5.5 斯卡量预测
章节大纲
-
As an engineer, or a pilot, or racecar driver, or even a chef, it can often be useful to determine the result of different amounts and directions of force applied to a particular action to decide on the best use of added strength, altitude, speed, or heat in order to achieve the optimum result.
::作为工程师、飞行员、驾驶员、赛车驾驶员、甚至厨师,通常可以确定适用于特定行动的不同数量和武力指示的结果,以决定如何最佳利用增加的强度、高度、速度或热量,以取得最佳结果。This lesson is about , which allow you to do the things above and a whole host of others.
::这是关于这个教训, 它允许你做 上面的事情 和一大堆其他人。Scalar Projections
::Scal 预测A scalar projection allows you to investigate the result of different "lengths" of one vector on an overall study. The projection of a vector onto a particular direction is, in effect, the result of applying a specific value in that direction. Recall that the dot product of a vector is a scalar quantity describing only the magnitude of a particular vector. A scalar projection is given by the dot product of a vector with a unit vector for that direction.
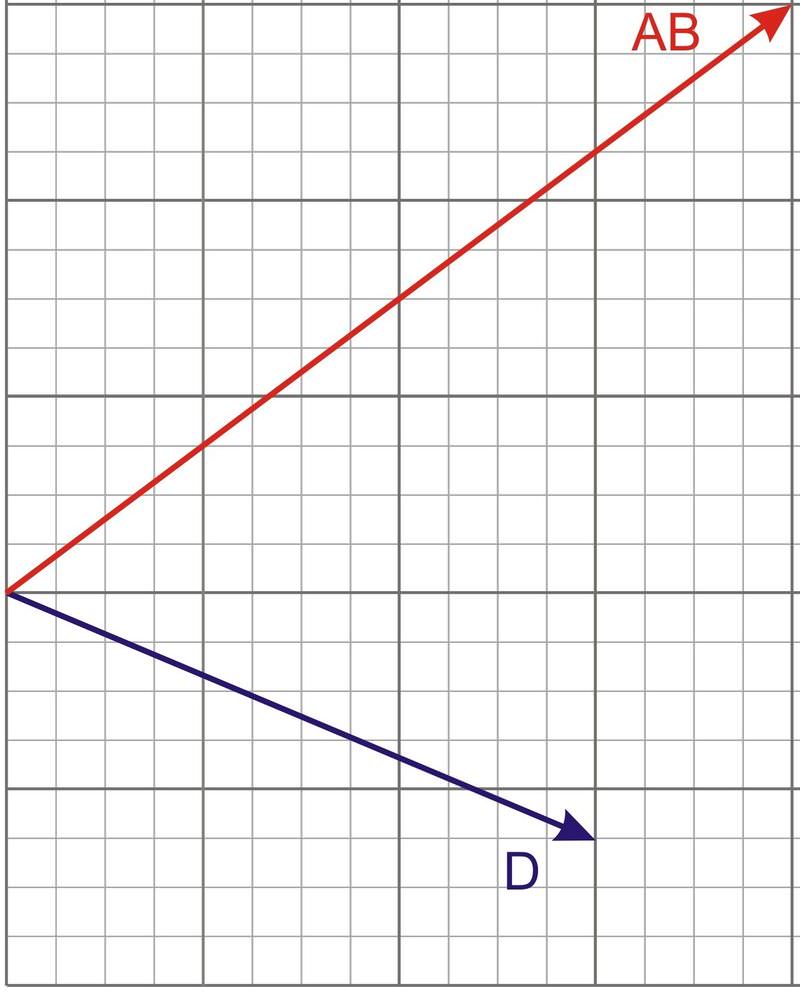
::calar 投影允许您在总体研究中调查一个矢量的不同“长度”的结果。 向某一特定方向投影实际上是向该方向应用特定值的结果。 提醒注意, 矢量的点产物是标量, 仅描述特定矢量的大小。 由带有此方向单位矢量的矢量的点产物提供 calar 投影。For example, the component notations for the vectors shown below are and .
::例如,下列矢量的成分标记为AB4,3和D3,2-1.25。The scalar projection of vector AB onto is given by
::矢量 AB 向 x__ 上方 x__ 的星际投影 :
::ABx(41)+(30)+(00)=4The scalar projection of vector AB onto is given by
::y 的矢量 AB 向 y 的 矢量 AB 的星级投影由
::ABY( 40) +( 31) +( 00) =3And the scalar projection of vector AB onto is given by
::向导 AB 向 z 的 AB 矢量的 ACAL 投射 由
::ABz(40)+(30)+(01)=0The scalar projections of AB onto the x and y directions are non-zero numbers because the vector is located in the x-y plane. The scalar projection of AB onto the z direction is equal to zero, because the z direction is perpendicular to AB .
::x 和 y 方向上的 AB 星标预测值为非零数,因为矢量位于 x-y 平面上。 AB 星标预测值在 z 方向上等于 0, 因为 z 方向与 AB 垂直。Vector Projections
::矢量预测The of a vector onto a given direction has a magnitude equal to the scalar projection. The direction of the vector projection is the same as the unit vector of that given direction. Recall that when a vector is multiplied by a scalar s , its components are given by
::矢量投向给定方向的矢量向某一方向的矢量的大小与斜度投影的大小相等。矢量投向的方向与给定方向的单位矢量的方向相同。请注意,当矢量 v...乘以弧度时,其组件由
::svzvvx,svy,svzvvvx,svzvvvvx,svzvvvx,svzvvvvvx,svvzTo calculate the vector projection of AB onto the direction of vector D , use the scalar projection calculated in the previous example and the unit vector .
::要计算AB向矢量D方向的矢量投影,请使用上一个例子和单位矢量DQ计算的天平投影。
:AB ×D)D(1.230.923),(1.230.385) 1.135,-0.474
Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1The diagram below shows both vectors AB and D together on the same grid. Determine the scalar projection of vector AB onto the direction of vector D .
::下图显示同一网格上的矢量 AB 和 D 并列。 确定矢量 AB 向矢量 D 方向的星标投影 。To find the scalar projection onto the direction of another vector we need to know the unit vector in the direction of vector D .
::要找到向另一个矢量方向的斜线投影 我们需要了解向矢量D方向的单位矢量。First, the components of are
::首先,D__的构成部分是:
::D3,-1.25Now the magnitude of is
::现在DQ的大小是
::D(Dx)2+(Dy)2=32+(- 1. 252)=9+1. 5625=10. 5625=3. 25Finally, the direction vector of is
::最后,D的方向矢量是.
::DD3x(- 1. 25y3. 25= 33. 25 x 1. 2. 2.5 x 1. 2. 2.5 y ) 。
::D0.923,-0.385Now we can use the dot-product to calculate the scalar projection of AB onto the direction of vector D .
::现在我们可以使用点产品来计算 AB 向矢量 D 方向的 ACAL 投影。
::AB ×D(30.923)+(40.385)+(00)= 2.769+(-1.54)=1.23Example 2
::例2Determine the scalar projection of the vector onto the direction of .
::确定矢量R27,39,52向T44,26,17方向的天平投影。The scalar projection of one vector onto the direction of the other is the dot product of the first vector with the unit vector representing the direction of the second vector. To calculate the scalar projection, we need to determine the unit vector in the direction of vector . Remember that a unit vector is equal to the ratio of the vector and its magnitude, therefore we first need to calculate the length of vector
::一个矢量向另一个矢量方向的星际投影是第一个矢量的点产物,其单位矢量代表第二个矢量的方向。要计算星际投影,我们需要确定向矢量方向的单位矢量 T44、26、17。记住一个单位矢量等于矢量及其规模的比例,因此我们首先需要计算矢量 T的长度。
::TTx2+Ty2+Tz2=(442+(262+(177=1936+676+289=2901=53.86)
::TT44,26,17,53.864453.86,2653.86,2653.86,1753.86,1753.86,0.8169,0.4827,0.3156Now we can calculate the scalar projection of onto by calculating the dot product
::现在我们可以通过计算点产品计算出R的 星标投射到 T的星标投影
::=22.0563+18.6253+16.4112=57.0928Example 3
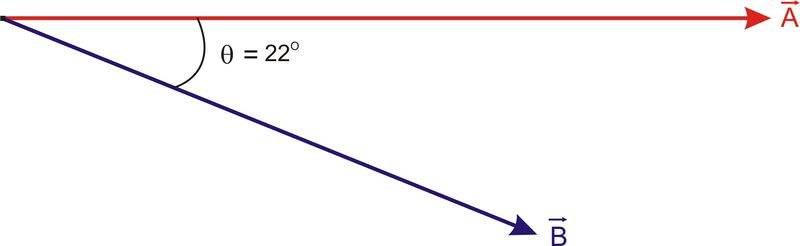
::例3Determine the vector projection of onto the direction of and the vector projection of onto the direction of . @ and @ .
::确定 A 的矢量投射到 B 的 方向上, B 的 矢量投射到 A 的 方向上。 A + 7 cm @ 0 和 B + 4 cm @ ~ 22 。The vector projection of one vector onto the direction of another vector is given by , where is the unit vector in the direction of . Since it is a unit vector has a magnitude of 1 and has the same direction as @ . Therefore, @ @
::一个矢量投向另一个矢量方向的矢量投影由(AB)B(B)B(B)作为单位矢量向B方向投影。由于是单位矢量B(B)的大小为1级,方向与B(B)B1 22(22)相同。因此,(AB)B(ABB(Cos)B((7)(1) cos 22) @-226.49@-22@-22@The vector projection of one vector onto the direction of another vector is given by , where is the unit vector in the direction of . Since it is a unit vector has a magnitude of 1 and has the same direction as , @ . Therefore, @ @
::一个矢量投向另一个矢量方向的矢量投影由 (BA) AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA((4)(1)cos 22) = 03.71@ 0Example 4
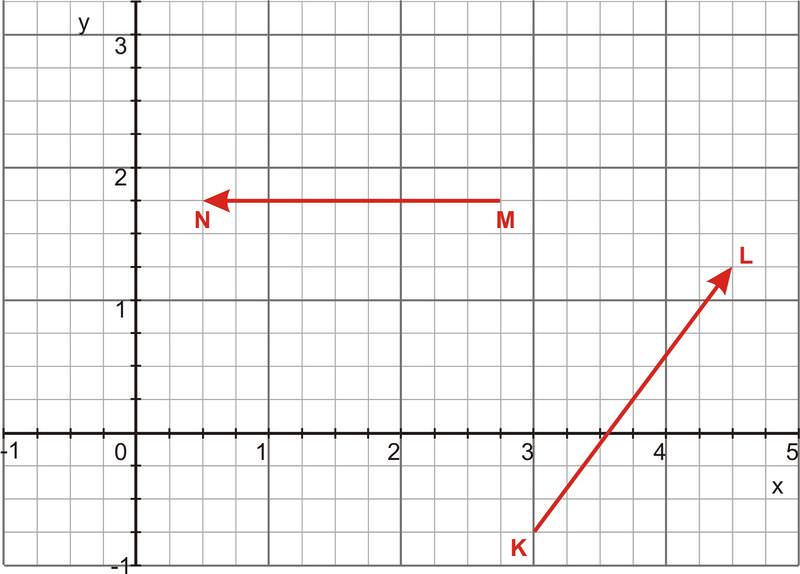
::例4Determine the vector projection of vector onto the vector .
::确定矢量 KL 上矢量 MN 的矢量投影 。The vector progression of one vector onto a second vector is the multiplication of the of the two vectors and the unit vector defining the direction of the second vector. In this case, . First we need to identify the components of the two vectors by using the information given on the graph. In this case, and . Then we need to determine the dot product of the two vectors.
::将一个矢量递增到第二个矢量是两个矢量的乘法和确定第二个矢量方向的单位矢量的乘法。在此情况下, (MNKL) KL。 首先,我们需要使用图上提供的信息来识别两个矢量的构成成分。 在这种情况下, MN2.25, 0.0和 KL1.5, 2,0。 然后,我们需要确定两个矢量的点产物。
::MNKL(MN)x(KL)x+(MN)y(KL)y +(MN)z(KL)z=(2.25)(1.5)+(2)(0)+(0)(0)=3.375We also need to determine the unit vector in the direction of .Remember that a unit vector is equal to the ratio of the vector and its magnitude, therefore we first need to calculate the length of vector .
::我们还需要确定 KL 方向的单位矢量。 请记住单位矢量等于矢量及其规模的比率, 因此我们首先需要计算矢量 KL 的长度 。
::KL(KL)x2+(KL)y2+(KL)y2+(KL)z2=(1.5)2+(2)2+(0)2=2.25+4+0=6.25=2.5
::KLQKLKL1.5,2.0,02.5 1.52.5,22.5,02.50.6,0.8,0Lastly, we multiply the dot product of the two vectors by this unit vector,
::最后,我们将两种矢量的点产物乘以该单位矢量,
:MNKL)KL(3.3750.6,0.8,0.02.025,2.7,0.0)
Review
::回顾-
Calculate the result of a scalar multiple of 6 on the vector
::计算矢量% 1, 19 和% 1 的弧度乘以 6 的结果 。 -
Calculate the result of a scalar multiple of (-8) on the vector
::计算矢量 7,8 矢量上的 Qalar 倍数 (-8) 的结果 -
Calculate the result of a scalar multiple of 15 on the vector
::计算矢量 +++7 3 + 的 15 的弧度乘数结果。 -
Calculate the result of a scalar multiple of (-11) on the vector
::计算矢量 {% 9, 20 } 上的(- 11) 弧度乘数(- 11) 的结果 。 -
Calculate the result of a scalar multiple of 16 on the vector
::计算矢量 {9,10} 上的 16 的弧度乘数结果。
-
Given Vector A =
and Vector B =
. What is the projection of A onto B?
::给定矢量 A = 4,6 和 矢量 B = $9,15。 A 到 B 的预测值是多少? -
What is the projection of
onto
?
::2,10对1,3的预测值是多少? -
Given Vector C =
and Vector D =
. What is the projection of C onto D?
::给定矢量 C = 1,2 和 矢量 D = 1,11。 C 对 D 的预测值是多少 ? -
Given Vector E =
and Vector F =
. What is the projection of E onto F?
::给定矢量 E = 5,3 和 向量 F = 1,18 。 E 到 F 的预测值是多少? -
What is the projection of
onto
?
::2,1对5,6的预测是多少? -
Given Vector H =
and Vector I =
What is the projection of H onto I?
::鉴于矢量H = 8i+11j和矢量I = 2i+15j,H对I的预测值是多少? -
What is the projection of
onto
?
::在8,16之间,1,6的预测值是多少? -
What is the projection of
onto
?
::7,8的预测值是多少? -
Given Vector J =
and Vector K =
. What is the projection of J onto K?
::鉴于矢量 J = 4i+8j和矢量 K = 8i+10j。 -
Given Vector L =
and Vector M =
. What is the projection of L onto M?
::根据矢量L = 4,3和矢量M = 7,17。L 投射到 M 是什么?
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Calculate the result of a scalar multiple of 6 on the vector