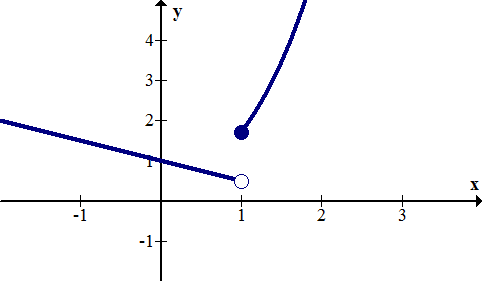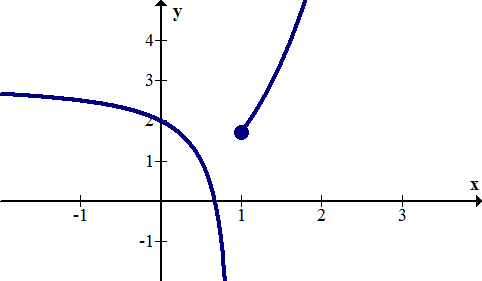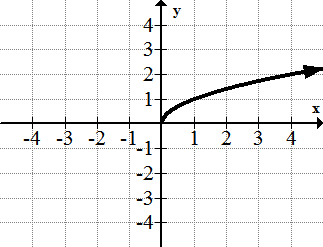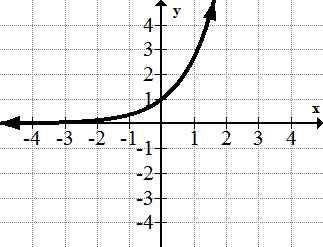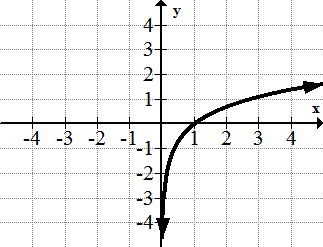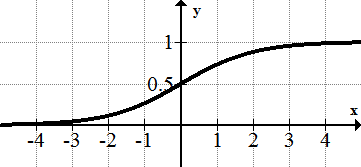1.10 连续性和中断性
章节大纲
-
Continuity is a property of functions that can be drawn without lifting your pencil. Some functions, like the reciprocal functions, have two distinct parts that are unconnected. Functions that are unconnected are discontinuous. What are the three ways functions can be discontinuous and how do they come about?
::连续性是函数的属性, 无需举起您的铅笔即可绘制。 有些函数, 如对等函数, 有两个不同部分没有连接。 没有连接的函数不连续。 三种函数可以不连续, 如何产生 ?Continuity and Discontinuity of Functions
::职能的连续性和终止Functions that can be drawn without lifting up your pencil are called continuous functions . You will define continuous in a more mathematically rigorous way after you study limits.
::在不举起您的铅笔的情况下可以绘制的函数被称为连续函数。在学习限制之后,您将以数学上更加严格的方式定义连续函数。There are three types of discontinuities: Removable, Jump and Infinite.
::有三种不连续类型:可移动、跳跃和无限。Removable Discontinuities
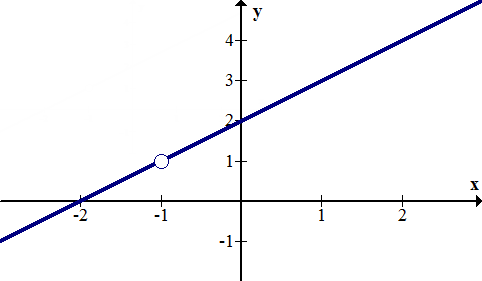
::可移动中断Removable discontinuities occur when a rational function has a factor with an that exists in both the numerator and the denominator. Removable discontinuities are shown in a graph by a hollow circle that is also known as a hole. Below is the graph for . Notice that it looks just like except for the hole at . When graphing function, you should cancel the removable factor, graph like usual and then insert a hole in the appropriate spot at the end. There is a hole at because when .
::当一个理性函数有一个在分子和分母中都存在 x 的系数时, 就会出现可移动的不连续性。 可以通过一个空圆( 也称为空洞) 在图形中显示。 下面是 f( x) = (x+2( x+1) x+1 +1 +1 +1 的图形。 注意它看起来就像 y= x+2 。 除了 x\\\\ 的洞外。 图形化函数时, 您应该取消可移动系数, 和通常的一样, 图形化, 然后在末端的适当位置插入一个洞。 x* 1 上有一个洞, 因为当 x\\ 1, f( x) = 00 时会有一个洞 。Removable discontinuities can be “filled in” if you make the function a piecewise function and define a part of the function at the point where the hole is. In the example above, to make continuous you could redefine it as:
::可移动的不连续性可以“填充 ” , 如果您将函数变成一个片段函数, 并在洞所在点定义函数的一部分。 在以上示例中, 要让 f( x) 连续, 您可以重新定义它为 :
::f( x) ( x+2)( x+1x+1, x%11, x%1)Jump Discontinuities
::跳动中断Jump discontinuities occur when a function has two ends that don’t meet even if the hole is filled in. In order to satisfy the vertical line test and make sure the graph is truly that of a function, only one of the end points may be filled. Below is an example of a function with a jump discontinuity.
::当函数有两端,即使洞洞被填满也不符合要求时,就会出现跳动不连续。为了满足垂直线测试,确保图形是函数的垂直线测试,只有一个终点可以被填满。下面是跳动不连续函数的例子。Infinite Discontinuities
::无限断裂I nfinite discontinuities occur when a function has a vertical asymptote on one or both sides. This is shown in the graph of the function below at .
::当函数的一面或两面垂直无序时,就会发生无限的不连续。这在以下 x=1 的函数图中显示。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier you were asked how functions can be discontinuous. There are three ways that functions can be discontinuous. When a rational function has a vertical asymptote as a result of the denominator being equal to zero at some point, it will have an infinite discontinuity at that point. When the numerator and denominator of a rational function have one or more of the same factors, there will be removable discontinuities corresponding to each of these factors. Finally, when the different parts of a piecewise function don’t “match”, there will be a jump discontinuity.
::早些时候有人问您如何使函数不连续。 有三种方法可以使函数不连续。 当理性函数由于分母值在某个时刻等于零而出现垂直无序状态时, 此时就会有无限的不连续状态。 当一个理性函数的分子和分母有一个或一个以上相同因素时, 就会出现与上述每个因素相对应的可移动不连续状态。 最后, 当一个片断函数的不同部分不“ 匹配 ” 时, 就会出现跳跃不连续状态 。Example 2
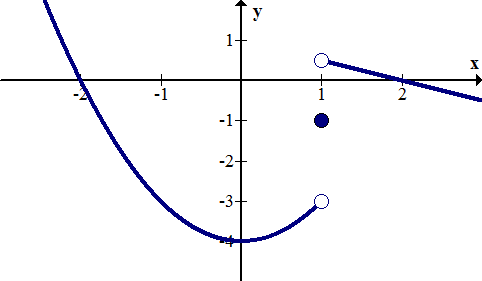
::例2Identify the discontinuity of the piecewise function graphically.
::图形化地识别片段函数的不连续性 。
::f( x) x2 - 4x < 1 - 1x=1 - 12x+1x > 1There is a jump discontinuity at . The piecewise function describes a function in three parts; a parabola on the left, a single point in the middle and a line on the right.
::x=1 时有跳跃不连续性。 片段函数描述三个部分的函数; 左边的抛物线, 中间的单点, 右边的一条线 。Example 3
::例3Describe the continuity or discontinuity of the function .
::描述函数 f( x) =sin( 1x) 的连续性或不连续性 。The function seems to oscillate infinitely as approaches zero. One thing that the graph fails to show is that 0 is clearly not in the domain. The graph does not shoot to infinity, nor does it have a simple hole or jump discontinuity. Calculus and Real Analysis are required to state more precisely what is going on.
::函数似乎随着 x 接近零而无穷无尽地显示。 图表未能显示的一件事是, 0 明显不在域内。 图形没有无穷无尽地拍摄, 也没有简单的洞或跳跃不连续。 计算和真实分析需要更精确地说明正在发生的事情 。Example 4
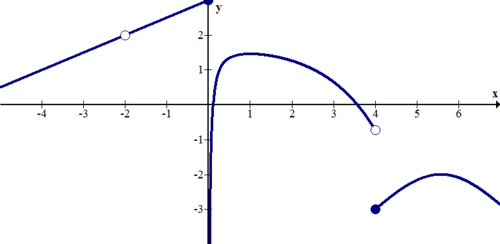
::例4Describe the discontinuities of the function below.
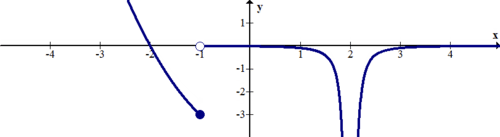
::描述以下函数的不连续性。There is a jump discontinuity at and an infinite discontinuity at .
::x1 有跳跃不连续, x=2 有无限不连续。Example 5
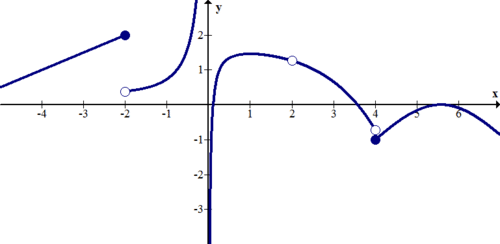
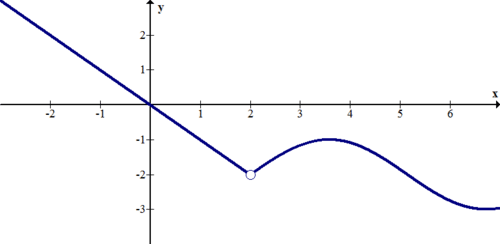
::例5Describe the discontinuities of the function below.
::描述以下函数的不连续性。There are jump discontinuities at and . There is a removable discontinuity at . There is an infinite discontinuity at .
::x2 和 x=4 有跳跃不连续的情况。 x=2 有可移动不连续的情况。 x=2 有无限不连续的情况。 x=0 有无限不连续的情况。Summary -
A function is considered
continuous
if there are no breaks in the graph.
There are three types of discontinuities : Removable, Jump, and Infinite.
::函数如果在图形中没有间断,则被视为连续函数。存在三种不连续类型:可移动、跳跃和无限。 -
Removable discontinuities
occur when a rational function has a factor with an x that exists in both the numerator and the denominator, and can be shown as a hole in the graph.
::当一个合理函数有一个在分子和分母中都有 x 的系数,并且可以在图形中显示为空洞时,就会出现可移动的不连续性。 -
Jump discontinuities
occur when a function has two ends that don't meet.
Infinite discontinuities occur when a function has a vertical asymptote on one or both sides of the discontinuity.
::当函数有两端无法满足时,即发生跳动不连续。当函数在不连续的一方或两侧有一个垂直无序状态时,即发生无限不连续。
Review
::回顾Describe any discontinuities in the functions below:
::描述下列职能中的任何不连续性:1.
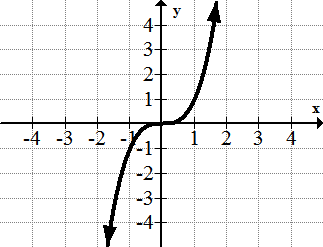
::1.y=x2.
::2. y=x23.
::3. y=x34.
::4.y=x5.
::5. y=1x6.
::6. y=ex7.
::7.y=ln(x)8.
::8. y=11+e-x9.
10.
11.
12. has a jump discontinuity at , a removable discontinuity at , and another jump discontinuity at . Draw a picture of a graph that could be .
::12.f(x) 在 x=3 时有跳跃不连续性,在 x=5 时有可移动不连续性,在 x=6 时有另一个跳跃不连续性。13. has a jump discontinuity at , an infinite discontinuity at , and another jump discontinuity at . Draw a picture of a graph that could be .
::13. g(x) 在 x2 上具有跳跃不连续性,在 x=1 上具有无限不连续性,在 x=3 上则具有另一个跳跃不连续性。14. has a removable discontinuity at , a jump discontinuity at , and another jump discontinuity at . Draw a picture of a graph that could be .
::14. h(x) 在 x4 上具有可移动的不连续性,在 x=1 上具有跳跃不连续性,在 x=7 上具有另一个跳跃不连续性。15. has an infinite discontinuity at , a removable discontinuity at , and a jump discontinuity at . Draw a picture of a graph that could be .
::15. j(x) 在 x=0 时具有无限不连续性,在 x=1 时具有可移动不连续性,在 x=4 时具有跳跃不连续性。绘制一张可能是 j(x) 的图形。Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
A function is considered
continuous
if there are no breaks in the graph.