5.8 点与平板之间的距离
章节大纲
-
The distance between a specific point and a plane is important to a number of different activities.
::某一点与某一平面之间的距离对若干不同活动很重要。For instance, a bungee jumping tower would not be very safe if the distance to the ground were not measured at the point directly under the tower, since any angle away from straight down would make the distance measure further and lead to a cord too long!
::例如,如果不直接在塔下方的距离测量到地面的距离,那么大盖跳塔就不会非常安全,因为从直下方的任何角度都将使距离更远,导致电线过长!A computer game programmer needs to know how to calculate the distance between the location of a character on the screen and the walls around it to tell the game how to identify when a projectile hits a target, or when the character hits a wall.
::计算机游戏程序员需要知道如何计算屏幕上字符的位置和屏幕周围的墙壁之间的距离,以便告诉游戏如何识别投射物何时击中目标,或者字符何时击中墙壁。Distance Between a Point and a Plane
::点与平面之间的距离Identifying the Point Closest to the Origin
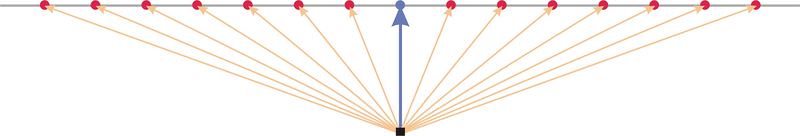
::识别与来源最接近的点No matter what the orientation of a plane, there will always be one point located closer to the origin than any other point on the plane. This means that the position vector for this point is shorter than any other point in the plane. The diagram below shows a two-dimensional projection of a plane, in grey, near a point not on the plane, in black. The position vectors to a variety of points are shown in the diagram. The position vector marked in blue is shorter than the position vectors for the other points. This shortest vector is perpendicular to the plane. You can also see that the blue line is the of any orange vector onto the perpendicular direction.
::无论一个平面的方向如何,总有一个点的位置会比平面上的其他点更接近原点。 这意味着此点的位置矢量比平面上其他任何点都短。 下面的图表显示一个平面的二维投影, 灰色的, 接近在平面上不在平面上的一个点, 黑色的。 图中显示向多个点的矢量的位置。 以蓝色标定的位置矢量比其他点的位置矢量短。 这个最短的向量与平面垂直。 您也可以看到, 蓝线是任何直角方向的橙色矢量。This orthogonality (i.e. being perpendicular) is useful for us because it means that the position vector for this special point is parallel to the normal vector. Therefore, if we know the equation for a normal vector and the position vector for any point on the plane, we can determine the location of the point on the plane closest to the origin by finding the projection of the given point’s position vector onto the normal direction.
::这种直径( 即直角) 对我们有用, 因为它意味着此特殊点的位置矢量与正常矢量平行。 因此, 如果我们知道正常矢量的方程式和平面上任何点的位置矢量, 我们就可以通过将给定点的位置矢量投射到正常方向来确定最接近原点的平面上的点的位置 。The Dihedral Angle
::分角角The angle between two planes is called the dihedral angle . The angle between two planes is the same as the angle between their normal vectors. If we want to determine the dihedral angle between two planes, we identify normal vectors to the two planes, then we can use the dot-product of the two normal vectors to determine the angle between the two normals which is also the two planes. Recall .
::两个平面之间的角称为双向角角。 两平面之间的角与其正常向量之间的角相同。 如果我们想要确定两个平面之间的正向角, 我们就可以确定两个平面之间的正向角, 那么我们就可以使用两个正向矢量的点结果来确定两个正向之间的角, 也就是两个正向之间的角。 回顾 ABABBBCos 。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1The three points P = (3, 7, 2), Q = (1, 4, 3), and R = (2, 3, 4) define a plane. Determine the point on the plane which is closest to the origin.
::三点P = (3, 7, 2),Q = (1, 4, 3),R = (2, 3, 4) 和 R = (2, 3, 4) 定义一架飞机。 确定最接近始发地的飞机上的点 。First find the vectors between two pairs of the points.
::首先在两对点之间找到矢量。
::P(Qx-Px),(Qy-Py),(Qz-Pz) (1-3),(4-7),(3-2),(2)-3,1
::PR(Rx-Px),(Ry-Py),(Rz-Pz) (2-3),(3-7),(4-2),(1) - 4,2The of these two vectors is normal to the plane.
::这两个向量对飞机来说是正常的
::P(PQyPRz-PQzPRy),(PQzPRx-PQxPRz),(PQxPRy-PQPRx)
::PP[(-32)-(14)],[(11)-(-22),[(-24)-(-13)]
:-6)-(-4),[-1)-(-4)],[(8)-(3)-],[2,3,5]
The point on the plane which is nearest to the origin can be found by determining the projection of the position vector of either of these three points onto the normal vector. Remember that the vector projection of one vector onto the direction of another, is given by the dot-product of the first vector onto the unit vector defining the direction of the second vector: .
::通过确定这三个点中任何一个点的位置矢量对正常矢量的投影,可以找到最接近原点的平面上的点。请记住,一个矢量对另一个矢量方向的矢量投影是由第一个矢量的点产物对确定第二个矢量方向的单位矢量的单位矢量提供的AB)B。
Since we know three points on the plane, we can use one of them to solve the problem. Let’s start with point P. The vector projection of onto is given by , so first we need to determine the unit vector which is given by
::由于我们在飞机上知道三点, 我们可以用其中之一来解决问题。 让我们从P点开始。 P的矢量投影由( Pn) n提供, 所以首先我们需要确定由nnnnux,ny,nznx2+ny2+Nz2+Nz2+Nz2+Nz2+Nz2+Nz2,2,3552+52+52,355_380.32,0.49,0.81\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\1\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\
::PnPxnxPynyPznz(3)(-0.32)+(7)(0.49)+(2)(0.0.81)+0.96+3.43+1.62=4.09
:Pn)(4.0990.32,0.49,0.811.3088,2.0041.3129)
Therefore, the point on the plane closest to the origin is (-1.3088, 2.0041, 3.3129).
::因此,最接近原产地的飞机上的点数是(-1.3088, 2.0041, 3.3129)。Example 2
::例2The three points P = (3, 7, 2), Q = (1, 4, 3), and R = (2, 3, 4) define a plane. Determine the dihedral angle between this plane and the x-y plane.
::三点P = (3, 7, 2),Q = (1, 4, 3),R = (2, 3, 4) 定义一个平面。确定此平面与 x-y 平面之间的三角角 。As we saw in the example above, these three points define a plane which has a normal vector
::正如我们在上文的例子中看到的那样,这三个点定义了具有正常矢量的平面。
::2,3,5________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________The normal to the x-y plane is the unit vector . To find the angle between these two vectors we use the fact that and that
::X-y 平面的正常值是单位矢量 z0,0,1。要找到这两个矢量之间的角,我们使用ABABCos 和 ABAxBx+AyBy+AzBzFirst find a numerical value for the dot product:
::首先找到点产品的数字值 :
::nznxzx+nyzy+nzzz=(-20)+(30)+(51)=5
::nx2+ny2+nz2=(-2)2+(3)2+(5)2=4+9+25=38
::zx2+zy2+zz2=02+02+12=1Then find the cosine version of the dot product:
::然后找到点产品的余弦版 :
::nz38 cosNow equate the two and solve for the angle, θ
::现在将两者等同, 并解决角度,
::nz5=38 cos
::cos-1(538)=62.5Example 3
::例3Determine the dihedral angle between the two planes 12 x + 23 y + 14 z - 5 = 0 and 7 x + 3 y + z + 12 = 0.
::确定两平面之间12x + 23y + 14z - 5 = 0 和 7x + 3y + z + 12 = 0 之间的三角角。The dihedral angle is defined as the angle between two planes. This angle is also equal to the angle between the normals to the two planes. In two of the previous problems we determined the unit vectors which are perpendicular to these two planes and . We can then use the dot-product of these two normal vectors to determine the angle between the two. The dot-product is defined as and as . First, we need to find the component version of the dot product and the magnitudes of the two normal vectors.
::斜角被定义为两个平面之间的角。 这个角度也等于两个平面之间的角。 在前面的两个问题中, 我们确定了与这两个平面垂直的单位矢量 n11229.5、 23.5、 1429.5、 23.5、 1429.5 和 n2759、 359、 159 。 然后我们可以使用这两个普通矢量的点产物来确定两个向量之间的角。 点产物被定义为 ABAxBx+AyBy+AzBz+... 和 ABAB cos 。 首先, 我们需要找到两个正向量的元件和大小 。
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}n2\n2y\n2y\n1z\n2z\\\\\\\\\12\729.559+23_329_559+14}129.559
::n212729.559+23329.559+14129.559=119226.6+69226.6+142226.6=202226.6=0.891Since these two vectors are unit-vectors, their magnitudes are both equal to 1.
::由于这两种矢量是单位向量,其数量均等于1。
::n1n2n1n20.891(1)=0.891
::*cos-10.891=27.0 *cos-10.891=27.0 *cos-10.891=27.0 *cos-10.891=27.0Example 4
::例4Determine the angle between the plane 2 x - 5 y + 8 - 10 = 0 and the y - z plane.
::确定平面 2x - 5y + 8 - 10 = 0 和 Y - z 平面之间的角。The dihedral angle is defined as the angle between the two planes and is also equal to the angle between the two normal unit vectors. In this case, we already know the normal unit vector for the y-z plane, . We still need to determine, however, the unit vector for the plane 2 x - 5 y + 8 z - 10 = 0.
::斜角被定义为两个平面之间的角, 也等于两个正常单位矢量之间的角。 在这种情况下, 我们已经知道 y-z 平面的正常单位矢量 x1,0,0 。 但是, 我们还需要确定 2x - 5y + 8z - 10 = 0 的单位矢量 。Comparing this equation to , we can see that .
::将这个方程比作 nxx+nyy+nzz+d=0, 我们可以看到n%2, - 5,8。Now we can use the definition of the unit vector
::现在我们可以使用单位矢量的定义
::nnnnnnn929.64,-59.64,-59.64,89.64The angle between the two planes is equal to the angle between the two normal vectors.
::两个平面之间的角等于两个正常向量之间的角。We can then use the dot-product of these two normal vectors to determine the angle between the two. The dot-product is defined as and as . First, we need to find the component version of the dot product and the magnitudes of the two normal vectors.
::然后我们可以使用这两个正常矢量的点产品来确定两者之间的角。 点产品的定义是 ABAxBx+AyBy+AzBz+... 和 ABABCos 。 首先, 我们需要找到点产品的组件版本和两个正常矢量的大小 。
::n1\n2\n2\n1xn2xn2xn1y}n2y}n1z\n2z\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\0.2074\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\0.2074\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Since these two vectors are unit-vectors, their magnitudes are both equal to 1.
::由于这两种矢量是单位向量,其数量均等于1。
::2074年1月1日(1)=0.2074年1月1日
::cos- 10.2074=16.18Example 5
::例5The three points and identify a plane. Determine the point on the plane which is closest to the origin.
::PQ2,3,4,5-6,7和RQ8,9,-1三点确定一架飞机。确定最接近原产地的飞机上的点。The point on the plane nearest to the origin can be found by determining the projection of the position vector of one of these three points onto the normal vector. Remember that the vector projection of one vector onto the direction of another is given by the dot-product of the first vector onto the unit vector defining the direction of the second vector: .
::通过确定上述三点之一的位置矢量对正常矢量的投影,可以找到最接近原点的平面上的点。请记住,第一个矢量的点产给确定第二个矢量方向的单位矢量(Pn)n的单位矢量,向另一个矢量方向的矢量投影由第一个矢量的点产品给定Pn)n。
We can use the position vectors for the three points to determine two vectors within the plane. Once we have those two vectors, their cross-product will define the direction normal to the plane. First find the two equations in the plane:
::我们可以使用三点的位置矢量来确定飞机内的两个矢量。 一旦我们掌握了这两个矢量, 它们的交叉产品将定义飞机的正常方向。 首先在平面中发现两个方程式 :
::AP5、-6、7、7、3、4、4、7、9、3
::BP8,9,9 -1,2,3,4,410,6,55Now determine the cross product of the two vectors
::现在确定两个矢量的交叉产品
::nAB(AyBz-AzBy),(AzBx-AxBz),(AxBy-AyBx)
::nAB(45-18),(30-(35)),(42+90)
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}什么?Now we need to determine the unit vector associated with this normal vector
::现在我们需要确定与此正常矢量相关的单位矢量
::nnnnnx2+ny2+Nz2+Nz2+Nz227,65,132272+(655)2+(132)2}27,65,13222378
::nnn0.181,0.435,0.882Now we determine the vector progression of one of the three initial position vectors onto the direction of this normal unit-vector: . Remember that the dot product is given by .
::现在我们确定三个初始位置矢量之一的矢量递增到此正常单位矢量的方向上Pn)n。 记住点产品由 ABAxBx+AyBy+AzBz+...
::+3(0.435)+4(0.882)+0.181,0.435,0.882
:Pn)n(4.4710.181,0.435,0.882)
:Pn)n(4.4710.181,0.435,0.8820.809,1.945,3.943)
Example 6
::例6Determine the point on the plane 7 x + 3 y + z + 12 = 0 which is closest to the origin.
::确定7x + 3y + z + 12 = 0 最接近原产地的平面上的点。The point on the plane nearest to the origin can be found by determining the projection of the position vector of any point on the plane onto the normal vector. The vector projection of one vector onto the direction of another is given by the dot-product of the first vector onto the unit vector defining the direction of the second vector: .
::通过确定平面上任何点的位置矢量投射到正常矢量上,可以找到最接近原点的平面上的点。一个矢量投向另一个方向的矢量投射由第一个矢量的点产品投向确定第二个矢量方向的单位矢量Pn)n。
In this case, we can determine a normal vector using the equation of the plane. Comparing 7 x + 3 y + z + 12 = 0 to the generic equation , we can see that and
::在此情况下, 我们可以使用平面的方程来确定正常矢量 。 将 7x + 3y + 3y + z + 12 = 0 与 nxx+ nyy+nzz+d=0 相比, 我们可以看到 n+7, 3, 1 + 和 nxx+ ny + nzz+d=0 。
::nnnnx2+ny2+nz2+nz2+7,3,1(7)2+(3)2+(1)2+7,3,149+9+1+7,3,1599,359,159}We also need to know the location of a point on the plane. If we write the equation of the plane in intercept form, we can determine the position vector for the x-, y-, and z-intercepts of the plane.
::我们还需要知道飞机上一个点的位置。如果我们以拦截形式写下飞机的方程式,我们可以确定飞机的 X 、 y 和 z 拦截的位置矢量。The equation must be true for all points on a plane. Therefore, we should first rearrange 7 x +3 y + z + 12 = 0 into the form .
::等式 1 = Xa+yb+zc 必须是适用于平面上所有点的。 因此, 我们应该首先将 7x+3y + z + 12 = 0 改为 1= Xa+yb+zc 。7 x + 3 y + z = -12 becomes
::7x + 3y + z = -12 变成 7-12x+3-12y+1-12z=1Therefore, , and and the position vectors of the three intercepts are , and .
::因此,a127,b1234,和c12112, 以及这3个拦截器的方位是A1.714,00.0,B0,4,0,和C0,0,-12。To complete the problem, compute the dot product.
::为了解决问题,计算点产品。
:Bnx+Byny+Bznz)n(0(759)-4(359)+0(159)) 759,359,159。
:b) 1259_759_759_359_159_8459_3659_1259_1.424_0.610_0.203________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Review
::回顾The three points define a plane. Determine the point on the plane which is closest to the origin.
::三点确定一个平面。 确定最接近原产地的平面上的点 。-
and
::P=(3,6,9,9)(9,6,3)和R=(6,9,9) -
and
::P=(1, - 7,2, (4, 2, 9) 和 R= (3, -5, 1) -
and
::P=(3,8,10)、(-2,5,8)和R=(7,4,8) -
and
::P=(9,-1,4), (6,2,-8)和R=(12,9,10) -
and
::P=(5,5,8,-9)(-5,3,9)和R=(10,4,-6)
Determine the dihedral angle between each of the planes in questions 1-5 and the x-y plane. Use the you calculated for each plane and recall that the normal to the x-y plane is the unit vector .
::确定问题1-5中每个平面与 X-y 平面之间的三角角。 请使用您为每平面计算过的 n , 并提醒注意 X- y 平面的正常值是单位矢量 z0, 0, 1 。-
and
::P=(3,6,9,9)(9,6,3)和R=(6,9,9) -
and
::P=(1, - 7,2, (4, 2, 9) 和 R= (3, -5, 1) -
and
::P=(3,8,10)、(-2,5,8)和R=(7,4,8) -
and
::P=(9,-1,4), (6,2,-8)和R=(12,9,10) -
and
::P=(5,5,8,-9)(-5,3,9)和R=(10,4,-6)
Determine the dihedral angle between the two planes.
::确定两个平面之间的三角角。-
and
::9x+17y-4z-7=0和-17x+24y+14z+2=0 -
and
::2x-4y+10z-11=0和2x-9y+4z+12=0 -
and
::-7x+20y+6z+4=0和-19x-3y+z+5=0 -
and
::5-8y+20z-5=0和6x+y+19z-7=0 -
and
::14x+11y-5z-16=0和11x-13y+8z+4=0 -
and
::-10x+9y+2z+8=0和21x+7y+4z+15=0
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
and