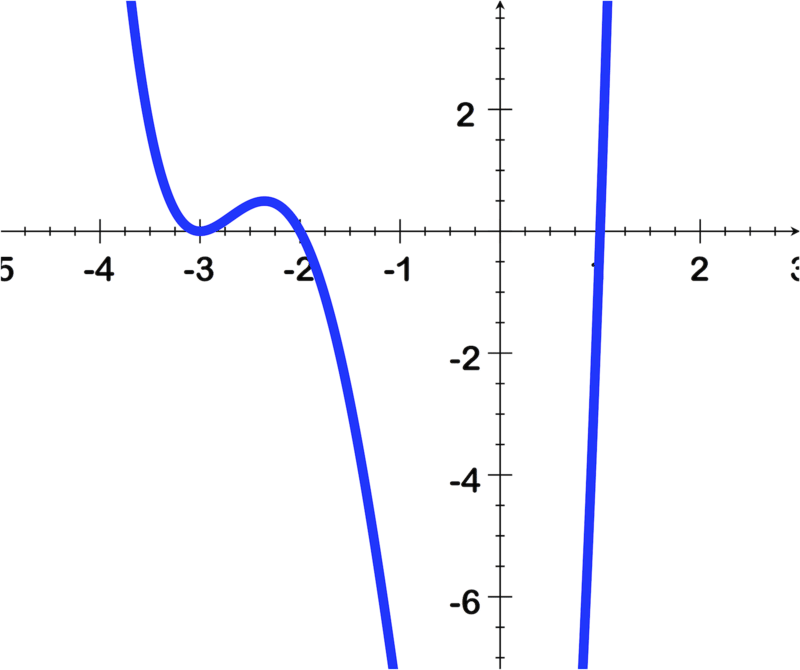
::例5Identify or estimate the values of the zeros from the following graph and state their multiplicities.
::确定或估计下图中零的值,并说明其多功能性。A 4th degree equation:
::第4度方程式:Recall that the roots are locations where the graph contacts the axis. The image indicates this happens at and .
::提醒大家注意, 根是图形连接 x - 轴的位置。 图像显示在 x 3, 2- 2 和 1 发生这种情况 。Applying the rule from the solution to question 1 tells us that the root "-3" has an even multiplicity since it bounces off of the axis. The other 2 roots have odd multiplicities since they pass through.
::应用问题1解决方案的规则告诉我们,根“-3”具有甚至多重性,因为它从轴中弹出。其他两个根自通过以来就有奇特的多重性。The question specifies that this is a 4th degree equation; therefore, the root "-3" has a multiplicity of 2 and the other two roots displayed each have a multiplicity of 1.
::问题明确指出,这是一个四度方程;因此,根的“-3”有2个倍数,其他两个显示的根各有1个倍数。Example 6
::例6Identify or estimate the values of the zeros from the following equation and state their multiplicities: .
::确定或估计以下方程式的零值,并说明其多功能性: g(x) =(x2+6x+9) (x3+6x2+12x+8)。First, factor the polynomial:
::第一,多数值系数: g(x)=(x+3)2(x+2)3The roots are and .
::根是 x% 2 和 x% 3 。The multiplicities stem from the multiples of the same binomial , so the root has a multiplicity of 3 and has a multiplicity of 2.
::多重性来自同一个二元制的多重性, 因此根 x2 的多重性为 3, x3 的多重性为 2 。A graph of this equation would show the line passing through and bouncing off at .
::此方程式的图形将显示通过 x3 的线条, 并在 x2 时弹出 。Example 7
::例7Find a polynomial function with real coefficients that has the following values as its zeros: .
::找到一个带有实际系数的多元函数,该系数的零值如下: 2,3,-3,1。To find a function with the specified zeros:
::要找到带有指定零的函数 :Recall that the zeros of a function are the additive inverse of the constant term in each binomial of the factored polynomial, giving:
::回顾函数的零是因数多元数的每个两义中常数值的反常值的添加值,说明x-2)(x-3)(x+3(x-1))
Distribute:
::分布x2- 5x+6)(x2+2x-3)
Multiply the :
::乘以: (x4-3x3-7x2+27x-18)is the specified polynomial.
:x4-3x3-7x2+27x-18)是指定的多元性。
Review
::回顾In questions 1-5, find a polynomial function with real coefficients that has the given numbers as its zeros.
::在问题1至5中,找到一个带有实际系数的多元函数,其给定数字为零。-
::1,2,2,2,i -
::2,2,2,1-i -
::i,i,0,2i -
::1,1,1,(1-i3) -
::0 0,2i -
If
is a root of the polynomial
, find all other roots of
.
::如果 i - 1 是多边 f( x) =x4+2x3- 4x-4 的根, 请查找 f 的所有其他根 。 -
If
is a zero of the polynomial
, find all other zeros of
.
::如果- 2i 是多元 f(x) =x4+x3 - 2x2+4x-24 的零,请找到所有其他f零。
In question s 8-10, determine whether the given number is a zero of the given polynomial. If so, determine its multiplicity.
::在问题8-10中,确定给定数字是否为给定多元数的零。如果是,则决定其多重性。-
::f(x) = 9x4 - 12x3+13x2 - 12x2 - 12x+4, x=23 -
::f(x) =x4 - 4x3+5x2 - 4x+4, x=2 -
::f( x) = 3x5 - 4x4+2x3 - 34x2+2x+12, x23
For questions 11 - 15, sketch the graph, properly indicating multiplicities.
::问题11-15,绘制图表,适当显示多重性。-
::g(x) =x2(x) =x2(x-1)(x-3)(x) +2 (x+4) 2 -
:xxxxxx2x-3)3(x-1)(x-2)
-
:xx)xxxx(x-1)(x+2)3
-
::g(x) =x3(x+3) 4(x-2) -
::f(xx) = (x+3) 2(x- 1) (x+1)
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -